
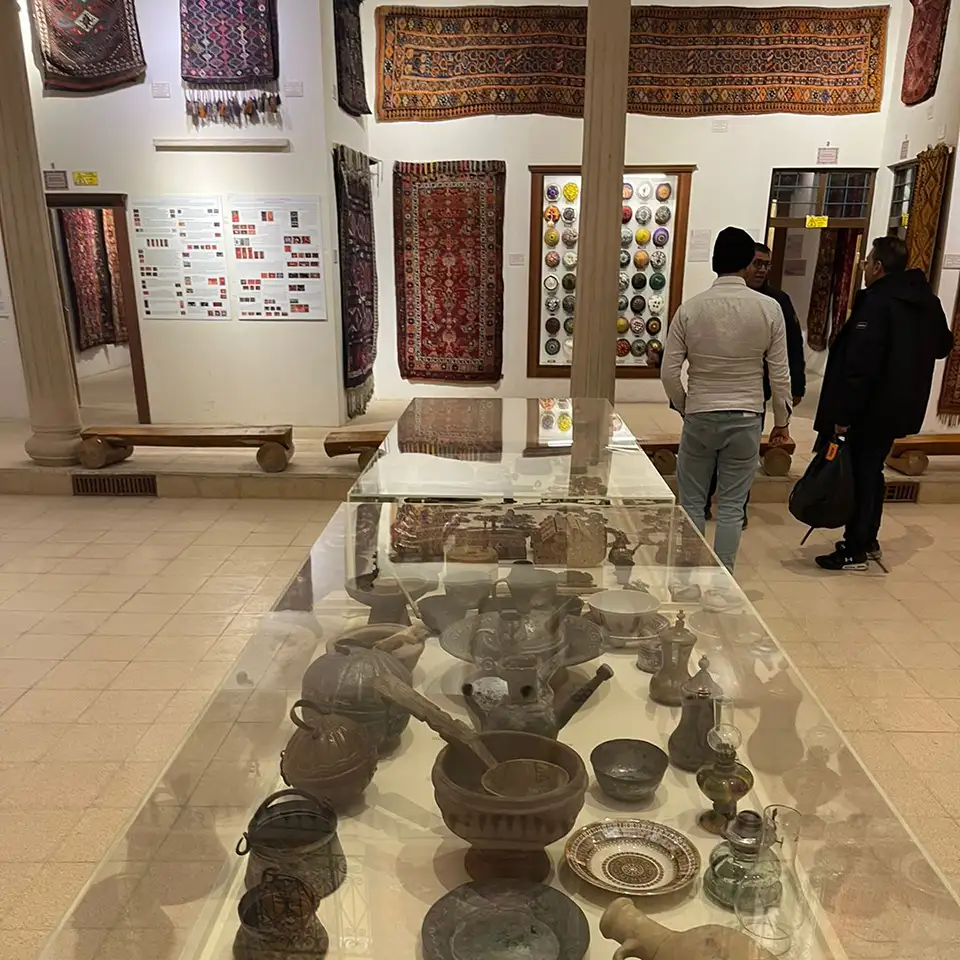
Ancient Mesopotamia

- 1 Understand
- 2.2 Akkad, Babylon and Assyria
- 2.3 Later cities
<a href=\"https://tools.wmflabs.org/wikivoyage/w/poi2gpx.php?print=gpx&lang=en&name=Ancient_Mesopotamia\" title=\"Download GPX file for this article\" data-parsoid=\"{}\"><img alt=\"Download GPX file for this article\" resource=\"./File:GPX_Document_rev3-20x20.png\" src=\"//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f7/GPX_Document_rev3-20x20.png\" decoding=\"async\" data-file-width=\"20\" data-file-height=\"20\" data-file-type=\"bitmap\" height=\"20\" width=\"20\" class=\"mw-file-element\" data-parsoid='{\"a\":{\"resource\":\"./File:GPX_Document_rev3-20x20.png\",\"height\":\"20\",\"width\":\"20\"},\"sa\":{\"resource\":\"File:GPX Document rev3-20x20.png\"}}'/></a></span>"}'/> Mesopotamia is in the Middle East , mainly in present-day Iraq , with parts of it in Syria and Turkey and influence extending into what are now Iran and the Persian Gulf states. The name translates literally as 'between rivers', and an alternate term is the Land of the Two Rivers. The rivers involved are the Tigris and Euphrates; both rise in the mountains of Eastern Anatolia , run more-or-less parallel, then join near Basra to form the Shatt al-Arab which flows into the Persian Gulf.
As of mid-2024, most of the region is too dangerous to visit; see warnings in the Syria and Iraq articles.
Mesopotamia forms part of a historically important region called the Fertile Crescent ; the other main part is the Levant . The region was one of the cradles of civilisation, where farming and cities first arose.
Mesopotamia was one of the great Bronze Age civilizations, along with Ancient Egypt , Ancient China , the Indus Valley Civilisation and others. All of those built cities and empires, and developed or imported innovations such as bronze-working, irrigation, writing, glass, mathematics , natural science, measurements of time, city planning, and the wheel. Historians debate who was first with each, and Mesopotamia is a candidate for most of them.

Mesopotamia has a prominent role in the Abrahamic religions — Judaism , Christianity and Islam — and a shared history with the Holy Land . The Israelites' exile in Babylon around 600 BCE is well described in the Old Testament, and is one of the oldest Biblical events supported by historical records. Like many other ancient empires, Babylon primarily became known among Europeans through the Bible .
Most languages native to the region — including Akkadian which was the main language of the Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires, and Aramaic which became important later — were from the Semitic family which includes Arabic and Hebrew. Sumerian — spoken in Sumer and used by priests and scholars for centuries after Akkadian replaced it in general use — was a language isolate, unrelated to any other known language.
The land later became a subject under many empires: the Hittites , the Hellenic Empire of Alexander the Great and his successors, the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Empire , various incarnations of the Persian Empire , the Mongol Empire , the Caliphate of Baghdad (see Islamic Golden Age ), the Ottoman Empire , and the British Empire .
Mesopotamia has been devastated by war many times in history, including in the 21st century. Iraq and Syria are, as of 2024, still dangerous destinations; see warnings in those articles.
Destinations
This article focuses on the great Mesoptamian civilisations of the Bronze Age; see Fertile Crescent for archeological sites dating back before those.

Sumer was the earliest known civilisation, starting before 5000 BCE. Quite likely it was the first to enter the Bronze Age, and the first to evolve from city-states to an empire.
Not far from those were other Sumerian cities:

Akkad, Babylon and Assyria

Around 2270 BCE, the Sumerians were conquered by the Akkadian Empire. The later empires of the region all spoke Akkadian and had their main cities north of Sumer.
Many of the cities listed were smashed by the Medes around 610 BCE as the Assyrian Empire fell.
Both Nimrud and Nineveh were severely damaged by the so-called Islamic State during the 2014-17 Civil War.
Later cities
The Assyrian Empire fell in about 610 BCE, with the Medes and the Mittani picking up many of the pieces. Then the region was taken by Persia around 539 BCE, and Alexander the Great conquered the Persian Empire, including this area, around 330 BCE. Some cities in Mesopotamia were built after those events.
- Pre-Islamic Arabia
- Fertile Crescent
- Has custom banner
- Has map markers
- Has mapframe
- Listing with Wikipedia link but not Wikidata link
- Usable topics
- Usable articles
- Historical travel
- Topics in Middle East
- Topic articles
- Pages with maps
Navigation menu

Explore Mesopotamia
Discover the ancient wonders of Mesopotamia with our expert guides.
Learn about the rich history and culture of Mesopotamia through our immersive tours.
Our services.
Experience Mesopotamia like never before with our tailored travel packages.

Ensure your safety during your visit with our reliable security services.
Stay informed about upcoming events and festivals in Iraq through our blog.

Mission Statement
Welcome to our journey through Mesopotamia, Iraq's cradle of civilization! At our core, we're driven by a passionate mission: to unveil the timeless allure of Mesopotamia and beckon travelers to discover its ancient wonders. Our goal is to open doors to the birthplace of human civilization, inviting adventurers, history enthusiasts, and culture seekers to immerse themselves in the richness of this historic land. We strive to offer immersive experiences that transcend mere sightseeing, aiming to forge connections between past and present, fostering understanding and appreciation for Mesopotamia's profound legacy. Through our tailored tours, we aspire to showcase the mesmerizing tapestry of archaeological marvels, diverse cultures, and warm hospitality that define this extraordinary region. Join us as we embark on an expedition to Mesopotamia, where the echoes of history resonate and where every step tells a story waiting to be heard.
Community Initiatives
Empowering Communities Through Tourism
How We Make a Difference:
Creating Opportunities: We're dedicated to generating jobs and income for locals, providing employment in hospitality, guiding, and various tourism-related sectors.
Preserving Heritage: By promoting tourism, we actively contribute to conserving Iraq's rich cultural heritage, ensuring its preservation for generations to come.
Economic Boost: Through increased tourist spending, we drive economic growth within communities, benefiting local businesses and services.
Building Infrastructure: Our efforts improve local infrastructure, enhancing accessibility and convenience for both residents and visitors alike.
Cultural Exchange: We foster cultural exchange and understanding, encouraging interactions between visitors and locals for mutual appreciation and learning.
Sustainable Practices: We're committed to sustainable tourism, implementing eco-friendly initiatives that protect the environment and resources while benefitting local livelihoods.

Join us on a journey that not only explores the beauty of Iraq but also makes a meaningful impact on the lives of its communities. Together, let's create unforgettable experiences while supporting the heart and soul of this remarkable country.

The tour was amazing! I learned so much about the ancient history of Mesopotamia.

I highly recommend Mesopotamia Tours. The guides were knowledgeable and friendly.
Subscribe to our newsletter
+964 777 777 7777
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Mesopotamia
By: History.com Editors
Updated: April 24, 2023 | Original: November 30, 2017

Mesopotamia is a region of southwest Asia in the Tigris and Euphrates river system that benefitted from the area’s climate and geography to host the beginnings of human civilization. Its history is marked by many important inventions that changed the world, including the concept of time, math, the wheel, sailboats, maps and writing. Mesopotamia is also defined by a changing succession of ruling bodies from different areas and cities that seized control over a period of thousands of years.
Where is Mesopotamia?
Mesopotamia is located in the region now known as the Middle East, which includes parts of southwest Asia and lands around the eastern Mediterranean Sea. It is part of the Fertile Crescent , an area also known as “Cradle of Civilization” for the number of innovations that arose from the early societies in this region, which are among some of the earliest known human civilizations on earth.
The word “mesopotamia” is formed from the ancient words “meso,” meaning between or in the middle of, and “potamos,” meaning river. Situated in the fertile valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the region is now home to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, Turkey and Syria .

Mesopotamian Civilization
Humans first settled in Mesopotamia in the Paleolithic era. By 14,000 B.C., people in the region lived in small settlements with circular houses.
Five thousand years later, these houses formed farming communities following the domestication of animals and the development of agriculture, most notably irrigation techniques that took advantage of the proximity of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Agricultural progress was the work of the dominant Ubaid culture, which had absorbed the Halaf culture before it.

How Mesopotamia Became the Cradle of Civilization
Environmental factors helped agriculture, architecture and eventually a social order emerge for the first time in ancient Mesopotamia.
The Earliest Known Author Was a Woman from Mesopotamia
A priestess named Enheduanna claimed authorship to poetry and other texts—sometimes in first‑person—more than a millennium before Homer.
9 Ancient Sumerian Inventions That Changed the World
The Sumerian people of Mesopotamia had a flair for innovation. Here's how they left their mark.
Ancient Mesopotamia
These scattered agrarian communities started in the northern part of the ancient Mesopotamian region and spread south, continuing to grow for several thousand years until forming what modern humans would recognize as cities, which were considered the work of the Sumer people.
Uruk was the first of these cities, dating back to around 3200 B.C. It was a mud brick metropolis built on the riches brought from trade and conquest and featured public art, gigantic columns and temples. At its peak, it had a population of some 50,000 citizens.
Sumerians are also responsible for the earliest form of written language, cuneiform, with which they kept detailed clerical records.

By 3000 B.C., Mesopotamia was firmly under the control of the Sumerian people. Sumer contained several decentralized city-states—Eridu, Nippur, Lagash, Uruk, Kish and Ur.
The first king of a united Sumer is recorded as Etana of Kish. It’s unknown whether Etana really existed, as he and many of the rulers listed in the Sumerian King List that was developed around 2100 B.C. are all featured in Sumerian mythology as well.
Etana was followed by Meskiaggasher, the king of the city-state Uruk. A warrior named Lugalbanda took control around 2750 B.C.
Gilgamesh, the legendary subject of the Epic of Gilgamesh , is said to be Lugalbanda’s son. Gilgamesh is believed to have been born in Uruk around 2700 B.C.
The Epic of Gilgamesh is considered to be the earliest great work of literature and the inspiration for some of the stories in the Bible. In the epic poem, Gilgamesh goes on an adventure with a friend to the Cedar Forest, the land of the Gods in Mesopotamian mythology. When his friend is slain, Gilgamesh goes on a quest to discover the secret of eternal life, finding: "Life, which you look for, you will never find. For when the gods created man, they let death be his share, and life withheld in their own hands."
King Lugalzagesi was the final king of Sumer, falling to Sargon of Akkad, a Semitic people, in 2334 B.C. They were briefly allies, conquering the city of Kish together, but Lugalzagesi’s mercenary Akkadian army was ultimately loyal to Sargon.

