

6 a's of tourism
The "6 a's of tourism" is a concept that outlines key factors contributing to the success of a tourist destination. these factors are often considered crucial for attracting and retaining tourists. the 6 a's of tourism are:.
Attractions: These are the primary reasons people visit a destination, including natural wonders, historical sites, cultural events, entertainment venues, and unique experiences.
Accessibility: Easy access to a destination through well-developed transportation infrastructure, such as airports, highways, and public transit, is essential for attracting tourists.
Accommodation: A range of lodging options, from hotels and resorts to vacation rentals and campsites, is necessary to accommodate the diverse needs and preferences of travelers.
Activities: Providing a variety of activities and experiences for tourists, such as outdoor adventures, cultural immersion, shopping, dining, and entertainment, enhances the overall visitor experience.
Amenities: Amenities like restaurants, shopping centers, medical facilities, and other services contribute to the comfort and convenience of tourists during their stay.
Advocacy: Local support and promotion of tourism, including efforts by governments, businesses, and communities to preserve and promote the destination, play a vital role in sustaining tourism growth.
These 6 A's work together to create an appealing and well-rounded tourist destination, making it attractive to a broader range of visitors and contributing to the destination's economic and cultural vitality.
Subscribe newsletter
Barcelona, Spain.

What Are the 6 A’s of Tourism?
By Robert Palmer
Are you planning a trip anytime soon? If yes, then you must be aware of the 6 A’s of tourism.
These are the essential components that determine the quality of your travel experience. In this article, we will discuss each of these A’s in detail and understand how they impact your overall vacation.
1. Accessibility
Accessibility refers to how easily a destination can be reached.
It includes factors like transportation options, distance, and cost. If the location is too far away or too expensive to get to, it may not be an ideal vacation spot for you. However, if it is easily accessible with multiple transportation options and affordable prices, it can make for a great travel experience.
2. Accommodation
The second A stands for accommodation.
This includes the quality and availability of lodging options at the destination. Whether you prefer luxurious hotels or budget-friendly hostels, having a comfortable place to stay is crucial for an enjoyable trip.
3. Attractions
The third A represents the attractions at the destination.
This includes natural wonders like beaches or mountains, as well as cultural landmarks like museums or historical sites. The more diverse and unique these attractions are, the better your vacation experience will be.
4. Activities
The fourth A stands for activities available at the destination. These may include adventure sports like bungee jumping or skiing, recreational activities like spas or golf courses, or simply local experiences like food tours or cultural events.
5. Amenities
Amenities refer to facilities that make your stay more comfortable and convenient. This may include things like restaurants, shopping centers, public restrooms, or access to Wi-Fi.
6. Affordability
The final A is affordability.
This doesn’t necessarily mean the cheapest option, but rather good value for money. If a destination offers high-quality experiences and amenities at a reasonable price, it’s more likely to attract travelers.
These 6 A’s of tourism play a crucial role in determining the success of your vacation. When planning your next trip, make sure to consider all these factors and choose a destination that meets your needs and expectations.
10 Related Question Answers Found
What are the 6 a of tourism, what are the 6 as of tourism, what are the 6 categories of tourism, what are the 6 types of tourism, how does tourism work in civ 6, what are the duties and responsibilities of tourism, what are the geographical components of tourism, what is the difference between travel industry and tourism industry, what is the main definition of tourism, what are the five classifications of tourism, backpacking - budget travel - business travel - cruise ship - vacation - tourism - resort - cruise - road trip - destination wedding - tourist destination - best places, london - madrid - paris - prague - dubai - barcelona - rome.
© 2024 LuxuryTraveldiva

Components of tourism: Structure of the tourism industry
The travel and tourism industry is argued by many as being the largest industry in the world. It is, therefore, no surprise that the structure of the tourism industry is quite complex, involving many components of tourism.
