- Press Releases
- About Who We Are Why Select Us Careers
- Services Consulting Other Services Research

Search Result
Space tourism market size, growth, opportunity, report, 2024-2032.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Non vel laborum, eveniet eos mollitia error in sequi quasi repudiandae libero iure, nemo deleniti, tempore deserunt voluptas eaque debitis quaerat recusandae?
What's Included in Full Report?
- PDF Format Report
- Industry Dynamics
- Market Size and Share Analysis
- Industry Trends and Growth Outlook
- Major Market Players Detailed Analysis
- Key Driving Factors and Analysis by Segments
- Regional Analysis (Can be Customized based on Region and Country)
- Future Commercial Growth Analysis
Request Sample Report
Request a Sample report to know overview of the report's scope and coverage.
Know more about key segmentations and regional analysis during the current and forecast periods. Discover market top players share, their industry performance, and strategies.
Your data is secure and will never be shared with third parties.

Space Tourism Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report, By Type(Sub-Orbital, Orbital, Others); By End-User; By Region; Segment Forecast, 2024 - 2032
- Published Date:Feb-2024
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM4521
- Base Year: 2023
- Historical Data: 2019 – 2022
- Description
Table of Contents
- Analysis Type
- Research Methodology
Request Free Sample
Report outlook.
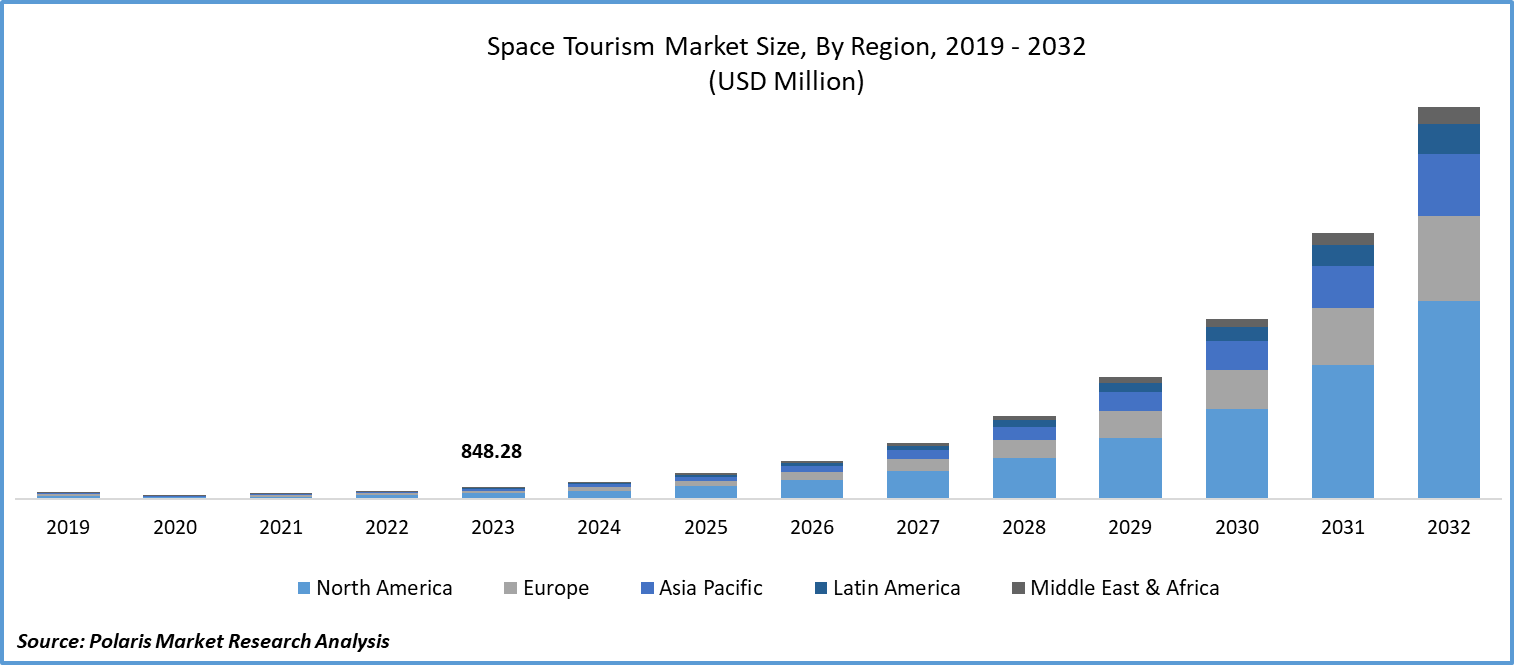
Space tourism market size was valued at USD 848.28 million in 2023. The market is anticipated to grow from USD 1,248.32 million in 2024 to USD 27,861.99 million by 2032, exhibiting the CAGR of 47.4% during the forecast period.
Space Tourism Market Overview
Rising technological advancements, a growing interest among adventure travelers, elevated attention on research and development efforts, and a high net worth of the individuals in spaceflight are driving the space tourism market growth. Space tourism allows people to journey beyond Earth's orbit for leisure or business purposes. In the future, space tourism will become more accessible to the general public, even to those who are not trained astronauts. This will allow more people to explore space and experience its wonders.
- For instance, in April 2022, Axiom, SpaceX, and NASA cooperated to send a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS) with four people on board - three civilians and a former NASA astronaut. The journey, which lasted for a week, cost USD 55 million per participant and involved scientific research, outreach efforts, and various commercial activities .
Space tourism is offering space travel experiences to tourists or private individuals, primarily for leisure, recreational, and adventure processes. It consists of a range of activities, including orbital and suborbital spaceflights, deep space or lunar missions, and other space-based related adventures that allow customers to travel near the Earth's atmosphere and get firsthand experience. Space tourism is an emerging industry that has been gaining popularity in recent years. Key players in this industry include those that offer space exploration experiences, spacecraft manufacturers, spaceports, and related service providers. These companies work to provide high-end encounters to a growing number of customers who are willing to pay for such experiences.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The space tourism market is expected to experience growth due to the rising number of suborbital space offerings from key market players. This increase in demand for space tourism is also expected to create ample opportunities in the future. Additionally, the growing awareness of moon tourism and the increased efforts by key players to send people to the moon are expected to offer further possibilities for growth in the space tourism market.
As the market continues to evolve, companies are seeking strategic partnerships, acquisitions, and collaborative ventures to combine resources, share expertise, and overcome financial and technological challenges. Mergers and acquisitions present businesses with opportunities to leverage synergies, enhance operational efficiency, and facilitate the exchange of knowledge and technologies. This dynamic corporate transaction landscape highlights the industry's dedication to achieving economies of scale and creating a collaborative environment that fosters innovation.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant negative impact on the space tourism market. As the governments implemented the lockdown across all the nations around the globe, the key market players suspended their operations, and the manufacturing plants were forced to shut down owing to the shortages of labor. COVID-19 has also affected supply chain management as there are border restrictions imposed by the government, which results in the decline of the space tourism market growth rate.
Space Tourism Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Technological advancements in space tourism drive the growth of the market
The technological advancements in space tourism drive the space tourism market growth. Advancements in spacecraft design and engineering have significantly enhanced efficiency, safety, and overall experience for passengers. The introduction of reusable rockets and spacecraft has significantly reduced launch and transportation costs, making space travel more economically attractive and viable to a broader audience. Improved life support systems, upgraded habitats, and advanced onboard medical facilities have instilled greater confidence in prospective space tourists regarding the safety and comfort of their space expedition.
Advancements in immersive technologies like virtual reality allow for pre-flight training to prepare passengers for their space trip. Also, internet and communication capabilities on spacecraft enable visitors to instantly share their experiences, creating a sense of community and sparking interest among potential space explorers worldwide.
The development of private space enterprises and partnerships with government space agencies have given rise to innovative business models in recent years. These models offer a range of space tourism experiences, from short suborbital joyrides to longer stays on space stations. This variety of options appeals to a wide audience, attracting adventurers, scientists, researchers, and enthusiasts alike. With advancements in technology, space tourism is becoming more accessible, providing humanity with unprecedented opportunities to explore the cosmos.
Rising interest beyond the different types of space tourism is facilitating the growth of the market
Rising interest among the millionaires and billionaires in various types of space tourism is driving the space tourism market growth. Suborbital space tourism offers short but exciting trips to the outer reaches of Earth's atmosphere. It is particularly attractive to people who want an experience of space exploration without committing to prolonged journeys. The fascination with experiencing weightlessness and marveling at Earth from an exclusive perspective fuel both interest and financial backing for suborbital initiatives.
Orbital space tourism involves longer stays on space stations such as the International Space Station (ISS), providing people with a more immersive space experience. This opportunity appeals to wealthy individuals who are attracted by the prospect of conducting research, advancing science, and enhancing their space travel experiences.
Lunar tourism is an ambitious and forward-thinking concept that involves missions to the Moon and potential excursions on its surface. Venturing beyond Earth's orbit is a daring endeavor that captures the fascination and curiosity of high-net-worth individuals, contributing to the expansion of lunar tourism initiatives. The prospect of setting foot on the Moon, along with the prestige of participating in lunar exploration history, serves as a persuasive reason for wealthy individuals to support these pioneering ventures financially.
Market Restraints
Environmental concerns associated with the rocket launching and space shuttle hampering on the growth of the market
Environmental concerns associated with the rocket launching and space shuttle hampering the growth of the market
The space tourism industry is facing a challenge as environmentally conscious consumers are becoming increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of space launches. Issues like greenhouse gas emissions and pollution of air and water are forcing the industry to prioritize environmentally friendly practices. As regulations on environmental sustainability become more stringent, companies in the space tourism sector must allocate resources to research and development to minimize the ecological impact of their launches. This is necessary to ensure long-term sustainability and growth prospects of the space tourism market, as sustainability becomes a crucial factor in consumer decision-making and industry advancement.
The growing concern over the environmental damage caused by space shuttle and rocket launches is hindering the space tourism market growth. The chemical pollutants, carbon emissions, and other environmental effects associated with these launches are viewed as harmful to the planet. This increased awareness is causing potential space tourists to opt for more environmentally friendly options, dampening their enthusiasm for space travel experiences. This will ensure a more eco-conscious approach that aligns with the changing expectations of environmentally conscious consumers today, ultimately reducing the factors that are anticipated to hinder space tourism market growth.
Report Segmentation
The market is primarily segmented based on type, end-user, and region.
To Understand the Scope of this Report: Speak to Analyst
Space Tourism Market Segmental Analysis
By Type Analysis
- The sub-orbital segment held the largest market share in 2023. Suborbital tourism allows individuals to experience weightlessness and see space without leaving Earth's orbit. This advancement in human spaceflight expands the possibility of space travel without requiring spaceships to enter orbit. Suborbital flights are slower and need more acceleration to enter orbit. Instead, they go up to a predetermined altitude and then come back down when the engines shut off. Many companies are focusing on suborbital flights because they can reuse rockets, which reduces the cost of manufacturing.
- The orbital segment has witnessed the fastest growth in the market. Orbital missions can last from a few days to several weeks, depending on the destination, such as Mars, the Moon, or the International Space Station (ISS). Companies like Orion Span and SpaceX are primarily focused on achieving orbital flights, while Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin mostly concentrate on suborbital missions.
By End-User Analysis
- Based on end-user analysis, the market has been segmented on the basis of commercial, government, and others. The commercial segment dominated the space tourism market in 2023. In 2021, thirteen commercial spaceflight missions were undertaken by numerous government and private organizations; out of them, seven missions were executed successfully. The space tourism industry is on the rise, and technological innovations are making it easier to expand commercial space tourism. Industry stakeholders are putting in their best efforts to make space experiences more accessible by reducing the barriers associated with space tourism.
- The government segment has witnessed the fastest growth in the space tourism market. Governments and space agencies around the world have sent astronauts beyond Earth's atmosphere. For example, NASA currently permits amateur astronauts to visit the International Space Station (ISS). To promote commercial space tourism in Low Earth Orbit, NASA has formed a partnership with SpaceX and Axiom.
Space Tourism Market Regional Insights
North America dominated the largest market in 2023
North America dominates the space tourism market; the region has a wide research and development base and is equipped with a hugely developed infrastructure that makes the region a top revenue contributor in the space tourism market over the forecast period. North America is anticipated to maintain its dominance over the forecast period due to the leaning of rich individuals towards space tourism and increasing technological investment in the region.
Asia-Pacific has witnessed for the fastest growth in the space tourism market. China has been manufacturing rockets in more numbers for commercial satellite launches. Also, the Indian Space Research Organizations (ISRO), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and China National Space Administration (CNSA), are the substantial contributors for the space tourism market growth in the region.
Competitive Landscape
The space tourism market is characterized by intense competition, with established players relying on advanced technology, high-quality products, and a strong brand image to drive revenue growth. These companies employ various strategies such as research and development, mergers and acquisitions, and technological innovations to expand their product portfolios and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Some of the major players operating in the global market include:
- Axiom Space
- Blue Origin
- Rocket Lab USA
- Space Adventures
- Space Perspective
- Virgin Galactic
- World View Enterprises, Inc.
- Zero 2 Infinity
- Zero Gravity Corporation
Recent Developments
- In June 2023, Virgin Galactic launched its commercial spaceflight service, with the first-ever commercial space voyage scheduled to begin on June 27 and run through June 30 during the first "Galactic-01" flight window.
- In May 2023, Vast plans to launch Vast Haven-1, the first commercial space station, on a Falcon 9 rocket with two crewed spaceflights in August 2025. They are also developing a larger space station to be integrated into Haven-1. The partnership with SpaceX aims to expand space exploration and make space more accessible.
- In November 2022, Axiom Space and Virgin Galactic partnered up to perform a mission that centers around microgravity research and training. The two companies will combine their expertise and resources to conduct the mission, promote scientific advancement, and offer valuable training opportunities in the field of microgravity.
Report Coverage
The space tourism market report emphasizes on key regions across the globe to provide better understanding of the product to the users. Also, the report provides market insights into recent developments, trends and analyzes the technologies that are gaining traction around the globe. Furthermore, the report covers in-depth qualitative analysis pertaining to various paradigm shifts associated with the transformation of these solutions.
The report provides detailed analysis of the market while focusing on various key aspects such as competitive analysis, type, end-user, and their futuristic growth opportunities.
Space Tourism Market Report Scope
Gain profound insights into the 2024 Space Tourism Market with meticulously compiled statistics on market share, size, and revenue growth rate by Polaris Market Research Industry Reports. This thorough analysis not only provides a glimpse into historical trends but also unfolds a roadmap with a market forecast extending to 2032. Immerse yourself in the comprehensive nature of this industry analysis through a complimentary PDF download of the sample report .
Browse Our Top Selling Reports
Peptide and Oligonucleotide CDMO Market Size, Share 2024 Research Report
Energy Engineering Service Outsourcing (ESO) Market Size, Share 2024 Research Report
Scooters Market Size, Share 2024 Research Report
Trim Tabs Market Size, Share 2024 Research Report
Universal Remote Controls Market Size, Share 2024 Research Report
Lipsum generator: Lorem Ipsum - All the facts www.lipsum.com Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s
The space tourism market size is expected to reach USD 27,861.99 million by 2032, according to a new study by Polaris Market Research.
Key players in the market are Airbus, Axiom Space, Blue Origin, Boeing, Rocket Lab USA, Space Adventures, SpaceX, Space Perspective, Virgin Galactic
North America contribute notably towards the global Space Tourism Market
Space tourism market exhibiting the CAGR of 47.4% during the forecast period.
The Space Tourism Market report covering key segments are type, end-user, and region.
1. Introduction 1.1. Report Description 1.1.1. Objectives of the Study 1.1.2. Market Scope 1.1.3. Assumptions 1.2. Stakeholders 2. Executive Summary 2.1. Market Highlights 3. Research Methodology 3.1. Overview 3.1.1. Data Mining 3.2. Data Sources 3.2.1. Primary Sources 3.2.2. Secondary Sources 4. Global Space Tourism Market Insights 4.1. Space Tourism Market – Industry Snapshot 4.2. Space Tourism Market Dynamics 4.2.1. Drivers and Opportunities 4.2.1.1. Technological advancements in space tourism drive the growth of the market 4.2.1.2. Rising interest beyond the different types of space tourism is facilitating the growth of the market 4.2.2. Restraints and Challenges 4.2.2.1. Environmental concerns associated 4.3. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis 4.3.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers (Moderate) 4.3.2. Threats of New Entrants: (Low) 4.3.3. Bargaining Power of Buyers (Moderate) 4.3.4. Threat of Substitute (Moderate) 4.3.5. Rivalry among existing firms (High) 4.4. PESTLE Analysis 4.5. Space Tourism Industry trends 4.6. Value Chain Analysis 4.7. COVID-19 Impact Analysis 5. Global Space Tourism Market, by Type 5.1. Key Findings 5.2. Introduction 5.2.1. Global Space Tourism, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 5.3. Sub-Orbital 5.3.1. Global Space Tourism Market, by Sub-Orbital , by Region, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 5.4. Orbital 5.4.1. Global Space Tourism Market, by Orbital , by Region, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 5.5. Others 5.5.1. Global Space Tourism Market, by Others , by Region, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 6. Global Space Tourism Market, by End-User 6.1. Key Findings 6.2. Introduction 6.2.1. Global Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 6.3. Commercial 6.3.1. Global Space Tourism Market, by Commercial , by Region, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 6.4. Government 6.4.1. Global Space Tourism Market, by Government , by Region, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 6.5. Others 6.5.1. Global Space Tourism Market, by Others , by Region, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7. Global Space Tourism Market, by Geography 7.1. Key findings 7.2. Introduction 7.2.1. Space Tourism Market Assessment, By Geography, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.3. Space Tourism Market – North America 7.3.1. North America: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.3.2. North America: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.3.3. Space Tourism Market – U.S. 7.3.3.1. U.S.: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.3.3.2. U.S.: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.3.4. Space Tourism Market – Canada 7.3.4.1. Canada: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.3.4.2. Canada: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4. Space Tourism Market – Europe 7.4.1. Europe: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.2. Europe: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.3. Space Tourism Market – UK 7.4.3.1. UK: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.3.2. UK: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.4. Space Tourism Market – France 7.4.4.1. France: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.4.2. France: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.5. Space Tourism Market – Germany 7.4.5.1. Germany: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.5.2. Germany: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.6. Space Tourism Market – Italy 7.4.6.1. Italy: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.6.2. Italy: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.7. Space Tourism Market – Spain 7.4.7.1. Spain: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.7.2. Spain: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.8. Space Tourism Market – Netherlands 7.4.8.1. Netherlands: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.8.2. Netherlands: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.9. Space Tourism Market – Russia 7.4.9.1. Russia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.4.9.2. Russia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5. Space Tourism Market – Asia Pacific 7.5.1. Asia Pacific: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.2. Asia Pacific: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.3. Space Tourism Market – China 7.5.3.1. China: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.3.2. China: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.4. Space Tourism Market – India 7.5.4.1. India: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.4.2. India: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.5. Space Tourism Market – Malaysia 7.5.5.1. Malaysia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.5.2. Malaysia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.6. Space Tourism Market – Japan 7.5.6.1. Japan: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.6.2. Japan: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.7. Space Tourism Market – Indonesia 7.5.7.1. Indonesia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.7.2. Indonesia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.8. Space Tourism Market – South Korea 7.5.8.1. South Korea: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.5.8.2. South Korea: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6. Space Tourism Market – Middle East & Africa 7.6.1. Middle East & Africa: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.2. Middle East & Africa: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.3. Space Tourism Market – Saudi Arabia 7.6.3.1. Saudi Arabia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.3.2. Saudi Arabia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.4. Space Tourism Market – UAE 7.6.4.1. UAE: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.4.2. UAE: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.5. Space Tourism Market – Israel 7.6.5.1. Israel: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.5.2. Israel: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.6. Space Tourism Market – South Africa 7.6.6.1. South Africa: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.6.6.2. South Africa: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7. Space Tourism Market – Latin America 7.7.1. Latin America: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7.2. Latin America: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7.3. Space Tourism Market – Mexico 7.7.3.1. Mexico: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7.3.2. Mexico: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7.4. Space Tourism Market – Brazil 7.7.4.1. Brazil: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7.4.2. Brazil: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7.5. Space Tourism Market – Argentina 7.7.5.1. Argentina: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 7.7.5.2. Argentina: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) 8. Competitive Landscape 8.1. Expansion and Acquisition Analysis 8.1.1. Expansion 8.1.2. Acquisitions 8.2. Partnerships/Collaborations/Agreements/Exhibitions 9. Company Profiles 9.1. Airbus 9.1.1. Company Overview 9.1.2. Financial Performance 9.1.3. Product Benchmarking 9.1.4. Recent Development 9.2. Axiom Space 9.2.1. Company Overview 9.2.2. Financial Performance 9.2.3. Product Benchmarking 9.2.4. Recent Development 9.3. Blue Origin 9.3.1. Company Overview 9.3.2. Financial Performance 9.3.3. Product Benchmarking 9.3.4. Recent Development 9.4. Boeing 9.4.1. Company Overview 9.4.2. Financial Performance 9.4.3. Product Benchmarking 9.4.4. Recent Development 9.5. Rocket Lab USA 9.5.1. Company Overview 9.5.2. Financial Performance 9.5.3. Product Benchmarking 9.5.4. Recent Development 9.6. Space Adventures 9.6.1. Company Overview 9.6.2. Financial Performance 9.6.3. Product Benchmarking 9.6.4. Recent Development 9.7. SpaceX 9.7.1. Company Overview 9.7.2. Financial Performance 9.7.3. Product Benchmarking 9.7.4. Recent Development 9.8. Space Perspective 9.8.1. Company Overview 9.8.2. Financial Performance 9.8.3. Product Benchmarking 9.8.4. Recent Development 9.9. Virgin Galactic 9.9.1. Company Overview 9.9.2. Financial Performance 9.9.3. Product Benchmarking 9.9.4. Recent Development 9.10. World View Enterprises, Inc. 9.10.1. Company Overview 9.10.2. Financial Performance 9.10.3. Product Benchmarking 9.10.4. Recent Development 9.11. Zero 2 Infinity 9.11.1. Company Overview 9.11.2. Financial Performance 9.11.3. Product Benchmarking 9.11.4. Recent Development 9.12. Zero Gravity Corporation 9.12.1. Company Overview 9.12.2. Financial Performance 9.12.3. Product Benchmarking 9.12.4. Recent Development
List of Tables
Table 1 Global Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 2 Global Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 3 Space Tourism Market Assessment, By Geography, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 4 North America: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 5 North America: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 6 U.S.: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 7 U.S.: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 8 Canada: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 9 Canada: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 10 Europe: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 11 Europe: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 12 UK: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 13 UK: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 14 France: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 15 France: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 16 Germany: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 17 Germany: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 18 Italy: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 19 Italy: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 20 Spain: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 21 Spain: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 22 Netherlands: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 23 Netherlands: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 24 Russia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 25 Russia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 26 Asia Pacific: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 27 Asia Pacific: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 28 China: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 29 China: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 30 India: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 31 India: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 32 Malaysia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 33 Malaysia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 34 Japan: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 35 Japan: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 36 Indonesia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 37 Indonesia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 38 South Korea: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 39 South Korea: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 40 Middle East & Africa: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 41 Middle East & Africa: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 42 Saudi Arabia: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 43 Saudi Arabia: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 44 UAE: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 45 UAE: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 46 Israel: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 47 Israel: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 48 South Africa: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 49 South Africa: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 50 Latin America: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 51 Latin America: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 52 Mexico: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 53 Mexico: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 54 Brazil: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 55 Brazil: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 56 Argentina: Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Table 57 Argentina: Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2019-2032 (USD Million)
List of Figures
Figure 1 Global Space Tourism Market, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Figure 2 Integrated Ecosystem Figure 3 Research Methodology: Top-Down & Bottom-Up Approach Figure 4 Market by Geography Figure 5 Porter’s Five Forces Figure 6 Market by End-User Figure 7 Global Space Tourism Market, by End-User, 2022 & 2032 (USD Million) Figure 8 Market by Type Figure 9 Global Space Tourism Market, by Type, 2022 & 2032 (USD Million) Figure 10 Space Tourism Market Assessment, By Geography, 2019-2032 (USD Million) Figure 11 Strategic Analysis – Space Tourism Market
Report Scope
Space Tourism Market, Type Outlook (Revenue - USD Million, 2019-2032)
- Sub-Orbital
Space Tourism Market, End-User Outlook (Revenue - USD Million, 2019-2032)
Space Tourism Market, Regional Outlook (Revenue - USD Million, 2019-2032)
Qualitative Analysis
- Industry trends
- Market drivers and restraints
- Market size
- Growth prospects
- Porter’s analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- Value Chain Analysis
- Key market opportunities prioritized
- Type benchmarking
- Latest strategic developments
- Price Trend Analysis
Quantitative Analysis
- Market size, estimates, and forecasts from 2019-2032
- Market revenue estimates for Type up to 2032
- Market revenue estimates for End-User up to 2032
- Regional market size and forecast up to 2032
- Company financials
We take great pride in "Delivering game-changing business opportunities reports with report customizations", so please don't hesitate to share with us your unique interests and business difficulties in much more detail.
This website is secure and your personal details are safe. Privacy Policy
© 2024 Polaris Market Research and Consulting. All rights reserved
- Report Store
- AMR in News
- Press Releases
- Request for Consulting
- Our Clients