HISTORY Vault: Ancient History
From the Sphinx of Egypt to the Kama Sutra, explore ancient history videos.
Sargon and the Akkadians
The Akkadian Empire existed from 2234-2154 B.C. under the leadership of the now-titled Sargon the Great. It was considered the world’s first multicultural empire with a central government.
Little is known of Sargon’s background, but legends give him a similar origin to the Biblical story of Moses. He was at one point an officer who worked for the king of Kish, and Akkadia was a city that Sargon himself established. When the city of Uruk invaded Kish, Sargon took Kish from Uruk and was encouraged to continue with conquest.
Sargon expanded his empire through military means, conquering all of Sumer and moving into what is now Syria. Under Sargon, trade beyond Mesopotamian borders grew, and architecture became more sophisticated, notably the appearance of ziggurats, flat-topped buildings with a pyramid shape and steps.
The final king of the Akkadian Empire, Shar-kali-sharri, died in 2193 B.C., and Mesopotamia went through a century of unrest, with different groups struggling for control.
Among these groups were the Gutian people, barbarians from the Zagros Mountains. The Gutian rule is considered a disorderly one that caused a severe downturn in the empire’s prospects.
In 2100 B.C. the city of Ur attempted to establish a dynasty for a new empire. The ruler of Ur-Namma, the king of the city of Ur, brought Sumerians back into control after Utu-hengal, the leader of the city of Uruk, defeated the Gutians.
Under Ur-Namma, the first code of law in recorded history, The Code of Ur-Nammu, appeared. Ur-Namma was attacked by both the Elamites and the Amorites and defeated in 2004 B.C.
The Babylonians
Choosing Babylon as the capital, the Amorites took control and established Babylonia .
Kings were considered deities and the most famous of these was Hammurabi , who ruled 1792–1750 B.C. Hammurabi worked to expand the empire, and the Babylonians were almost continually at war.
Hammurabi’s most famous contribution is his list of laws, better known as the Code of Hammurabi , devised around 1772 B.C.
Hammurabi’s innovation was not just writing down the laws for everyone to see, but making sure that everyone throughout the empire followed the same legal codes, and that governors in different areas did not enact their own. The list of laws also featured recommended punishments to ensure that every citizen had the right to the same justice.
In 1750 B.C. the Elamites conquered the city of Ur. Together with the control of the Amorites, this conquest marked the end of Sumerian culture.
The Hittites
The Hittites, who were centered around Anatolia and Syria, conquered the Babylonians around 1595 B.C.
Smelting was a significant contribution of the Hittites, allowing for more sophisticated weaponry that lead them to expand the empire even further. Their attempts to keep the technology to themselves eventually failed, and other empires became a match for them.
The Hittites pulled out shortly after sacking Babylon, and the Kassites took control of the city. Hailing from the mountains east of Mesopotamia, their period of rule saw immigrants from India and Europe arriving, and travel sped up thanks to the use of horses with chariots and carts.
The Kassites abandoned their own culture after a couple of generations of dominance, allowing themselves to be absorbed into Babylonian civilization.
The Assyrians

The Assyrian Empire under the leadership of Ashur-uballit I rose around 1365 B.C. in the areas between the lands controlled by the Hittites and the Kassites.
Around 1220 B.C., King Tukulti-Ninurta I aspired to rule all of Mesopotamia and seized Babylon. The Assyrian Empire continued to expand over the next two centuries, moving into modern-day Palestine and Syria.
Under the rule of Ashurnasirpal II in 884 B.C., the empire created a new capitol, Nimrud, built from the spoils of conquest and brutality that made Ashurnasirpal II a hated figure.
His son Shalmaneser spent the majority of his reign fighting off an alliance between Syria, Babylon and Egypt, and conquering Israel . One of his sons rebelled against him, and Shalmaneser sent another son, Shamshi-Adad, to fight for him. Three years later, Shamshi-Adad ruled.
A new dynasty began in 722 B.C. when Sargon II seized power. Modeling himself on Sargon the Great, he divided the empire into provinces and kept the peace.
His undoing came when the Chaldeans attempted to invade and Sargon II sought an alliance with them. The Chaldeans made a separate alliance with the Elamites, and together they took Babylonia.
Sargon II lost to the Chaldeans but switched to attacking Syria and parts of Egypt and Gaza, embarking on a spree of conquest before eventually dying in battle against the Cimmerians from Russia.
Sargon II’s grandson Esarhaddon ruled from 681 to 669 B.C. and went on a destructive campaign of conquest through Ethiopia, Palestine and Egypt, destroying cities he rampaged through after looting them. Esarhaddon struggled to rule his expanded empire. A paranoid leader, he suspected many in his court of conspiring against him and had them killed.
His son Ashurbanipal is considered to be the final great ruler of the Assyrian empire. Ruling from 669 to 627 B.C., he faced a rebellion in Egypt, losing the territory, and from his brother, the king of Babylonia, whom he defeated. Ashurbanipal is best remembered for creating Mesopotamia’s first library in what is now Nineveh, Iraq. It is the world’s oldest known library, predating the Library of Alexandria by several hundred years.
Nebuchadnezzar

In 626 B.C. the throne was seized by Babylonian public official Nabopolassar, ushering in the rule of the Semitic dynasty from Chaldea. In 616 B.C. Nabopolassar attempted to take Assyria but failed.
His son Nebuchadnezzar reigned over the Babylonian Empire following an invasion effort in 614 B.C. by King Cyaxares of Media that pushed the Assyrians further away.
Nebuchadnezzar is known for his ornate architecture, especially the Hanging Gardens of Babylon , the Walls of Babylon and the Ishtar Gate. Under his rule, women and men had equal rights.
Nebuchadnezzar is also responsible for the conquest of Jerusalem , which he destroyed in 586 B.C., taking its inhabitants into captivity. He appears in the Old Testament because of this action.
The Persian Empire
Persian Emperor Cyrus II seized power during the reign of Nabonidus in 539 B.C. Nabonidus was such an unpopular king that Mesopotamians did not rise to defend him during the invasion.
Babylonian culture is considered to have ended under Persian rule, following a slow decline of use in cuneiform and other cultural hallmarks.
By the time Alexander the Great conquered the Persian Empire in 331 B.C., most of the great cities of Mesopotamia no longer existed and the culture had been long overtaken. Eventually, the region was taken by the Romans in A.D. 116 and finally Arabic Muslims in A.D. 651.
Mesopotamian Gods
Mesopotamian religion was polytheistic, with followers worshipping several main gods and thousands of minor gods. The three main gods were Ea (Sumerian: Enki), the god of wisdom and magic, Anu (Sumerian: An), the sky god, and Enlil (Ellil), the god of earth, storms and agriculture and the controller of fates. Ea is the creator and protector of humanity in both the Epic of Gilgamesh and the story of the Great Flood.
In the latter story, Ea made humans out of clay, but the God Enlil sought to destroy humanity by creating a flood. Ea had the humans build an ark and mankind was spared. If this story sounds familiar, it should; foundational Mesopotamian religious stories about the Garden of Eden, the Great Flood, and the Creation of the Tower of Babel found their way into the Bible, and the Mesopotamian religion influenced both Christianity and Islam.
Each Mesopotamian City had its own patron god or goddess, and most of what we know of them has been passed down through clay tablets describing Mesopotamian religious beliefs and practices. A painted terracotta plaque from 1775 B.C. gives an example of the sophistication of Babylonian art, portraying either the goddess Ishtar or her sister Ereshkigal, accompanied by night creatures.
Mesopotamian Art

While making art predates civilization in Mesopotamia, the innovations there include creating art on a larger scale, often in the context of their grandiose and complex architecture, and frequently employing metalwork.
One of the earliest examples of metalwork in art comes from southern Mesopotamia, a silver statuette of a kneeling bull from 3000 B.C. Before this, painted ceramics and limestone were the most common art forms.
Another metal-based work, a goat standing on its hind legs and leaning on the branches of a tree, featuring gold and copper along with other materials, was found in the Great Death Pit at Ur and dates to 2500 B.C.
Mesopotamian art often depicted its rulers and the glories of their lives. Also created around 2500 B.C. in Ur is the intricate Standard of Ur, a shell and limestone structure that features an early example of complex pictorial narrative, depicting a history of war and peace.
In 2230 B.C., Akkadian King Naram-Sin was the subject of an elaborate work in limestone that depicts a military victory in the Zagros Mountains and presents Naram-Sin as divine.
Among the most dynamic forms of Mesopotamian art are the reliefs of the Assyrian kings in their palaces, notably from Ashurbanipal’s reign around 635 B.C. One famous relief in his palace in Nimrud shows him leading an army into battle, accompanied by the winged god Assur.
Ashurbanipal is also featured in multiple reliefs that portray his frequent lion-hunting activity. An impressive lion image also figures into the Ishtar Gate in 585 B.C., during the reign of Nebuchadnezzar II and fashioned from glazed bricks.
Mesopotamian art returned to the public eye in the 21st century when museums in Iraq were looted during conflicts there. Many pieces went missing, including a 4,300-year-old bronze mask of an Akkadian king, jewelry from Ur, a solid gold Sumerian harp, 80,000 cuneiform tablets and numerous other irreplaceable items.
Babylon: Mesopotamia and the Birth of Civilization. Paul Kriwaczek . Ancient Mesopotamia. Leo Oppenheim . Ancient Mesopotamia: This History, Our History. University of Chicago . Mesopotamia 8000-2000 B.C. Metropolitan Museum of Art . 30,000 Years of Art. Editors at Phaidon . Ancient Mesopotamian Gods and Goddesses. UPenn.edu .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

Multi Day Tours
Explore all of mesopotamias tours with us
Mesopotamia Tourism offers multi day tours through the country either with our own theme focused itinerary or a customized tour if needed. Our itineraries cover most important topics to understand a country that was covered dominantly by negative news outlets focussing on war, conflict and corruption. The past years the security of the country changed and the borders are open again for visitors.
Now is the best time to rediscover the land of 1000 and 1 nights and it’s beautiful people in a different way. Come and get to know Iraq in a way you will not see in the media. We help you to understand and connect with this country that will make you feel travel through time.

What does our Multi-Day Tour service include?
- Accommodation
- Transportation on the ground
- Local guide (speaking English, German, Arabic, Kurdish)
- Breakfast & Dinner (not incl. Alcoholic beverage)
- Entry fees (Archaeological sites & Museums)
- Tailored Guidebook from Mesopotamia Tourism*
*Traveling through Iraq and trying to understand its rich history of over thousands of years can be overwhelming. No other region housed so many different capitals for empires like the land between the Euphrates and Tigris. During our tour we will provide you with our custom-made Mesopotamia Tourism Guidebook which is specifically made for your itinerary.
Capitals Of Mesopotamia - 8 Days Central Iraq + Northwest Iraq + Kurdistan region
In this itinerary, we will take a route through the small and big capitals that existed through the past millennia. Some are to this day flourishing despite periods of ups and downs, while others remained abandoned in ruins.
Tour will start in Baghdad and will end in Erbil and will take 8 days.