With many different types of tourism and types of businesses operating within the tourism industry, from private companies to charities and NGOs, the structure of the tourism industry is made up of many different segments and components.
In this article I will provide you with an overview of the structure of the tourism industry, outlining the types of organisations and stakeholders in tourism that are involved.
Structure of the tourism industry
Components of tourism, international organisations, national tourist boards, regional tourist boards, tourist information centres, travel by air, travel by road, travel by train, travel by water, hotels chains, hostels and budget accommodation, holiday parks and campsites, accommodation innovations, world travel market, football world cup, glastonbury, holi festival, day of the dead, natural attractions, built attractions, tour operators, travel agents, ancillary services, components of tourism | structure of the tourism industry, structure of the tourism industry | components of tourism: further reading.
The importance of tourism is demonstrated when you can see how big the industry is!
The structure of the industry is made up of several components of tourism and involves many different stakeholders. These components are all interrelated in one way of another. The components of tourism make up the entire tourism system.

There are several integral components of tourism. Without these components, the tourism industry would struggle to function. I have explained what this means below, but before you read on, take a look at this short video that I made (and if you like what you see, don’t forget to subscribe to my YouTube channel)!
This was demonstrated, for example, during the Coronavirus pandemic, which halted air travel around the world. Travel services are a vital component of tourism and without these services being operational, the tourism industry struggled to survive!
There are six major components of tourism, each with their own sub-components. These are: tourist boards, travel services, accommodation services, conferences and events, attractions and tourism services.

Below, I will explain what each of the components offer to the tourism industry and provide some relevant examples.
Components of tourism: Tourist boards
A tourist board is an essential component of tourism and an integral part of the structure of the tourism industry.
A tourism board is responsible for the promotion of tourism in a particular area. This could be a city, a region, a country or a group of countries.
A tourism board is usually Government funded and is usually a public travel and tourism organisation (although this is not always the case).
A tourism board is also often referred to as a Destination Marketing Organisation (DMO).
Most tourist boards focus on promoting tourism in a particular area, city or country. There are, however, some organisations which aim to promote tourism across more than one country.
Whilst these organisation often have many functions other than tourism, they will also play a role in the promotion of tourism in particular parts of the world. This could include the European Union , the ASEAN network or organisations such as the United Nations.
A national tourist board is a national organisation whose aim is to promote tourism across the country.
There are usually several management bodies that are involved with a national tourist board. They are essential stakeholders who determine many aspects of tourism in the country, such as budgets, taxation and regulations.
Said management bodies include the parliament, the tourist board, an auditing committee and the Prime Minister, President or Head of State.
The national tourist board is funded from tourist taxes, membership fees, Government funding and other sources.
Examples of national tourist boards (often most commonly referred to by their ‘campaign title’ as opposed to the Government title) include Visit Britain , Incredible India and Amazing Thailand .
A regional tourist board is a tourist board that focusses on a particular region of a country. They are often a sub-division of a country’s national tourist board.
Regional tourism boards are often funded and operated in the same way as national tourist boards.
Examples of successful regional tourism boards include: Visit Cornwall in the UK, Kerala Tourism in India, Visite Montreal in Canada and Cape Town Tourism in South Africa.
A tourist information centre is the place where tourists can go for advice and help with regards to all matters related to tourism in the area.
In the tourist information centre (TIC) you will find staff who are knowledgeable about the local area. There will often be a range of printed and digital information for you, including leaflets, maps, coupons and guidebooks. Sometimes there will be virtual tourism facilities.
Tourist information centres have been an important component of tourism throughout the history of travel and tourism , however, they are coming under increasing pressure as a result of information that is available online. This has resulted in fewer people visiting TICs in person.
Most major tourist areas will have a tourist information centre. These are usually centrally located.
Tourist information centres are funded by the local Government.
Other posts that you might be interested in: – What is tourism? A definition of tourism – The history of tourism – Stakeholders in tourism – Dark tourism explained – What is ABTA and how does it work? – The economic impacts of tourism
Components of tourism:Transport services
The relationship between transport and tourism is strong.