Space Tourism Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report, by Type, End Use : Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2022-2031
Report Code: A10674
Get Sample to Email
Thank You For Your Response !
Our Executive will get back to you soon
The space tourism market size was $598.4 million in 2021 and is expected to reach $12,690.6 million by 2031, registering a CAGR of 36.4% from 2022 to 2031.
Space tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital and suborbital. Space tourism is a type of vacation where travelers pay to fly into space. The phrase "space tourism" has evolved to refer to the practice of regular people purchasing tickets for trips to and from space. This concept is considered futuristic by many. But since more and more expert work has been done on the topic in recent years, it is now evident that establishing commercial space tourism services is a viable business goal in the present day.
The space tourism industry is projected to be fueled by the rise in technological advancements, consistent transformations in technology are proliferating the demand for the space tourism market globally. Moreover, technological advancements in the field of space travel are fueling the development of spacecraft and superior rockets at a robust pace. This way, space tourists are allowed to travel into space and gain the expected experience. Moreover, major emerging economies across the globe are exploring space programs, which, in turn, is anticipated to fuel the space tourism market growth.
Moreover, the rising trend of space tourism is the major driver which propels the Space tourism market demand. The market for space tourism is expected to grow faster than expected throughout the projected period as the practice becomes more widely accepted in international markets. In addition, it is anticipated that increasing competition in the space tourism sector will drive down prices. Furthermore, as the orbit is reached by the next-generation space planes, the cost of entering space is anticipated to fall sharply. As a result, the price of launching satellites is probably going to drop significantly, which would lower the overall cost of space exploration operations. Such factors are propelling the space tourism market growth.
Additionally, a decline in the costs of space tourism flights is also a key factor boosting market growth. The downfall in the ticket prices of space tourism is attracting a large number of consumers. A journey into space now costs only $250,000 overall, down from its initial price of roughly $600,000. Customers that typically fall among the top 1% of income earners make up the entire client base for this market.
Moreover, the focus on Research and Development (R&D) initiatives by market players is creating many opportunities in the space tourism market. There are numerous commercial suborbital spacecraft being developed right now, each with a different set of characteristics. The Suborbital Applications Research Group (SARG), founded by the Commercial Spaceflight Federation, aims to increase public awareness of the research and educational possibilities of the suborbital reusable launch vehicles now under development.
However, technical risks with these types of activities are a factor hampering the growth of the market. Despite the fact that space missions have been successfully conducted for more than 50 years, there are many technical dangers associated with commercial, high-volume space flights employed for space tourism.
Additionally, Strict Government rules related to spaceships are restraining the market growth.
The Space tourism market forecast is segmented on the basis of type, end use, and region. On the basis of type, the market is classified into orbital and sub orbital. By end use, the market is bifurcated into Government, and commercial. By region, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
The Orbital segment would witness the fastest growth, registering a CAGR of 37.2% during the forecast period.
By Type, the Space tourism market is segmented into orbital, and sub orbital. The sub orbital segment accounted for a major space tourism market share in 2021, and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Sub orbital tourism packages that can provide the longest duration of zero-gravity and the most thrilling Earth view from space to its consumer can be considered superior than the others. Suborbital tourism is on the rise as it allows individuals to experience weightlessness and observe space without actually exiting the Earth's orbit. As a result, human spaceflight can reach the edge of the universe without entering orbit.
The government segment would witness the fastest growth, registering a CAGR of 37.2% during the forecast period.
By end use, the Space tourism market is segmented into Government, and commercial. The commercial segment accounted for a major share in the Space tourism market in 2021, and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Commercial space tourism means the private companies in the space industry such as space x, blue origin, and others. The commercial space tourism market is rising and expected to dominate the market. There were thirteen commercial spaceflight missions undertaken by several private and government organizations, of which seven missions were executed successfully. Billionaires have invested considerable sums in traveling to space and witnessing the Earth from above. Such factors are surging the demand for this segment in the near future.
The LAMEA region would witness the fastest growth, registering a CAGR of 68.1% during the forecast period.
By region, the space tourism market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. The North America Space tourism market is accounted for a major share in the Space tourism market in 2021 and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. The area has a highly developed infrastructure and a sizable research and development base, which will enable it to dominate the global market in terms of revenue throughout the anticipated time. Modern technology has been implemented more quickly thanks to an established infrastructure.
The major players operating in the market focus on key market strategies, such as mergers, product launches, acquisitions, collaborations, and partnerships. They have been also focusing on strengthening their market reach to maintain their goodwill in the ever-competitive market. Some of the key players in the Space tourism market include Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, SpaceX, Airbus Group SE, Boeing, ZERO-G, Axiom Space, Bigelow Aerospace, Orion Span, Space Adventures, Space Perspective, World View Enterprises, Zero2Infinity.
KEY BENEFITS FOR STAKEHOLDERS
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the Space tourism market analysis from 2021 to 2031 to identify the prevailing market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and Space tourism market opportunities.
- Porter’s five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders to make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the Space tourism market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global Space tourism industry.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global Space tourism market trends, key players, market segments, distribution channel areas, and Space tourism market growth strategies.
Space Tourism Market Report Highlights
Analyst Review
According to the insights of the CXOs, the global space tourism market is expected to witness robust growth during the forecast period. This is attributed to the rising trend of space tourism across the globe. The trend of space tourism is gradually gaining recognition in the global markets and is anticipated to accelerate the growth of the global space tourism market during the forecast timeframe. In addition, the growing completion in the space tourism industry is expected to decrease the cost of space tourism. Furthermore, to attract consumers around the globe, key players in the market are focused on Research and Development (R&D) initiatives.
CXOs further added about the increase in technological advancements. Global demand for space tourism is growing as a result of ongoing technological advancements. Moreover, the construction of spacecraft and better rockets is advancing at a rapid rate thanks to technological developments in the field of space travel. Space tourists are able to go into space in this fashion and have the experience they desire. Major growing economies all around the world are also investigating space projects, which is expected to promote the expansion of the space tourism industry globally. However, despite the fact that space missions have been successfully conducted for more than 50 years, there are many technical dangers associated with commercial, high-volume space flights employed for space tourism. Thus, such factors are hampering the market growth.
- Travel Destinations
- Luxury Accommodations
- Travel Packages
- Adventure Travel
- Travel Experiences
- Adventure Destinations
- Sustainable Travel
- Outdoor Activities
The CAGR of Space Tourism Market is 36.4%.
Kindly get in touch with the sales person for better options.
2021 is the base year calculated in the Space Tourism Market report.
The key players profiled in the report include Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, SpaceX, Airbus Group SE, Boeing, ZERO-G, Axiom Space, Bigelow Aerospace, Orion Span, Space Adventures, Space Perspective, World View Enterprises, Zero2Infinity.
Type and end use are the segments of Space Tourism Market.
Increasing competition in the space tourism sector and rise in technological advancements, consistent transformations in technology are the key trends in the Space Tourism Market report.
North America has the highest Space Tourism market share in 2021.
Loading Table Of Content...
- Related Report
- Global Report
- Regional Report
- Country Report
Enter Valid Email ID
Verification code has been sent to your email ID
By continuing, you agree to Allied Market Research Terms of Use and Privacy Policy
Advantages Of Our Secure Login
Easily Track Orders, Hassel free Access, Downloads
Get Relevent Alerts and Recommendation

Wishlist, Coupons & Manage your Subscription

Have a Referral Code?
Enter Valid Referral Code
An Email Verification Code has been sent to your email address!
Please check your inbox and, if you don't find it there, also look in your junk folder.
Space Tourism Market
Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2022-2031
- Travel, Tourism & Hospitality ›
Leisure Travel
Space tourism - statistics & facts
What is the public’s opinion on space tourism, do the public want to travel to space, key insights.
Detailed statistics
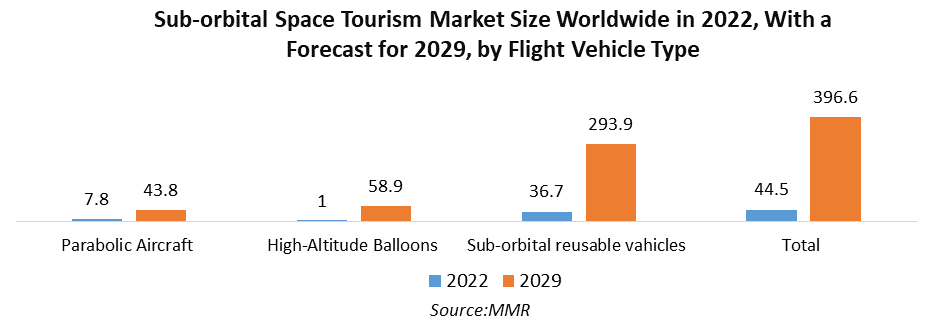
Global sub-orbital space tourism market size 2021-2031, by flight vehicle type
Amount invested globally into space companies by venture capitalists 2013-2022
Equity investments in space companies worldwide 2013-2022, by type
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
Forecast revenue of orbital space travel and tourism worldwide 2021-2030
Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021
Further recommended statistics
Market overview.
- Premium Statistic Global sub-orbital space tourism market size 2021-2031, by flight vehicle type
- Premium Statistic Forecast revenue of orbital space travel and tourism worldwide 2021-2030
- Premium Statistic Amount invested globally into space companies by venture capitalists 2013-2022
- Premium Statistic Equity investments in space companies worldwide 2013-2022, by type
- Premium Statistic Share of investment deals in space start-ups worldwide by company in 2020
- Premium Statistic Distribution of space start-up investors by type 2000-2020
Sub-orbital space tourism market size worldwide in 2021, with a forecast for 2031, by flight vehicle type (in million U.S. dollars)
Forecast revenue of the orbital space travel and tourism market worldwide from 2021 to 2030 (in million U.S. dollars)
Amount venture capitalists invested into space companies worldwide from 2013 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Cumulative equity investment in space companies worldwide from 2013 to 2022, by type (in billion U.S. dollars)
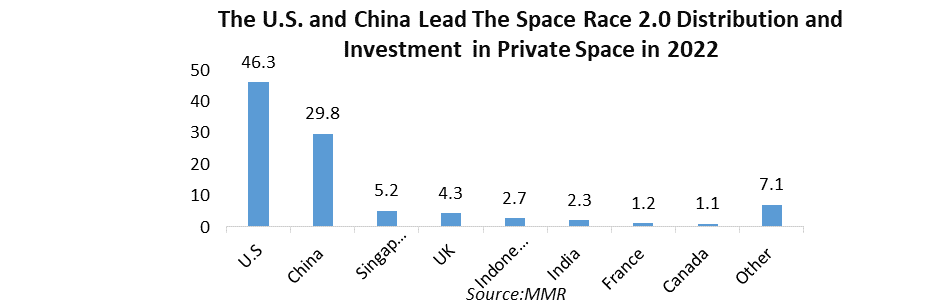
Share of investment deals in space start-ups worldwide by company in 2020
Distribution of investment deals on space start-ups worldwide in 2020, by company
Distribution of space start-up investors by type 2000-2020
Distribution of investor groups in space start-ups from 2000 to 2020, by investor type
Public opinion
- Premium Statistic U.S. public opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021
- Premium Statistic U.S. opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021, by age
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults that believe space travel should be accessible to everyone 2021
- Premium Statistic U.S. public opinion on profitability of space exploration companies in future 2021
- Premium Statistic U.S. adults that believe billionaires should spend money on space travel 2021
U.S. public opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021
Public opinion on which space companies are leading the private sector's push into space in the United States as of December 2021
U.S. opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021, by age
Public opinion on which space companies are leading the private sector's push into space in the United States as of December 2021, by generation
Share of U.S. adults that believe space travel should be accessible to everyone 2021
Share of adults that believe space travel should be accessible to everyone and not just those that can afford the costs in the United States as of September 2021
U.S. public opinion on profitability of space exploration companies in future 2021
Share of the public that believe private companies focused on space exploration will make a profit in the next 10 years in the United States as of December 2021
U.S. adults that believe billionaires should spend money on space travel 2021
Share of adults that believe billionaires should be spending money traveling to space in the United States as of September 2021
Traveler interest
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021, by gender
- Premium Statistic Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon if money was not a factor 2021
- Premium Statistic Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by generation
- Premium Statistic Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by gender
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who would travel to the moon 2021, by age
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who would spend over 100 thousand USD to travel to space 2021
Share of adults that would want to travel to space if money was not an issue in the United States as of September 2021
Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021, by gender
Share of adults that want to travel to space if money was not an issue in the United States as of September 2021, by gender
Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon if money was not a factor 2021
Share of the public that would go to the moon as a tourist if money was not a factor in the United States as of December 2021
Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by generation
Share of the public that would go to the moon as a tourist if money was not a factor in the United States as of December 2021, by generation
Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by gender
Share of the public that would go to the moon as a tourist if money was not a factor in the United States as of December 2021, by gender
Share of U.S. adults who would travel to the moon 2021, by age
Share of adults that would travel to the moon in the United States as of May 2021, by age
Share of U.S. adults who would spend over 100 thousand USD to travel to space 2021
Share of adults that would spend more than 100 thousand U.S. dollars to travel to space in the United States as of September 2021
Further reports
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
- European aerospace industry
- Space industry worldwide
- Space tourism
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
Report Code: 12971
- Get Free Sample
- Customize Report
Space Tourism Market Size & Share Analysis - Trends, Drivers, Competitive Landscape, and Forecasts (2024 - 2030)
Get a Comprehensive Overview of the Space Tourism Market Report Prepared by P&S Intelligence, Segmented by Type (Orbital, Sub-Orbital), End User (Commercial, Government), and Geographic Regions. This Report Provides Insights From 2017 to 2030.
- Report Code: 12971
- Order this report
- Inquire Before Ordering
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Sample Pages
Space Tourism Market Size
Market statistics, market size comparison.
Key Players

Key Report Highlights
Explore the market potential with our data-driven report Get Sample Pages
Space Tourism Market Analysis
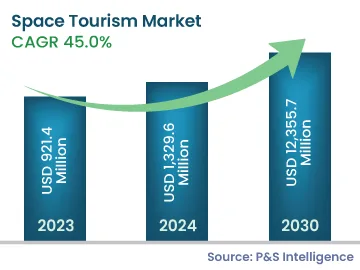
The space tourism market generated revenue of USD 921.4 million in 2023, it is predicted to witness a CAGR of 45.0% during 2024–2030, to reach USD 12,355.7 million by 2030. The key drivers for the market are the evolution of the technologies being used for space exploration and the increasing curiosity of people about the cosmos.
This subindustry of the aerospace sector aims to provide amusement, leisure, and adventure to individuals by sending them into space. However, the market is in its initial stage, but shows the potential of becoming a multi-billion-dollar market. The growth of the market solely depends on technological advancements and price reduction, which will lead space tourism to become accessible and affordable for consumers.
The market space for space tourism has a relatively small customer base, which includes both affluent people looking for unique experiences and organizations funding scientific research and promotional activities. The market is heavily dependent on one group of consumers, but businesses nevertheless need to periodically assess and adjust their products according to the shifting demands and preferences of a wide range of clients.
Space Tourism Market Trends & Drivers
Technological advancements are trending in market.
The continuous technological advancements are the key trend in the space tourism market. The significant advancements in space technology over time have increased the viability, safety, and accessibility of space travel.
- The creation of reusable rockets and spacecraft, pioneered by companies such as SpaceX is one of the major breakthroughs. Reusing launch vehicles results in a major reduction in space travel costs, making commercial space tourism ventures more financially feasible.
- Furthermore, the improvements in materials science, propulsion technology, and spaceship design have raised the overall efficiency and safety of space travel. Moreover, while developments in navigation and communication technologies improve the entire experience and safety of space travelers, innovations in life support systems guarantee the wellbeing of passengers during their journey. These advancements have greatly impacted the market by increasing the interest in space tourism.
- Momentus, a U.S.-based firm, uses reusable rockets to lower the cost of travel. The reusable vehicles de-orbit to another orbit, following the last drop-off. Robust robotic arms enable the ship to execute docking, refueling, and proximity maneuvers.
Growing Interest in Experimental Tourism Is Major Market Driver
Experimental tourism is becoming increasingly popular, which is driving the growth of the market.
- Space tourism offers a once-in-a-lifetime chance to explore the cosmos and offer the experience of being an astronaut, which is something modern-day travelers are increasingly looking for, without undergoing the physically and psychologically demanding training of most national space agencies.
- One of the biggest factors that drive The market is the desire to see earth from space and become a part of a select group of individuals who have traveled beyond earth, which was not possible in the past even for the uber rich.
- The popularity of space travel has also been aided by the growth of social media and experience sharing. People have the chance to capture breathtaking photos and videos, sharing them on social networks, and making enduring memories. This market has a great chance to extend its clientele and draw in a wider spectrum of tourists due to rising demand for immersive travel.
Space Tourism Industry Outlook
Safety and regulatory hurdles restraint market growth.
After more than 50 years’ experience of space exploration, meeting regulatory obstacles and guaranteeing passenger safety are still major challenges for the industry.
- These challenges are because of the inherent hazards in a space flight, wherein it is critical to ensure space tourists’ safety. Strict safety guidelines and procedures must be followed by businesses in the space tourism sector in order to reduce risks and guarantee the successful completion of every mission.
- Governments and international agencies set such policies and require valid licenses, which are granted only to companies once they demonstrate adherence to the safety mandates.
- Finding the ideal balance between promoting industry growth and safety is the problem. Governments, regulatory agencies, and industry stakeholders must work together to create strong, transparent frameworks that address safety issues and support innovation and expansion in the space tourism sector.
Type Insights
- The orbital category is predicted to experience the faster growth, with a CAGR of 45.3%, during the forecast period. This is because orbital tourism would provide a better experience of space, by taking individuals to earth’s orbit by achieving the ideal escape velocity.
- The sub-orbital category will hold the dominant market position, with a share of around 70%, in 2030.
- As these spacecrafts will travel with a velocity lower than that of an orbital variant, it will be feasible, less complex, and, most of all, safer. The affordability of sub-orbital flights makes them more appealing for consumers with a lower safety risk.

During the study, we have analyzed two types in the report:
- Orbital (Faster-Growing Category)
- Sub-Orbital (Larger Category)
End User Insights
- The commercial category holds the dominant position in the market, with a more than 65% share in 2023. This is because of the stiff competition between private space exploration companies resulting in technological advancement, cost reduction, and increased accessibility.
- Additionally, the economic potential of space tourism has benefitted the business sector. Private companies operating in this domain have made large expenditures in spacecraft and testing & launch infrastructure development.
- The government bifurcation will witness the higher CAGR, of 45.4%, over the forecast period. This will be because governments have recognized the potential economic benefits of the market.
- Governments will invest heavily in this market as it is a profitable business and can also help countries growth.
During the study, we have analyzed two end users in the report:
- Commercial (Larger category)
- Government (Faster-Growing Category)
Drive strategic growth with comprehensive market analysis Preview With a Free Sample
Regional Insights
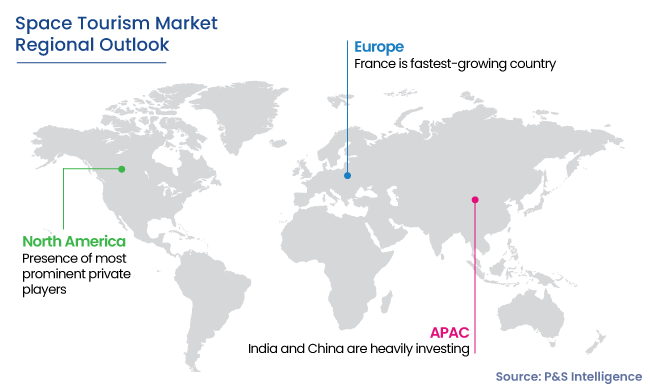
- Geographically, North America dominated the space tourism market, with a revenue share of around 55%, in 2023. The fact that U.S. is the home of the foremost space exploration agency and numerous established aerospace firms makes it largest market worldwide.
- Most prominent private players in the market, including SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic, are headquartered the region, and they have been at the forefront of technological development.
- The region’s dominance on the sector is also due to the strong financial support of the U.S. government for space-related projects. Space technology and tourism ventures witness an intense desire among investors to provide vital funding for research and development as well as operational scaling.
- In addition, the region has a long tradition of space exploration and a well-established aerospace infrastructure. This is because NASA has already acquired advanced technology and created a culture that is strongly in favor of space exploration activities.
- APAC is predicted to become the fastest-growing region in the forecast period, with a CAGR of 45.7%. India and China are heavily investing in this sector for tourism purposes and to advance national interests.
- China has invested heavily in space infrastructure, including the development of its own space station and lunar exploration missions. Companies such as Galactic Energy and iSpace are investing in its space sector.
The regions and countries analyzed in this report include:
- U.S. (Larger Country Market)
- U.K. (Largest Country Market)
- France (Fastest-Growing Country Market)
- Rest of Europe
- China (Largest Country Market)
- Japan (Fastest-Growing Country Market)
- South Korea
- Rest of APAC
- Brazil (Largest Country Market)
- Rest of LATAM
- Saudi Arabia (Fastest-Growing Country Market)
- South Africa (Largest Country Market)
- U.A.E.
- Rest of MEA
Space Tourism Market Share
The main companies operating in the industry are concentrating on new product launches, mergers, collaboration, partnerships, and acquisitions. They are also focusing on expanding their market reach to keep their reputation in the business.
Moreover, the key players are investing significantly in R&D in order to integrate advanced technologies in spacecraft to give consumers the best experience at reasonable prices and with increased safety.
Major Space Tourism Offering Companies:
- Space Exploration Technology Corp.
- Blue Origin Enterprises L.P.
- Virgin Galactic
- Airbus Group SE
- The Boeing Company
- Zero Gravity Corporation
- Axiom Space Inc.
- Zero 2 Infinity S.L.
- World View Enterprises Inc.
- Space Adventures Inc.
Space Tourism Industry News
- Virgin Galactic operated its first commercial spaceflight, Galactic 01, on June 29, 2023. Moreover, the second ever commercial spaceflight, Galactic 02, operated on August 10, 2023.
- NASA awarded Blue Origin a sustaining lunar development contract in May 2023, under NextSTEP-2 Appendix P. Under the terms of the deal, Blue Origin is in charge of creating and operating a lunar lander that can land anywhere on the moon, as well as creating a cislunar transporter.
- The Axiom Space Access Program, which enables nations to recognize the potential of permanent economic and scientific benefits of microgravity, was unveiled by Axiom Space in April 2023.
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
During the forecast period (2024-2030), the market for space tourism will propel at a CAGR of 45.0%.
The major players in the market for space tourism are focused on mergers, new product launches, partnerships, acquisitions, and collaboration. They are also concentrating on increasing their market reach to enhance their presence.
The space tourism industry will reach a value of USD 12,355.7 million in 2030.
Commercial is the leading end-user in the space tourism industry, with a share of 65% in 2023.
APAC is the fastest-growing regional industry for space tourism.
The major drivers in the space tourism market are the development of the technologies being employed for space exploration and the increasing interest in experimental tourism.
Want a report tailored exactly to your business need?
We are Trusted by