Lalesh + Assyrian Monuments

Book a Tour
How many persons 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10+ Choose the date
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
World history
Course: world history > unit 1, ancient mesopotamia.
- Ancient Mesopotamia and the Hebrew Bible
Ancient Mesopotamian civilizations
- Mesopotamia
- Mesopotamian civilizations formed on the banks of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in what is today Iraq and Kuwait.
- Early civilizations began to form around the time of the Neolithic Revolution—12000 BCE.
- Some of the major Mesopotamian civilizations include the Sumerian, Assyrian, Akkadian, and Babylonian civilizations.
- Evidence shows extensive use of technology, literature, legal codes, philosophy, religion, and architecture in these societies.
Civilizations born along rivers
Akkadian empire, assyrian empire, what do you think.
- Why did Mesopotamian rulers decide to build ziggurats if they required such massive amounts of human labor?
- How did trade with faraway civilizations likely impact Mesopotamians’ views of the world?
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


ten day Mesopotamia tour
Arrival in diyarbakir 10 arches bridge, tigris river ulu mosque, caravan saray, city walls and citadel, mount nemrut, commagene kingdom, colossal statue of gods, gaziantep castle, mosaic museum, museum of archeology, euphrates boat tour, jacob's well, sanliurfa archeology museum, pool of abraham, birth place of abraham, sanliurfa mosaic museum, job's cave, unesco world heritage site: gobekli tepe "potbelly hill", old city mardin, mosques and churches, kasimiye madrassa, midyat mansions, saffron monastery, dara cistern, dara necropolis, airport transfer , mesopotamia tour.
Discover the civilizations of Mesopotamia. This is where it all began, and the region has been inhabited ever since. Visit the ancient home of the patriarch Abraham, the cave of Job, and Jacob's well. See UNESCO World Heritage sights of Gobekli Tepe, the Diyarbakir Fortress, Hevsel Gardens, and Mount Nemrut. Explore Roman Cities, roads, and cisterns and see palaces and mosques from the Ottoman Empire.
Day 1 Arrival in Diyarbakir
Arrive in Diyarbakir and meet your driver who will take you to the hotel. After you settle in, you'll meet your tour guide and hear the details of the trip. Before calling it a night, have dinner near the 10 Arches Bridge on the Tigris River.
Day 2 Diyarbakir
Hit the streets of Diyarbakir with your guide and see the Ulu Mosque, Caravan Saray, and the famous city walls. After a day of touring, you'll head for Mount Nemrut along the Euphrates River.
Day 3 Mount Nemrut
Get up early (optional) to catch a captivating sunrise on top of Mount Nemrut. Here you'll see tombs of the Commagene Kingdom and the Colossal Statues of Gods. This iconic sight is unforgettable! After descending from the mountain you'll stop by other sights in the area before heading to Gaziantep!
Day 4 Gaziantep
After breakfast at your hotel, you'll walk the winding streets of the old city center of Gaziantep with your guide, soaking in the sights and history of this fascinating city. You will visit the castle, museums and have some time for shopping in the bazaar. The stunning mosaic museum houses a priceless collection of 2nd-century mosaics from the now sunken city of Zeugma.
Day 5 Gaziantep
In the morning, visit the Gaziantep Museum of Archeology. Finish off your time in Gaziantep with a boat tour on the Euphrates and see the sunken city of Halfeti. From Halfeti, you're off to the next destination -- Sanliurfa!
Day 6 Sanliurfa Buckle up and drink your coffee (or Turkish tea!) this morning, because Sanliurfa is full of ancient historical sights you do not want to miss! Today you'll see the Biblical city of Haran (500-year-old mud houses) where you'll have a chance to ride camels and visit Jacob's well! After a delicious local lunch, visit the Sanliurfa Archeology Museum. This is a new museum full of ancient artifacts collected from around the province. The museum will take you on a walk from the beginning of civilization through different periods of time ending with the Ottoman Empire-- there are even tablets housed here with writing that is what experts believe was the world's earliest writing system! Experience a picturesque sunset at the famous Pool of Abraham (Fish Lake). This pool is believed by Muslims to be where Nimrod threw Abraham into the fire. Abraham is an important patriarch in Islam, Judaism, and Christianity. Sanliurfa is where Abraham lived before his migration to Canaan.
Day 7 Sanliurfa After breakfast at your hotel, see the Sanliurfa Mosaic Museum. These mosaics, some dating back as old as the 1st-Century, were uncovered on accident while the local municipality was preparing to create a parking lot! The mosaics were restored and kept in their original locations and the museum was built around them. Walk the glass pathways and look down over beautiful 2000-year-old mosaic pictures laying just as they always have. After lunch, head to "Potbelly Hill" or in Turkish, Gobekli Tepe. This is believed to be the world's oldest temple. Experts date these incredible ruins to 10,000 BC, predating Stonehenge by a whopping 6,000 years! After you're done exploring, head east to the city of Mardin.
Day 8 Mardin In Mardin, spend the day exploring the streets of the old limestone city (no cars allowed!) and see mansions, stone houses, and museums. Every turn in this maze-like town brings a new sight to see or a shop to visit. Walk the courtyard of the 15th century Kasimiye Madrassa with your guide and hear about the intriguing story behind its fountain before heading back to your hotel for some well-earned rest!
Day 9 Mardin Today, you will explore the sights around the city of Mardin. See important monasteries with incredible history. Deir-Al-Zafaran (Saffron Monastery) was once the center of the ancient Syriac Christian Patriarchy. The sight has been the center of religious worship for many centuries; the monstery itself is built over an ancient temple. This temple was built in 1000 BC and dedicated to the worship of the sun. When the people here converted to Christianity in the 1st-Century, they buried their temple and built a monastery on top of it! The temple has been recovered and you will visit both the monastery buildings and ancient temple. From there, visit Dara, a ruined Roman military city with an incredibly intact cistern as well as a necropolis. Day 10 Head Home
Rest, reflect and get ready for your journey home. Say goodbye to your tour guide who is sure to have become a friend. Your driver will escort you to the airport. You have just experienced the trip of a lifetime!

Tour Information
Inclusions: Hotel, Entrance Fees, Meals, Transfers, English Speaking Tour Guide
Fitness Level: All Prices From: $1699 Tour Length: 10 Days, 9 Nights Start Location: Diyarbakir, Turkey End Location: Mardin, Turkey

Get more info and start planning your trip with our travel experts!
Thanks for submitting! We will get back to you within one business day.

"It was a magical, once-in-a-lifetime experience. I really felt as though I was given the best Kemaliye had to offer.
World History Edu
- Ancient Mesopotamia
Ancient Mesopotamia: 9 Greatest Cities
by World History Edu · June 4, 2020

Ancient Mesopotamia cities
Ancient Mesopotamia, the cradle of mankind’s civilization, was home to some of the most well-known ancient empires and city-states in the world. The region, which is located in southwest Asia, was most famous for the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In fact, many of the Mesopotamian cities (i.e. Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian, Persian, etc) that we are about to explore relied heavily on those rivers. Inhabitants of those cities made immense contributions to agricultural technology, legal codes, science, philosophy and religion of future civilizations.
Here is a look at 9 of the greatest cities of ancient Mesopotamia that changed the world forever.

Ancient Mesopotamia cities – Uruk
Uruk was an ancient city-state of the Sumer people (i.e. Sumerians). Dating back to about 3200 BC, the city is generally considered as one of the first civilized cities to spring up in the region.
Situated in southern Mesopotamia, Uruk took about 300 years to reach its zenith in 2900 BC. Littered with a host of mud brick houses, Uruk is believed to have had about 50-80 thousand inhabitants, making it the largest city on earth at the time.
The city’s developed agricultural and administrative structures made it possible for such large population to thrive. Up until the Akkadians came unto the scene, the city of Uruk’s boundaries stretched very far; it gulped up several neighboring cities around the Euphrates River.
The city of Akkad was the largest city among the Akkadians (the Akkadian Empire). It came to greatness starting around 2400 BC, after Sumerian city states in the south went into decline. This resulted in Akkadian language replacing Sumerian language.
Under Sargon the Great , the city-state of Akkad (as well as the Empire itself) developed in leaps and bounds. Sargon was able to make Akkad the center of his expanding empire, bringing in people from the north as well.
Akkad was not much different from other Sumerian cities. The city had similar religious beliefs and local system of governance as that of Uruk. Owing to its multicultural environment and central government structure, Akkad was able to build upon several Sumerian technologies in irrigation, sailing, and literature.

Ancient Mesopotamia cities | Ashurbanipal with officials from the city
Nineveh was famous because it contributed immensely to the development of local government structures and legal codes for the Assyrians. Its tag as the greatest city to emerge from the Assyrian Empire is rightly deserved.
Nineveh’s path to greatness was largely carved out by King Sennacherib around 700 BC. Subsequent rulers made Nineveh famous because of their immense contributions to the development of local government structures and legal codes in the city. The city spent a great deal of resources in building irrigation canals, which propelled the city’s agricultural produce to even greater heights.
Inhabitants of the city were kept relatively safe by the city walls, which spanned about 6 miles long. About 15 large gates were strategically placed to control the movement of people in and out of the city. The Great Walls of Nineveh also fortified the city, preventing invaders from sacking the city.
It’s been estimated that the library of Nineveh, built by King Ashurbanipal, had about 20,000 clay tablets. The library helped in disseminating knowledge and good agricultural practices throughout the city.

Hammurabi receiving the laws from Code of Hammurabi
In some regard, the city-state of Babylon was the greatest city in ancient Mesopotamia. Babylon also became famous due to it being mentioned a number of times in both Christian and Islamic literature.
In archaeological terms, Babylon is famous simply because of two renowned kings – Hammurabi and Nebuchadnezzar. King Hammurabi (reign – 1792 – 1750 BC) was credited with the introduction of the Hammurabi Code (around 1755 BC) – one of the world’s first legal codes that pronounced just punishments on offenders, regardless of gender or social status.
As for Nebuchadnezzar, his story abounds in the Christian Bible. The King was a deeply polytheist ruler who stretched the boundaries of the empire into other parts of the region. Nebuchadnezzar and subsequent rulers from the Semitic dynasty reinforced the need for equal rights for women and men in the city of Babylon.
The ancient city of Babylon, located in modern-day Baghdad, was also famous for housing the Hanging Gardens of Babylon – one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World . Legend has it that the garden, which was filled with all sorts of trees and flowers, was built as a gift for the Nebuchadnezzar’s wife, Amytis of Media.
As the capital city of the Babylonian Empire, Babylon’s population of over 250,000 made it the largest city in the world at the time.
ASSUR ( ASHUR )
Archaeologists today commonly believe that the Mesopotamian city of Assur was situated around the western part of the Tigris River. The city of Assur burst onto the scenes after the Assyrian Empire was formed. It was the first capital of the Assyrians.
Doubling as the religious and administrative hub of the Assyrians, Assur held a very significant place in ancient Mesopotamia. Archaeological evidences from the ruins today even point to the fact that there was a god called “Assur”, the god of war. It was believed that the god accompanied the Assyrian King Ashurbanipal in all his war campaigns.
Located in the heart of the Assyrian Empire, Nimrud was a very influential city in the 13th and 14th centuries BC. Similar to Assur, the city of Nimrud had one of the most advanced architectures in the region at the time. After a few centuries on the top, Nimrud declined only for it to be revived by subsequent Assyrian emperors starting around the 10th century BC.
Historians and archaeologists state that Nimrud became the capital of the Assyrian Empire around 884 BC. The ruler behind the elevation of the city to prominence was King Ashunasirpal II. The king, as well as his descendants, was known for building spectacular palaces in the city.

Ancient Mesopotamia cities | The lamassu in Persepolis, ancient Persian Empire
Persepolis comes in on our list of greatest Mesopotamia cities because it was one of the most important (if not the most important) cities in the Persian Empire (also known as the Achaemenid Empire ).
Located in present-day Iran (southeastern Iran), the city’s name “Persepolis” is actually Greek for “Persian city”.
It is generally believed that Persepolis was built by Cyrus the Great of Persia in 515 BC. Cyrus went ahead and made the city the economic and political hub of the Persian Empire. His descendants, such as Darius I and Xerxes I , followed in his footsteps and developed Persepolis into one of the greatest cities in the world at the time.
Persepolis’ architecture marvels such as the Throne Hall and Apadana Palace drew people from all over the region into the Persian Empire.

Artwork of Ur-Namma (right) with the goddess Nanna, goddess of the moon
The Sumerian city-state of Ur came into prominence around 2100 BC, after the decline of the Akkadian Empire. The city was propelled to its zenith by two kings – Ur-Namma and Shulgi. Owing to their immense contributions, city’s inhabitants took to deifying them.
Ur-Namma (reign – 2047 – 2030 BC) for example was the one who built the famous Ziggurat of Ur – shrine of the god Nanna – in the 21st century BC. The Ziggurat of Ur –pyramid-like structure – can be found in present-day Dhi Qar Province in Iraq.
The city of Ur worshiped Nanna as their patron god. Nanna was also the god of the moon in many Mesopotamian city-states.
During Ur-Namma, the Sumerian city of Ur also witnessed the first known code of law – the Code of Ur- Nammu. It is believed that the code precedes the Code of Hammurabi by a whopping 300-400 years
In the 18th century BC, Ur went into decline, allowing it to be incorporated into the empire of the first dynasty of Babylonia (the Amorites).
HATTUSA (HATTUSHA)

Sphinx Gate entrance of the city of Hattusa
Not only was the city of Hattusa the capital city of the Hittites (located in the Anatolian region of Turkey), it was also the artistic and religious hub of the Hattian people.
The city’s geographic conditions enabled greater access to timber. They inhabitants also planted wheat, barley and lentils.
From the evidence we have today, the first inhabitants came to the area around the sixth millennium BC. Over centuries, the place became a central trading spot that drew people in from Assur in Assyria.
Like many ancient cities, Hattusa had several major religious deities. For example the god Teshub was the god of storm. And the goddess of the sun was known as Hebat. The Rockshrine remains at Yazilikaya paint a detailed picture about the type of gods and goddesses (i.e. “the thousand gods of Hatti”) that prevailed in Hattusa. Prior to its ultimate demise in 1200 BC, Hattusa reached a population of about 50,000 people.
Hattusa’s present-day location is at Boğazkale District of the Çorum Province, close to Ankara, Turkey. The ancient city of Hattusa entered the UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1986.
Tags: Akkad Babylon Code of Hammurabi Hattusa Mesopotamia cities Nimrud Persepolis Ur Uruk
You may also like...