According to the most commonly accepted definitions of tourism, a person must travel away from their home environment for at least one night in order to be a tourist (although I would argue that this definition needs updating given that it doesn’t account for novel forms of tourism such as a staycation or virtual tourism ).
Based on this fact, therefore, transport is an integral component of tourism. Without transport, people cannot reach their intended destination.
There are a range of different transport types. The most common and popular methods of transport that make up the structure of the tourism industry, however, are: air, road, train and water .

Travel by air has grown exponentially in the past few decades. With the introduction of low cost airlines and deregulation, the competitive market has been a tourist’s paradise.
New routes opening up has introduced tourists to areas that they may never have been able to reach before and low prices have resulted in more of us taking more trips abroad using air travel as our means of transportation.
Travel by air is an essential component of tourism and this was demonstrated during the Coronavirus epidemic. During this time most air traffic was halted, which had a devastating impact of the tourism industry world-wide.
Travel by road is also a core component of tourism, particularly for domestic tourism .
Travel by road is more popular in some countries than others. This largely depends on accessibility options (i.e. what is accessible by road), distances required and road conditions.
In destinations where travel by road is popular, there are often many car hire or rental companies.
Travel by train is very popular in destinations that have good rail networks in infrastructure.
In some parts of the world, such as China and Japan, there are world-class high-speed railways that can be more efficient than flying.
In other parts of the world, the rail journey is part of the tourism experience. A good example of this is the Siberian Railway.
In Europe you can buy an affordable interrail pass , which allows you to travel throughout Europe using the rail system.

Travel by water is also an important component of tourism.
The structure of the tourism industry includes cruises, ferries and leisure boats, among other types of travel by water.
Travel by water can vary considerably in price and can include anything from a round the world cruise to a short long tail ride in Thailand .
Components of tourism: Accommodation services
Accommodation services make up an important part of the structure of the tourism industry.
Whilst accommodation services were traditionally focussed mainly around the hotel industry, nowadays accommodation options for tourists are much more varied. This adds an additional layer of complexity to the structure of the tourism industry.
There are many hotel chains that operate throughout the tourism industry and that are a key component of tourism.
Multinational corporations have expanded throughout the tourism industry with key players being hotel chains such as Marriott, Radisson, Hilton, Travel Lodge and Holiday Inn.
However, hotel chains such as these have come under increased scrutiny as a result of the economic leakage in tourism that they cause.
Hostels and budget accommodation options are popular with budget travellers and backpackers.
There are a range of hostels found throughout the world. These are particularly popular in destinations where accommodation is expensive, such as London, New York and Singapore.
The Youth Hostel Association (YHA) and Hostelling International are popular hostel providers that are found across the UK and overseas.
Billy Butlin changed the face of the British holiday market with the introduction of his seaside holiday parks back in 1936.
Since this time, other similar chains have expanded throughout the UK and the rest of the world.
Camping is also an important component of tourism. There are camp sites situated throughout the world ranging from safari camps to glamping (glamorous camping).
Homestays have become an increasingly prominent component of tourism.
Whilst bed and breakfast accommodation has been around for a very long time, nowadays there are many more options that are grounded on the concept of a homestay.
The sharing economy has seen the growth and introduction of many types of accommodations into the travel and tourism sector that did not exist before.
The most popular of these is Airbnb, where people rent out a room or an entire property to tourists. You can read more about how Airbnb works here .
In recent years consumers have been demanding new and unusual experiences more than ever. In response to this, we have seen many accommodation innovations emerge throughout the world.
From staying in an ice hotel in Finland, to sleeping in a hammock in Borneo to a night in a haunted castle in Wales, there are many different types of accommodation options that can make your holiday a little bit more exciting!
Components of tourism: Conferences and events
Conferences and events make up a significant part of the structure of the tourism industry.