Working with P&S Intelligence and their team was an absolute pleasure – their awareness of timelines and commitment to value greatly contributed to our project's success. Eagerly anticipating future collaborations.
McKinsey & Company
Our insights into the minutest levels of the markets, including the latest trends and competitive landscape, give you all the answers you need to take your business to new heights
We take a cautious approach to protecting your personal and confidential information. Trust is the strongest bond that connects us and our clients, and trust we build by complying with all international and domestic data protection and privacy laws
- Request Customization
- Request Free Sample
Customize the Report to Align with Your Business Objectives
Request the Free Sample Pages
Christmas and New Year Offer : Single User - 20% Discount | Corporate User - 25% Discount | Regional Report - 15% Discount
Space Tourism Market: Global Industry Analysis and Forecast (2023-2029)
“ Christmas and New Year Offer : Single User - 20% Discount | Corporate User - 25% Discount | Regional Report - 15% Discount ”
- Request Sample
- Customization
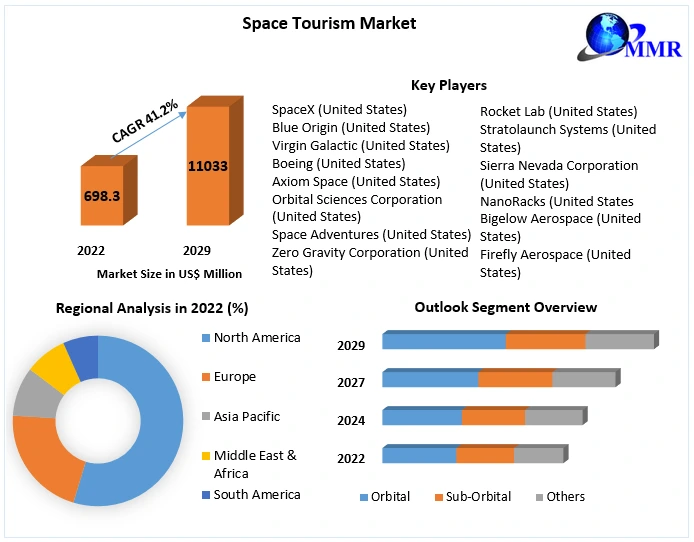
Space Tourism Market Dynamics:
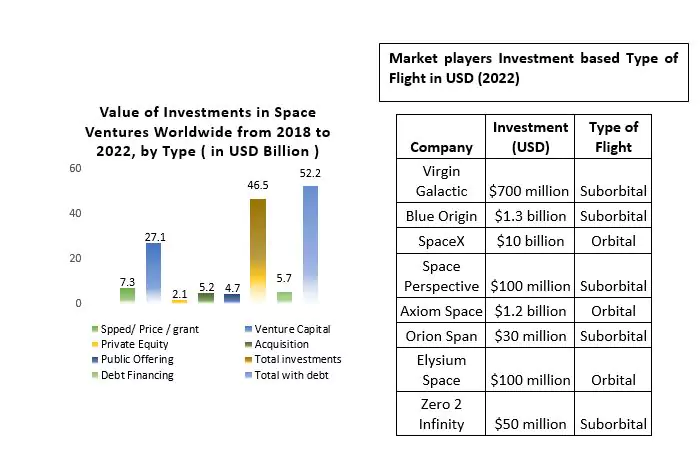
Space Tourism Market Segment Analysis
Space Tourism Market Regional Insights:
Space Tourism Market Scope: Inquire before buying
Space tourism market by region:, space tourism companies analysis, about this report.
- INQUIRE BEFORE BUYING
Related Reports
Runtime application self-protection market: global industry analysis and forecast (2022-2029).
- Price for Single User : 4600 USD
- Report ID : 882
- July 13, 2019
Runtime Application Self-Protection Market size was valued at US$ 666.65 Mn. in 2021 and the total revenue is expected to grow at 31.98 % through 2021 to 2029, Runtime Application Self-Protection Market is reaching nearly US$ 6137.16 Mn. by 2029. Runtime Application Self-Protection Market Overview and Dynamics: Runtime application self-protection […]
Europe Virtual Data Room Market: Industry Analysis and Forecast (2024-2030)
- Price for Single User : 2600 USD
- Report ID : 2435
- August 07, 2019
The Europe Virtual Data Room Market size was valued at USD 5152.80 Million in 2023 and the total Europe Virtual Data Room revenue is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2024 to 2030, reaching nearly USD 9914.25 Million by 2030. The Europe Virtual Data Room market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand for secure and […]
South America Smart Fleet Management Market: Outlook 2027 & Key Trends
- Price for Single User : 3900 USD
- Report ID : 3176
- August 04, 2019
- Pages : Feb 2022
South America Smart Fleet Management Market was at 3.47 Billion in 2020. Automotive is one of the segments reviewed in the MMR report dominating the Smart Fleet Management market. South America Smart Fleet Management Market Overview: A smart fleet solution is a fully integrated system for creating effective maintenance plans in the automotive […]
Data Governance Market: Data Quality and Accuracy to boost the Market growth
- Report ID : 5668
- October 07, 2019
Global Data Governance Market size was valued at USD 3.84 Bn in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 15.73 Bn by 2030, at a CAGR of 22.32 % over the forecast period. Data Governance Market Overview Data Governance is a principled approach to manage data during its life cycle, from acquisition to use to disposal. Ensure that data is accurate, […]
Global User Provisioning Market Key Trends – Market size
- Report ID : 6559
- May 06, 2018
- Pages : 225
Global User Provisioning Market Key Trends (2017-2018) _ by Component, Deployment Mode, Organization Size, Services, Business Application, Business Function, Application, Vertical and Geography Global User Provisioning Market include the growing awareness and the seriousness of user compliance management and governance and rapid growth in the […]
Global Space Tourism Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2031
- Upcoming Report
- No of Tables: 220
- No of Figures: 60
Global Space Tourism Market, By Type (Sub-Orbital Space Tourism, Orbital Space Tourism, Lunar Tourism, Inter-Planetary Tourism, Space Hotel Tourism), End User (Government, Commercial, Others), HNW Communities (20M to 40M, 40M to 60M, More than Above Ranges), and Sales Channel (Launch Provider, Third Party Partnership, OTAs) - Industry Trends and Forecast to 2031.
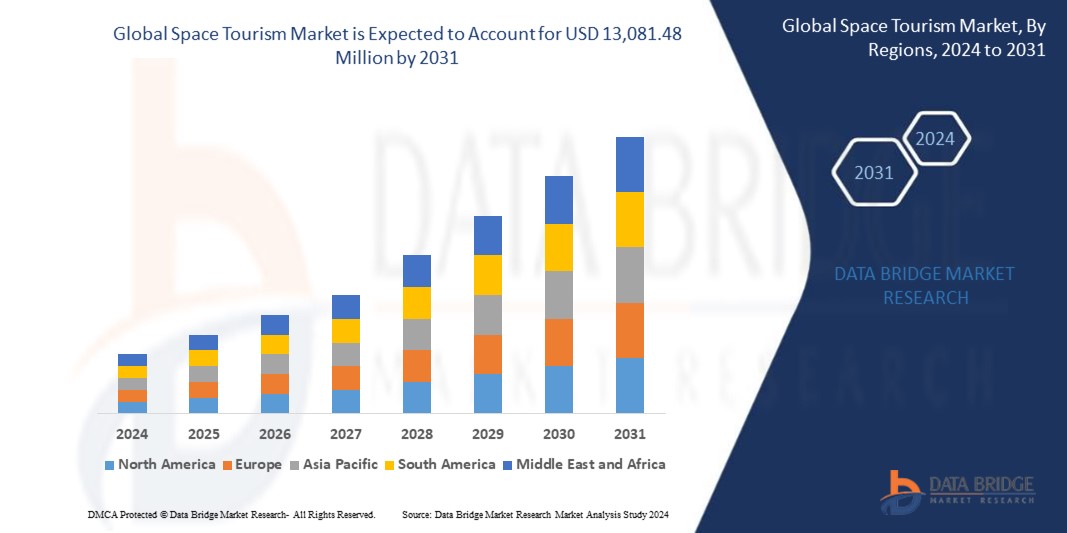
Space Tourism Market Analysis and Size
The essential factors contributing to the growth of the space tourism market in the forecast period of 2024 to 2031 include allure of experiencing weightlessness and witnessing Earth. Also, the advancements in virtual reality and immersive technologies allow for realistic pre-flight training are significantly contributing to the market’s growth. Growing government support in the realm of space tourism has emerged as a crucial catalyst, unlocking immense potential within the market.
Data Bridge Market Research analyzes that the global space tourism market which was USD 876.34 million in 2023, is expected to reach USD 13,081.48 million by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 40.2% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2031. In 2024, the sub-orbital space tourism segment will dominate the market due to the growing interests and motivations among billionaires and billionaires in diverse types of space tourism. In addition to the insights on market scenarios such as market value, growth rate, segmentation, geographical coverage, and major players, the market reports curated by the Data Bridge Market Research also include in-depth expert analysis, geographically represented company-wise production and capacity, network layouts of distributors and partners, detailed and updated price trend analysis and deficit analysis of supply chain and demand.
Space Tourism Market Scope and Segmentation
Market Definition
Space tourism refers to the space travel experiences for individuals or tourists, typically for recreational, leisure, or adventure purposes. It encompasses a range of activities, including suborbital and orbital spaceflights, lunar or deep space missions, and other related space-based adventures that allow paying people to travel beyond Earth's atmosphere and experience space first-hand.
Global Space Tourism Market Dynamics
- Technological Advancement in Space Tourism
Technological advancements in space tourism are revolutionizing the market, propelling it into a new era of accessibility and potential growth. Innovations in spacecraft design and engineering have significantly enhanced safety, efficiency, and overall passenger experience. Reusable rockets and spacecraft have lowered the cost of launching and transportation, making space travel more economical and appealing to a broader demographic. Advanced life support systems, improved habitats, and sophisticated onboard medical facilities have bolstered the confidence of potential space tourists in the safety and comfort of their space journey.
- Growing Interests and Motivations
Growing interests and motivations among billionaires and billionaires in diverse types of space tourism are propelling the space tourism market into a new era of growth and investment. Suborbital space tourism, offering brief yet exhilarating journeys to the edge of space, appeals to individuals seeking a taste of space travel without the extended time commitment. The allure of experiencing weightlessness and witnessing Earth from a unique vantage point drives interest and investment in suborbital ventures. In addition, orbital space tourism, involving longer stays aboard space stations, such as the International Space Station (ISS), attracts those aspiring for a more immersive space adventure.
Opportunity
- Government Support in Space Tourism
Government support in the realm of space tourism has emerged as a crucial catalyst, unlocking immense potential within the market. Investment initiatives and regulatory frameworks backed by governments are fostering a favorable environment for private enterprises to flourish and innovate. Financial incentives, research grants, and collaborative partnerships with governmental space agencies provide essential resources and credibility to budding and established space tourism ventures. These strategic alliances not only bolster the industry credibility but also encourage the development of cutting-edge technologies and infrastructure, essential for the growth and sustainability of space tourism.
Restraint/Challenge
- Environmental Damage Through Space Shuttle or Rocket Launching
The adverse environmental impact stemming from space shuttle and rocket launches presents a significant restraint to the market growth. The environmental concerns associated with these launches, such as greenhouse gas emissions and air and water pollution, have prompted a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers to reconsider their support for space tourism. This shift in consumer behavior poses a notable challenge for companies within the space tourism sector.
This space tourism market report provides details of new recent developments, trade regulations, import-export analysis, production analysis, value chain optimization, market share, the impact of domestic and localized market players, analyses opportunities in terms of emerging revenue pockets, changes in market regulations, strategic market growth analysis, market size, category market growths, application niches and dominance, product approvals, product launches, geographic expansions, technological innovations in the market. To gain more info on the space tourism market contact Data Bridge Market Research for an Analyst Brief, our team will help you make an informed market decision to achieve market growth.
Recent Developments
- In September 2023, according to Firefly Aerospace, Inc., L3Harris Technologies and Firefly Aerospace, Inc. have inked a multi-launch agreement for three dedicated launches on Firefly's Alpha vehicle in 2026. The arrangement strengthens Firefly's position as the industry's top provider of small-lift launch services as it increases Alpha vehicle manufacturing to meet the expanding demands of both government and commercial clients
- In June 2023, Virgin Galactic commercial spaceflight service launch was announced. The "Galactic -01" flight window, the first commercial space mission, was scheduled for June 27 to June 30. The second mission was then scheduled for early August
Impact and Current Market Scenario of Raw Material Shortage and Shipping Delays
Data Bridge Market Research offers a high-level analysis of the market and delivers information by keeping in account the impact and current market environment of raw material shortage and shipping delays. This translates into assessing strategic possibilities, creating effective action plans, and assisting businesses in making important decisions. Apart from the standard report, we also offer in-depth analysis of the procurement level from forecasted shipping delays, distributor mapping by region, commodity analysis, production analysis, price mapping trends, sourcing, category performance analysis, supply chain risk management solutions, advanced benchmarking, and other services for procurement and strategic support.
Expected Impact of Economic Slowdown on the Pricing and Availability of Products
When economic activity slows, industries begin to suffer. The forecasted effects of the economic downturn on the pricing and accessibility of the products are taken into account in the market insight reports and intelligence services provided by DBMR. With this, our clients can typically keep one step ahead of their competitors, project their sales and revenue, and estimate their profit and loss expenditures.
Global Space Tourism Market Scope
The space tourism market is segmented on the basis of type, end user, HNW communities, and sales channel. The growth amongst these segments will help you analyse meagre growth segments in the industries and provide the users with a valuable market overview and market insights to help them make strategic decisions for identifying core market applications.
- Sub-Orbital Space Tourism
- Orbital Space Tourism
- Lunar Tourism
- Interplanetary Tourism
- Space Hotel Tourism
HNW Communities
- More than Above Ranges
Sales Channel
- Launch Provider
- Third Party Partnership
Global Space Tourism Market Regional Analysis/Insights
The space tourism market is analyzed and market size insights and trends are provided by country, type, end user, HNW communities, and sales channel as referenced above.
The countries covered in the market report are U.S., Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, rest of South America, Germany, France, Italy, U.K., Belgium, Spain, Russia, Turkey, Netherlands, Switzerland, rest of Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, rest of Asia-Pacific, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Israel, South Africa, and rest of Middle East and Africa.
North America is expected to dominate the market due to the active participation from the private sectors.
Asia-Pacific is expected to grow with the highest growth rate in the forecast period of 2024 to 2031 due to its rising research and development and planning in space tourism manufacturing.
The country section of the report also provides individual market impacting factors and changes in regulations in the market domestically that impacts the current and future trends of the market. Data points like down-stream and upstream value chain analysis, technical trends and porter's five forces analysis, case studies are some of the pointers used to forecast the market scenario for individual countries. Also, the presence and availability of global brands and their challenges faced due to large or scarce competition from local and domestic brands, impact of domestic tariffs and trade routes are considered while providing forecast analysis of the country data.
Competitive Landscape and Global Space Tourism Market Share Analysis
The space tourism market competitive landscape provides details by competitor. Details included are company overview, company financials, revenue generated, market potential, investment in research and development, new market initiatives, global presence, production sites and facilities, production capacities, company strengths and weaknesses, product launch, product width and breadth, application dominance. The above data points provided are only related to the companies' focus related to space tourism market.
Some of the major players operating in the space tourism market are:
- Virgin Galactic (U.S.)
- Boeing (U.S.)
- SPACEX (U.S.)
- BLUE ORIGIN (U.S.)
- SPACE ADVENTURES (U.S.)
- Bigelow Aerospace (U.S.)
- Lockheed Martin Corporation (U.S.)
- ROCKET LAB USA (U.S.)
- MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES LTD. (Japan)
- Elysium Space, Inc. (U.S.)
- fireflyspace (U.S.)
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (China)
- World View Enterprises, Inc. (U.S.)
- Space Perspective (U.S.)
Get online access to the report on the World's First Market Intelligence Cloud
- Interactive Data Analysis Dashboard
- Company Analysis Dashboard for high growth potential opportunities
- Research Analyst Access for customization & queries
- Competitor Analysis with Interactive dashboard
- Latest News, Updates & Trend analysis
- Harness the Power of Benchmark Analysis for Comprehensive Competitor Tracking
Research Methodology
Data collection and base year analysis are done using data collection modules with large sample sizes. The stage includes obtaining market information or related data through various sources and strategies. It includes examining and planning all the data acquired from the past in advance. It likewise envelops the examination of information inconsistencies seen across different information sources. The market data is analysed and estimated using market statistical and coherent models. Also, market share analysis and key trend analysis are the major success factors in the market report. To know more, please request an analyst call or drop down your inquiry.
The key research methodology used by DBMR research team is data triangulation which involves data mining, analysis of the impact of data variables on the market and primary (industry expert) validation. Data models include Vendor Positioning Grid, Market Time Line Analysis, Market Overview and Guide, Company Positioning Grid, Patent Analysis, Pricing Analysis, Company Market Share Analysis, Standards of Measurement, Global versus Regional and Vendor Share Analysis. To know more about the research methodology, drop in an inquiry to speak to our industry experts.
Customization Available
Data Bridge Market Research is a leader in advanced formative research. We take pride in servicing our existing and new customers with data and analysis that match and suits their goal. The report can be customized to include price trend analysis of target brands understanding the market for additional countries (ask for the list of countries), clinical trial results data, literature review, refurbished market and product base analysis. Market analysis of target competitors can be analyzed from technology-based analysis to market portfolio strategies. We can add as many competitors that you require data about in the format and data style you are looking for. Our team of analysts can also provide you data in crude raw excel files pivot tables (Fact book) or can assist you in creating presentations from the data sets available in the report.
Frequently Asked Questions
Browse related pages.
- Global Space Tourism Market Companies