7 Major Mesopotamian Inventions
June 14, 2019

Nabopolassar: History, Accomplishments and Facts
May 27, 2021

Cuneiform Writing: History, Meaning, Symbols, and Facts
May 26, 2021
- Pingbacks 0
A map showing the location and period of each city would be of great value.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Next story Who were the 12 Most Famous Gods in Ancient Mesopotamia?
- Previous story Jamestown Colony: England’s first, thriving settlement in the Americas
- Popular Posts
- Recent Posts

Alien and Sedition Acts: Definition, Origin Story, & Significance

The Pergamon Altar

Life and Political Career of Konrad Adenauer, the First Chancellor of West Germany

What was the source of the Conflict between Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung?

Why did Alexander Hamilton and Aaron Burr duel?

Greatest African Leaders of all Time

Queen Elizabeth II: 10 Major Achievements

Donald Trump’s Educational Background

Donald Trump: 10 Most Significant Achievements

8 Most Important Achievements of John F. Kennedy

Odin in Norse Mythology: Origin Story, Meaning and Symbols

Ragnar Lothbrok – History, Facts & Legendary Achievements

9 Great Achievements of Queen Victoria

Most Ruthless African Dictators of All Time

12 Most Influential Presidents of the United States

Greek God Hermes: Myths, Powers and Early Portrayals

Kamala Harris: 10 Major Achievements

Kwame Nkrumah: History, Major Facts & 10 Memorable Achievements

8 Major Achievements of Rosa Parks

How did Captain James Cook die?

Trail of Tears: Story, Death Count & Facts

5 Great Accomplishments of Ancient Greece

10 Most Famous Pharaohs of Egypt

The Exact Relationship between Elizabeth II and Elizabeth I

How and when was Morse Code Invented?
- Adolf Hitler Alexander the Great American Civil War Ancient Egyptian gods Ancient Egyptian religion Apollo Athena Athens Black history Carthage China Civil Rights Movement Cold War Constantine the Great Constantinople Egypt England France Hera Horus India Isis John Adams Julius Caesar Loki Medieval History Military Generals Military History Napoleon Bonaparte Nobel Peace Prize Odin Osiris Ottoman Empire Pan-Africanism Queen Elizabeth I Religion Set (Seth) Soviet Union Thor Timeline Turkey Women’s History World War I World War II Zeus
- Car Rentals
- Airport Transfers
- Attractions & Tours
- Flight + Hotel
- Destinations
- Trip.com Rewards
Popular Attractions in Mesopotamia (2024)
- Recommended
- Traveler Rating
- Most Booked
- Distance (Nearest First)

1 . Dragon's Cave
2 . Megalo Meteoro Monastery
3 . Κέντρο Προστασίας Αρκούδας - Bear Conservation Area

4 . Stone bridge Konitsa

5 . Prehistorical Lakeside Settlement of Dispilio

6 . Aquarium of Kastoria

7 . Basilica of Saint Achillius (10th c.)

8 . Holy Monastery of the Virgin Mary Mavriotissa (11th c.)

9 . Pantelidis

10 . Vasilitsa Ski Center
- Customer Support
- Service Guarantee
- More Service Info
- About Trip.com
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Statement
- About Trip.com Group
Other Services
- Investor Relations
- Affiliate Program
- List Your Property
- Become a Supplier
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is thought to be one of the places where early civilization developed. It is a historic region of West Asia within the Tigris-Euphrates river system. In fact, the word Mesopotamia means "between rivers" in Greek. Home to the ancient civilizations of Sumer, Assyria, and Babylonia these peoples are credited with influencing mathematics and astronomy. Use these classroom resources to help your students develop a better understanding of the cradle of civilization.
Anthropology, Archaeology

View the Majesty of a Sumerian Ziggurat in 3D Virtual Tour (Video)
- Read Later
A Sumerian ziggurat was a towering, stepped structures built in ancient Mesopotamia over 4,000 years ago. They were constructed by the Sumerians , who were one of the earliest civilizations in human history. These impressive structures were made of mud bricks and featured a temple at the top, which was believed to be a place where the gods could dwell and communicate with humans. Ziggurats were considered sacred and were built as a symbol of the civilization's devotion to their gods. They were also believed to have played a role in the flood myth of the region, where they were thought to provide a safe haven for humans and animals during the great deluge. While most ziggurats have since crumbled, a few ruins still remain, serving as a reminder of the ancient world and its grand architectural achievements.
This 3D virtual tour allows you to experience the majesty of a Sumerian ziggurat in exceptional detail. As you explore the intricate details of the ancient structure, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the Sumerians' impressive engineering and architectural skills. This immersive experience is a great way to learn more about the fascinating history and culture of the ancient Near East.
Top image: Sumerian Ziggurat. Source: Michael Rosskothen / Adobe Stock
By Joanna Gillan
Rock quarries can be made anywhere. But it takes knowledge, skills, abilities and desire to do the heavy work.
Nobody gets paid to tell the truth.
Or maybe it was because good building stone is scarce in the Euphrates river valley.
Unlike the Atlantean-era megalith stone ruins, which include Egypt and still stand strong, drawing tourists, ziggurats were built with mud bricks, which gradually eroded over the centuries, becoming dangerous and inhabitable, and eventually ugly relics of that lesser, but more modern culture.

Joanna Gillan is a Co-Owner, Editor and Writer of Ancient Origins.
Joanna completed a Bachelor of Science (Psychology) degree in Australia and published research in the field of Educational Psychology. She has a rich and varied career, ranging from teaching... Read More
Related Articles on Ancient-Origins

(Formerly Kurdistan Iraq Tours)
30 YEARS JOURNEYING THROUGH THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION
Your browser does not support HTML5 video.
Explore Mesopotamia
The cradle of civilization
WHY TRAVEL WITH EXPLORE MESOPOTAMIA?
Explore Mesopotamia is the only locally and internationally registered Tour Company in the region. We have been hosting world travelers for over 30 years. In the world of Adventure Travel—experience matters—especially in the Middle East! We custom design every tour to meet the needs and desires of our guests. We can provide the highest level of luxury or, if budget is an issue, we will make the magic of Mesopotamia come alive at a price you can afford. We attend to every detail from the moment you set foot at the airport until the moment you depart. If you want the best — travel with the best! Tell us what you want to see and where you want to go, and we will do our utmost to make it happen.

MESOPOTAMIA
Mesopotamia (from the Greek, meaning 'between two rivers') was an ancient region located in the eastern Mediterranean bounded in the northeast by the Zagros Mountains and in the southeast by the Arabian Plateau, corresponding to today's Iraq, mostly, but also parts of modern-day Iran, Syria, and Turkey. Our service includes modern ‘airport to airport” transportation, the finest hotels and restaurants and the services of an experienced tour coordinator who will be with you throughout the journey. Lectures are provided on Kurdish history and Archeological and Historic Sites. You will also have the opportunity to interact with local residents and experience the culture firsthand including a taste of local entertainment. Our Company is well known for its attention to detail and special requests, ensuring that your visit will be AN INCREDIBLE JOURNEY!
DESTINATIONS

A Short Tour of Kurdistan
From our Guests
Join our list
Get the latest updates on travel in Mesopotamia delivered to your inbox from the most experienced company in the region.

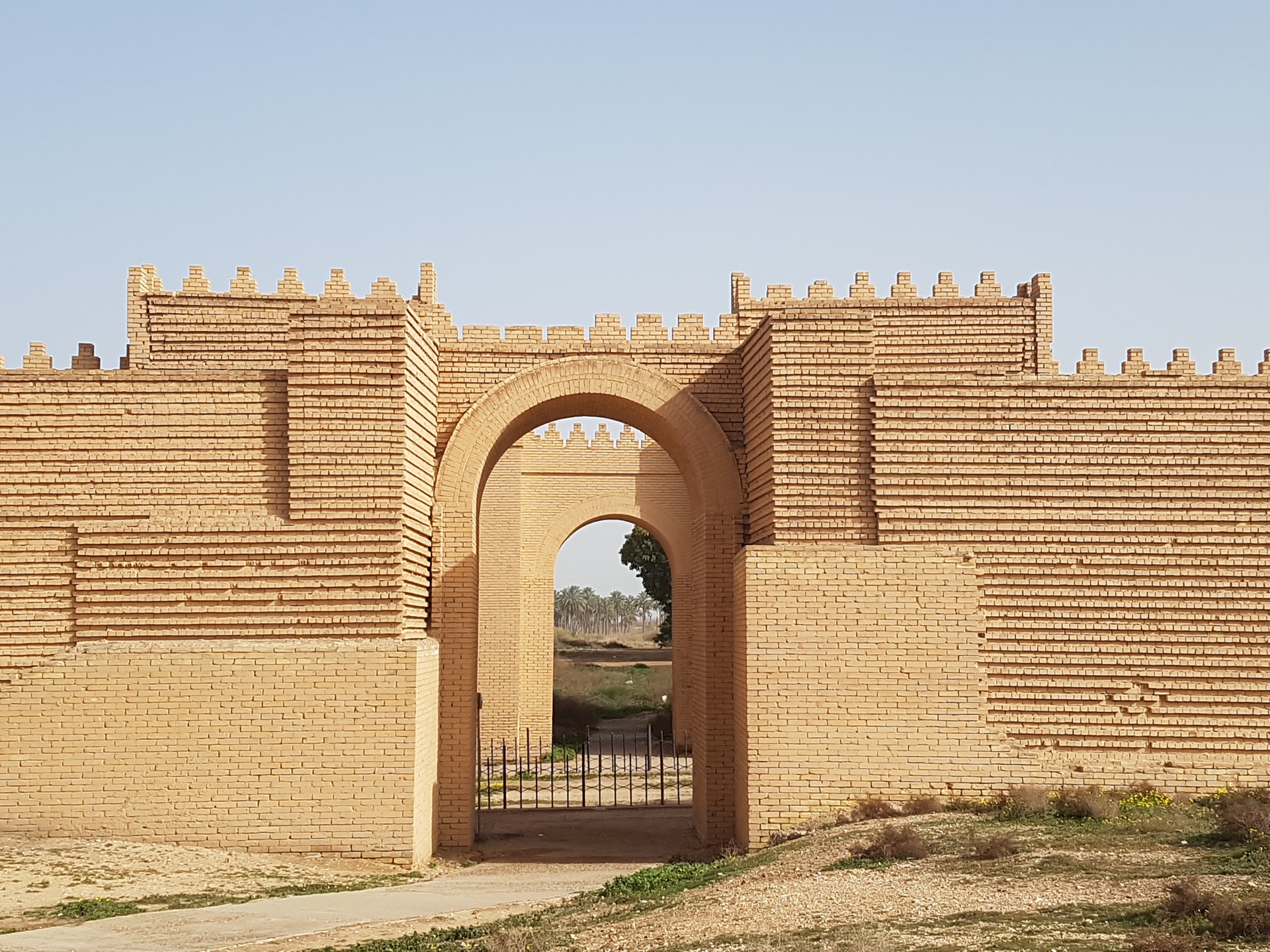
Visiting the Babylon Ruins | Where Is Babylon Today?
By Author Christian L.
Posted on Published: October 5, 2020 - Last updated: November 26, 2021
Categories Destinations , Historical Places , Iraq , Middle East
No other place in the world has a more historical sound to its name than the ancient city of Babylon in Iraq. It was one of the most important kingdoms that the world has ever seen and the place where Alexander The Great passed away, aged 32 years old.
After years of colonial looting coupled with the crazy dreams of Saddam Hussein, along with massive American destruction during the Iraq 2003 invasion, the legendary city of Babylon today has almost vanished.

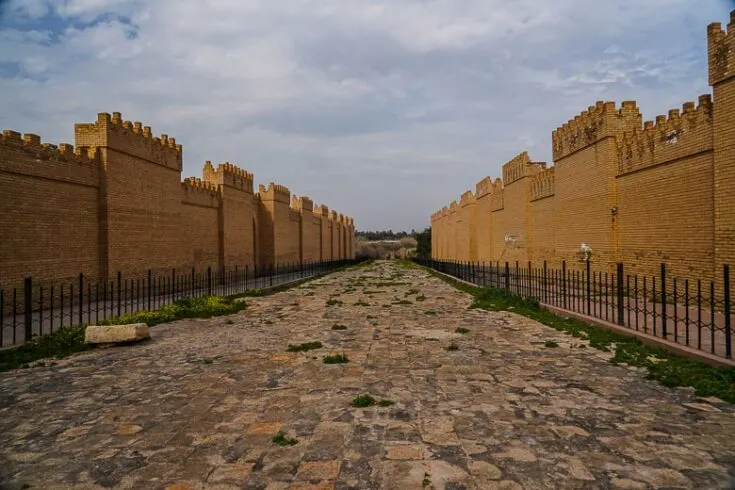
Of all the world’s ancient cities, none can compete with the legendary ancient city of Babylon, Iraq. This site is where one of the seven original seven wonders of the ancient world was once believed to stand. It was known as “the hanging gardens of Babylon” and home to the Tower of Babylon/Babel.
The Historical Babylon ruins were finally added to the UNESCO World Heritage list on 5th July 2019. Although there’s not much left these days, old relics are laying all over the area unprotected. After heavy rain old pottery and coins become visible.