Conferences, which often come under business tourism , come in all shapes and sizes around the world.
From a small academic gathering to a large-scale summit involving national leaders from around the world, conferences are an important component of tourism.
Likewise, the event sector is also a significant part of the tourism industry.
There are millions of events that take place around the world each year that vary in size and function. Many of these form an integral part of the tourism industry.
Examples of major conferences and events around the world
There are many major conferences and events that take place around the world every year. Here are a few of my favourites:
The World Travel Market (WTM) is held in London each November. This is a large event that is held at the Excel venue.
WTM provides travel industry experts with the opportunity to showcase their work, learn more about the industry and to network.
ITB is the world’s leading international travel trade show. It is held in Berlin each year.
Similar to the WTM, this large-scale event enables industry professionals to network and undertake continuous professional development.
The vast majority of people are familiar with the Football World Cup.
The Football World Cup is held every four years in a different location.
The Football World Cup attracts millions of tourists from all over the world. The event also acts as a stimuli for tourism as the nation will often use the opportunity of hosting the event as a chance to market tourism in the area to those who are tuning in from their TVs from around the world.
Sports tourism , which includes events such as the Football World Cup, contributes significantly to the overall tourism industry.
Glastonbury is a popular British music festival. It takes place each summer in Somerset.
Glastonbury is a five-day festival of contemporary performing arts. In addition to music, the festival hosts dance, comedy, theatre, circus, cabaret, and other arts to entertain visitors.
Glastonbury attracts many domestic tourists as well as international tourists.
San Fermin is a festival that is held in Pamplona, Spain each July.
San Fermin, also known as the ‘Running of the Bulls’ is a historically-rooted festival that lasts five days. It involves dancing, eating and drinking, games and the famous bull races and fights.
San Fermin has been subject to a lot of controversy in recent years, with many people protesting that it is a cruel form of animal tourism .

Holi Festival is known as the ‘festival of spring’, the ‘festival of colours’ or the ‘festival of love’.
Holi Festival is celebrated in India each year during the month of March.
Holi Festival is famous for the way in which coloured paints are used and often thrown onto people’s faces and clothes.
This is a Hindu festival that signifies the victory of good over evil.
The Day of the Dead festival, locally referred to as ‘Dia de los Muertos’, is a festival that is celebrated in November each year in Mexico.
This day is a celebration of the deceased, whereby it is believed that the alive and the dead are reunited. On this day many people will create offerings for the deceased.
Many people choose to dress up as skeletons and in halloween-type outfits and they celebrate with food, drink and music.
Components of tourism: Attractions
An essential component of the tourism industry are the tourist attractions.
There are a multitude of different tourist attractions around the world.
Some are built, some are natural. Some are paid, some are free. Some are famous, others are not. Some are large and some are small.
Natural attractions are just as it says on the tin – natural. In other words, they are attractions that have not been made by man.
Natural attractions are found all over the world and vary in size and scope. There is even a definitive list of the seven natural wonders of the world .
I have visited many natural attractions around the world, here is a list of some of my favourites:
- Drakansburg Mountains, South Africa
- Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania
- Mount Toubkal, Morocco
- Sahara Desert, Morocco
- Red Sea, Egypt
- Dead Sea, Israel
- Sierra Nevada, Spain
- Chicken Island, Thailand
- Niagara Falls, USA
- Rocky Mountains, Canada
- Pammukale Thermal Pools, Turkey
- Iceland (the island is filled with wonderful natural attractions!)
- Amazon Rainforest , Ecuador
- Cenotes, Mexico
- Iguazu Falls, Brazil
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia
- Ha Long Bay, Vietnam
- Waterways of Kerela, India
- Mount Hallasan, South Korea
Built attractions also make up an important part of the structure of the tourism industry.