Avail PDF Sample Reports

By clicking the "Submit" button, you are agreeing to the Data Bridge Market Research Privacy Policy. and Terms and Conditions
Corporate Email ID Only (Avoid Using Generic mail ID such as Gmail)
Consent preferences.
We use cookies to improve your experience We use cookies to deliver the best possible experience on our website. To learn more, visit our Privacy Policy. By continuing to use this site, or closing this box, you consent to our use of cookies. Cookie Notice.
- [email protected]
- +1 718 618 4351 (International)
- +91 78878 22626 (Asia)
More Results
Home ➤ Aerospace and Defence ➤ Aviation and Aerospace ➤ Space Tourism Market
Global Space Tourism Market by Type (Orbital, Sub Orbital), By End-User (Government, Commercial), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2023-2032
- Published date: March 2024
- Report ID: 11819
- Number of Pages: 392
- Table of Contents
- Major Market Players
- Request a Sample
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
Analyst viewpoint, key takeaway, type analysis, end-user analysis, key market segments, opportunity, regional analysis, key players analysis, recent developments, report scope.
The global space tourism market size is expected to be worth around USD 17742.4 Million by 2032 , from USD 1,158.0 Million in 2023 , growing at a CAGR of 36.6% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2032.
Space tourism, an emerging sector within the aerospace industry, refers to the commercial activity of sending private individuals into space for recreational, leisure, or adventure purposes. This market has garnered significant attention and investment in recent years, driven by advancements in space technology and a growing interest in space exploration.
The space tourism market is relatively emerging but has been gaining momentum in recent years. It encompasses various players, including space tourism companies, spacecraft manufacturers, spaceports, and related service providers. These entities collaborate to offer space travel experiences to a growing number of customers who are willing to pay a premium for the opportunity.
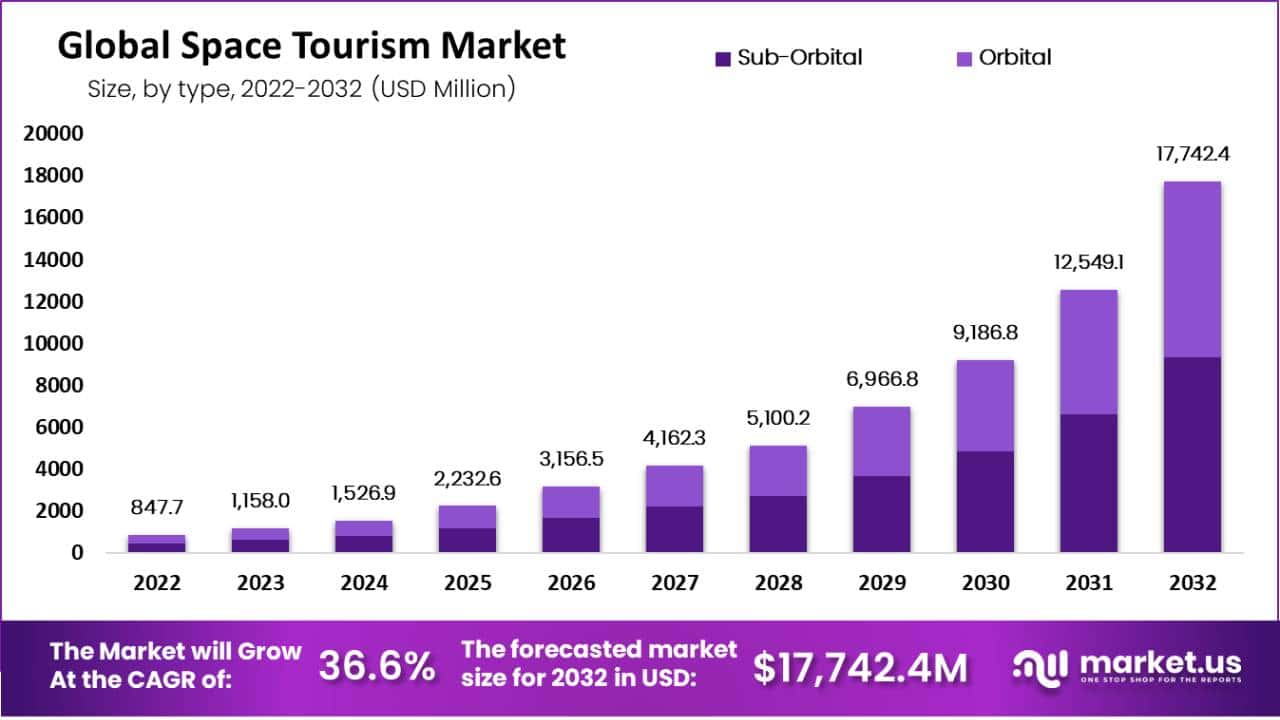
The market for space tourism is rapidly evolving, propelled by significant investments from pioneering companies. For instance, Virgin Galactic raised $400 million in October 2023 to enhance its commercial spaceflight operations and develop the SpaceShip III vehicle.
Similarly, Blue Origin’s acquisition of $1 billion funding, led by BlackRock, is advancing its suborbital tourism programs and lunar exploration initiatives. SpaceX , a key player in this realm, has also attracted substantial private investments, recently securing $750 million , likely supporting its Starship development and expanding the Starlink satellite network.
Innovations in space tourism are broadening the scope of what these experiences can offer. Companies like Space Perspective are introducing luxurious stratospheric balloon capsules, slated for launch in 2024, designed to provide breathtaking views of Earth from the edge of space.
Orion Span aims to construct the first luxury space hotel, Aurora Station , by 2030, offering orbital accommodations with features like panoramic views and artificial gravity. Zero 2 Infinity , planning to initiate suborbital flights from Spain in 2025, will provide passengers with a unique experience of floating seats and expansive windows.
The space tourism market is on a trajectory of rapid growth, with forecasts suggesting it could reach a valuation of $1 trillion by 2040. This growth is supported by the evolving regulatory landscape, with bodies like the FAA introducing new frameworks to foster industry development. The Space Summit held in Dubai in December 2023 further underscored the global interest and potential in space tourism, highlighting the sector’s current developments and future opportunities.
- The global space tourism market is projected to reach a substantial value of USD 17,742 million by 2032. This impressive growth is driven by a remarkable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.6% from 2023 to 2032.
- Sub-Orbital travel dominates the market, capturing more than a 52.7% share in 2022, with a CAGR of 37.8%.
- In 2022, the Commercial segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 57.3% share. This is attributed to companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, offering suborbital space tourism experiences to individuals.
- North America emerged as the leading region in the global space tourism market in 2022, capturing more than a 39.8% share. This is due to the presence of pioneering companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic.
- Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing region in the forecast period, with a CAGR of 35.5%. This is driven by significant investments in space tourism programs by countries like India and China.
- 676 people have journeyed to space, according to the U.S. definition of reaching an altitude of 50 miles (80 kilometers) .
- Out of these, 643 astronauts have reached the Kármán line, which is internationally recognized at 100 km (62 miles) above Earth.
- Approximately 86% of astronauts complete their journey with at least one orbit around the Earth, while an additional 4% venture beyond Earth orbit.
- SpaceX Starship system: Plans to use its Starship system for space tourism flights, capable of carrying up to 100 passengers .
- Around 60,000 people have expressed interest in flying to space, many of whom are expected to take the trip once commercial operations commence.
In 2022, the sub-orbital segment held a dominant position in the space tourism market, capturing more than a 52.7% share with CAGR of 37.8% . This dominance can be attributed to several key factors that make sub-orbital travel more accessible and appealing to a broader audience.
Firstly, sub-orbital flights are significantly shorter and less complex than orbital missions, making them a more feasible option for private companies in terms of technology and investment requirements. The relatively lower cost of sub-orbital flights, compared to orbital experiences, also makes them more attainable for potential space tourists. This affordability widens the customer base, allowing more individuals to experience space travel.
Furthermore, sub-orbital flights require less extensive training for passengers, reducing preparation time and costs, and making the experience more user-friendly for those without professional astronaut training. This aspect is crucial in attracting customers who are interested in space tourism but are not necessarily looking for an extensively demanding experience.
The technological advancements in this segment have been significant, with companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin leading the way in offering commercial sub-orbital flights. These companies have successfully conducted test flights and are advancing towards regular commercial operations. The high-profile nature of these ventures, backed by prominent figures and extensive media coverage, has also played a role in popularizing sub-orbital space tourism.
In 2022, the Commercial segment held a dominant market position in the space tourism industry, capturing more than a 57.3% share. This segment’s dominance can be attributed to several key factors.
Firstly, commercial space tourism companies have played a pivotal role in driving the market’s growth by leveraging private investments and innovative business models. Companies such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin have been at the forefront, offering suborbital space tourism experiences to individuals. Their efforts have spurred competition, resulting in technological advancements, cost reductions, and increased accessibility.
Additionally, the commercial segment has capitalized on the growing consumer demand for unique space travel experiences. There is a significant interest among individuals to witness the awe-inspiring views of our planet from space and experience weightlessness. By catering to this demand, commercial space tourism companies have been able to attract a substantial customer base, further bolstering their market position.
Moreover, the commercial segment has benefited from the economic potential associated with space tourism. These companies have recognized the revenue-generating opportunities within the industry and have made significant investments in infrastructure, spacecraft development, and marketing. This proactive approach has allowed them to offer competitive pricing, making space tourism more attainable for a broader range of consumers.
Furthermore, the commercial segment’s dominance can be attributed to the support and regulatory flexibility provided by governments worldwide. Governments have recognized the potential economic benefits and have encouraged private sector participation in space tourism. They have introduced regulatory frameworks that foster innovation and ensure safety while allowing commercial space tourism companies to operate and flourish.
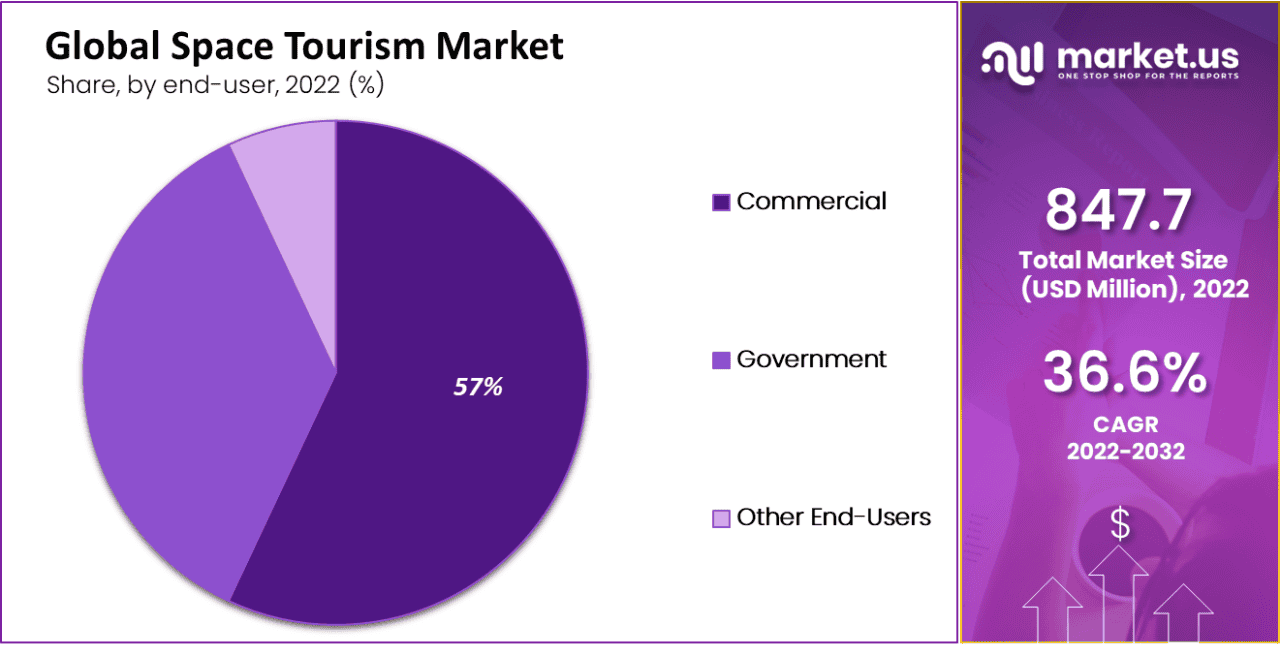
Government Segment is Identified as Fastest Growing Material Segment in Projected Period.
Government is also an important end-user segment in the space tourism market, and it is expected to grow faster in the end-user segment in the space tourism market with a CAGR of 38.3% and a market share is 36.7%.
Commercial space tourism means private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and others working in the space industry. Various private and government organizations undertook thirteen spaceflight missions, and seven missions were executed successfully. As a result, Billionaires invested a significant amount in traveling to space and seeing Earth from above.
Based on Type
- Sub-Orbital
Based on End-User
- Other End-Users
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have been a significant driver of growth in the space tourism market. Over the years, there have been remarkable developments in space technology, making space travel more feasible, safe, and accessible. One of the key advancements is the development of reusable rockets and spacecraft, pioneered by companies like SpaceX. By reusing launch vehicles, the cost of space travel has significantly decreased, making it more economically viable for commercial space tourism ventures.
Additionally, advancements in spacecraft design, propulsion systems, and materials have improved the overall safety and efficiency of space travel. Innovations in life support systems ensure the well-being of passengers during their journey, while advancements in navigation and communication systems enhance the overall experience and safety of space tourists. These technological breakthroughs have instilled confidence in potential customers and have sparked interest in space tourism.
High Costs of Space Travel
One of the major restraints faced by the space tourism market is the high cost associated with space travel. Currently, space tourism experiences come with a hefty price tag, limiting the market to a relatively small segment of high-net-worth individuals. The high costs are primarily driven by the complex nature of space travel, including research and development expenses, operational costs, and the need for advanced technology and infrastructure.
However, it is important to note that the cost of space travel is gradually decreasing as advancements in technology and increased competition among space tourism companies drive down prices. The development of more efficient and reusable spacecraft, along with economies of scale, is expected to significantly reduce the cost barrier, paving the way for a broader market of potential space tourists.
Growing Interest in Experiential Travel
An opportunity for the space tourism market lies in the growing interest in experiential travel. Modern travelers are increasingly seeking unique and extraordinary experiences, and space tourism provides an unparalleled opportunity to explore the cosmos. The desire to witness Earth from space, experience weightlessness, and be part of a select group of individuals who have traveled beyond our planet is a powerful motivator for many.
The rise of social media and the sharing of experiences have also contributed to the appeal of space tourism. Space travel provides a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity for individuals to capture breathtaking photos and videos, share them with their networks, and create lasting memories. This growing interest in experiential travel, combined with advancements in technology and decreasing costs, presents a significant opportunity for the space tourism market to expand its customer base and attract a broader range of travelers.
Safety and Regulatory Hurdles
A key challenge for the space tourism market is ensuring the safety of passengers and addressing regulatory hurdles. Space travel involves inherent risks, and ensuring the well-being of space tourists is of paramount importance. Companies in the space tourism industry must adhere to strict safety standards and protocols to minimize risks and ensure the successful completion of each mission.
Furthermore, space tourism is a highly regulated industry due to the potential risks involved and the need to protect both passengers and the environment. Governments and regulatory bodies play a vital role in establishing guidelines, licensing requirements, and safety regulations for space tourism operations.
The challenge lies in striking the right balance between safety and enabling the growth of the industry. Collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, governments, and regulatory bodies are essential to establish clear and robust frameworks that address safety concerns while allowing for innovation and growth in the space tourism market.
In 2022, North America emerged as the leading region in the global space tourism market, capturing more than a 39.8% share. This dominant position can be attributed to several factors unique to the region. First and foremost, North America is home to some of the most pioneering companies in the space tourism sector, including SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic. These companies have been at the forefront of technological advancements in space travel, contributing significantly to the development of the industry.
The region’s robust financial backing for space-related endeavors plays a critical role in its market dominance. North American investors, both private and institutional, have shown a strong inclination to invest in space technology and tourism ventures, providing essential capital for research, development, and operational scaling. This financial support has been instrumental in advancing the commercial space tourism industry.
Furthermore, North America benefits from a well-established aerospace infrastructure and a long history of space exploration. This legacy, spearheaded by agencies like NASA, has fostered a skilled workforce, advanced technological capabilities, and a culture that is highly supportive of space exploration endeavors. The regulatory environment in North America, particularly in the United States, has also been conducive to the growth of the space tourism industry. The government has shown a willingness to work with private companies, offering regulatory guidance and support that has helped propel the industry forward.
Additionally, the region’s strong emphasis on research and innovation in the field of aerospace and related technologies continues to drive advancements in space tourism. From the development of reusable rockets to the creation of luxury space accommodations, North American companies are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible in space travel.
Asia Pacific is expected to be as fastest growing region in the forecast period in the space tourism market, with a CAGR of 35.5% . Due to many factors, like it being the home of some of the world’s fastest-growing economies like India & China, they are heavily investing in space tourism programs.
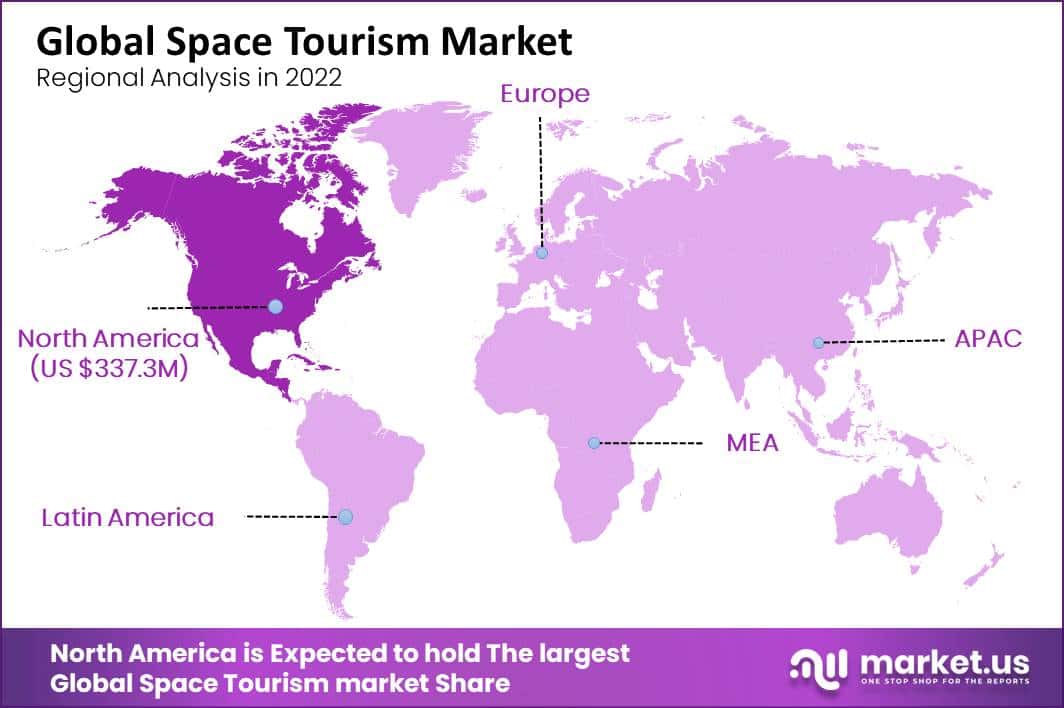
Key Regions and Countries Covered in this Report:
- Rest of Europe
- South Korea
- New Zealand
- Rest of APAC
- Rest of Latin America
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- Rest of MEA
The major players working in the market focuses on key strategies in the market, like product launches, merger, acquisitions, partnerships, and collaborations. They also focus on strengthening their market reach for maintaining their goodwill in the competitive market.
Key players are spending significantly on research & development activities to integrate advanced technologies in spacecraft. The key players are mainly focusing on offering individuals a day or a week tour which creates an adventurous experience for the tourists.
Top Key Players
- Blue Origin
- Virgin Galactic
- Airbus Group SE
- Axiom Space
- Bigelow Aerospace
- Space Adventures
- Space Perspective
- World View Enterprises
- Zero2Infinity
- Other Key Players
- Blue Origin: On December 19th, 2023, Blue Origin successfully completed its first New Shepard mission since September 2022, demonstrating a safe return to flight and paving the way for future tourism flights.
- Space Perspective: This company secured $70 million in Series A funding in December 2023, propelling their development of stratospheric balloon capsules for near-space tourism experiences.
- Spaceports: Construction of the world’s first dedicated space tourism spaceport, Spaceport Cornwall in the UK, is now 50% complete and on track for opening in 2025.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
In 2022, the global space tourism market accounted for USD 847.7 million. It is projected to reach USD 17,742 million by 2032.
Prominent players in the space tourism market include SpaceX, Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, and more.
The space tourism market is segmented into Orbital and Sub-Orbital types.
The end-user segments in the space tourism market include Government and Commercial entities.
The sub-orbital segment is the most lucrative segment in the space tourism market, offering zero gravity experiences and observations of space without leaving Earth's orbit.
Technological advancements in spacecraft and space technology, along with growing public interest in space exploration, are driving the market growth of the space tourism industry.
Launch services, spacecraft manufacturing, space tourism operators, and businesses providing support services for space tourism activities have opportunities for growth and revenue generation.

- The Boeing Company Company Profile
Related Reports
- Travel Planner App Market
- Legal Process Outsourcing Market
- Insurance Agency Software Market
- E-Commerce Personalization Software Market
- Security Safes Market
- Immersive-Reality Technologies Market
Our Clients

- Report ID 11819
- Published Date March 2024
- ★★★★★ ★★★★★

- location_on 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300 New York City, NY 10170, United States
- phone +1 718 618 4351 (International)
- phone +91 78878 22626 (Asia)
- email [email protected]
- How to Order
- Privacy Policy
- Refund Policy
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Terms and Conditions
- All Reports
- All Sectors
- Infographics
- Statistics and Facts


Space Tourism Market
Space tourism market - global industry assessment & forecast, aerospace and defense, segments covered, customization offered.
- Description
- Table Of Content
- Market Segmentation
- Request Sample
- Buying Inquiry

The global Space Tourism Market is valued at USD 1198.5 Million in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 16500 Million by 2032 at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 31.6% between 2024 and 2032.
Key Highlights
- North America predominantly led the Space Tourism market in 2023, with 84% of the total market share
- Europe is projected to remain the second most revenue-generating region during the forecast period
- The Orbital segment significantly contributed to the market’s expansion, constituting over 63.5% of the overall revenue share in 2023
- The Commercials segment took the lead in the market in 2023, constituting over 91.8% of the market share
- In the United States, the FAA plays a central role in regulating commercial space activities, including Space Tourism. The FAA's Office of Commercial Space Transportation (AST) issues licenses and permits for Space Tourism operations, ensuring that they comply with safety and environmental standards. Companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin have obtained licenses from the FAA for their suborbital spaceflights
- Space Tourism technology has applications beyond tourism itself. Remote sensing and Earth observation technologies allow Space Tourism companies to offer services to industries such as agriculture, forestry, and climate monitoring
Space Tourism Market Size, 2023 To 2032 (USD Million)
Ai (gpt) is here ask questions about space tourism market.
More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form.
More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form.
More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form.
More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form. More report information will load here after submitting the form.
Regional Overview
In 2023, North America's Space Tourism market holds a significant share of the revenue with 84%. The U.S. plays an important role in developing and commercializing this sector, with North America being a major hub for the emerging space tourist market. North America is home to some of the world's biggest Space Tourism companies, like Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin and SpaceX. Several spaceports, which are essential for launching Space Tourism missions, are located in the United States. Spaceport America in New Mexico and Mojave Air and Space Port in California are key facilities for suborbital flights.
U.S. Space Tourism Market Overview
The Space Tourism market in the United States, with a valuation of USD 1003.6 Million in 2023, is projected to reach around USD 8980 Million by 2032. A significant Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 27.5% from 2024 to 2032 is projected in this forecast. The U.S. is at the forefront of spacecraft development, spaceports, regulations and market innovation when it comes to global Space Tourism. Some of the most influential Space Tourism companies, including Virgin Galactic founded by Sir Richard Branson and one of the leading operators in suborbital space travel, are located in the United States. The company's SpaceShipTwo offers suborbital experiences for paying passengers, with its spaceflights taking off from Spaceport America in New Mexico.

The global Space Tourism market can be categorized as Tourism Type, End-User, and Region.
Tourism Type Overview
In 2023, substantial expansion was observed in the Global Space Tourism market within the Orbital category, i.e., 63.5%. Based on the Tourism Type, the Space Tourism market is divided into Orbital, Sub-Orbital, and Others.Orbital tourism, often considered the zenith of Space Tourism experiences, offers travelers the opportunity to embark on an extraordinary journey to Earth's orbit and even make their way to the International Space Station (ISS). Distinguished by its venture far beyond the Earth's stratosphere, reaching altitudes exceeding 160 kilometers, orbital tourism provides passengers with an extended sojourn in the boundless realm of space, characterized by weightlessness and an authentic space station experience.
End-User Overview
In 2023, the global Space Tourism market experienced significant growth, with a 91.8% share in the Commercials segment. Based on the End-User, the Space Tourism market is segmented into Government and Commercials. In this area, the commercial sector has an important role to play, which includes a wide range of businesses that support and enhance the experience of space travel. They are also responsible for contributing to the growth and development of this sector, not only providing access to Space Tourism. In the Space Tourism sector, a dynamic and thriving segment characterized by private companies that are at the forefront of providing such experiences in space travel is commercial Space Tourism. This sector is defined by the involvement of commercial enterprises that offer sub-orbital, orbital, and other space journeys to private individuals and entities.
- Sustainable Space Travel: Sustainability is becoming a paramount concern in the Space Tourism market. The impact of the sector on the environment is also an issue as it grows. Space Tourism operators are becoming more and more concerned with the development of greener propulsion systems, better reusability of rockets as well as addressing issues like space debris. It is not only a moral obligation to promote sustainable tourism, but also an answer to the increasing demand for ecoconscious tourism.
- Evolving Regulations and Safety Standards: With the commercial Space Tourism sector gaining momentum, there is a pressing need for well-defined regulations and safety standards. The development of guidelines to ensure the safety of passengers and the security of space assets is being actively pursued by government agencies and international organizations. Negotiations are ongoing on issues relating to liability, crew training and accident investigations. Effective rules need to be developed which are consistent in order to strengthen the confidence of the industry and establish a framework for its further development.
- Expanding Accessibility and Competition: A major trend in Space Tourism is the drive to enhance accessibility and competitiveness. This includes efforts to reduce the cost of space travel, so that it can be made more accessible. With more competition, technology and business approaches are being improved as a result of an influx of new players. The space industry is expected to revolutionize with greater availability of orbit and orbital flights, allowing companies to compete more effectively for reduced costs, better customer experience as well as an increase in service.
Premium Insights
R&D The research and development industry is playing a key role in the Space Tourism market, driven by innovation, safety improvements, cost reduction as well as overall growth of this sector. One of the main research and development areas is developing spacecraft that can be used for Space Tourism. The creation of suborbital and orbital vehicles that can safely transport passengers into space and back to Earth is also part of this. Companies like Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin, and SpaceX invest heavily in R&D to design and build reliable and reusable spacecraft. Advances in propulsion technology are essential for improving the efficiency and safety of space travel. R&D efforts focus on developing more powerful and eco-friendly engines, such as reusable rocket engines. This can reduce the cost of launches and enhance the environmental sustainability of Space Tourism. Safety is paramount in the Space Tourism industry. R&D is directed at enhancing safety measures, improving crew training, and developing emergency response protocols.

Report Coverage & Deliverables
PDF report & online dashboard will help you understand:
- Real-Time Data Updates:
- Competitor Benchmarking
- Market Trends Heatmap
- Custom Research Queries
- Market Sentiment Analysis
- Demographic and Geographic Insights
Get Access Now
Track market trends LIVE & outsmart rivals with our Premium Data Intel Tool : Vantage Point
Market Dynamics
A technological wave, which has changed our perception of how people travel in outer space, is driving exponential growth within the Space Tourism Industry. Innovation in the design of spacecraft, propulsion systems and launch platforms has been facilitated by technical progress at the heart of this industry. This discovery is at the heart of space travel becoming more accessible, safe and cost effective. The development of modern spaceships has been a major achievement. With their cutting-edge spaceplanes, SpaceShipTwo and New Shepard, companies such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin innovated the way we travel in outer space. Using the latest techniques in materials and aeronautics, this spacecraft is constructed with precision.
Spaceports are terrestrial gateway to the universe, and they're a crucial element in the success of space travel. These facilities are used by space travellers as departure and return points. In order to ensure the safety and effectiveness of space travel, it is essential that we build Spaceports which are both well-equipped and modernised. Space Tourism companies can provide passengers with a seamless and secure experience from preparation of the first flight to its launch and return, by investing in spaceport developments. These facilities in regions with favourable weather conditions and airspace are often situated at strategic locations to facilitate regular and reliable launches.
Competitive Landscape
A key factor influencing the competitive dynamics in this sector is the intensity of competition within the Space Tourism market. The number of competitors, their strategies and overall market conditions influence rivalry. There are currently only a limited number of established players in the Space Tourism market, such as Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, SpaceX, Axiom Space and so on. The first mover advantage was granted to companies such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, which entered the market immediately. They've created a reputation and made themselves known, making it difficult for new entrants to be directly competitive with them. The pace of technological innovation has an impact on competition.
Recent Market Developments
- In January, 2023 SpaceX unveiled another drone ship named A Shortfall of Gravitas, landing a booster from CRS-23.
- In January, 2023 World View announced that it had agreed to go public through a SPAC merger later that year. The company would be listed at New York Stock Exchange. The merger would value the company at $350 million.
- In December, 2022 SpaceX's Falcon 9 became the world record holder for the most launches of a single vehicle type in a single year. SpaceX launched a rocket approximately every six days in 2022, with 61 launches in total. All but one (a Falcon Heavy in November) was on a Falcon 9 rocket.

Frequently Asked Question
What is the global demand for space tourism in terms of revenue.
The global Space Tourism valued at USD 1198.5 Million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 16500 Million in 2032 growing at a CAGR of 31.6%.
Which are the prominent players in the market?
The prominent players in the market are Airbus SE, Axiom Space Inc., Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin LLC, The Boeing Company, Space Exploration Technologies Corp., Zero 2 Infinity, Space Perspective, World View Enterprises Inc., Space Adventures Inc..
At what CAGR is the market projected to grow within the forecast period?
The market is project to grow at a CAGR of 31.6% between 2024 and 2032.
What are the driving factors fueling the growth of the market.
- growing inclination of adventure travelers
Which region accounted for the largest share in the market?
North America was the leading regional segment of the Space Tourism in 2023.
Related Reports
Request sample report for space tourism market, vantage point interactive dashboard.
Space Tourism Market
A Detailed Analysis of the Space Tourism Market by Orbital and Suborbital Tourism Type, 2024 to 2034
The Government’s Unconditional Support for the Space Industry in Making Space Tourism a Highly Lucrative Business Can Transform the Market
- Report Preview
- Request Methodology
Space Tourism Market Outlook from (2024 and 2034)
The global space tourism market size reached US$ 747.1 million in 2023. Demand for space tourism recorded a y-o-y growth of 14.0% in 2023. Hence, the market valuation is expected to reach US$ 851.7 million by 2024. Over the forecast period, the global space tourism industry is predicted to exhibit a 19.8% CAGR, reaching US$ 5,191.7 million by 2034.
Several factors are expected to drive the space tourism market growth. These include the increasing inclination of adventure travelers & high net worth income (HNWI) individuals toward spaceflight, the rising affordability of space travel, and technological advancements.
The market for space tourism is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing government initiatives and investments worldwide. Governments are playing a pivotal role in fostering the development of space tourism by providing financial support, regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure.
The increasing awareness of environmental sustainability is leading to the exploration of greener and more efficient propulsion systems. This is projected to help space tourism companies address concerns related to the carbon footprint of space tourism.
Cutting-edge developments in propulsion systems, materials, and manufacturing techniques are also leading to the creation of safer, more efficient, and accessible spacecraft. The development of these novel space technologies will offer tourists the opportunity to experience space travel like never before.
Don't pay for what you don't need
Customize your report by selecting specific countries or regions and save 30%!
Historical Performance Vs. 2024 to 2034 Global Space Tourism Market Forecast
The market for space tourism exhibited a CAGR of 9.4% between 2019 and 2033. It attained a valuation of US$ 747.1 million at the end of 2023. Over the assessment period, the global space tourism market is set to progress at a 19.8% CAGR.
The space tourism industry is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to expand into a multi-billion-dollar industry in the years to come. As technology continues to advance and costs come down, space travel is expected to become more accessible to the general public. This could lead to a new era of space exploration and discovery in the assessment period.
The space tourism market encourages travelers across the Earth to experience leisure, recreational activities, and business purposes as well. There have been technological innovations that are contributing to the fast growth of space tourism.
The high net-worth income individuals are significantly contributing toward the rise of spaceflight and the growth in adventure travel. This will enhance the growth of the space tourism market, and the trend is expected to continue through 2034.
Top space tourism companies are investing in research and development programs for building new suborbital and orbital vehicles for traveling into space. This will boost revenues for space tourism companies.
Key Factors Expected to Boost the Space Tourism Market Size and Growth
- The growing popularity of space tourism globally is expected to spur growth in the space tourism market.
- The introduction of next-generation space technologies is predicted to boost the market.
- Rising government initiatives and investments to develop space tourism will create lucrative prospects for space tourism companies.
- Emerging trends in orbital space travel, including the development of new orbital and suborbital vehicles, will bode well for the market.
- A rise in lunar space tourism is projected to boost revenues for space tourism companies.
- Penetration of more and more private companies in the commercial space travel industry will foster market growth.
- Decline in the cost of space tourism flights will shape the future of the commercial space exploration sector.
- The surging popularity of hypersonic space travel is anticipated to create growth prospects for the global space tourism industry.