Where is Babylon located?
Modern-day Babylon’s location is in the southern part of the country, around 95 km (59 miles) south of Iraq’s capital – Baghdad . It runs along the Euphrates river and 49 km east of the holy city of Karbala.
The closest city to Babylon is the city of Hillah, the capital of the province. Hillah itself was once a major center of Islamic scholarship and education.
The Jewish prophet Ezekiel’s tomb is located just outside Hillah. The tomb is the oldest and most important Jewish religious site in all of Iraq. The tomb was once put under the protection of Saddam Hussein.
Where Was Babylon Located? A Short History Lesson
Babylon was established during the 19th century BC in the historical region of Mesopotamia, which means “The Land Between Two Rivers”. The two rivers are the Tigris and the Euphrates river.

The history of Babylon city goes back almost 4,000 years. Starting from the Bronze Age when the area was occupied by tribes known as the Amorites . The ancient city then developed into a minor city-state, but it was not until King Hammurabi’s reign that they truly flourished (1792 to 1750 BC).
King Hammurabi was most famous for making the world’s first written law, “ the code of Hammurabi ”. The original tablets are now on display in the Louvre Museum in Paris.

King Hammurabi also conquered all of the surrounding cities, including the famous city of “Ur” and all other minor city-states in the southern part of Mesopotamia. He combined them into one kingdom, and the group of cities was known as Babylonia.
After the death of King Hammurabi in the year 1750 BC, the power over the city regularly changed hands between different tribes and empires before the Assyrians took power over the land in 1000 BC.
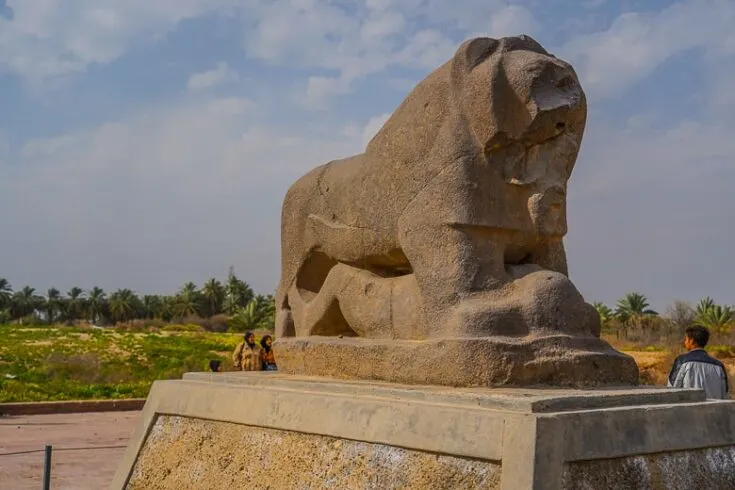

The Lion of Babylon statue was discovered in 1876 by a German archaeological mission, and it´s believed it was built during king Nebuchadnezzar.
This lasted until the death of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal in 627 BC. His death resulted in political instability that leads to a series of brutal civil wars in which Babylonia eventually rebelled under Nabopolassar.
Nabopolassar created The Neo-Babylonian Empire (also known as the Chaldean Empire ) in 626 BC. It was considered to be the Golden Age of the city-state. But it was under his son Nebuchadnezzar that Babylon rose to its full glory and became the world’s largest city at that time with what is believed to have been a population of 200,000.

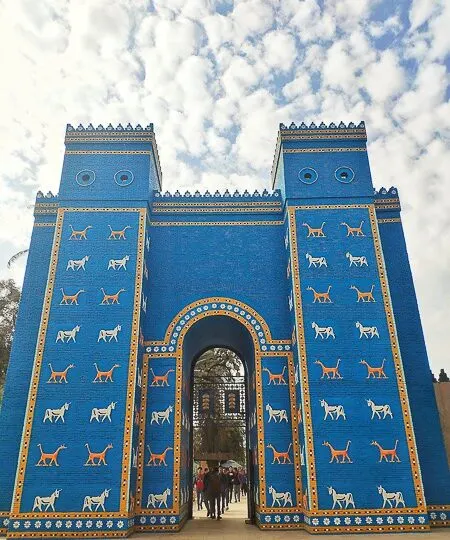
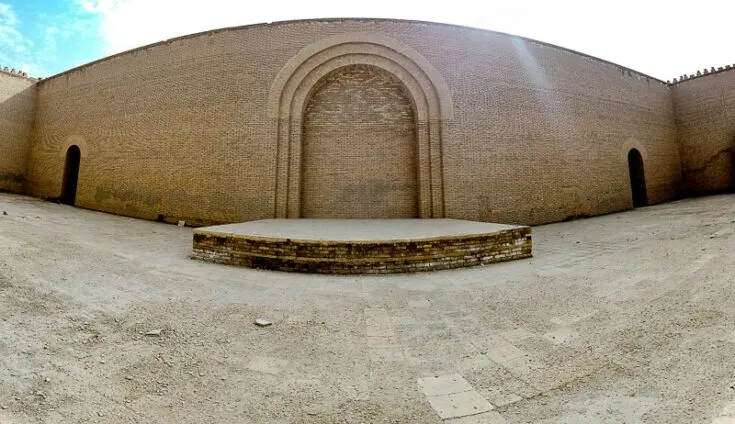
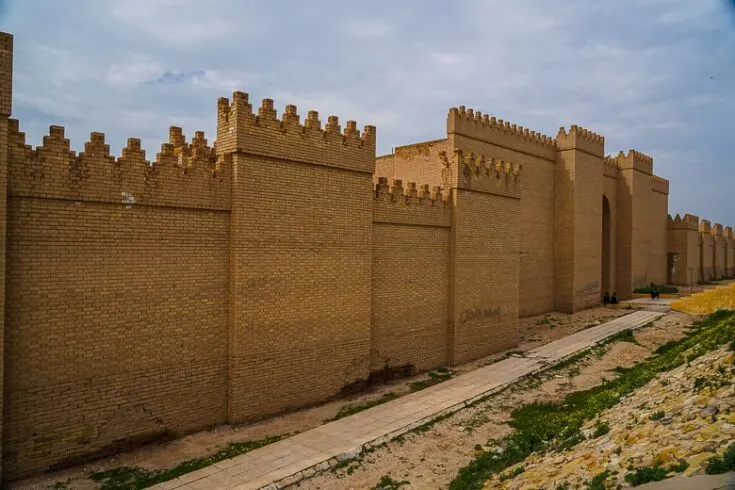
Nebuchadnezzar ordered the complete reconstruction of the imperial grounds, including the Etemenanki ziggurat , and the construction of the Ishtar Gate, the most prominent of eight gates that once stood around Babylon.
Nebuchadnezzar is also believed to have ordered the building of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Many historians believe that the Hanging Gardens were actually located in the Assyrian capital of Nineveh.

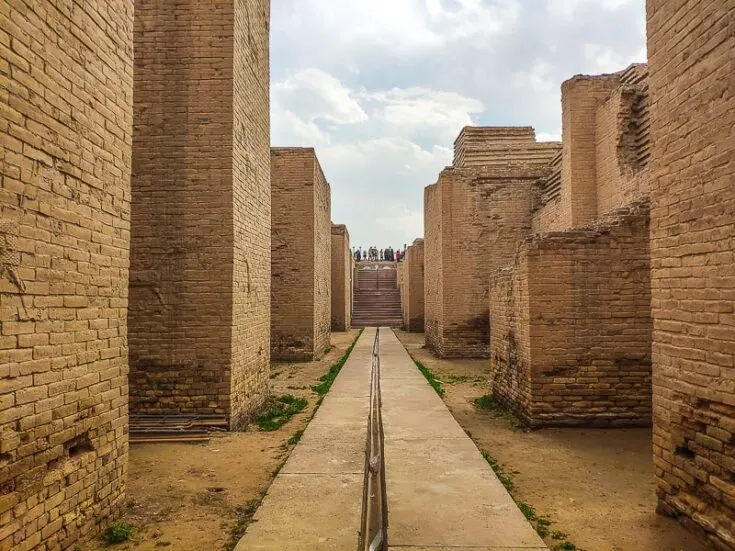
The work of Nebuchadnezzar’s Babylon is spread over two thousand acres. It formed the most significant archaeological site in the Middle East. Only about 5% of Babylon is believed to have been excavated by archaeologists today.
Nebuchadnezzar was considered to be a very successful military leader after his campaigns in Syria and Arabia. His takeover of Jerusalem in 589 BC, where he was in charge of the destruction of Solomon’s Temple (also known as the First Temple), was a stand-out point.

By 572 BC, Nebuchadnezzar was in full control of Babylonia, Assyria, Phoenicia, Israel, Philistinia (present-day Palestine), northern Arabia, and parts of Asia Minor. He also invaded Egypt in the year 568 BC. Nebuchadnezzar died in the year 562 BC after 40 years of power.
After the death of Nebuchadrezzar, the city then had four more kings before the Persian ruler, Cyrus the Great, took control in the year 539 BC. Babylon would stay under the Persian Empire’s rule for two centuries before Alexander the Great then conquered Babylon in 331 BC.
He had plans to make Babylon the capital of his empire but died there in 323 BC before his dream came into reality. Alexander’s generals divided his empire among themselves immediately after his death. This is how general Seleucus obtained the historical city of Babylon.
Not long after, he moved most of the population to his new capital Seleucia, which left the city decaying and deserted. unfortunately, so was Babylon was then plundered for materials for building new cities like mighty Ctesiphon, Baghdad, and even Basra in far south Iraq .
Between the years 1889 and 1917, the area was extensively excavated by a German archaeology team led by Robert Koldewey. Various parts were cleared, including Ishtar Gate, which was dismantled and re-erected in Berlin, a project which took over 20 years to complete. It can now be viewed in the Pergamon Museum in Germany.
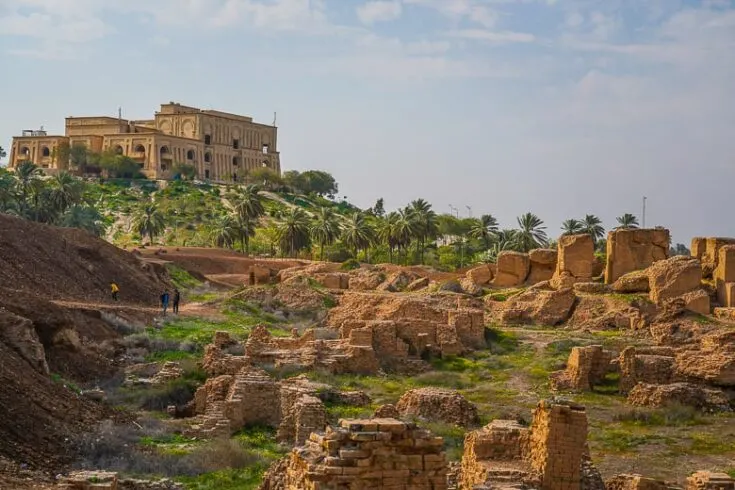
The Ruins of Babylon Now & During Saddam Hussein’s Time
During the reign of Saddam Hussein, a lot of reconstruction took place around this historical place. One of his massive Palaces was built on a hill overlooking the ancient city.
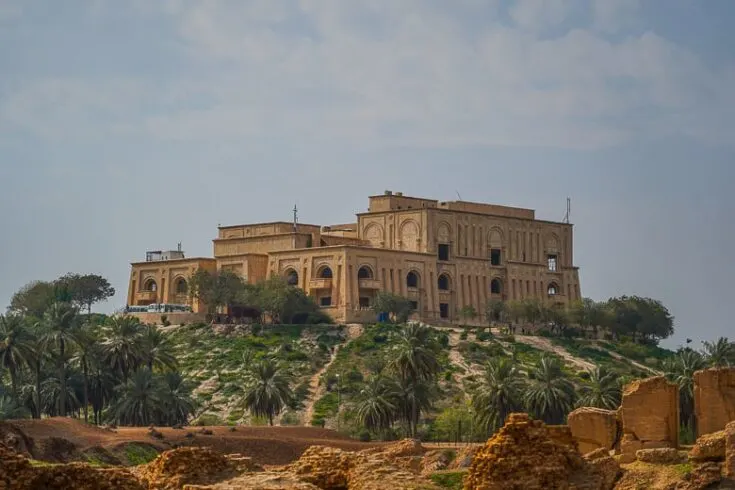

Saddam Hussein imagined himself as a modern-day Nebuchadnezzar. So, he ordered the rebuilding of the ancient ruins. In 1983, the reconstruction of the historical ruins began, and new bricks were placed directly on top of the ruins, some 2500 years old. This sparked big protests from UNESCO and many scholars around the world.