There are many built attractions throughout the world. Some attractions are built for the purpose of tourism, such as theme parks or museums. Other attractions are built for other purposes but then become tourist attractions, such as the Empire State Building or the Sydney Opera House.
I have visited many built attractions throughout the world. Here are some of my favourites:
- Robin Island, South Africa
- The Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
- La Sagrada Familia, Spain
- The Eiffel Tower, France
- The United States Capitol Building, USA
- Statue of Liberty, New York
- Petronas Towers, Malaysia
- Marina Sands Bay Hotel, Singapore
- Angkor Wat, Cambodia
- Taj Mahal, India
- Sydney Harbour Bridge, Australia
- Houses of Parliament, UK
- Sheikh Zayed Mosque, UAE
Components of tourism: Tourism services
Tourism services are an essential component of tourism. Without many tourism services, the tourism industry would fail to adequately function.
Below I will explain the three major tourism services that make up the structure of the tourism industry.
A tour operator is the individual or organisation who puts together a trip.
Typically, a tour operator would package together essential elements including accommodation, transport and transfer. They would then sell this package to the tourists.
However, tour operators are becoming fewer in recent years. Consumers are now far more Internet savvy and are more capable of researching the individual elements of their holiday and booking this independently. This is known as dynamic packaging .
Traditionally, a travel agent would sell the product that the tour operator has produced i.e. the package holiday.
While travel agents have and continue to sell individual holiday components, they have historically been most commonly used by tourists who wish to book a package holiday.
In today’s society, there is far less scope for travel agents than there used to be. A few years ago it would be easy to finish school and to get a job in a travel agent selling holidays. Now, however, people are more likely to set up their own travel agent business online or to be employed by an online retailer.
Many high street stores have now closed as there is little demand these days for holidays to be booked in this way. Instead, many people are selling holidays and travel services via their blogs or websites.
The travel agent does still exist, but he has changed the way he looks.
Ancillary services are another core component of tourism.
Ancillary basically means ‘extra’ or ‘additional’. An ancillary service in the context of tourism, therefore, is any product or service that is additional to the core elements of accommodation, transport and transfer.
Here are some examples of ancillary products:
- Attraction tickets
- Meal tickets
- Extra luggage
- Currency exchange
- Airport parking
As you can see, the tourism industry is large and complex, but understanding the different components of tourism isn’t too difficult.
All of the components of tourism are interconnected in one way or another and many rely on one another to be successful.
Want to learn more about the structure of tourism? I have listed some recommended texts below.
- An Introduction to Tourism : a comprehensive and authoritative introduction to all facets of tourism including: the history of tourism; factors influencing the tourism industry; tourism in developing countries; sustainable tourism; forecasting future trends.
- The Business of Tourism Management : an introduction to key aspects of tourism, and to the practice of managing a tourism business.
- Tourism Management: An Introduction : gives its reader a strong understanding of the dimensions of tourism, the industries of which it is comprised, the issues that affect its success, and the management of its impact on destination economies, environments and communities.

By: Bastian Herre and Veronika Samborska
Tourism has massively increased in recent decades. Aviation has opened up travel from domestic to international. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of international visits had more than doubled since 2000.
Tourism can be important for both the travelers and the people in the countries they visit.
For visitors, traveling can increase their understanding of and appreciation for people in other countries and their cultures.
And in many countries, many people rely on tourism for their income. In some, it is one of the largest industries.
But tourism also has externalities: it contributes to global carbon emissions and can encroach on local environments and cultures.
On this page, you can find data and visualizations on the history and current state of tourism across the world.
Interactive Charts on Tourism
Cite this work.