Principal Consultant
Talk to Analyst
Find your sweet spots for generating winning opportunities in this market.
Key Dynamics in the Global Space Tourism Market
- Emergence of Commercial Space Travel Companies to Boost Space Tourism Sales
The emergence of commercial space travel companies has significantly propelled the growth of the space tourism market. Companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic have pioneered reusable rocket technology, making space travel more cost-effective and accessible.
Innovations by companies have led to the development of suborbital and orbital flights for paying customers, sparking a new era of space tourism. This competitive market has driven companies to continuously improve their technology, reduce launch costs, and enhance passenger safety, ultimately expanding the opportunities for individuals to experience space travel.
The space tourism industry is witnessing surging interest and investment, opening up a new frontier for commercial space ventures and transforming space exploration into a viable business sector. Hence, a robust growth trajectory has been predicted for the global space tourism industry.
- Developing Insurance Products Tailored to the Unique Risks of Space Travel
The rapid advancement of space technology and the emergence of private space exploration companies have ushered in a new era of space travel, opening up unprecedented opportunities for the space tourism market. As more individuals and corporations express interest in space travel, there is a growing need for insurance products specifically tailored to the unique risks associated with space exploration.
Unlike traditional travel insurance, space travel insurance must account for a myriad of exceptional risks. This includes equipment malfunctions, spacecraft accidents, extreme environmental conditions, and even space debris.
The potential for accidents or failures during launch, orbital travel, re-entry, and landing stages necessitates highly specialized coverage. Insurance companies have a substantial growth opportunity in this niche market by developing innovative and comprehensive insurance products that address these unique risks.

Key Challenge
Concerns about the Environmental Impact of Space Tourism Limit Market Expansion
The space tourism industry has generated both excitement and trepidation due to its potential environmental impact. This is raising concerns about sustainability and long-term consequences.
Suborbital and orbital flights, while offering a unique experience for a handful, are notorious for their carbon footprint. This is mainly attributed to the immense energy required for rocket launches and the release of greenhouse gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere.
The increased traffic of spacecraft in near-Earth orbit can exacerbate the growing issue of space debris, posing a hazard to future space missions and satellites. The rapid growth of the space tourism market, if not adequately regulated, can contribute to an even more congested and polluted space environment, further challenging the sustainability of space activities.
Get the data you need at a Fraction of the cost
Personalize your report by choosing insights you need and save 40%!
Country-wise Insights
The section brings to the fore key highlights of the space tourism market across prominent countries. Out of all the countries profiled, the market in the United States is expected to witness a CAGR of 17.3%.
Strong Presence of Space Companies Boosting Growth in the United States
The United States space tourism market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 17.3% during the projection period. It will likely hold a prominent share of the global space tourism industry by the end of 2034.
Several factors are expected to drive the United States space tourism industry forward. These include a strong presence of space companies, the development of advanced space technologies, and favorable government support.
The country’s government strongly supports space exploration and is investing heavily in developing new space technologies. This is creating a favorable environment for the development of the space tourism industry.
The United States is also home to a handful of the world's leading space companies, such as SpaceX, Virgin Galactic, and Blue Origin. These companies are developing cutting-edge technologies and infrastructure that are further driving the growth of the space tourism market.
Strong Technological Base and Supportive Government Fostering Growth in Russia
As per the latest space tourism market analysis, Russia's space tourism market is poised to exhibit a robust CAGR of 15.5% during the forecast period. This is attributable to the presence of a robust technological base and increasing support from the government.
The government is also supportive of the development of space tourism, and it has allocated funds to enhance the development of new technologies and infrastructure. The government is working to create a regulatory framework for space tourism, which will help to ensure the safety and security of space tourists.
After sending the first human into space, Russia has continued to be a leader in space technology ever since. This has given Russia a significant advantage in the development of space tourism infrastructure, and the country is now home to several companies that offer space tourism experiences.
Rising Focus on Offering Space Tourism Services to Boost Market in India
Space agencies such as the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) are focusing on exploring the possibilities of offering space tourism services. Similarly, the Indian Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe) is encouraging private companies to carry on with space activities, including space tourism. This will boost the target market.
The Department of Space is further undertaking the process of a space policy that is comprehensive and integrated. This will offer direction to the activities of the Private Indian Space Industry.
IN-SPACe plans on sharing the technical facilities across ISRO centers along with private entities. This will create dimensions of space advancement and will also bring economic benefits as space tourism evolves.
As per the latest report, India is expected to emerge as a highly lucrative market for space tourism companies during the forecast period. It will likely thrive at a CAGR of 16.2% between 2024 and 2034.
Growing Interest in Space Tourism to Drive Demand in China
As per the latest report, China's space tourism market is predicted to expand at a healthy CAGR of 14.8% between 2024 and 2034. This is due to the rising interest in space tourism, reduction in space tour costs, and increasing investments by the government in the space industry.
Citizens across China are showing a keen interest in space tourism owing to the growing popularity of space-related entertainment and raising awareness of China’s achievements in space exploration. This is expected to drive the demand for space tourism in the country.
Space organizations in China are also striving to advance in space technologies and make space tourism affordable. For instance, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) announced that it will likely launch space tourism flights as early as 2025. This will boost the target market.
Development of Next-generation Space Technologies Pushing Japan’s Market
Japan’s space tourism market is predicted to expand at a CAGR of 13.3% during the assessment period. This can be attributed to the development of new space technologies and favorable government support.
Japan’s government is focusing on building new spaceports to make the country Asia’s hub in the space business. This is expected to push the growth of the space tourism market in Japan during the forecast period.
Category-wise Insights
The below section shows the 36 to 40 segment dominating the space tourism market. It is expected to thrive at a 23.2% CAGR during the forecast period. Based on tourism type, the suborbital segment is poised to exhibit a CAGR of 25.9%. By booking channel, the online booking segment will likely progress at a CAGR of 21.1%.
Popularity of Space Tourism Remains High Among the Age Group of 36 to 45
Market Growth Outlook by Key Age
In terms of age group, the 36 to 45 age category is expected to rise with a prolific CAGR of 23.2% during the forecast period. The 36 to 40 age group is particularly well-positioned to take advantage of the growing space tourism industry. This group is typically at the peak of their careers and earning power, and they are more likely to have the disposable income to afford a space tourism experience.
The age group of 36 to 40 years is more likely to be interested in space exploration and willing to take risks. This will boost the growth of the target segment.
As the space tourism market grows, it is expected to attract an increasingly diverse range of participants. However, the 36 to 40 age group will likely remain the most prominent demographic for space tourism during the assessment period.
Demand in the Market to Remain High for Suborbital Space Tourism
Market Growth Outlook by Key Tourism Type
Based on tourism type, the suborbital segment is anticipated to propel with a stupendous CAGR of 25.9% during the assessment period. The growth of this segment is driven by the increasing demand for adventure travel and the rising disposable income of consumers.
Technological advancements are also making suborbital flights more affordable and accessible to a wider range of people. Technology developments such as reusable spacecraft and new launchers are lowering the cost and increasing the accessibility of space travel.
For instance, SpaceX announced that it would begin offering commercial suborbital spaceflights in 2024. The company has already sold tickets to several customers, including Japan’s billionaire Yusaku Maezawa.
Suborbital space tourism is rapidly growing. As a result, companies are developing safe, reliable, and affordable suborbital space vehicles that will be well-positioned to capitalize on this growth.
Convenience and Ease of Booking Making Online Booking Preferable
Market Growth Outlook by Booking Channel
In terms of booking channels, online booking is anticipated to surge with a CAGR of 21.1% in the forecast period. This is attributable to the convenience and ease of booking online, as well as the wide availability of information about space tourism providers and experiences.
Online booking allows potential space tourists to compare prices and options before making a decision. Further, online booking platforms specializing in space tourism typically offer a variety of experiences, including suborbital flights, spacewalks, and orbital missions.
Online booking platforms also provide information about the different space tourism providers, as well as customer reviews, which enhances its future adoption. Hence, the target segment is projected to progress rapidly through 2034.
Competitive Landscape
The space tourism market is in the early stage of development, with key players employing multiple strategies to capture market share. The technological landscape in the space tourism market is constantly evolving, and new technologies are emerging all the time.
As technology continues to advance, companies are focusing on making space tourism more appealing and commercially viable for a broader range of individuals and companies. Further, support channels of suppliers are pacing up, and companies are collaborating well with the direct suppliers. Several space tourism companies are promoting and boosting space tourism through advertisements and celebrity endorsements.
Recent Developments in the Space Tourism Market
- In 2023, Virgin Galactic launched two 2 million-year-old fossils of human ancestors into space on a tourist flight.
- In 2023, According to Vast's announcement, SpaceX will be launching the world's first commercial space station, Vast Haven-1. Two human spaceflight missions will shortly follow it to the space station. Haven-1 is set to become a fully functional space station that will be connected as a module to the larger Vast space station currently being developed and will operate independently.
Scope of the Report
Global space tourism market outlook by category, by direct supplier:.
- Hotel Companies
- Tour Operators
- Government Bodies
By Indirect Supplier:
- OTA (Online Travel Agency)
- Traditional Travel Agencies
- TMCs (Travel Management Companies)
- Corporate Buyers
- Aggregators
By Number of Bookings:
By Tourism Type:
- Stratospheric
By Demographics:
By nationality:.
- International
By Booking Channel:
- Offline Booking
- Online Booking
By Tour Type:
- Individual Travel
- Professional Groups
- Group Travels
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the space tourism market.
The global space tourism market value is expected to reach US$ 851.7 million in 2024.
What is the expected size of the space tourism market?
The global space tourism market size is predicted to reach US$ 5,191.7 million in 2034.
What is the demand outlook for space tourism?
Demand for space tourism is anticipated to expand at a 19.8% CAGR through 2034.
Which tourism type will witness high demand?
Thriving at a 25.9% CAGR, the suborbital type is expected to witness high demand.
Which companies do space tourism?
Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, and Space X are a handful of space tourism companies.
At what rate did the global space tourism market grow from 2019 to 2023?
Global space tourism demand grew at a 9.4% CAGR from 2019 to 2023.
What is the trend in the space tourism industry?
The development of next-generation space technologies is a key trend.
Table of Content
Recommendations.
Travel and Tourism
Medical Tourism Market
January 2021
Tourism Industry Big Data Analytics Market
REP-GB-3171
Outbound Medical Tourism Market
REP-GB-3051
Tourism Market
October 2024
Explore Travel and Tourism Insights
- Get Free Brochure -
Your personal details are safe with us. Privacy Policy*
- Get a Free Sample -
- Request Methodology -
- Customize Now -
I need Country Specific Scope ( -30% )
- Talk To Analyst -
I am searching for Specific Info.
- Download Report Brochure -