Like on other historical sites around Iraq, Saddam Hussein had his name inscribed on the new bricks. A sample inscription translates to: ”In the reign of the victorious Saddam Hussein, the president of the Republic, may God keep him, the guardian of great Iraq and the renovator of its renaissance and the builder of its great civilisation”.
The rebuilding of the ruins was done in 1987 by thousands of workers from Sudan during the middle of the Iraq – Iran war.

At the end of the Persian Gulf War, he commissioned a personal palace to be built over more of the ruins in the same pyramid style as a Sumerian ziggurat, calling it Saddam Hill.
The massive gaudy structure almost completely covered the original ruins, outraging archaeologists. He also had plans for a cable car to run over the ruins, but it was halted with the 2003 invasion.

What happened to Babylon During the 2003 Iraq Invasion?
During the illegal 2003 invasion of Iraq, the occupation of US Forces did a lot of damage to the old ruins. This was caused by troops driving their 60-ton Abrams tanks around the ruins. The US Army also set up Camp Alpha around the ruins, which further led to its decay.
A huge area was leveled to create landing pads for helicopters and parking lots for vehicles. Tanks rumbled over the ancient bricks, and Polish troops dug trenches through a temple. Soil, holding artifacts and bones, was scooped into sandbags and taken back to America.
Even when walking around the ruins now, you will see thousand-year-old pottery just laying around.
Babylon Ruins Today
Is Babylon inhabited today? No, but the site was once again open to tourists in 2009. However, after years of destruction, there is not much left of the historical ruins today.
You can see the rebuilt ruins from Saddam Hussein’s area. Even his castle, which overlooks the ruins, is now open to the public. But unfortunately, the whole inside of the palace has been looted.
There are no fences around the crumbling ruins, so locals climb all over. They break off small parts of buildings every day. So, if nothing is done soon to preserve the ruins, Babylon will be all gone.
On my walk around the outskirts of the ruins, I saw thousand-year-old pottery broken all over the ground. Nobody is taking care of it, which is such a shame. My local guide found 2 old coins in the rubble during my visit, and this was completely normal, according to him.
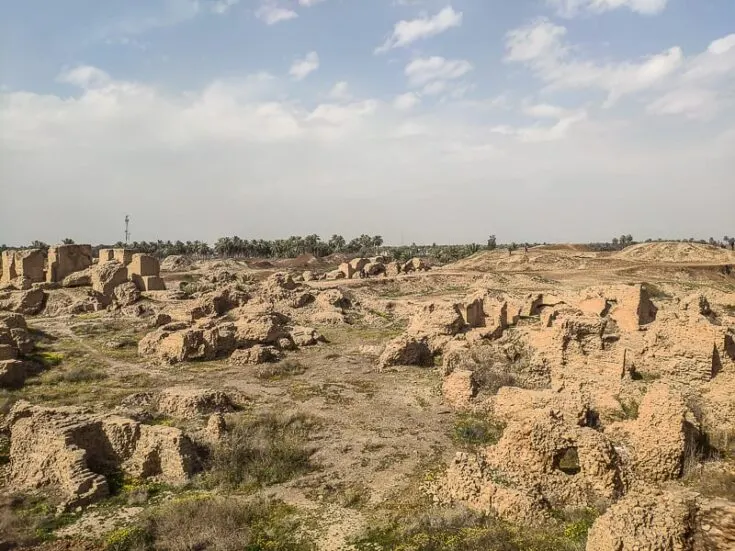

Even an oil pipeline runs through the eastern part of the ancient city these days, going right through the outer wall of ruins.
Like all other locals that worked here with the local tourism industry before 2003, my guide openly admitted that everything was better under Saddam’s rule. A common phrase to hear in Iraq is “Saddam Hussein was a horrible person, but the Americans were so bad that they made Saddam look like an Angel.”
Can You Visit Babylon Today?
Although many local tourists now enjoy frequent visits to this historical place, few tourists have made the journey since it reopened to the world in 2009. Even tho more and more western travel companies now arrange trips here. However, since being made a UNESCO-heritage site in 2019, this is sure to change.
There are a few English-speaking guides available for hire. Most of them worked there before the 2003 invasion and are happy to share all their information about this place and how much of it was destroyed by the foreign military forces.
If you are a fan of ancient history, then what better place to explore than Babylon ruins in Iraq or Persepolis in neighboring Iran another historical place that Alexander the Great conquered.

Thursday 18th of May 2023
Can you cite your sources about US invasion of Iraq helping to destroy parts of Babylonian ruins? Even without reading the original sources (if any), I find your claims INCREDULOUS, even LUDICROUS! I am not am American btw.
Christian L.
Friday 19th of May 2023
From the guides in Babylon and the locals, and you could clearly see broken ruins
Tuesday 9th of August 2022
Can you leave your religious ignorant nonsense out of the conversation here? This blog is for educated open minded travelers who love historical sites and archeology. And facts. And science.
Saturday 12th of August 2023
History is about to repeat it self. Jesus is coming for us that is the rapture. Babylon is of the devil will dwell
Friday 7th of April 2023
@CK, May you feel Jesus's love calling you. He is the Way, the Truth, and the Life. - No better historical site, facts, or science than Jesus!
Sunday 5th of March 2023
@CK, you're LITERALLY talking about a religious location, who had religion as it's lead, in a country that has religion in the fore. Could you please leave your white atheist logic out the conversation? It was due to your people's disrespectful behaviors that caused FURTHER ruin, and further fulfilment of that very prophecy.. brainiac.
Tuesday 10th of May 2022
Babylon will never be rebuilt. Bible prophecy does not lie. Over 2500 years ago it was written in Jeremiah 51:37- And Babylon will become piles of stones, A lair of jackals, An object of horror and something to whistle at, Without an inhabitant. This is exactly what it is today. IT WILL NEVER BE REBUILT!
Monday 7th of March 2022
jeremiah 50 .39 -43 GOD says it will not be inhabited only animals live there .because marduk was set up there same judgement as sodom . see we have a GOD of judgment and justice who does get angry and who resides from generation to generation
Friday 18th of February 2022
This was a good article, but a little too much America hating in it. Yes, there was probably some damage to the area during the invasion and occupation in 2003, but there were strict orders for American personnel not to disturb the archaeology. Our platoon was given a tour of the ruins and rebuilt parts during our time there in 2003. We were not even allowed to scoop up a small sample of dirt for a keepsake. Much of the damage to Babylon was actually a result of the rampant looting in Iraq after the fall of the Hussein regime. It is one e of my best memories from my time there and it is one many American service members have talked about from there time in Iraq.
Sarah Hedger
Wednesday 24th of May 2023
@James, thanks for your service
- Mesopotamia Tourism
- Mesopotamia Itineraries
- Mesopotamia Hotels
Top Tourist Attractions in Mesopotamia
- North America
- Saint Vincent And The Grenadines
- Mesopotamia
- Things To Do In Mesopotamia
Best Things To Do in Mesopotamia, Saint Vincent And The Grenadines
Have you ever visited a new place and felt ‘wow’ about it? For many visitors, it happens at Mesopotamia.
Mesopotamia may not be as popular as other cities in Saint Vincent And The Grenadines, but don’t let that fool you. Mesopotamia is a smaller but beautiful upcoming tourist destination that is worth a visit. You will be surprised by some of the unique things to do and places you can explore at this hidden destination.
You might wish to revisit it someday again, to take a break and relax at Mesopotamia.
If you have plans to visit Saint Vincent And The Grenadines and are not sure if Mesopotamia should be included in your itinerary, keep reading. In this list, we have put together some of the things to do in Mesopotamia and around. We have a hunch that if you include this city in your travel plans, you will be thrilled you did so.
- Leisure Activities in Mesopotamia
Tourist Attractions in Mesopotamia
Here is the list of things to do in Mesopotamia and tourist attractions in city.
Montreal Gardens
- Things to do in Saint George's
- Things to do in Gros Islet
- Things to do in Port Elizabeth
- Things to do in Castries City
- Things to do in Kingstown
- Things to do in Stubbs
- What to do in Mesopotamia in 1 day
- What to do in Mesopotamia in 2 days

Touropia Travel
Discover the World
10 Best Places to Visit in Mesopotamia, Argentina
By Alex Schultz · Last updated on November 2, 2023
Making up the northeast corner of Argentina , Mesopotamia is a wonderful part of Argentina to explore, as it is home to some of the most astounding scenery imaginable. Dominated and, in many ways, defined by the Parana and Uruguay rivers that run through it, the region was actually named after Mesopotamia in modern-day Iraq, by Spanish settlers who saw similarities between the two landscapes.
When traveling around the region, you will never be far away from the two rivers, as many of its main sights and cities hug the riverbanks. While Iguazu Falls is the undoubted star of the show with its immense and incredible waterfalls, cities such as Gualeguaychú and Corrientes are well worth a visit for their colorful, fun-filled carnivals.
The crumbling ruins of Jesuit missions such as San Ignacio Mini are also fascinating to check out. All in all, Mesopotamia offers a great mix of history, culture, and breathtakingly beautiful nature.
Map of Mesopotamia, Argentina
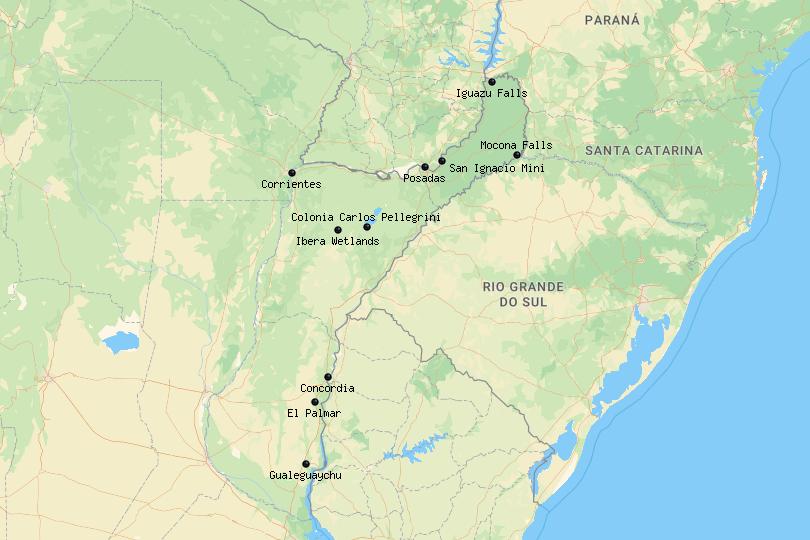
10. Concordia [SEE MAP]

Lying in the northeast of the country right on the border with Uruguay, Concordia is a delightful, laidback place that is at the heart of the nation’s citrus production. As such, agriculture plays a significant role in the city’s identity, and lots of picturesque fields and orchards stretch away from it.
While there is not all that much to do in town, Concordia’s location on the Uruguay River means there are some great riverside beaches for you to hang out on, while the fantastic El Palmar National Park makes for a lovely day trip. The main reason that people stop by Concordia, however, is to pass over into Salto in neighboring Uruguay .
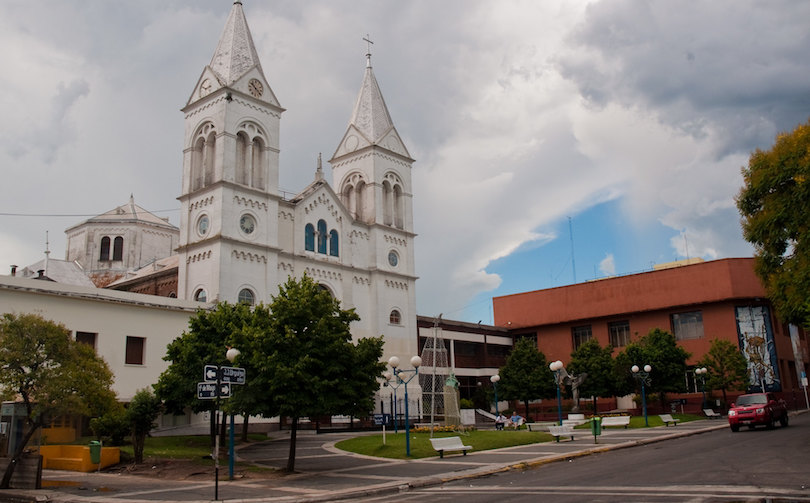
9. Corrientes [SEE MAP]