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
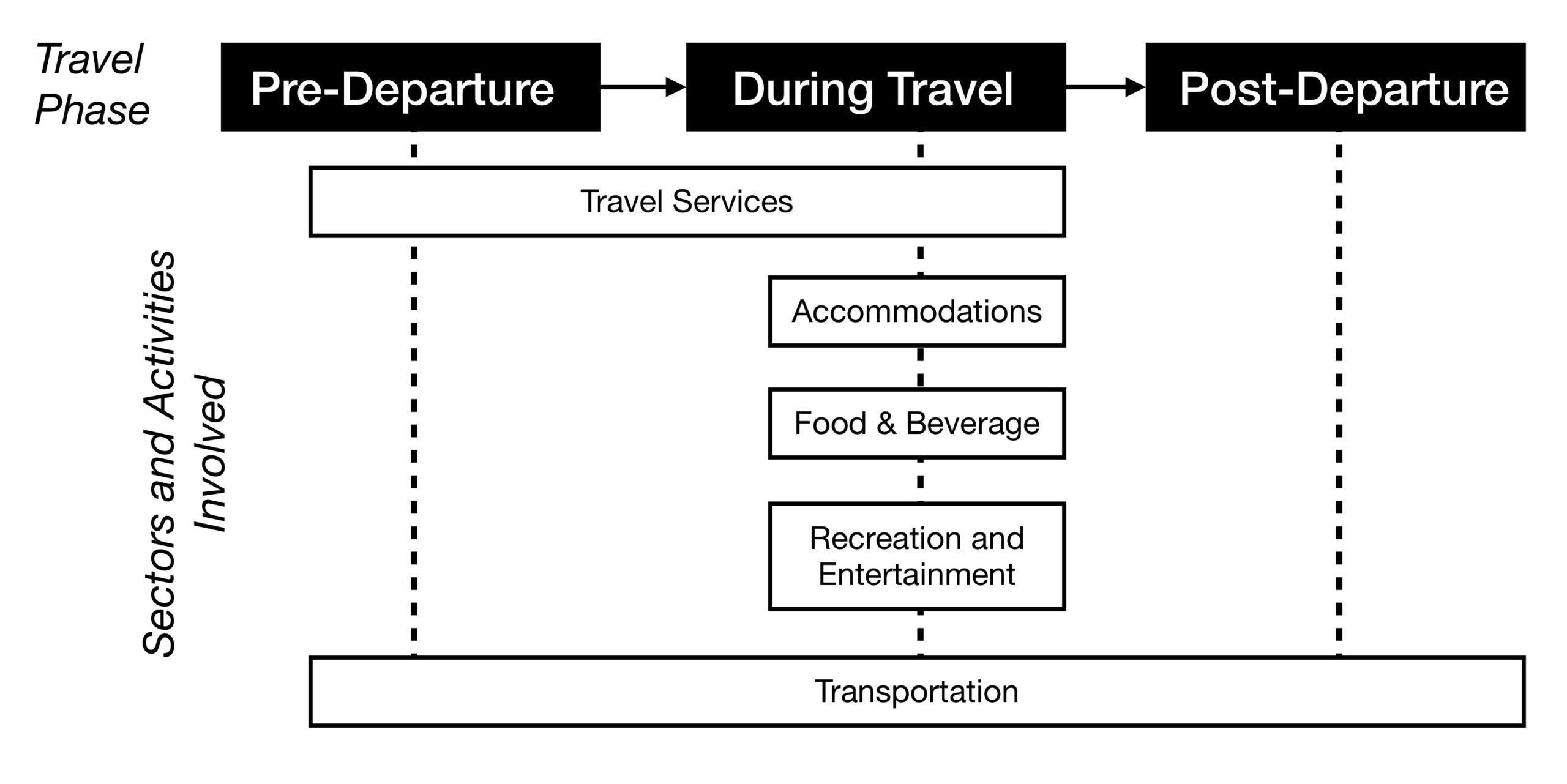
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]
Media Attributions
- Front Desk by Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence .
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Tourism – Definition, Types & Forms, History & Importance of Tourism
Tourism is one of the world’s fastest-growing industries and a major foreign exchange and employment generation for many countries. It is one of the most remarkable economic and social phenomena.