You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
We use cookies to improve your experience
We value your privacy and strive to enhance your experience. By continuing to browse our site, you agree to our use of cookies to offer you tailored content and seamless services. Learn more
- Report Store
- Press Releases
Our Services
- Syndicated Reports
- Customized Reports
- Expert Consultation
- Go-to-Market (GTM)
- Cross-Sectional Analysis
- Generative AI
- Healthcare IT
- Biotechnology
- Electric Vehicle
- Semiconductor
Space Tourism Market Size, Trends, Growth, Report By 2032
List of Contents
Space tourism market size, share, and trends 2024 to 2034.
Space Tourism Market (By Type: Orbital, Sub orbital; By Customer: Government, Commercial, Others; By Form: Innovators Early adopters, Early majority; By Product: High altitude jet fighter, lights, Atmospheric zero-gravity flights, Aircraft replacement flights, Others; By Destination; By Customers; By Service Provider) - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, Regional Outlook, and Forecast 2023 to 2032
- Last Updated : June 2023
- Report Code : 1906
- Category : ICT
- Report Description
- Table of Content
Space Tourism Market Size to Reach USD 3,884.18 Mn by 2032
The global space tourism market size was estimated at USD 869.20 million in 2022 and is projected to surpass around USD 3,884.18 million by 2032, poised to grow at a registered CAGR of 16.20% from 2023 to 2032.
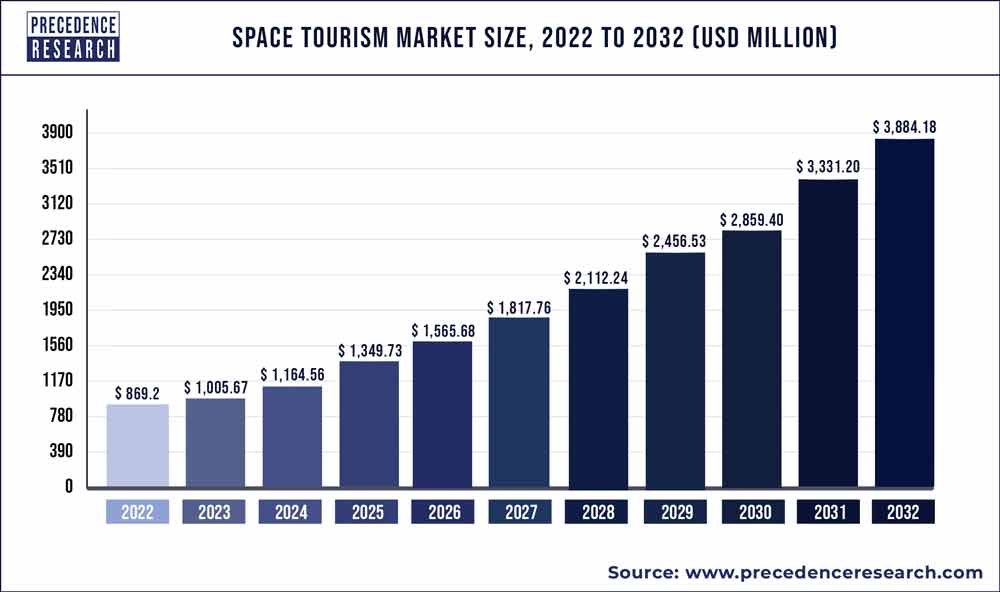
Key Takeaways:
- By type, the U.S. space tourism market was valued at USD 201.52 million in 2022.
- By type, the sub-orbital segment accounted highest revenue share of 51% in 2022 with a CAGR of 36% from 2023 to 2032.
- The orbital type segment is projected to reach a CAGR of 37% from 2023 to 2032.
- The commercial segment has contributed 58% market share in 2022 and is poised to grow at a CAGR of 36% from 2023 to 2032.
- The government end user segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 37.5% from 2023 to 2032.
- North America accounted largest market share of over 40% in 2022.
- The Asia-Pacific is projected to reach a CAGR of 37.6% in 2022.
Space tourism is the recreational journey of people to space. Until now, space travel has been limited to the wealthiest. Only seven people have ever paid to travel to space, beginning with multimillionaire Dennis Tito in 2001. Nonetheless, Wired Magazine named 2019 the year space travel became a "reality," naming many private businesses as pioneers in the space tourism sector, including SpaceX, Virgin Galactic, Boeing, and Blue Origin. The Karman line, which is 100 kilometres above sea level, marks the beginning of space. This is the generally acknowledged border between the Earth's atmosphere and space.
However, the Space Shuttle, International Space Station, and other satellites orbit within Earth's atmosphere (particularly, the thermosphere), prompting some to contend that these objects are not actually in "space." It's better to think of space as a gradient, similar to how the ocean "ends" at the shore. Tides, waves, and weather all have an impact on where the ocean stops. Previously, the space economy was limited to satellites and their subsystems, but the willingness of wealthy individuals and forward-thinking corporations to venture beyond Earth has allowed tourism to enter this embryonic industry.
Satellites, space debris, space mining, space exploration, space tourism, and space infrastructure manufacturing will comprise the future space economy. Furthermore, high-profile commercial missions have prompted some to refer to the current stage of the space industry as the "billionaire space race." The launches of Richard Branson's Virgin Galactic and Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin missions, respectively, emphasized the possibilities for space travel. However, the cancellation of Space Adventures' Crew Dragon mission revealed that pricing, time, and the present experience must be regularly reassessed.
In 2020, the space sector experienced unprecedented growth as investors poured over $9 billion into private enterprises, despite the COVID-19 pandemic. While some of these companies are just selling components and services to government entities such as NASA, others seek to send their own people and rockets into space. Space tourism for any private individual willing to pay a large charge is one ambitious objective that multiple firms are already pursuing. Because of the massive cost and severe hazards involved, governments monopolized space exploration in its early days. Exhibit 1 depicts some of the early milestones in space travel, as well as other significant breakthroughs up to the year 2000. Private firms, with far lower resources, saw little need to study crewed missions because the chances of obtaining government clearance and achieving a reasonable return were slim.
Growth Factors
Although space tourism will be limited to a few, new players will likely enter the market offering lower-cost options. One such example is Space Perspective's stratospheric ballooning service. Until major businesses like SpaceX, Virgin Galactic, and Blue Origin can scale their technology to make it affordable to non-millionaires, they will have a small target market of about 1% of the world population. The United States will be the primary source market for space tourism enterprises. When advertising their excursions and hotels, all participants in the space tourism sector should focus on the US source market, since efforts geared at this market are likely to have the most impact. China and Japan have the second and third most high-net-worth and ultra-high-net-worth persons, respectively, making these source markets potential alternatives for space tourism enterprises. As shown in 2021, Japan's wealthiest residents may be interested in space exploration. Yusaku Maezawa, a Japanese businessman, returned to Earth in December 2021 following a 12-day flight to the International Space Station.
The overall cost of a journey into space has decreased dramatically from around $600,000 to $250,000. This market's client base consists only of consumers who fall inside the top 1% of income earners. With price declines, new client groups are expected to enter the market that is willing to pay a large premium for a once-in-a-lifetime space experience. The cost is expected to be less than $2000 per kilogram over the next few years. Further price reductions are predicted to make space tourism more accessible to a larger populace, boosting the potential client base. Several commercial suborbital spacecraft with various capacities are currently under development.
The SARG was formed by the Commercial Spaceflight Federation to increase awareness of the research and education possibilities of the suborbital reusable launch vehicles under development. In addition, in preparation for human-tended studies on commercial suborbital spacecraft, the NASTAR and the SwRI established a suborbital space scientist training course. These activities are expected to have a favorable influence on the worldwide space tourism business. These new endeavors have sparked interest and produced headlines, resulting in even greater investment in private space enterprises. For example, numerous special-purpose acquisition corporations (SPACs) are looking to acquire space firms based on their predicted future income, allowing them to become public. 5 Aside from these endeavors, three recent uncrewed trips to Mars, including the arrival of NASA's Perseverance rover, are also giving the impression that we are entering a new era of discovery and possibility.
The growing applications of Space Tourism across numerous end-use sectors are driving the market. Technological progress is a crucial trend that is gaining traction in the Space Tourism business. To lead this industry, the top essential players are working on innovative technologies. This will provide the reader an advantage over others because a well-informed decision may be made by looking at the market as a whole.
Although the actual size and sustainability of the commercial-space industry remain unknown, it looks to be set for tremendous expansion. If the private firms that want to operate in late 2021 and 2022 make their deadlines, we may expect even more interest from both investors searching for possibilities and customers wishing to book future trips. If the cislunar economy comes to fruition, it will give reasons to fly to space that go beyond bragging rights—and that might be the door to a strong and long-lasting market for commercial trips.
Report Scope of the Space Tourism Market
Type Insights
During the projected period, suborbital spaceflight services are expected to account for the majority of total revenue share. This is mostly owing to reduced prices associated with suborbital space flight compared to orbital space travel expenses. Because of the high cost of orbital tourism, demand is projected to be restricted. Suborbital flights carrying space passengers and researchers at altitudes ranging from 50 to 68 miles are being tested by companies such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin. Suborbital tourism is projected to begin sooner and develop faster because to increased frequency and cheaper ticket pricing, whereas orbital tourism is expected to significantly expand the commercial space ecosystem alongside government projects.
Customers Insights
The travel sector is undergoing major changes. The number of people interested in space travel is expected to rise between 2022 and 2030. More than 500 individuals signed up, each prepared to pay roughly $250,000 for tickets to suborbital space journeys on the VSS Unity in New Mexico in 2019. NASA revealed plans to open the International Space Station to visitors in 2019. Each voyage to the space station is expected to cost roughly $60 million.
In addition, Cowen and UBS both recently conducted surveys of high-net-worth people to determine their interest in suborbital tourism. Cowen's poll outperformed Whitesides' estimate, with the business discovering a total addressable market of around 2.4 million persons among those with a net worth of more than $5 million. UBS polled over 6,000 high-net-worth people on flying with Virgin Galactic. Approximately 20% of respondents polled by UBS stated they are "likely to purchase a ticket on a spaceship within 1 year" of the firm starting regular flights. This figure rises to more than 35% "after several years of safe operation," according to UBS. Recent occurrences have demonstrated that commercial space travel is technologically viable. However, "commercial feasibility" has yet to be proved, he said, adding that this viability is dependent on more than the existence of a few "willing and affluent" people. While the signals are encouraging, commercial space tourism businesses still have significant marketing questions, according to Crouch. What, for example, is the demand-price relationship? And what features will make a space tourist's experience "worth for money"? There are several variables that space travelers may encounter and interpret differently. Among these are the following: launch site, vehicle type, weightlessness period, and degree of training required.
Space Tourism Market Share, By Region, 2022 (%)
Regional Insights
The North American area, particularly the United States, dominates the market. The space tourism business began in the United States, and the majority of the prominent industry operators are based there. High average disposable income and the presence of the most billionaires are two significant reasons driving the expansion of the space tourism business in the United States. The majority of industry companies, including Virgin Galactic, SpaceX, and Blue Origin, are based in the United States.
The space tourism business in the United States is expected to be worth US$ 201.52 million by 2022 . China, the world's second-biggest economy, is expected to reach a market size of US$ 480 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 20% from 2023 to 2032. Other notable geographic markets include Japan and Canada, which are expected to increase at 11.4% and 13.8% , respectively, between 2023 and 2032. Germany is expected to expand at a CAGR of about 20% in Europe . The research provides succinct insights into how the pandemic has affected output and the buy side in 2020 and 2021. A staged short-term recovery per significant region is also addressed.
Key market developments in Space Tourism Market
- SpaceX, a US-based aerospace corporation, sent two people into orbit in May 2020, reusing the Falcon 9 rocket that had delivered the crew into orbit. This is seen as a significant technological breakthrough for the corporation, as rocket reuse results in considerable cost savings for space exploration.
- Virgin Galactic sent test passenger Beth Moses into space in February 2019. The spaceship, which can carry six passengers and two pilots, costs $250,000 apiece.
- Blue Origin had planned to begin customer test flights in 2020, however this has been postponed owing to the COVID-19 epidemic.
Key market players
- Airbus Group SE
- Boeing Company
- Excalibur Almaz, Limited (Isle of Man)
- Space Adventures, Inc.
- Space Island Group
- Spacex
- Virgin Galactic, LLC.
- Zero 2 Infinity S. L.
Segments covered in the report
(Note*: We offer report based on sub segments as well. Kindly, let us know if you are interested )
- Sub orbital
By Customer
- Innovators Early adopters
- Early majority
- High altitude jet fighter flights
- Atmospheric zero-gravity flights
- Aircraft replacement flights
By Destination
- Other Earth Destinations
- Earth Orbit
By Customers
By Service Provider
- The Government
- Commercial Institutions
By Geography
- North America
- Asia-Pacific
- South Korea
- Philippines
- Latin America
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- North Africa
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current size of space tourism market, what will be the cagr of global space tourism market, who are the prominent players operating in the space tourism market, which are the driving factors of the space tourism market, which region will lead the global space tourism market, proceed to buy.
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
Related Reports
Space technology market size to worth usd 916.85 bn by 2033, iot in aerospace & defense market size, report 2032, space launch services market size to hit usd 57.94 bn by 2033, space robotics market size to worth usd 11.23 bn by 2033, connect with us now; your solution awaits on the other side.
- Aerospace and Defense
Space Tourism Market
Space tourism market report by type (orbital, sub orbital), end use (government, commercial), region and competitive landscape (market share, business overview, products offered, business strategies, swot analysis and major news and events) 2024-2032.
- Report Description
- Table of Contents
- Methodology
- Request Sample
Space Tourism Market Size:
The global space tourism market size reached US$ 0.94 Billion in 2023 . Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach US$ 16.3 Billion by 2032 , exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 35.8% during 2024-2032 . Rapid technological advancements, increasing competition among private space companies, rising public interest in space exploration, government support, and diversification of offerings are driving the market.
Space Tourism Market Analysis:
- Major Market Drivers: Rising interest in space exploration, increasing competition among private space companies, and growing demand for unique experiences beyond Earth's atmosphere are driving the market.
- Key Trends: The development of reusable spacecraft, partnerships between space tourism companies and luxury travel providers, etc. are the trends.
- Geographical Trends: The market is witnessing some major activity in regions such as the United States.
- Competitive Landscape: Some of the market players are Airbus, Blue Origin, Boeing, Space Adventures, among others.
- Challenges and Opportunities: Challenges include high costs associated with space travel. Opportunities lie in the expanding market demand.
Space Tourism Market Drivers:
Growing Space Exploration Interest
The rapidly increasing enthusiasm for travelling to outer space is a key driving factor behind the space tourism market growth. Space agencies and commercial entities carry out exploratory expeditions of celestial bodies and establish human beings beyond the Earth. As they do this, people become more interested in travelling through space. This growing curiosity creates a demand for space tourism as individuals yearn to experience the marvels of space and participate in the era of exploration. For instance, SpaceX promotes growing interest in space exploration by regularly streaming live launches and landings, engaging with enthusiasts on social media platforms, and hosting events like the Inspiration4 mission, which sent civilians into orbit for several days, showcasing the accessibility of space travel to the public. Moreover, rising media coverage, technology developments, and lowering costs of venturing into space are making it possible for more people to visit outer-space. Therefore, these factors have democratized access to such regions hence making it easier for many people to get involved with this kind of business.
Increasing Comfort and Easy Accessibility
Increase in comfort and ease of access is driving the growth of space tourism market. More comfortable spacecrafts designs and technology are being used in ensuring that the passengers’ experience is better, making it more enjoyable rather than terrifying. For instance, Blue Origin is focused on increasing comfort and easy accessibility to space. Through its New Shepard suborbital rocket system, Blue Origin aims to provide passengers with a comfortable and relatively easy experience of space travel. They prioritize safety and comfort by designing the capsule with large windows for stunning views, reclining seats to minimize discomfort during launch and re-entry, and a spacious cabin for freedom of movement during weightlessness. On top of this, efforts to improve booking processes and launch infrastructure have further made space tourism available to many people. With a cost cutting program and simplified logistics on board, space tourism has become practical for those adventure-seeking travelers looking for remarkable experiences beyond what is above the earth’s atmosphere.
Rise in Commercial Space Tourism Companies
Commercial space tourism companies are increasing the size of the space tourism market. The advent of firms has increased the availability of possible trips into outer-space. For these reasons, they are developing spaceships, infrastructures as well as experiences which can be accessed by private citizens. Their new methods of traveling through space along with heightened competition within this industry results in higher technological advancements and lower costs thereby positioning commercialized space travel within reach for larger numbers. For instance, through its SpaceShipTwo suborbital spaceplane, Virgin Galactic aims to offer relatively affordable trips to the edge of space. They are making space travel accessible by developing reusable spacecraft technology, which helps to reduce the overall cost per flight. Additionally, Virgin Galactic plans to operate multiple SpaceShipTwo vehicles simultaneously, increasing the frequency of flights and accommodating a larger number of passengers over time.
Development of Space Tourism Eco System
The growth of an environment for space vacationing is important as it results in sustainable development of the industry. A number of elements make this ecosystem, which include, spacecraft manufacture, launch infrastructure, tourism operators, spaceports, supporting industries and regulatory frameworks. Companies are working on developing spacecrafts that can transport tourists to space and back safely while the other companies are constructing or modifying their facilities to accommodate commercial space travel. In addition, tourism operators are crafting tailored experiences for travelers ranging from suborbital joyrides to orbital hotels. Space Adventures is known for facilitating private space missions for individuals to the International Space Station (ISS) using spacecraft like the Russian Soyuz. They are expanding the space tourism ecosystem by offering a range of services beyond just suborbital or orbital flights. For instance, they had booked two passenger seats on a Russian Soyuz capsule headed to the International Space Station in 2023, and one of those tourists will take part in a spacewalk. Furthermore, regulatory bodies also come up with guidelines that ensure safety and responsibility in space tourism. Moreover, this ecosystem encourages innovation as well as investment promotion and expansion of the space tourism.
Space Tourism Market Opportunities:
Partnership Among Key Players
Partnership among players in the field of space tourism facilitate innovation, expand capabilities and guarantee success in the sector. Blue Origin, founded by Jeff Bezos, partnered with NASA to develop technologies for future space missions. This partnership brought financial support and also lent credibility to Blue Origin's ambitions in the space tourism sector. Partnerships involving governments even research institutions private companies among others have been known to aid knowledge sharing along with technology advancement besides resource combining. For instance, partnerships between aerospace firms and tour operators may lead to better spacecrafts hence more customized tourist’s experiences. Collaborations between space agencies and private companies can leverage expertise and resources to advance exploration missions and infrastructure development. These partnerships not only accelerate progress but also foster a sense of collective responsibility and collaboration in advancing humanity's presence in space.
Rising Private Investment
The growth of space tourism market is driven by the increase in private investment. Space tourism ventures have increasingly been recognized as being potentially lucrative and also beneficial to society by way of private investors. This capital flow makes it possible for space tourism firms to finance research, develop cutting-edge technologies and scale up their business operations. As per a report by UBS, the space tourism industry is expected to be of worth $3 billion by 2030. This estimation is based on the rising number of private companies entering the market and the increasing demand from wealthy individuals who are willing to pay top dollar for a once-in-a-lifetime experience. Additionally, private investments promote competition within the industry, which drives companies into making better products while lowering prices for a wider audience. Furthermore, private investors come with experience from other sectors that help space tourism companies go through legal barriers and business difficulties.
Advancement in Technology
Technology has been one of the major factors driving this market forward. Safer, more efficient and cheaper space travel is being made possible with spacecraft design breakthroughs, propulsion systems advancements, materials science improvements as well as life support system inventions. Tourist missions such as launching payloads into space are considerably less expensive due to reusable rocket technology for instance. Longer duration travel is also possible now thanks to new designs for life support systems and habitats in space which can accommodate more people thus creating opportunities for orbital tourism among others beyond earth’s orbit where humans can live. Furthermore, advancements in virtual reality and telepresence technologies enhance the pre-flight training experience for space tourists and offer immersive experiences for those unable to physically travel to space. The design and engineering of spacecraft have changed significantly, focusing on improving safety, comfort, and efficiency. New spacecraft, such as SpaceX's Crew Dragon and Boeing's CST-100 Starliner, prioritize your well-being while providing an unforgettable experience.
Targeting Untapped Market
Tapping untapped markets is a strategic approach that has been pushing the space tourism industry into new territories. Initially, early endeavours of space tourism mainly aimed at affluent persons. However, the realization of its wider demographic reaches is coming to be seen emerging. Companies are working on ways to make space travel affordable and inclusive, by way of taking advantage of the ambitions or dreams of more people. Thus, market targeting includes innovations in pricing models such as tiered packages and installment plans that would enable middle-income earners to afford travelling to space. Additionally, partnerships with travel agencies and marketing campaigns aimed at adventure seekers and space enthusiasts are broadening the appeal of space tourism beyond traditional demographics.
Government Support
The space tourism industry greatly depends on government support. Funding, infrastructure and regulatory frameworks provided by governments enable safe and efficient operations of space tourism companies. In addition to grants and tax breaks as financial incentives for space tourism start-ups, this kind of investment stimulates innovation and economic expansion. Governments are also known to collaborate with private entities in the construction of spaceports, launch facilities as well as other necessary infrastructure for commercial space travel. Furthermore, regulatory bodies put in place safety standards, licensing requirements, and airspace regulations in order to protect passengers and the general public. For instance, in the USA, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates commercial space transportation. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have got licenses from the FAA to conduct space tourism operations.
Key Technological Trends & Development:
Virtual Reality (VR) Technology
Virtual Reality (VR) technology is accelerating the growth of space tourism market by delivering captivating experiences that imitate space. With virtual reality (VR), aspirational tourists are able to go on imaginary voyages to far-off planets, experience zero gravity and tour inside a spacecraft. This technology allows space tourism companies to provide pre-flight training which will give-a-hint what passengers should expect during their actual space flight. Also, VR experiences help increase public involvement in space exploration thus creating curiosity among potential explorers. As VR technology continues to advance, offering increasingly realistic and interactive simulations, it becomes a powerful tool for marketing space tourism experiences and expanding the market to a wider audience, ultimately fueling the growth of the industry.
Reusable Rocket Technology
Through reusable rocket technology, there is a remarkable change in the space tourism market as it minimizes launch costs for payloads and passengers heading into space. Many companies have developed and successfully demonstrated the ability to recover and reuse rocket boosters, drastically lowering the overall expenses associated with space travel. This advancement makes it possible for operators of Space Tourism to offer tickets at cheaper prices enabling many people enjoy the benefits of such trip. Additionally, reusable rockets enhance the viability and attractiveness of ventures in this industry through increase reliability as well as frequency of launches. Companies like SpaceX revolutionized the space tourism industry by developing reusable rocket technology. For instance, the design of Falcon 9's enables it to land back on Earth after launching its payload. This, in turn, allows it to be refurbished and used for subsequent missions.
Space Elevators
Groundbreaking space transportation concept, space elevators can possibly completely overturn the market of space tourism. Essentially, this idea involves constructing a lofty structure jutting from the Earth up into the sky and beyond with a counterweight at the upper end and a tether that connects to a base station on the planet’s surface. It is possible to use centrifugal force and gravity to achieve energy-efficient and cost-effective transport of passengers as well as cargo for orbital stations or even far places. The development of space elevators will lower significantly the expenses involved in launching rockets normally while reducing environmental hazards related to such developments thus increasing access to tourists. Additionally, the concept offers the potential for regular, reliable access to space, enabling more frequent and affordable space travel experiences.
Integration of Artificial intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration is enhancing security, productivity as well as customer experience within the area of space tourism. AI-based solutions are being used in several areas of operations in space tourism such as spacecraft design, mission planning, crew training, and onboard systems. For instance, AI algorithms employed in spacecraft design help analyze massive data sets available so that vehicle performance is optimized through fuel consumption reduction and increased reliability. This results in effective and low-priced spaceships ready for commercial purposes. AI also plays a crucial role in mission planning by assisting in route optimization, trajectory planning, and risk assessment. By analyzing real-time data and predicting potential hazards, AI systems help ensure the safety and success of space tourism missions. For instance, SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft can autonomously dock with the International Space Station, lowering the need for constant human intervention. It showcases AI’s safety contributions.
Space Tourism Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the global, regional, and country levels for 2024-2032. Our report has categorized the market based on type and end use.
Breakup by Type:
- Sub Orbital
Sub orbital accounts for the majority of the market share
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes orbital and sub orbital. According to the report, sub orbital represented the largest segment.
There is significant growth in sub-orbital space tourism due to major advancements in technology. The advancements are increasing the availability and affordability of space travel, mainly by creating reusable spacecraft. The allure of distinct experiences, like feeling weightless and viewing Earth from space, is captivating the imagination of wealthy individuals, driving interest in this sector. Improved safety measures and thorough training for travelers are boosting confidence in these businesses, making them more attractive. Governments are actively involved in creating policies and regulations to promote a favorable environment for space tourism initiatives. The rise of collaborations between the public sector and private companies is spurring investment and innovation, boosting the sub-orbital space tourism industry.
Breakup by End Use:
- Commercial
Commercial holds the largest share of the industry
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end use have also been provided in the report. This includes government and commercial. According to the report, commercial accounted for the largest market share.
Due to the ambitious goals of private companies, the commercial space tourism industry is experiencing significant growth and progress in making space travel more achievable. Investing in critical infrastructure such as spaceships and space terminals is establishing a strong base for the industry's expansion. Rivalry among top players in the space tourism industry is driving innovation, leading to more secure and reliable space travel options. Partnerships between tourism firms and schools are opening up fresh opportunities for learning and study in outer space. Industry stakeholders are now making efforts to reduce the environmental impact of their operations, making environmental stewardship a priority. The expansion of this industry is not only related to providing exceptional experiences, but also to its positive impact on the economy by creating more job opportunities and stimulating growth in related industries.
Breakup by Region:
United States
- South Korea
United Kingdom
- Middle East
- Africa
North America leads the market, accounting for the largest space tourism market share
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include North America (the United States and Canada); Asia Pacific (China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, and others); Europe (Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, and others); Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, and others); the Middle East; and Africa. According to the report, North America accounted for the largest market share.
North America, especially the United States, is leading the way in the global market. This superiority is emphasized by a strong history in space discovery and a thriving aviation sector, as well as regulations that support creativity and safety in space travel. The collaboration between public authorities and private companies is crucial, propelling progress and maintaining North America's dominance in this sector. The area's advanced technology is allowing for the development of complex spacecraft and infrastructure, vital for the prosperity of space tourism. In addition, it is essential to use strategic marketing and engage globally to attract a diverse customer base and secure funding. In North America, strong public interest in space exploration is a major factor contributing to the industry's expansion. Regulatory agencies in the area are leading the way in creating thorough safety and legal frameworks to oversee the sustainable growth of space tourism.
Leading Key Players in the Space Tourism Industry:
The key players have been investing in spacecraft design and infrastructure to improve safety, reliability, and passenger experience. Such partnerships are also fueled by the need for collaboration between space tourism operators, aerospace companies, and government agencies. The key players behind these campaigns are also stoking up interest in space tourism through public events and media coverage. However, promoting it as an aspirational travel option is important for the key players who are engaged in promotional campaigns. By using different stakeholders’ expertise, resources and funding, such collaborations help in developing new technologies, launch facilities, and space tourism destinations. On top of this, marketing efforts to raise awareness of space travel are broadening market size and attracting more clients. To promote it as a viable option for everyone who wants to travel the key players conduct promotional campaigns such as media coverage through press releases or other means like public events. These players are fueling interest in space tourism and positioning it as a viable and aspirational travel option.
The market research report has provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape covering market structure, market share by key players, market player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant, among others. Detailed profiles of all major companies have also been provided. This includes business overview, product offerings, business strategies, SWOT analysis, financials, and major news and events. Some of the key players in the market include:
- Blue Origin
- Space Adventures
- Space Perspective
- Virgin Galactic
- World View Enterprises, Inc.
- Zero 2 Infinity
- Zero Gravity Corporation
(Please note that this is only a partial list of the key players, and the complete list is provided in the report.)
Analysis Covered for Each Player:
- Market Share
- Business Overview
- Products Offered
- Business Strategies
- SWOT Analysis
- Major News and Events
Latest News :
- January 16, 2024 : Voyager Space and Airbus Defence and Space announced their partnership to develop the Starlab commercial space station. They are seeking to win customers for it from both sides of the Atlantic.
- December 19, 2023 : Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin, an unmanned tourist rocket, was launched from west Texas in its first successful launch since a failed mission fifteen months ago stalled the New Shepard program and drew the ire of the Federal Aviation Administration.
- February 26, 2024 : Space Perspective, a Florida-based startup, unveiled a test capsule for its new Neptune spacecraft. The Neptune is anticipated to start carrying passengers into the stratosphere using a massive balloon instead of rockets as early as next year. The company touts the Neptune capsule as the third commercial suborbital spacecraft ever built after Virgin Galactic's SpaceShipTwo space plane and Blue Origin's New Shepard crew capsule.
Space Tourism Market Report Scope:
Key questions answered in this report:.
- How has the global space tourism market performed so far, and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What are the drivers, restraints, and opportunities in the global space tourism market?
- What is the impact of each driver, restraint, and opportunity on the global space tourism market?
- What are the key regional markets?
- Which countries represent the most attractive space tourism market?
- What is the breakup of the market based on the type?
- Which is the most attractive type in the space tourism market?
- What is the breakup of the market based on the end use?
- Which is the most attractive end use in the space tourism market?
- What is the competitive structure of the market?
- Who are the key players/companies in the global space tourism market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the space tourism market from 2018-2032.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global space tourism market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the space tourism industry and its attractiveness.
- The competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
India Dairy Market Report Snapshots Source:
Statistics for the 2022 India Dairy market share, size and revenue growth rate, created by Mordor Intelligence™ Industry Reports.
- India Dairy Market Size Source
- --> India Dairy Market Share Source
- India Dairy Market Trends Source
- India Dairy Companies Source
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
Purchase options

Benefits of Customization
Personalize this research
Triangulate with your data
Get data as per your format and definition
Gain a deeper dive into a specific application, geography, customer, or competitor
Any level of personalization
Get in Touch With Us

UNITED STATES
Phone: +1-631-791-1145

Phone: +91-120-433-0800

UNITED KINGDOM
Phone: +44-753-714-6104
Email: [email protected]
Client Testimonials

IMARC made the whole process easy. Everyone I spoke with via email was polite, easy to deal with, kept their promises regarding delivery timelines and were solutions focused. From my first contact, I was grateful for the professionalism shown by the whole IMARC team. I recommend IMARC to all that need timely, affordable information and advice. My experience with IMARC was excellent and I can not fault it.

The IMARC team was very reactive and flexible with regard to our requests. A very good overall experience. We are happy with the work that IMARC has provided, very complete and detailed. It has contributed to our business needs and provided the market visibility that we required

We were very happy with the collaboration between IMARC and Colruyt. Not only were your prices competitive, IMARC was also pretty fast in understanding the scope and our needs for this project. Even though it was not an easy task, performing a market research during the COVID-19 pandemic, you were able to get us the necessary information we needed. The IMARC team was very easy to work with and they showed us that it would go the extra mile if we needed anything extra

Last project executed by your team was as per our expectations. We also would like to associate for more assignments this year. Kudos to your team.
.webp)
We would be happy to reach out to IMARC again, if we need Market Research/Consulting/Consumer Research or any associated service. Overall experience was good, and the data points were quite helpful.

The figures of market study were very close to our assumed figures. The presentation of the study was neat and easy to analyse. The requested details of the study were fulfilled. My overall experience with the IMARC Team was satisfactory.

The overall cost of the services were within our expectations. I was happy to have good communications in a timely manner. It was a great and quick way to have the information I needed.

My questions and concerns were answered in a satisfied way. The costs of the services were within our expectations. My overall experience with the IMARC Team was very good.

I agree the report was timely delivered, meeting the key objectives of the engagement. We had some discussion on the contents, adjustments were made fast and accurate. The response time was minimum in each case. Very good. You have a satisfied customer.
.webp)
We would be happy to reach out to IMARC for more market reports in the future. The response from the account sales manager was very good. I appreciate the timely follow ups and post purchase support from the team. My overall experience with IMARC was good.

IMARC was a good solution for the data points that we really needed and couldn't find elsewhere. The team was easy to work, quick to respond, and flexible to our customization requests.
- Market Entry and Opportunity Assessment
- Competitive Intelligence and Benchmarking
- Procurement Research
- Pricing and Cost Research
- Regulatory Approvals, and Licensing
- Factory Setup
- Factory Auditing
- Company Incorporation
- Incubation Services
- Recruitment Services
- Marketing and Sales
- Primary Research
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Sourcing Partner Identification
- Distribution Partner Identification
- Contract Manufacturer Identification
- Epidemiology Intelligence
- Asset and Indication Priortiztion
- Healthcare Competitive Intelligence
- R&D Analysis
- Patient and Prescriber Insights
- Regulatory Analysis
- Report Store
Quick Links
- Press Releases
- Case Studies
- Our Customers
- Become a Publisher
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
+1-631-791-1145
Level II & III, B-70, Sector 2, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301, India
+91-120-433-0800
30 Churchill Place London E14 5EU, UK
+44-753-714-6104
Level II & III, B-70 , Sector 2, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301, India
+44-20-8040-3201
We use cookies, including third-party, for better services. See our Privacy Policy for more. I ACCEPT X

+1-866-353-3335
- Custom Research
- Research Partners
- Enterprise Solution
PUBLISHER: Bizwit Research & Consulting LLP | PRODUCT CODE: 1543695

Global Space Travel or Tourism Market Size Study, by Destination, by Duration, by End-Users (Billionaires & Ultra-High-Net-Worth Individuals, Adventure Seekers & Science Enthusiasts), by Gender and Regional Forecasts 2022-2032
Add to Cart
Description
Table of contents.
Global Space Travel or Tourism Market was valued at USD 892.67 Million in 2023 and exhibiting a CAGR of 44.31% during the forecast period 2024-2032. Space travel or tourism refers to recreational, leisure, or business travel beyond Earth's atmosphere. This burgeoning segment of the space industry enables civilians to experience spaceflight, including suborbital and lunar spaceflights, where they can witness microgravity, view Earth from afar, and explore the vastness beyond our planet's atmosphere. Furthermore, companies such as Blue Origin, SpaceX, and Virgin Galactic are pivotal in this sector, offering civilians opportunities to experience space. Moreover, the decreasing cost of space travel, coupled with significant initiatives by governmental bodies like ISRO, is expected to bolster market growth significantly during the forecast period.
The market for space tourism is rapidly expanding due to increasing interest and technological advancements. Market players such as Blue Origin, SpaceX, and Virgin Galactic offer suborbital flights, fueling market growth. Moreover, regulatory hurdles and safety concerns persist. Rising affluence and burgeoning interest in lunar exploration further drive market expansion, with innovative experiences such as space walks and space hotels on the horizon. Industry collaborations are accelerating innovation, and advancements in space observation technology are contributing to this growth. Sustainable practices and international cooperation are key to ensuring long-term market viability, despite challenges in emerging economies.
The key region in the Global Space Travel or Tourism Market includes North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. In 2023, North American region is anticipated to dominate the space travel or tourism market driven by substantial investments in R&D and a rising number of companies. The presence of NASA and private aerospace companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic contribute significantly to market growth. Furthermore, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest CAGR during the forecast period 2024-2032 driven by the rapidly advancing space technology, with increasing investments in sustainable energy and significant government support.
Major market players included in this report are:
- Space Adventure Limited
- Blue Origin
- Axiom Space, Inc.
- Virgin Galactic
- Zero 2 Infinity S.L
- Rocket Lab USA Inc.
- Skyroot Aerospace Pvt. Ltd.
The detailed segments and sub-segment of the market are explained below:
By destination:.
- Orbital Spaceflight
- Sub-orbital Spaceflight
- Lunar Spaceflight
By Duration:
- Up to 8 Days
- More than 8 Days
By End-Users:
- Billionaires & Ultra-High-Net-Worth Individuals (UHNWI)
- Adventure Seekers & Science Enthusiasts
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- South Korea
- Latin America
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
Years considered for the study are as follows:
- Historical year - 2022
- Base year - 2023
- Forecast period - 2024 to 2032
Key Takeaways:
- Market Estimates & Forecast for 10 years from 2022 to 2032.
- Annualized revenues and regional level analysis for each market segment.
- Detailed analysis of geographical landscape with Country level analysis of major regions.
- Competitive landscape with information on major players in the market.
- Analysis of key business strategies and recommendations on future market approach.
- Analysis of competitive structure of the market.
- Demand side and supply side analysis of the market.
Chapter 1. Global Space Travel or Tourism Market Executive Summary
Chapter 2. global space travel or tourism market definition and research assumptions, chapter 3. global space travel or tourism market dynamics, chapter 4. global space travel or tourism market industry analysis, chapter 5. global space travel or tourism market size & forecasts by destination 2022-2032, chapter 6. global space travel or tourism market size & forecasts by duration 2022-2032, chapter 7. global space travel or tourism market size & forecasts by end-users 2022-2032, chapter 8. global space travel or tourism market size & forecasts by gender 2022-2032, chapter 9. global space travel or tourism market size & forecasts by region 2022-2032, chapter 10. competitive intelligence, chapter 11. research process.