Set in a beautiful location on the eastern shore of the Parana River, the city of Corrientes is a delightful mix of old and new, as elegant colonial buildings lie side by side with more modern additions.
Due to the pastel-colored buildings and fruit trees lining its streets, the city is awash with color. As such, it should come as no surprise to learn that Corrientes hosts one of the most vibrant carnival celebrations in the whole of Argentina.
Although it boasts a lot of fine colonial architecture, such as the beautiful Church of La Cruz, Corrientes also proudly showcases local Guarani culture in the shape of all of the indigenous arts and crafts that can be found around town.
A great thing to do when in town is to take a peaceful stroll along the city’s lovely waterfront and gaze out across the waters to Resistencia, Corrientes’s twin city, that lies on the opposite bank.
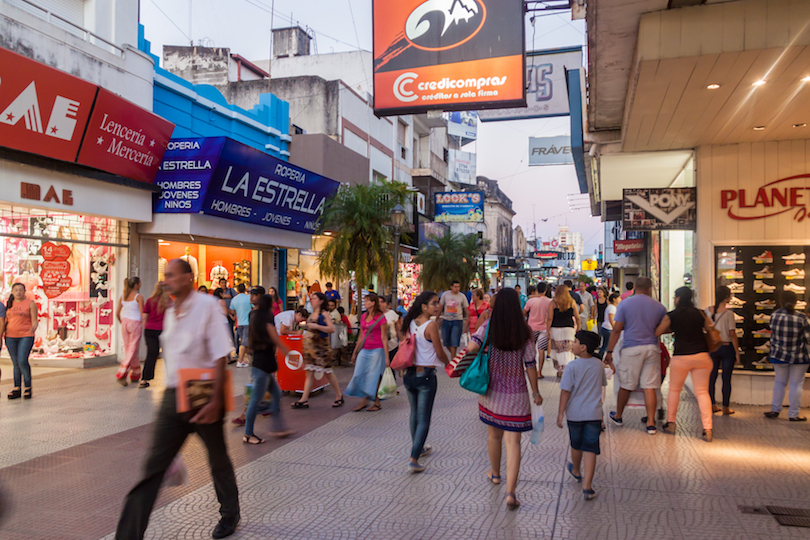
8. Gualeguaychu [SEE MAP]
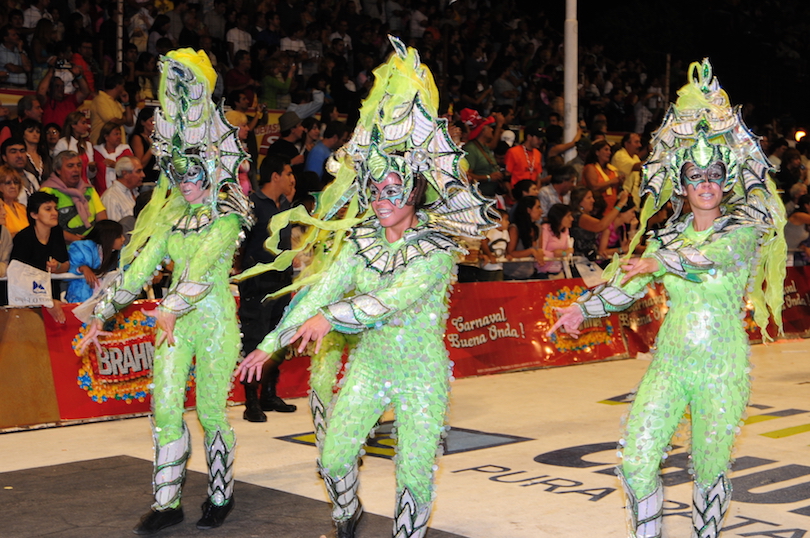

A very chilled out town for most of the year, Gualeguaychú really comes alive during carnival; its boisterous festivities are among the largest and loudest in the world. Hordes of people pour into town from all around Argentina and further afield, contributing to the cacophony of sounds and colors and the party atmosphere.
The rest of the year, Gualeguaychú is a quiet place to visit which is known for its hot springs and beach resorts rather than its nightlife. The banks of the river upon which Gualeguaychú lies have lots of resorts, hotels, and camping sites for visitors to choose from, and its proximity to Buenos Aires, Rosario, and Santa Fe means that lots of people come here for a relaxing getaway.
7. Colonia Carlos Pellegrini [SEE MAP]

Lying on the banks of the Mirinay River, the small village of Colonia Carlos Pellegrini is a very peaceful place to spend some time as it is very rural. Most people simply visit because it is located on the outskirts of Ibera National Park, which is home to vast expanses of wetlands and swamps boasting many types of fauna and flora.
In the village itself, there are only a few restaurants, bars, and hotels for guests to choose from. Most people spend their time trekking or horseback riding in the wetlands. With some of the most untouched and unspoiled nature in the country, Colonia Carlos Pellegrini certainly warrants a visit if you have the chance.
6. Mocona Falls [SEE MAP]
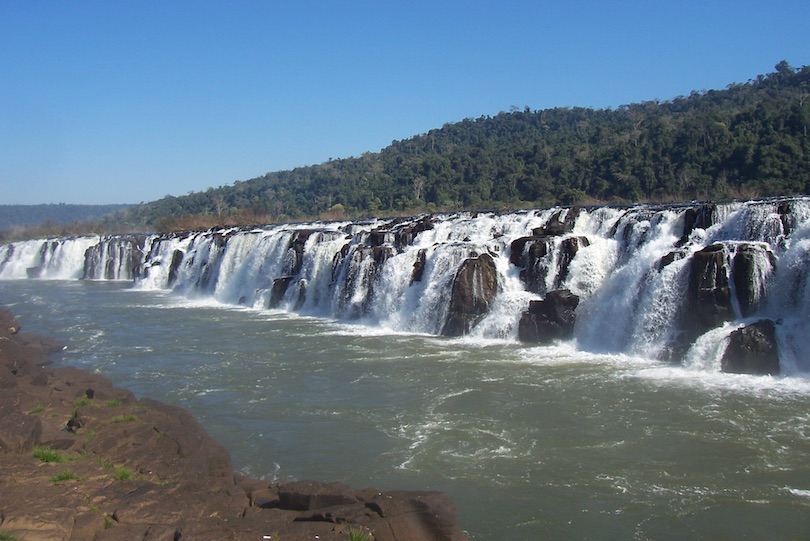

Very impressive to behold, the Mocona Falls are the second-widest waterfalls in the world. The seemingly endless wall of water that gushes forth from the Uruguay River actually stretches for a remarkable three kilometers.
Formed by a geological fault that created a trench in the riverbed, the falls and the river act as a natural frontier, and the border between Argentina and Brazil follows its course all the way down to Buenos Aires.
To get a good view of the majestic falls, visitors can either walk along the opposite riverbank or take a memorable boat trip beneath the cascade, both of which offer a myriad of great photo opportunities. As the falls sometimes disappear under a flood of water during the rainy season, they are best viewed from November to March, which is the region’s dry season.
After having seen the falls, many visitors head over to Brazil to explore the spectacular wilderness on show in Turvo State Park.
5. Posadas [SEE MAP]
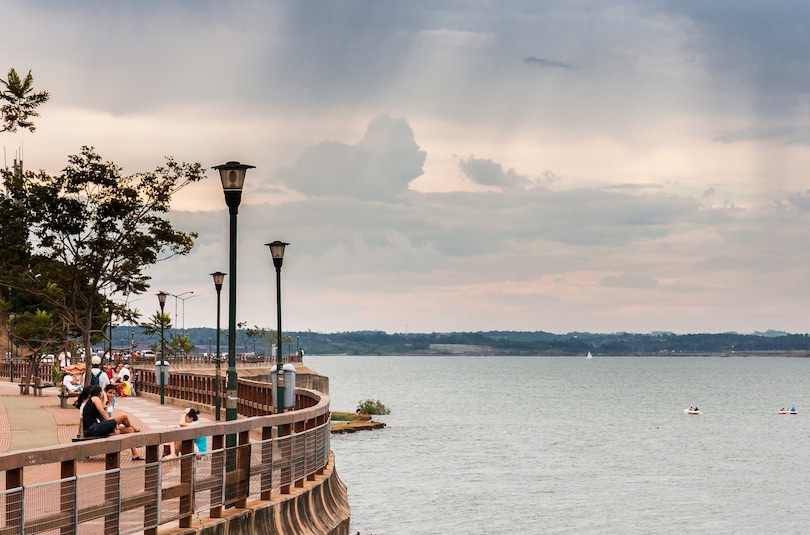

Located on the southern shore of the Parana River overlooking its sister city of Encarnacion in Paraguay, Posadas acts as the commercial and cultural center of the region. As such, it has all the amenities you would expect of a city of its size.
While it may not have all that much for you to see or do around town, there is an enjoyable atmosphere about the place, and wandering along its riverside boardwalk is a delightful way to pass the time. ‘La Costanera’ – as it’s known – is where you’ll find lots of great bars and restaurants, and its parks and beach are perfect if you want to kick back, relax and take in some rays.
The main attractions, however, are undoubtedly the marvelous Jesuit ruins of San Ignacio Mini, Santa Ana, and Loreto, which lie outside of town. Many people also take day trips to any one of the wonderful nature reserves that lie nearby.
4. El Palmar National Park [SEE MAP]
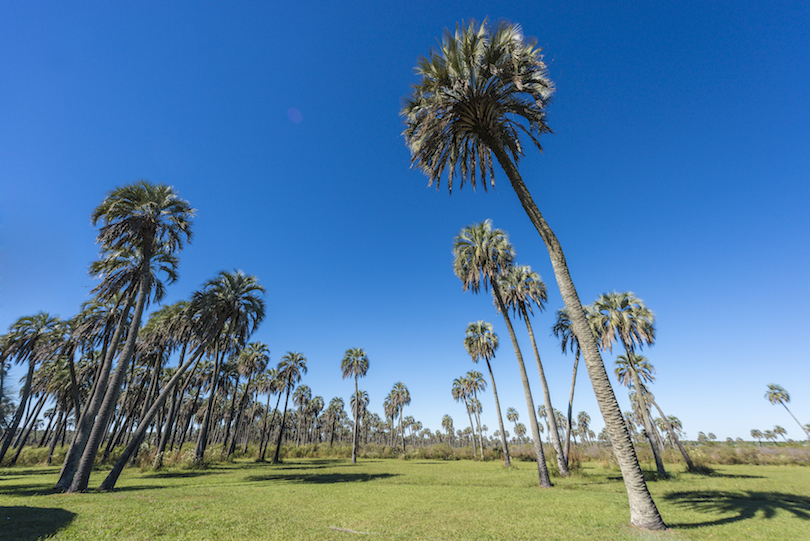

Lying on the western bank of the Uruguay River just across from neighboring Uruguay, El Palmar National Park was established in 1966 to preserve and protect the natural habitat of the distinctive yatay palm trees. Rising majestically towards the heavens, the unique palm trees tower over the surrounding savanna. Outlined against the bright blue sky, they really do paint a pretty picture.
One of the only places in the country that you can find so many of the once widely-spread yatay, the park’s subtropical landscape is lovely to navigate, whether on foot, horseback, or canoe. Both grasslands and forest, as well as sparkling streams, can be found in between the clumps of palm trees.
3. San Ignacio Mini [SEE MAP]
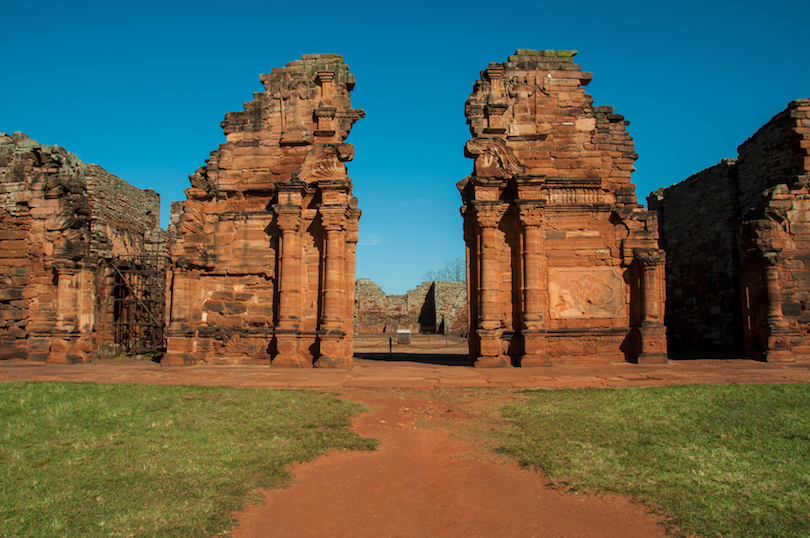

While the Jesuits first founded the mission all the way back in 1610, it wasn’t until 1696 that San Ignacio Mini was actually built; they first had to find the ideal location, away from marauding bandits.
Once a very impressive, richly ornamented mission that used to house around three thousand people, much of San Ignacio Mini was destroyed in 1817 by Luso-Brazilian forces, after which the site was abandoned and fell into disrepair.
Despite this, the ruins are among the best preserved in the country, and seeing the remains of the church, monastery, and plaza up close and personal is an awe-inspiring experience. The Gurani baroque architecture is particularly delightful. Located in the San Ignacio valley around sixty kilometers from Posadas, the mission ruins are well worth a visit; history lovers, in particular, will love wandering around the site.
2. Ibera Wetlands [SEE MAP]