Jeroen Van Heghe
Manager - EMEA
+32-2-535-7543

Christine Sirois
Manager - Americas
+1-860-674-8796

We have liftoff: Space Tourism and the Space Economy
The past year has been revolutionary for the space economy, with space tourism finally becoming a reality. While traveling to the stars seemed like a far-fetched dream, companies like SpaceX , Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic have seemingly made it possible, each having flown their first tourist-focused missions in 2021.
Following the milestone number of successful commercial space launches in 2021, it seems like every week there are new announcements of plans for space travel. With more private citizens than ever before making the trip outside of the Earth’s atmosphere in 2022, it is clear that Space Tourism is now a reality. But what does the emergence of space tourism mean for the space economy?
What is space tourism?
Simply put, space tourism refers to the activity of traveling into space for recreational purposes. While to many it seems like an unattainable dream, the concept of space tourism isn’t new, with Dennis Tito, the first space tourist, having paid $20 million in 2001 to go to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard the Russian Soyuz spacecraft.
While approximately 600 people have traveled into space, only a small fraction of them have been space tourists, meaning they traveled into space for leisure or recreational purposes, and not for any scientific research. Between 2001-2009 eight space tourists reached orbit, each of them utilizing government rockets and/or government space stations for their journey. In fact, the 2021 SpaceX voyage was the first all-private mission to orbit with the crew even planning their own itinerary.
The rapid growth of interest in space tourism has resulted in many companies researching, designing and testing spacecraft to carry tourists to space on a regular basis. Companies such as SpaceX and Virgin Galactic are leading the space tourism industry in outlining plans to deliver various forms of commercial space travel in the near future. Individuals who one daydream of being space tourists will be able to choose from three different types of space travel; suborbital space tourism, orbital space tourism, or lunar space tourism.
Suborbital Space Tourism
Suborbital space flights will aim to reach an altitude that will qualify as reaching space but will not achieve a full orbit. The spacecraft will fly at low speeds with its trajectory intersecting the atmosphere of the surface and will fall back to the earth after the engines are shut off. Suborbital space tourists will reach altitudes of approximately 100 kilometers and will have a few minutes in space, they will also experience some moments of weightlessness as the spacecraft free falls back to earth.
The suborbital space tourism market is currently dominated by two competing companies: Virgin Galactic, which debuted on the public market in 2019 and Blue Origin, the private space company funded almost exclusively by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos. Tickets for Virgin Galactic suborbital space flights are being sold at a cost of $450,000 for the 90-minute spaceflight.
Orbital Space Flights
Orbital space flights will reach altitudes of over 400 kilometers and orbital space tourists tend to spend days or even more than a week in space. The spacecraft will be placed on a trajectory to remain in space for at least one full orbit and should achieve the orbital velocity to remain in the orbital path. Due to the increased length, speed and distance, orbital space flights are significantly more expensive than suborbital space flights, with SpaceX’s four passengers on their September 2021 orbital space flight allegedly paying $50 million per ticket.
While in the past orbital space tourism has been largely limited to a few flights to the International Space Station that used Russian Soyuz spacecraft, new companies entering the market are making orbital space tourism more possible. SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, has been the market leader, having launched the first all-private orbital space flight in 2021.
Lunar Space Tourism
Lunar space tourism aims to complete full trips to the moon with a suitable lunar spacecraft. While no lunar space tourism flights have yet been launched, plans to launch Lunar tourism on the moon’s surface or around it between 2023 and 2043 have been announced.
SpaceX announced plans for the dearMoon project in 2021, the first ever lunar space tourism mission. The project is being financed by Japanese Billionaire Yusaku Maezawa, with a proposed launch in 2023. It will make use of a SpaceX Starship spacecraft with the aim of achieving a single circumlunar trajectory around the Moon. The mission is expected to last 6 days and is currently looking for eight crew members to take part in this historic project.
The space economy
The space economy, as defined by OECD , includes the full range of activities and the use of resources that create value and benefits to human beings while exploring, researching, understanding, managing, and utilizing space. It comprises all public and private sectors involved in developing, providing and using space-related outputs, space derived products and services as well as the scientific knowledge that comes from various space research. Space tourism is a small subsector of the larger space industry that is expected to see exponential growth in the coming decades.
The space economy can be further divided into two categories, space-for-earth and space-for-space activities. Space-for-earth activities are the activities that produce goods or services in space for use on earth. These activities currently dominate the space economy in terms of revenue and include activities such as telecommunications and internet infrastructure, earth observation capabilities, national security satellites, and more. In contrast, space-for-space activities are the activities that produce goods or services in space for use in space. These activities are currently experiencing high levels of growth, with space tourism opening the door for businesses to start creating an array of space-for-space goods and services over the next several decades.
The space economy is one that is continuously growing and evolving alongside the development of the space sector as well as the further integration of space into our society and economy.
Current trends in the space industry including the increasing public interest and investment in space activities worldwide, the unprecedented levels of private investment in space ventures, and the growing space industry revenues have led predictions of the space industry being the next trillion-dollar industry by 2040.
The space tourism market
Space tourism has finally become a reality, and while the ticket cost is still unobtainable to most, the cost of booking a trip to the stars is expected to gradually decrease as companies continue to find new and innovative ways to make space tourism more efficient and inexpensive.
Due to significant technological innovations coupled with the increased interest in having access to space, the space tourism market is expanding at a rapid growth rate.

(Graph 1: 2021 Global Space Tourism Market Share)
The global space tourism market size was valued at USD 598 million in 2021, with the commercial space tourism market dominating in 2021, gaining a market share of 56.7%. In 2021 alone, there were thirteen commercial spaceflight missions undertaken, with Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin, SpaceX, and NASA having undertaken the majority of spaceflight missions to transport non-astronaut individuals across space and bring them back to Earth after a certain period.
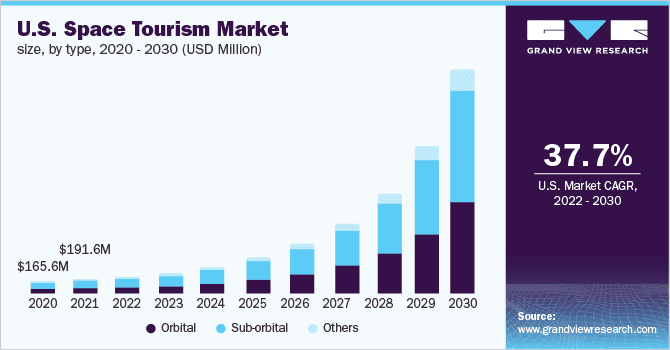
(Graph 2: U.S. Space Tourism Market Size 2020-2030)
North America led the overall market in 2021, with a market share of 38.3%. The U.S. Space tourism market is the largest globally, valued at USD 191.6 Million in 2021. Factors including advancements in technology, rising interest in space travel, and increased focus on research and development activities for space tourism are some of the factors fueling the growth of the market. The U.S. Space tourism market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.1% from 2022 to 2030, meaning the space tourism market is predicted to be a multi-billion-dollar market in the coming decade.
The future of Space Tourism
Space tourism is expected to grow far beyond tourists traveling to space just for the ride, with orbital space flights involving tourists staying in space for a period of time, while the international space station is the only habitable structure in space now, companies have begun to look beyond this.
Designs for Voyager Station , the first ever space hotel were released in 2019 by the Gateway Foundation. The project is now being overseen by Orbital Assembly Corporation , a space construction company, who has recently taken over the project from the Gateway Foundation and is now aiming to launch two space stations with tourist accommodation: Voyager Station, the original design, as well as a new concept design Pioneer Station . Voyager Station is scheduled to open in 2027 and will accommodate an expected 400 tourists. The Pioneer Station is expected to open in three years, housing 28 tourists at a much smaller capacity. While the international space station is primarily a place of work and research, Orbital Assembly’s space hotel fulfills a different niche; they offer a destination for space tourists. While collaborations between Orbital Assembly and the companies organizing space flight such as Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin and Elon Musk’s company SpaceX have not been publicly announced, they are expected.
It is likely that space tourism will continue to grow in the years to come, and competition between private space companies for leadership will intensify. There is no doubt that private space tourism will have a substantial economic impact. While space tourism is currently a small subsector of the larger space economy, it will redefine it in the coming decades.
It is likely that the space tourism industry will evolve during the next decade, as barriers to entry will be reduced, competition will grow, costs will be lowered, and eventually, space travel will be affordable for everyone. The future of space tourism has the ability to positively impact many socioeconomic factors on Earth including creating jobs, educating citizens about space and fostering further innovation in the space economy.
- 5 Recession-proof target sectors for investment attraction
- NASA highlights the economic impact of the mars mission
- Research Uncensored Podcast – Ft. Tracey Davenport and Anil Vaidya
- Here’s everything you need to know about Elon Musk’s ‘Tesla Bot’

Stefan Calimanu
Related posts.

- Destination Branding: Strategic Insights for Economic Development Experts

- Unpacking the Place Branding Process

- Place vs. Destination Branding: Their Vital Role in Economic Development
Recent Posts
- ResearchFDI Relocates to New Headquarters in Downtown Montreal
- ResearchFDI and Tractus Form Strategic Partnership to Enhance Global Investment and Trade Services
- Announcements
- FDI Insights
- News & Media
- Press Release
- Uncategorized

FDI365 is a customized online business intelligence platform designed for investment attraction and economic development professionals .
Our Services
- Lead Generation & Qualification
- B2B Trade Development
- FDI Training
- Business Intelligence Solutions
- Representation
- Business Retention & Expansion
- Economic Development Strategy
- Client Testimonials
- Case Studies
Subscribe to our newsletter
Search the website:, let's discuss your next project.

One of our consultants will review your strategy and provide actionable tips to help you reach your investment attraction goals. 100% free & no-obligation!

The Past, Present, and Future of Space Tourism
It’s been more than 20 years since the first space tourist took flight, but there’s a lot more to come in the emerging industry of space tourism..
- Copy Link copied

Are space vacations in our near future?
Illustration by Delcan & Co.
When Austrian journalist Gerhard Pistor requested to book a trip to the moon in 1964, his travel agency forwarded his query to Pan American World Airways—Pan Am. The now-defunct airline accepted the reservation and noted that the first flights to the moon would take off in the year 2000. So began a years-long space-tourism marketing stunt in which some 93,000 people joined Pan Am’s First Moon Flights Club, a waiting list for the first civilian trips to the moon.
That, of course, never happened. But as the Space Age advanced, space tourism did, too. In 2001, American entrepreneur Dennis Tito became the first true space tourist, launching aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft and spending more than a week aboard the International Space Station (ISS)—reportedly spending $20 million to do so.
Today, we’re in a new era of space tourism, with growing numbers of civilians leaving Earth for brief moments through private enterprises focusing on such endeavors. And in the coming decades, we may even see the dawn of regular long-duration space vacations.
The Birth of Space Tourism
After the Apollo era, companies investigated opportunities to send civilians rather than government professionals—that is, NASA astronauts—into space. In the 1970s, manufacturing conglomerate Rockwell International, a contractor for NASA’s Space Shuttle program, researched the possibility of passenger modules that could fit into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle, with similar concepts developed by other companies over the subsequent decade. None came to fruition.
NASA did open up its spaceflights to nongovernment professionals, though, primarily as payload specialists, who were tasked to complete specific in-flight projects by companies outside of NASA. NASA also developed the Teacher in Space and Journalist in Space programs to open up spaceflight to several civilians annually. But the programs were ended after the Challenger disaster in 1986, which killed the first Teacher in Space participant, Christa McAuliffe, along with her six crew members. The program was considered for a revival, but that, too, was ended after a Space Shuttle failure—this one, the fatal Columbia disaster in 2003.
Space tourism finally became successful in 2001 with Tito’s launch to the ISS. That trip was organized by a company called Space Adventures, which ultimately saw eight other space tourists take trips to the ISS through 2009, each launched on a Russian Soyuz spacecraft. But these tourist flights ended after the retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle program in 2011. Because the only spacecraft capable of human spaceflight at that time was the Soyuz , every seat on every launch was needed for professional astronauts from around the world, and tourism was put on the back burner.
Space Tourism Today
For the past decade, private space tourism companies have been developing spacecraft to take passengers on suborbital flights, which bring them to the edge of space and back down to Earth in relatively short “hops” lasting anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours. By comparison, the first nine Space Adventure clients flew orbital missions that encircled the planet for days.
The method of flight varies by company. Blue Origin , for instance, launches vertically like most rockets, whereas Virgin Galactic flies a rocket-powered space plane that is launched from the belly of a carrier aircraft. While these two companies are the only suborbital companies cleared by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for launches—both have already carried passengers to space—other companies are preparing for liftoff. That includes space-balloon companies Space Perspective and World View , which offer a far more leisurely journey than rocket-powered ascents, gently lifting passengers to high altitudes in a high-tech version of a hot air balloon. Across all suborbital space tourism companies, prices range from approximately $50,000 to $450,000 per seat.
Orbital tourism has also made a comeback, though at far higher prices: tens of millions of dollars per seat. SpaceX , which is contracted by NASA to launch astronauts to the ISS, is also available for private charters. In 2021, entrepreneur Jared Isaacman organized the Inspiration4 mission, the world’s first all-civilian mission, during which he and three crewmates orbited the Earth in a SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule as a fundraiser for St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. In 2022, SpaceX provided the launch vehicle for the Axiom mission 1 (Ax-1), the world’s first all-civilian mission to the ISS, during which four crew members spent eight days onboard the orbiting research facility.
Space Adventures is also back in business; it organized a flight to the ISS for Japanese entrepreneur Yusaku Maezawa, who traveled to space in December 2021. Maezawa intends to charter SpaceX’s under-development Starship spacecraft for a moon mission called the dearMoon project, taking with him eight civilians on the journey.
What’s Next for Space Tourism
Space tourism remains in its nascent phase, with plenty of work to be done. Existing suborbital companies are still tweaking launch vehicles and increasing launch cadence to approach regularity, while upcoming ones are waiting for FAA approval to begin their operations. And, hopefully, the space tourism companies will eventually be able to reduce the cost of flights, too.
But many enterprises are already eyeing the future when it comes to space tourism—a future in low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA itself is investing in that future through the Commercial LEO Development Program, through which it is funding the development of private space stations. As NASA and its international partners move toward retiring the ISS in the next decade or so, the agency hopes to rent facilities from private stations that will be able to host not only its professional astronauts but also commercial visitors.
Four projects have received funding from NASA’s Commercial LEO Development Program, including Axiom Space, the company that launched the Ax-1 mission. Axiom has partnered with avant-garde interior designer Philippe Starck to work on its Axiom Station. Another funded project, Starlab by Voyager Space and its subsidiary Nanoracks, has partnered with Hilton to develop astronaut accommodations.
Three of the four companies are expecting to launch their space stations by the end of the decade, but as space programs go, delays are highly likely. (NASA’s current Artemis program, for instance, was hoping to land humans on the moon in 2024, but that deadline has been pushed back to at least 2025.) Still, the future is bright for space tourism and certainly within the realm of reality—all we have to do is wait. And for travelers who have always wished to be among the stars, that wait will be worth it.

Space tourism: prospects, positioning, and planning
Journal of Tourism Futures
ISSN : 2055-5911
Article publication date: 16 March 2015
The purpose of this paper is to explain how the elements of a tourism policy class (historical, structural, economic, social, and technological) are employed in the discussion and analysis of space tourism.
Design/methodology/approach
The material serves as revision class of methods and concepts. The topics and methods covered depend in part on previous class content making use of space tourism materials available on the web and in the literature.
The sources cited cover a remarkable and growing range of space tourism endeavors worldwide. Whilst it is definitively not a forecast, the paper does appraise future directions in space tourism.
Practical implications
Further research is required in order to properly evaluate the value of space tourism to future human societies, and strategize accordingly.
Originality/value
As a source‐based review, the paper has limited originality, but shows the possibilities and limitations of tourism planning methods for space tourism.
- Forecasting
- Tourism policy
- Economic impact analysis
- Teaching and learning
- Future studies
- Tourism planning methods
Cole, S. (2015), "Space tourism: prospects, positioning, and planning", Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. 1 No. 2, pp. 131-140. https://doi.org/10.1108/JTF-12-2014-0014
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2015, Sam Cole
This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial & non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
As material for a slightly tongue in cheek revision class for a tourism policy course, my paper serves primarily as a reminder of the concepts and methods to be used in students’ term projects. The course itself similarly revises and applies methods from previous courses. Here, it should be said that methods used in tourism planning practice are considerably less exotic than the subject of space tourism, while the subject itself shows the power and importance of imagination, and by extension futures thinking in general. Tourism and the study of tourism has become explicitly such a multi‐dimensional field where globalization directly confronts locality and identity. However, it is a field in which future defies history, futurism confronts tradition, unprecedented wealth co‐exists with abject poverty, and imagination bends reality. For these reasons the study of tourism begs insights from many disciplines and illustrates many of the challenges for planning and policy.
Where to begin?
Students from planning programs typically enter city and county‐level planning departments that increasingly incorporate tourism promotion and development as a cornerstone of their activities. Methods in planning practice are relatively pragmatic and heuristic, unless some dubious policy or investment is to be advanced. The course aims to provide students with a supplementary grounding in heuristics such as Butler (1980) and Plog (2001) . Students’ final projects typically devise and detail aspects of a tourism strategy for some exotic destination or an exotic development in a familiar location, addressing economic, cultural, social, and ecological aspects of a tourism strategy. This course segment had its origins with a student who insisted on covering space tourism for his final project!
There are several starting points for thinking about space tourism for planning students: science fiction and science, defense in space, space tourism speculation, actual space tourists, or currently planned space tourism projects. Beyond a vehicle for revising tourism planning methods and indulging my own fantasies, the most important rationale for introducing the topic of space tourism into a tourism planning course is simply that space travel fiction has (almost) become fact. Since the industry is forecast to become a driver of the global economy and space tourism ports have been proposed for a number of island and rural locations, it is also possible, even likely, that some current students could be involved in some aspects of space tourism planning. Already research has left the solar system and there are currently five satellites from Earth around Mars. In the Americas alone, space tourism bases are planned for the Nevada desert, and others are under negotiation for the Caribbean islands of Puerto Rico and Curacao.
A useful starting point is the growing technical, specialist, and other literature on the prospects for space tourism. This covers a broad range of topics with the most current available on the web. There are a goodly number of books and technical reports, but not yet a dedicated “Journal of Space Tourism” but this can only be a matter of time. There is already a “Space Futures Journal” on the Space Futures web site. A selection of these publications and web sites dealing with aspects of space travel from craft design, health, accommodation, and other topics are referred to throughout this review. These web sites have over‐lapping, complementary, and sometimes contradictory information. In some cases, the sources are more topical or more detailed and less or more cautious about the challenges and prospects. For example, the first flight from the relatively small Caribbean island of Curacao will be carried out in 2016 by Space Expedition Corporation with the Lynx.
There are also several articles in the tourism literature, for example, Crouch (2001), in “The Market for Space Tourism: Early Indications” reviewed the hurdles facing the development and growth of space tourism, not least of which was simply making “credible and reliable estimates of market demand.” He identified several research challenges and methodological alternatives to improve research findings. Coincidentally, Crouch's article coincided with the first tourist in space. Patrick Collins (2000, 2014) appears to be the most consistently cited space‐tourism analyst and proponent of space tourism development, and his recent (May, 2014) video presentation updates this material and makes the strongest case for space tourism ( Collins, 2000, 2014 ). The most comprehensive web site, SpaceTourism.com, is an excellent on‐line tutorial on space tourism that appears to draw liberally on Collin's work, as I do in my tourism course review. The SpaceTourism.com site lists “some key documents from the archive to get you started”: First, what the growth of a space tourism industry could contribute to employment, economic growth, environmental protection, education, culture and world peace. Second, space tourism market demand and the transportation infrastructure. Third, general public space travel and tourism. Fourth, artificial gravity and the architecture of orbital habitats. Fifth, prospects of space tourism.
Space, stars, and status – marketing and positioning space tourism
In 2001 the world's first space tourist, American Dennis Tito, travelled on a Russian Soyuz rocket to the International Space Station, as did the second, South African Mark Shuttleworth, and the third, Greg Olsen, in 2005, and also Charles Simonyi in 2007 and 2009. As wealthy businessmen, they could afford the $20‐35 million (about half what NASA currently pays Russia for its own astronauts). International recording artist, Sarah Brightman, is slated to be the first female space tourist in 2015. In view of the astronomical cost of their trips, counting these space travelers as “tourists” may be a stretch. Nonetheless they are the acknowledged pioneers. Well before this, in 1964, Gerhard Pistor, an Austrian journalist, walked into a Vienna travel agency and asked for a booking on the Pan American World Airways first flight to the moon. By 1989, 20 years after man first set foot on the lunar surface, Pan Am had more than 93,000 wait‐listed for the airline's first passenger flight to the moon, sadly preempted by the airline's cash‐strapped demise in 1991! (Sun Sentinel September 3, 1989). Nonetheless, the latent demand was clear.
SpaceTourism.com sees “an enormous unsatisfied demand for space travel […] market research has revealed that most people, at least in the industrialized countries, would like to take a trip to space if it was possible.” They explain that “Space Tourism is the term that's come to be used to mean ordinary members of the public buying tickets to travel to space and back. Many people find this idea futuristic. But over the past few years a growing volume of professional work has been done on the subject, and it's now clear that setting up commercial space tourism services is a realistic target for business today.” And the reasons why it is going to happen this time include that “people want it, it's a realistic objective, it's the only way in which space activities can become profitable, it's the quickest way to start to use the limitless resources of space to solve our problems on Earth, living in space involves every line of business, from construction to marketing, fashion, interior‐design and law, and not least, because it will be fun!” Box 1 illustrates some of the space tourism stories to be found on the web.
The 2013 Virtuoso Life® “Travel Dreams” pitch for space travel epitomizes tourist marketing hype: “At Park Avenue Travel we help create your dream vacation. We can tailor your trip to provide a unique, unforgettable experience. We believe that travel should be a journey, not just a destination! Virgin Galactic's sub‐orbital space trips promise to be the most intense and wonderful experiences that passengers have ever had. Astronauts of the past 45 years have all returned to earth struggling to convey the enormity of what they have discovered and with their perceptions clearly changed. To be able to extend that privilege to people from all walks of life has been a long held ambition at Virgin.”
Despite that flights initially scheduled to begin in 2009 were repeatedly postponed, by 2012 more than 200 tickets had been sold. Seat numbers 1‐100 costing US$200,000 are sold out, as are the similarly‐priced 101‐199, 200‐299, and 300‐399 rides. “Call 1‐800‐220‐TRIP to reserve your ticket today”!! They are not alone in the space tourism promotion universe: HowStuffWorks.com encourages us to “Make your reservations now. The space tourism industry is officially open for business, and tickets are going for a mere $20 million for a one‐week stay in space.” Richard Branson cited in “Tough day’ for space travel as Virgin Galactic's spaceship crashes” says over 700 seats are now reserved. But as Encyclopedia Astronautica observes, few can afford the $20 million or the trip to the Mir space station and so far there are no takers for the Russian offer to take a trip around the moon for $100 million. In contrast, pre‐marketing of sub‐orbital rides suggests there are thousands willing and able to pay the $100,000‐$200,000 for a few minutes weightlessness with view of the earth as a planet. But, they say, “Orbital tourism is another matter.”
Surveys of the potential market for space travel began well in advance of its arrival. Indeed, the first space‐tourism market research was undertaken in Japan in 1993 showed “extremely positive” results: some 70 percent of respondents would like to travel to space, and almost half would pay three months’ salary to do so. Soon after, in 1995, nation‐wide telephone surveys in Canada and USA found that “the idea of space tourism is massively popular.” In 1997 the US “National Leisure Travel Monitor” survey included questions on space tourism for the first time. Of 1,500 Americans surveyed, 42 percent were interested in a space cruise, and were willing to spend an average of $10,800 for the trip. These findings are very similar to those for Japan.
There is an inevitable overlap between age, income, and geography, with the greatest interest 20‐40‐year‐olds. The published surveys do not show how this latent demand for space travel in the USA and elsewhere varies across the income spectrum, but like other forms of high‐end, very expensive recreation, one factor driving demand has to be shift in national and global income distribution. In the USA and several other counties, including emerging markets such as Russia and China, the income of richer top few percent of households has risen at an unprecedented rate, creating the necessary discretionary income for the target market.
It will be interesting to observe (say, by the year 2100) how space destinations correspond to Plog's (2001) useful heuristic – expressing how the distribution visitors’ personalities along a psychometric spectrum (from very cautious and conventional to risk‐taking and adventuresome) overlays the positioning of destination. It represents a cross‐section of destinations at a given point in time, whereby destinations (and visitors too) transform as they age. A speculative illustration is given in Figure 1 . Jules Verne's space tourism pioneers would be Plog's “venturers.” At some point in the future, these same personality types will be surfing Jupiter's moonbeams.
The space destination life cycle
Spacetourism.com explains that “Like any other business, once space tourism gets started it will develop progressively. It can be helpful to think of it as going through several phases. Starting with a relatively small‐scale and relatively high‐priced ‘pioneering phase,’ the scale of activity will grow and prices will fall as it matures. Finally it will become a mass‐market business, like aviation today.” This sequence is summarized in Table I .
The kind of service, volume of travelers, and expected price discussed are below. Segmentation of visitor markets and destinations, psychometric or otherwise, overlaps another core heuristic of the tourism literature, Butler's tourist area life cycle (TALC) that incorporates the ideas of Plog and others about the composition of a destination into the product life cycles theories associated with Vernon and others. Figure 2 shows the correspondence of these postulated phases of space tourism development when superimposed onto the “classic” Butler TALC. The first steps will be short sub‐orbital flights, similar to the space‐race flights of the 1960s. Whether “space” as a whole or “near earth‐orbits” or individual hotels, lunar sites, and so on are defined as the “tourist area,” the issue here (as with destinations on Earth) is the capacity of the destination and associated constraints and technologies.
This pioneering stage is closer to a nineteenth century Grand Tour, early balloonists or trans‐Atlantic airships, or a 1960s Hippie Trail. The next phase will see a maturing equivalent to the jet aircraft age. And as with most new technologies the initial stages are plagued by delays. The more important later stages of the TALC embody the ideas of congestion, sustainability, and the like. Given the volume of visitors anticipated, many space destinations – orbital, or moon‐based, or otherwise off‐worldly, are likely to become “over‐crowded.” Just as with the multitude of potent island and wilderness sites scattered across the globe, it is a fact that for reasons of scale economies, history, familiarity, marketing, herd‐instinct among investors and travelers, that destinations and resorts have become “overcrowded,” usually implying a considerable deterioration of the original attractions.
Spacetourism.com remarks that it is “Apparently unthinkable to most people in the space industry, even 1 million passengers per year is just 8 [ presumably million ] hours of aviation!” There's certainly no limit to the possible destinations. “And the access to space resources that low cost launch will bring about will ensure that economic growth needn’t end for a few more millennia at least!” Whilst it might not be implausible to explore the implications of rapid growth of space tourism in total, or even at the sub‐orbital, orbital, moon‐based, and inter‐planetary levels, every individual destination will likely face their own issues of capacity and congestion that underlie thinking about the tourist‐destination lifecycle. Thus, as with the projections of UNWTO and other agencies, one might give pause when exponentially extrapolated global trends are used to promote tourism at the destination level (see e.g. Cole and Razak, 2009 ).
Indeed, the future of space tourism with unlimited growth might be as some consider that we simply “mess up and move on” into an increasingly‐infinity of accessible destinations and spaces. There certain has to be some slowdown in the rate of increase – if the exponential growth period is extended then the annual number of passengers would eventually exceed the expected population of Earth. Of course, by then, travelers may make multiple trips and sub‐orbital flight may be the primary mode of inter‐continental travel, and business people may travel regularly to corporate subsidiaries on the Moon and wealthier tourists may have purchased timeshare, fractional ownership, and recreational homes, and the AirBnB.com web site graduated to SpaceBnB.com
Presumably, too, in the more distant future with more permanent colonies and dedicated off‐earth tourism destinations, there will be similar confrontations as portrayed in several science fiction movies. The point here is not to Cassandra humankinds’ potentially greatest‐ever endeavor, but to point out that there are many lessons to be incorporated into thinking about future space‐tourism from many tourist‐destination experiences, past and present.
Space travel for all?
An article on Spacetourism.com (from the 1999 50th International Astronautical Congress in Amsterdam) says that “According to current reports in the media, traveling to outer space should become possible for everyone by the beginning of the next century. Developing low‐cost passenger launch vehicles is not just to create an expensive pastime for the wealthy but develop a large ‘middle‐class’ market rich. Indeed, until access to space is cheap, it will not be possible to make use of the limitless resources available in space to solve the problems of our ever‐more‐crowded Earth. And here it is argued that tourism can generate the large‐scale launch activity needed to reduce costs sufficiently to start to use space resources. Hence, this is “one of the most important projects in the world today.” Collins (2014) projects that, by 2100, there could be annually 30 million sub‐orbital, 40 million orbital, and 10 million lunar surface travelers.
As with many business plans and proposals, it is especially tricky to evaluate and compare the various costings, forecasts, and marketing models. But as with any new technology, including hotel, travel, and entertainment enterprises, there are price reductions as the technology matures, and the scale of operations, operators, and markets increase. Over the last decade the precise costs have varied, but whether this is because of modified vehicle techniques and spaceport location, discount rates and margins, products and market appraisal, is not always clear. That said, there are differences in products and prices – although even these, on review, raise further questions.
Table II compares the estimated price and duration of the flight and weightlessness times associated with each of the soon‐to‐be introduced sub‐orbital offerings of Virgin and Lynx. (A full‐length video comparing the Lynx and Galactic is found at www.parabolicarc.com/2011/08/24/ ). The trade‐off for travelers in terms of “value for money” in terms or exclusivity and experience are not as clear cut as generally perceived. Luxurious pre‐flight offerings are similar: “After two or three fabulous days of preparing with your crew – you’re suited up and you’re raring to go.” But, while both offer a unique experience they may also be a very expensive one‐off thrill. They compete with skiing, mountain biking, scuba diving, hang gliding, base jumping, rock‐climbing, and the ever‐increasing plethora of activities for committed excitement seekers. All might be considered better value for money.
As Collins observes, the potentially huge market for space tourism “gives huge scope for reducing the cost of space travel by large‐scale operation like airlines.” There are a variety of scale economies in number of passengers per flight and number of flights per year: for example, once the technologies reach maturity the costs fall drastically, For example, a cost comparison between the Sänger launcher as “developed to airliner maturity” and a Boeing 747, indicated that the cost per seat to orbit is about 1,000 times less than that of the Space Shuttle. Of course, this may be a dubious comparison. There are also similar scale economies from the number of operations and flights. Table I illustrates the enormous potential “chicken and egg” feedbacks between the number of space travelers and the cost per trip.
Collins explains that at the same time that the cost of each version of space tourism becomes less expensive the experience will be extended (in both distance and duration) and trips will become more costly. Collins (2014) indicates that by the 2020s a sub‐orbital ride will cost $N,000, by the 2030s (with “N” being a number between 1 and 9), an orbital trip will cost $N0,000, and in the 2040s a lunar ride will cost $N0,000, about the same as sub‐orbital rise today. A rough estimate of price per mile is $20 ($2K/100), 40cents ($20K/50K), and 20 cents ($200K/1 m), a factor of 100 in 20 years (comparable to Moore's Law for the increasing speed and declining cost of computing power). Table III shows that there are substantial cost‐reductions in moving from small (20 passenger) two‐ to single‐stage reusable space vehicles, with less advantage trebling capacity from 60 to 180 seats. Indeed, the smaller craft appears to offer a slight advantage. It should be noted that the “costs” here are that for operating vehicles, rather than price to space tourists, and the prices quoted earlier indicate a healthy mark‐up reflecting risk investment, insurance, and so on. Similarly, there appears to be rather smaller advantage in multiple launch sites, at least for smaller craft, which suggests that several independent commercial enterprises might co‐exist, at least in the initial phase of space tourism.
The information in Table II allows various dimensions of the “value” of space flights to travelers to be scored. The overall cost with Virgin is double that of Xcor but since the flight time and weightless flight times are Virgin is cheaper in terms of cost per minute, but more expensive in terms of cost per weightless‐minute. Xcor is also cheaper in terms of cost per day and the Curacao operation extolls the advantage of its Caribbean location. On the other hand, the Virgin flight can be shared by honeymoon couples.
Multipliers in space
One of the more important concepts in tourism planning is that of the “multiplier.” Precisely which type of multiplier is most relevant, income, jobs, revenue, land footprint depend on the issue at hand; but in each case what matters is the net contribution of a tourist activity to the local community. With most international tourism there is a very high leakage of income, so only a small proportion of tourist spending is circulated within the local economy. Nonetheless, many sophisticated destinations focus on maximizing total tourist (and notably REVPAR) spending rather than the net impact on their population (product of the retained revenue and the appropriate multiplier).
For localities hosting the launch site, the main goal, in terms of its economic development, must be to generate jobs, income, and revenues. Unlike land‐based destinations where, from a development planning perspective, the goal is to use tourism to drive the local economy through the creation of jobs, building on local skills, culture, and ecology. This is especially difficult when enormous international commercial enterprises are involved, as is inevitably the case with the infrastructure and operation of space tourism. The model for conceptualizing space tourism development might be a “Disney World” in the case of the Nevada launch‐site of Virgin's Galactic, or a busy cruise port such as the Grand Bahamas for aspiring space‐tourism launch sites islands such as Curacao and Puerto Rico. For earth‐based space ports, it may be that a three‐day stay at a tax‐exempt all‐inclusive and exclusive spa resort is the better starting point for considering the local economic impacts on employment and revenues.
In contrast, a cruise ship analogy may be the appropriate starting point for assessing the impacts of space flight and accommodations: SpaceFuture.com observes that “Most cruise ships are owned by off‐shore companies operating out of countries with beneficial tax and regulatory regimes such as the Bahamas”. Thus, the mammoth cruise ship analogy also illustrate the eventual scale and operation of space hotels with an ever expanding variety of concessions, entertainment and activities, even sports stadia and theme parks.
As with cruise lines, space hotel operators will also try to minimize the taxes and deflect constraining legislation with corresponding income allocation and impacts. Figure 3 characterizes the likely income flows from space tourism showing the various leakages and circulation of income between investors, space tourists, space ports and their host communities, and space resorts (the density of line indicates the relative scale of income flows).
Eventually off‐planet space destinations will become “communities” with temporary and semi‐permanent residents living in company towns with their own local electronic currency and administration. Beyond this, new space island cultures will arise in migratory settlements, leading to their own unilateral declarations of independence.
Meanwhile, back on Earth, it is not implausible that major new economic regions based on the manufacture of spacecraft, supporting infrastructure, and launch sites will emerge. Indeed, it is not difficult to concur with Collins and others cited in this paper that space tourism could become a new driver for global development, and ultimately for human development beyond our planet and solar system. A short survey of students in the tourism class indicated that they share this view and they too have ambitions to travel in space (see Table IV ).
The very week this paper was completed saw two spacecraft disasters: a launch failure of an unmanned Antares space station delivery rocket and the more tragic Virgin Galactic Spaceship II test flight. The second especially potentially poses a significant setback for space tourism.
A psychometric mapping of space tourism destinations and activities
The tourist area life cycle in space
Multipliers in space: markets, space ports, and space resorts
Phases of space tourism
Cost versus value in space travel
Scale economies in the size and number of spaceports and vehicles
Students in space
Notes: a Very likely=5, Very Unlikely=0; b the survey was conducted two days after the Virgin Galactic disaster
Annotated adventures in space
Professor Sam Cole can be contacted at: [email protected]
Butler, R. ( 1980 ), “ The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: implications for management of resources ”, Canadian Geographer , Vol. 24 No. 1 , pp. 5 - 12 .
Cole, S. and Razak, V. ( 2009 ), “ Tourism as Future ”, Futures , Vol. 41 , pp. 335 - 45 .
Collins, P. ( 2000 ), “ How space tourism can help solving Italy's crisis ”, Congress of Space Proceedings of Space 2000, Presented at Space 2000, ASCE, Albuquerque, March , pp. 594 - 603 , available at : www.youtube.com/watch?v=iJ9dhMoKVi4
Collins, P. ( 2014 ), “ Renaissance Italia ”, held at the Politecnico di Milano, Campus Bovisa, May 8‐9.
Plog, S. ( 2001 ), “ Why destination areas rise and fall in popularity ”, The Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly , Vol. 42 No. 3 , pp. 55 - 8 .
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
Space tourism: What are the pros and cons?
Space tourism has its fans — and its critics.

Private companies are offering many opportunities to make the leap off Earth , ranging from a quick suborbital hop to a multi month stay on the International Space Station (ISS). But the advent of the space tourism industry has spurred a vigorous debate: Is it helping to propel humanity to the stars , or is it just letting rich people have a little fun while providing no real value?
Here's a look at the pros and cons of space tourism.
Related: How SpaceShipOne's historic launch 20 years ago paved the way for a new space tourism era
The pros of space tourism
A handful of private individuals, colloquially known as space tourists, managed to purchase tickets to the ISS or Russia's Mir station. However, with the end of the space shuttle program in 2011, NASA canceled any further opportunities. That picture changed with the emergence of private spaceflight companies headed by various billionaires, including Elon Musk's SpaceX , Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin and Richard Branson's Virgin Galactic .
Of the three, only Virgin Galactic has a stated long-term goal of promoting space tourism, offering quick suborbital flights just above the Kármán line — the arbitrary but internationally recognized edge of space. Paying customers can get a similar experience with Blue Origin, but that company hopes to pivot to orbital industries. With SpaceX, you can get a multiday stay in orbit, but you'll have to bid against numerous government contracts for the opportunity.

Promoters of space tourism have suggested various benefits of the industry. For example, many space tourists are actively running and participating in experiments, such as examining the effects of microgravity on human health , plant growth and material properties. This is real science that needs to be done to propel humanity to the stars.
There's also financial propulsion, with hundreds of millions of dollars of investment going into the newfound industry. Companies are developing new equipment, techniques, technologies and more so they can offer tickets to space. And the more we invest in space in general, the better off our shared ventures will be.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The frequent launches of space tourists, including celebrities such as William Shatner , have caught the media by storm. This, in turn, fuels more public interest, which can lead to more discussion, more awareness and more funding.
The cons of space tourism
On the other hand, critics of space tourism point out that the industry is catering solely to exceptionally wealthy individuals. Ironically, this can lead to a sense of public disillusionment with space: Instead of opening it up to everyone, it might cause people to roll their eyes at the inaccessibility. Basically, it's just rich people doing rich-people things.
Because of the enormous cost of a ticket — anywhere from hundreds of thousands to tens of millions of dollars — it's hard for most people to see the value in space tourism as an industry. They simply don't get to participate in it.
And while some space tourists have conducted experiments during their expeditions, those experiments haven't exactly been revolutionary or consisted of anything that couldn't be done by astronauts on the ISS. So space tourism isn't really advancing human spaceflight in any significant way.
Lastly, space tourism is a niche business. While some companies have developed technologies that are specific to this industry, those technologies will not necessarily transfer to other space-related activities, like industrial or scientific applications. We could be spending all this time, money and resources on a business venture that never grows significantly and never leads to anything else.

The bottom line
The bottom line is that space is hard — it's difficult to get to space, and it's difficult for humans to remain in space for any length of time. Most space tourism companies have folded well before their first attempted launch, and it's not clear that this business niche will grow all that much. Only roughly 60 people have been to space as tourists, and the vast majority of them have gone only on quick suborbital joyrides with a few minutes of weightlessness.
There are only a few launches, at most, every year dedicated to space tourism, and a peek at planned launch schedules reveals that this number will not change much over the coming years.
— Do space tourists really understand the risk they're taking?
— The rise of space tourism could affect Earth's climate in unforeseen ways, scientists worry
— Most Americans expect routine space tourism by 2073, but few would actually try it
Most people will never get the opportunity to become a space tourist; it will likely remain a niche industry serving a select set of very wealthy individuals. It's not a game changer in any direction. It will continue to be a component of the overall human interest in space but not a major driver of innovation or expansion.
But hey, if you're ever given the chance, go for it!
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Paul M. Sutter is an astrophysicist at SUNY Stony Brook and the Flatiron Institute in New York City. Paul received his PhD in Physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2011, and spent three years at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, followed by a research fellowship in Trieste, Italy, His research focuses on many diverse topics, from the emptiest regions of the universe to the earliest moments of the Big Bang to the hunt for the first stars. As an "Agent to the Stars," Paul has passionately engaged the public in science outreach for several years. He is the host of the popular "Ask a Spaceman!" podcast, author of "Your Place in the Universe" and "How to Die in Space" and he frequently appears on TV — including on The Weather Channel, for which he serves as Official Space Specialist.
NASA's solar sail successfully spreads its wings in space
NASA's Perseverance rover begins ambitious ascent up a Mars crater rim
Rocket Lab's Mars probes reach launch site ahead of 1st flight on Blue Origin New Glenn rocket (photos)
- GregB03 In its early days aviation was something that only the rich could afford to do. It took a while for it to reach prices that were affordable to the general population . It's early days for commercial space travel. Reply
GregB03 said: In its early days aviation was something that only the rich could afford to do. It took a while for it to reach prices that were affordable to the general population . It's early days for commercial space travel.
Osbert said: If these people were going someplace, I might agree with you but UP and then free-falling, is not a "destination". It's not a destination if you arrive, basically where you started from. Let's start launching people UP and over/out too actually land some place >> because they wanted to get to that/some place. Also, UP and freefall is not space travel. Far from it, lol. It's a fair/carnival ride - period. Nothing but an uncontrollable joy-ride in a tin-can - WEEeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee!!!!
ChrisA said: The Writght brothers were not rich. Their dad was a preacher and they owned a bicycle shop. In the early days, the people in the field were skilled tradesmen. The first passenger to die was a young army officer. But later when aviation was commercialized, yes ticket prices were high
- View All 5 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 Roll out with Optimus Prime in new 'Transformers One' trailer (video)
- 3 Who is Rook, the Renaissance station's robot science officer in 'Alien: Romulus?'
- 4 NASA's solar sail successfully spreads its wings in space
- 5 SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket can return to flight, FAA says

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The space tourism market in Germany is expected to grow significantly from 2024 to 2030, owing to huge research and development initiatives in space exploration and tourism. Germany fosters collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and private companies to drive innovation and investment in the space tourism sector.
Report Outlook. Space tourism market size was valued at USD 848.28 million in 2023. The market is anticipated to grow from USD 1,248.32 million in 2024 to USD 27,861.99 million by 2032, exhibiting the CAGR of 47.4% during the forecast period.
The space tourism market size was $598.4 million in 2021 and is expected to reach $12,690.6 million by 2031, registering a CAGR of 36.4% from 2022 to 2031. Space tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital and suborbital. Space tourism is a type of vacation where ...
The estimated revenue of the orbital space tourism market worldwide amounted to roughly 385 million U.S. dollars in 2021, and this figure was forecast to reach 555 million U.S. dollars by 2030 ...
The space tourism market size crossed USD 827.2 million in 2023 and is projected to observe around 36.5% CAGR from 2024 to 2032, driven by the rising demand from affluent individuals seeking unique experiences. ... The space tourism market research report includes in-depth coverage of the industry with estimates & forecast in terms of revenue ...
Space Tourism Market Growth & Trends. The global space tourism market size is expected to reach USD 10.09 billion by 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. It is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 44.8% from 2024 to 2030. Space tourism is defined as human space travel for recreational, leisure, or business purposes.
Space Tourism Market Analysis. The space tourism market generated revenue of USD 921.4 million in 2023, it is predicted to witness a CAGR of 45.0% during 2024-2030, to reach USD 12,355.7 million by 2030. The key drivers for the market are the evolution of the technologies being used for space exploration and the increasing curiosity of people ...
The Space Tourism Market size was valued at USD 698.3 Million in 2022 and the total Global Space Tourism Market revenue is expected to grow at a CAGR of 41.2%from 2023 to 2029, reaching nearly USD 11033.66 Million. Space tourism is human space travel that tends to provide tourists with the ability to become astronauts and experience space travel. There are several kinds of space tourism ...
Data Bridge Market Research analyzes that the global space tourism market which was USD 876.34 million in 2023, is expected to reach USD 13,081.48 million by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 40.2% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2031. In 2024, the sub-orbital space tourism segment will dominate the market due to the growing interests and ...
NSR's Space travel and tourism markets report offers industry-leading analysis of this emerging global market. Covering the entire value chain, from suborbital, orbital, to travel beyond Earth, from rockets and rocket-planes, to balloons for suborbital, from investment and updates on space stations, to its 10-year forecast, this latest NSR report offers the most comprehensive analysis of ...
The global space tourism market size is expected to be worth around USD 17742.4 Million by 2032, from USD 1,158.0 Million in 2023, ... The high costs are primarily driven by the complex nature of space travel, including research and development expenses, operational costs, and the need for advanced technology and infrastructure. ...
The global Space Tourism Market is valued at USD 1198.5 Million in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 16500 Million by 2032 at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 31.6% between 2024 and 2032.. Key Highlights. North America predominantly led the Space Tourism market in 2023, with 84% of the total market share; Europe is projected to remain the second most revenue-generating ...
Demand for space tourism recorded a y-o-y growth of 14.0% in 2023. Hence, the market valuation is expected to reach US$ 851.7 million by 2024. Over the forecast period, the global space tourism industry is predicted to exhibit a 19.8% CAGR, reaching US$ 5,191.7 million by 2034. Several factors are expected to drive the space tourism market growth.
The space tourism business in the United States is expected to be worth US$ 201.52 million by 2022. China, the world's second-biggest economy, is expected to reach a market size of US$ 480 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 20% from 2023 to 2032. Other notable geographic markets include Japan and Canada, which are expected to increase at 11. ...
The global space tourism market size reached US$ 0.94 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach US$ 16.3 Billion by 2032, with a 35.8% growth rate (CAGR) during 2024-2032. ... These players are fueling interest in space tourism and positioning it as a viable and aspirational travel option. The market research report has provided a comprehensive ...
Global Space Travel or Tourism Market Size Study, by Destination, by Duration, by End-Users (Billionaires & Ultra-High-Net-Worth Individuals, Adventure Seekers & Science Enthusiasts), by Gender and Regional Forecasts 2022-2032 - Global Space Travel or Tourism Market was valued at USD 892.67 Million in 2023 and exhibiting a CAGR of 44.31% during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The U.S. Space tourism market is the largest globally, valued at USD 191.6 Million in 2021. Factors including advancements in technology, rising interest in space travel, and increased focus on research and development activities for space tourism are some of the factors fueling the growth of the market.
1. Introduction. Space tourism is no longer a myth but significant research questions remain unexplored. Several magazines have been publishing brief articles on such advancements (e.g.: Technology Review, The Engineer, The Guardian, and The Daily Telegraph).In relation to tourism, Crouch (2001) gave early indications of the industry and research notes have outlined the potential of space ...
That includes space-balloon companies Space Perspective and World View, which offer a far more leisurely journey than rocket-powered ascents, gently lifting passengers to high altitudes in a high-tech version of a hot air balloon. Across all suborbital space tourism companies, prices range from approximately $50,000 to $450,000 per seat.
Indeed, the first space‐tourism market research was undertaken in Japan in 1993 showed "extremely positive" results: some 70 percent of respondents would like to travel to space, and almost half would pay three months' salary to do so. Soon after, in 1995, nation‐wide telephone surveys in Canada and USA found that "the idea of space ...
The pros of space tourism. A handful of private individuals, colloquially known as space tourists, managed to purchase tickets to the ISS or Russia's Mir station.
Russia's First Space Tourism Company Closes. April 6, 2021. Kosmokurs planned to develop a single-stage reentry rocket and a seven-seater spacecraft for the suborbital tourist flights. Roscosmos ...
perspectives, since this can encourage future research into this delicate and intriguing aspect of spaceflight. Currently, the literature ... and space tourism. npj Microgravity (2017) 3:2 ; doi ...
The Space Technology and Telecommunications cluster is intended to strengthen Russia's position in the respective industries. The scope of activity is wide: from space tourism to satellite navigation systems. Russian companies aim to increase their market share in this global market, the total volume of which is estimated at $300 billion. [21]