Located in the northeast of the country just south of Paraguay, the Ibera Wetlands cover a huge swathe of land. Nature lovers and outdoor enthusiasts will revel in exploring all that it has to offer. Encompassing rivers, lakes, swamps, and wetlands, the watery world is fascinating to hike, horseback ride, or kayak through.
Wildlife abounds, and residing within the confines of the park are everything from anacondas and armadillos to howler monkeys and wolves, with over 350 species of bird also present. Stretching as far as the eye can see, the Ibera Wetlands will leave you feeling free and unencumbered, at one with all the fantastic nature around you.
1. Iguazu Falls [SEE MAP]
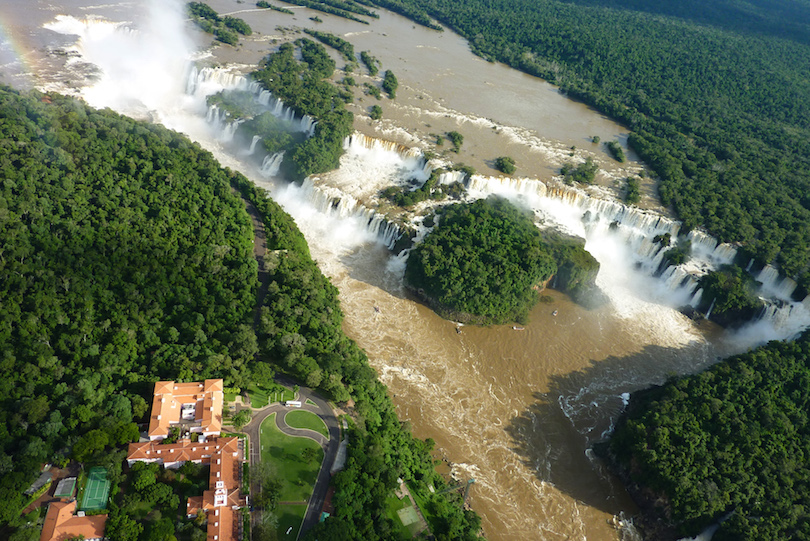

One of the natural wonders of the world, Iguazu Falls is the largest waterfall system on the planet and is a must-see when in Mesopotamia. Nothing can truly prepare you for what you are about to witness, as the sheer size and scale of the falls needs to be seen to believed.
Straddling the Argentine-Brazilian border, the waterfall stretches for almost three kilometers. Everywhere you go, you are greeted with the tumultuous roar of gallons of water pouring down rock faces and plunging over drops. While about 80 percent of the falls lie in Argentina, the other 20 percent are still well worth checking out, and visitors can easily cross over the border to see the Brazilian side.
Gazing upon the falls from below is an unforgettable experience as you feel the spray of the water cover you from head to toe. A boat trip on the river is a must if you want to get as close as possible. With verdant rainforest surrounding it and clumps of plants hanging to the sides of the waterfalls, Iguazu Falls really is the highlight of any trip to the region.
Share this post:

12 Best Places to Visit in Argentina
How to Spend 3 Weeks in Argentina: DIY Itinerary

15 Best Things to do in Bariloche, Argentina

23 Top Tourist Attractions in Buenos Aires

6 Best Day trips from Buenos Aires

23 Top Tourist Attractions in Argentina

Where to Stay in Buenos Aires: 8 Best Neighborhoods

10 Top Things to Do in Ushuaia, Argentina

15 Best Cities to Visit in Argentina

14 Best Places to Visit in Cuyo, Argentina
Reader interactions, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

When is Easter? How its date is determined each year and why some celebrate.
F or millions of Christians worldwide, Easter is an important day for members of the faith. The holiday celebrates the resurrection of Jesus Christ, which occurs after the 40-day period known as Lent .
Church services, reflection and prayer are some ways that people observe the holiday. Others enjoy a more secular celebration of Easter filled with bunnies, baskets and colorful eggs.
Each year, Easter falls on a different day. So, when does it occur in 2024? Here's some information on how Easter came to be and why it's celebrated.
Start the day smarter. Get all the news you need in your inbox each morning.
When is Easter?
This year, Easter will be Sunday, March 31, 2024.
Why is Easter so early in 2024?
Easter's date changes depending on the year. The holiday is one of several "moveable feasts" in the liturgical year, the History Channel reports. Others include Ash Wednesday and Palm Sunday .
Easter is observed on the first Sunday following the Paschal full moon , which is the first full moon on or after the spring equinox . Since Western Christianity uses the Gregorian calendar, Easter typically falls on a Sunday between March 22 and April 25, according to the History Channel.
In Eastern Orthodox Christianity, the date of Easter also varies. The branch follows the Julian calendar, meaning orthodox Easter falls between April 4 and May 8, the History Channel reports. This year, it will take place on Sunday, May 5, 2024.
History of Easter
Easter commemorates the resurrection of Jesus Christ. It is the last day of the Holy Week, consisting of several days — each with its significance. These include:
- Palm Sunday: commemorating when Jesus entered Jerusalem
- Holy Thursday: commemorating the Last Supper and washing of feet
- Good Friday: commemorating Jesus' crucifixion and death
- Easter Sunday: commemorating the resurrection of Jesus
Of the four canonical Gospels, each has a version of the Passion, or final period of Jesus' life. While the Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke are similar in their accounts, the Gospel of John varies.
According to the text, Judas Iscariot betrayed Jesus who was arrested by Roman authorities after saying he was the Son of God. Jesus predicted this would happen at the Last Supper.
Jesus was then put on trial and later sentenced to death by Pontius Pilate, the Roman prefect of Judea. The events of the stations of the cross followed, ultimately leading to the crucifixion of Jesus.
Jesus was then buried in a tomb. And on the final day (Easter Sunday), Jesus' tomb was found empty. The Bible proclaims he rose from the dead.
Why do we celebrate Easter?
Easter is celebrated to remember the sacrifices of Jesus Christ. As a result, many Christians will go to Church services and pray in observance. Other aspects of the holiday, such as Easter eggs, also derive from Christian traditions.
The colorful Easter eggs you might decorate with your family are actually symbols of new life and rebirth. Ancient Christian communities in Mesopotamia would stain eggs red to represent the blood of Christ, which was shed at the crucifixion, NBC Chicago reports . The eggs also signify the empty tomb of Jesus.
As for the Easter bunny, its origins are not necessarily rooted in Christianity. The exact origins of the anthropomorphic rabbit are unclear. However, since ancient times, the hare has been said to represent rebirth , according to Smithsonian Magazine.
German Lutherans used an Easter hare for the Easter season, similar to Santa Claus' role during Christmas. Known as "Osterhase" or "Oschter Haws ," the rabbit would gift baskets of toys and candy to good children the night before Easter, the History Channel reports.
Just Curious for more? We've got you covered
USA TODAY is exploring the questions you and others ask every day. From " When is the first day of spring? " to " How to protect plants from frost? " to " Can cats eat chocolate? ", we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Head to our Just Curious section to see what else we can answer.
This article originally appeared on USA TODAY: When is Easter? How its date is determined each year and why some celebrate.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
See also. Mesopotamia is in the Middle East, mainly in present-day Iraq, with parts of it in Syria and Turkey and influence extending into what are now Iran and the Persian Gulf states. The name translates literally as 'between rivers', and an alternate term is the Land of the Two Rivers. The rivers involved are the Tigris and Euphrates; both ...
Welcome to our journey through Mesopotamia, Iraq's cradle of civilization! At our core, we're driven by a passionate mission: to unveil the timeless allure of Mesopotamia and beckon travelers to discover its ancient wonders. Our goal is to open doors to the birthplace of human civilization, inviting adventurers, history enthusiasts, and culture ...
Plan an Unforgettable Experiencein Iraq today. We can help you fit your experience within your allotted budget. Discover the birthplace of civilization with Mesopotamia Tourism. Explore ancient ruins, historic sites, and cultural treasures with our expert guides. Book your trip to Mesopotamia today and experience the magic of this legendary land.
Mesopotamia was a region of southwest Asia between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers from which human civilization and world‑changing inventions emerged.
Join Mesopotamia Tourism on our multi-day tours and explore the rich cultural heritage of Mesopotamia. Visit ancient ruins, experience traditional customs, and immerse yourself in the beauty of this legendary land. Our expert guides will provide a unique perspective on Mesopotamia's history and culture, making this an unforgettable journey.
Mesopotamia —"the land between two rivers"—gave birth to many of the world's first great cities. The splendid city of Babylon, located between the waters of the Euphrates and the Tigris some 97 kilometers (60 miles) south of Baghdad, was one of them. Unlike the many towns that fell and disappeared, Babylon was resilient, rising from ...
Discover the history and culture of the ancient Mesopotamian civilizations, one of the oldest and most influential regions in the world. Learn about their achievements, inventions, religions, and conflicts with this interactive article from Khan Academy, a free online learning platform.
Discover Ancient Mesopotamia with Silk Road Moments. Our English-speaking guide will explain the fascinating history of this area as you experience Mesopotamia for yourself. See the birthplace of civilization!
Mesopotamia is the ancient Greek name (meaning "the land between two rivers", the Tigris and Euphrates) for the region corresponding to modern-day Iraq and parts of Iran, Syria, and Turkey. It is considered the "cradle of civilization " for the many inventions and innovations which first appeared there c. 10,000 BCE through the 7th ...
History of Mesopotamia, the region in southwestern Asia where the world's earliest civilization developed. Centered between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the region in ancient times was home to several civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians, and Persians.
Get to know more about the 9 greatest cities in Ancient Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization.
The idea of Mesopotamia has intoxicated the West for centuries. Alastair Sooke takes a look at a civilisation where much of modern culture took form.
Discover the best tourist attractions & things to do in Mesopotamia. From iconic landmarks to hidden tourist spots, find all the top places to go and explore in Mesopotamia with expert travel tips from Trip.com.
Mesopotamia is thought to be one of the places where early civilization developed. It is a historic region of West Asia within the Tigris-Euphrates river system. In fact, the word Mesopotamia means "between rivers" in Greek. Home to the ancient civilizations of Sumer, Assyria, and Babylonia these peoples are credited with influencing mathematics and astronomy. Use these classroom resources to ...
Ur ( / ʊər / OOR) [ a] was an important Sumerian city-state in ancient Mesopotamia, located at the site of modern Tell el-Muqayyar[ b] ( Arabic: تَلّ ٱلْمُقَيَّر, lit. ' mound of bitumen ') in Dhi Qar Governorate, southern Iraq.
Sumer ( / ˈsuːmər /) is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq ), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. Like nearby Elam, it is one of the cradles of civilization, along with Egypt, the Indus Valley, the Erligang culture of the Yellow River valley, Caral ...
A Sumerian ziggurat was a towering, stepped structures built in ancient Mesopotamia over 4,000 years ago. Now you can see one in exceptional detail.
Mesopotamian religion, the beliefs and practices of the Sumerians and Akkadians, and their successors, the Babylonians and Assyrians, who inhabited ancient Mesopotamia (now in Iraq) in the millennia before the Christian era. Read here to learn more about Mesopotamian religion.
We can provide the highest level of luxury or, if budget is an issue, we will make the magic of Mesopotamia come alive at a price you can afford. We attend to every detail from the moment you set foot at the airport until the moment you depart. If you want the best — travel with the best!
Can You Visit Babylon Today? Although many local tourists now enjoy frequent visits to this historical place, few tourists have made the journey since it reopened to the world in 2009. Even tho more and more western travel companies now arrange trips here. However, since being made a UNESCO-heritage site in 2019, this is sure to change.
The Hanging Gardens. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were built by the magnificent King Nebuchadnezzar, so that his lovely queen would have a private, terraced garden to enjoy. They gardens are about 400 feet wide, 400 feet long, and over 80 feet high! There are paths, steps, fountains, and lots of beautiful flowers and plants located in the ...
In Ancient Babylonia, soups and stews reigned supreme. Food historians are now using taste-tests to recover their forgotten flavours.
Things to do in Mesopotamia: Discover the top tourist attractions in Mesopotamia for your next trip. From must-see landmarks to off-the-beaten-path gems. Plan your visit to with our handy list and make the most of your time in this exciting destination.
, Mesopotamia is a wonderful part of Argentina to explore, as it is home to some of the most astounding scenery imaginable. Dominated and, in many ways, defined by the Parana and Uruguay rivers that run through it, the region was actually named after Mesopotamia in modern-day Iraq, by Spanish settlers who saw similarities between the two landscapes.
Developed by the ancient Sumerians of Mesopotamia, an ancient region centered in modern-day Iraq and the surrounding regions, more than 5,000 years ago, cuneiform is not a language in itself.
For many Christians, Easter is an important day within their faith. Each year, Easter falls on a different day. So, when does it occur in 2024?