The word ‘tour’ is derived from the Latin word tornus, meaning ‘a tool for making a circle.’ Tourism may be defined as the movement of people from their usual place of residence to another place ( with the intention to return) for a minimum period of twenty-four hours to a maximum of six months for the sole purpose of leisure and pleasure.
According to WTO (1993), ” Tourism encompasses the activities of persons traveling and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes.”
The Rome conference on tourism in 1963 defined tourism as ‘ a visit to a country other than one’s own or where one usually resides and works. This definition, however, did not take into account domestic tourism, which has become a vital money-spinner and job generator for the hospitality industry.
The UNWTO defines tourists as ‘ people who travel to and stay in place outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes not related to the exercise of an activity remunerated from within the place visited.
According to the Tourism Society of Britain ,” tourism is the temporary short-period movement of people to destination outside the places where they usually live, work; and activities during their stay at these destinations.” This definition includes the movement of people for all purposes.
The development of technology and transportation infrastructure, such as jumbos jets, low-cost airlines, and more accessible airports, have made tourism affordable and convenient. There have been changes in lifestyle – for example, now retiree-age people sustain tourism around the year. The sale of tourism products on the internet, besides the aggressive marketing of the tour operators and travel agencies , has also contributed to the growth of tourism.
27 September is celebrated as world tourism every year. This date was chosen as on that day in 1970, the Statutes of UNWTO were adopted. The purpose of this day is to raise awareness of the role of tourism within the international community.
History of Travel and Tourism
Inbound tourism, outbound tourism, domestic tourism, forms of tourism, classification of tourism, nature of tourism, importance of tourism, economic impacts, social impacts, cultural impacts, environmental impact, industries related to tourism, tourism products.
Travel is as old as mankind on earth. At the beginning of his existence, man roamed about the planet’s surface in search of food, shelter, security, and better habitat. However, with time, such movements were transformed into wanderlust.
About five thousand years ago, climate changes, dwindling food and shelter conditions hostile invaders made the people leave their homes to seek refuge elsewhere like the Aryans left their homes in Central Asia due to climate changes. Perhaps, this leads to the development of commerce, trade, and industry.
Religion, education, and cultural movement began during the Hindu and Chinese civilizations. Christian missionaries, Buddhist monks, and others traveled far and wide carrying religious messages and returned with fantastic images and opinions about alien people.
For centuries movement of people continued to grow due to the efficiency of transport and the assistance and safety with which the people could travel. By the end of the 15th century, Italy had become Europe’s intellectual and cultural center. It represented the classical heritage both for the intelligentsia and the aristocracy.
During the 16th century, travel came to be considered an essential part of the education of every young Englishman. Travel thus became a means of self-development and education in its broadest sense. The educational travel was known as the ‘ Grand Tour .’
The industrial revolution brought about significant changes in the pattern and structure of British society. Thus, the economy of Britain was greatly responsible for the beginning of modern tourism. It also created a large and prosperous middle class. Because of remarkable improvement in transportation systems in the latter half of the 18th century and the first quarter of the 19th century, an increasing number of people began to travel for pleasure.
Travel was inspired initially by the need for survival (food, shelter, and security), the desire to expand trade, and the quest to conquer. As the transportation system improved, the curiosity for transforming the vast and virgin world into a close neighborhood created a new industry, i.e., Travel and Tourism .
However, the developments of rails, roads, steamships, automobiles, and airplanes helped to spread technology across the globe. Earlier travel was a privilege only for wealthy people, but with the industrial revolution, the scenario altogether changed. Transportation, as well as accommodation, became affordable to middle and working-class citizens.
Essentially, with the development of jet travel, communication, new technology, tourism, and travel became the world’s largest and fastest-growing industry.
Travel and tourism have recently emerged as a dominant economic force on the global scene, accounting for more than 12% of total world trade and growing at 8 percent annually.
Types of Tourism
Tourism has two types and many forms based on the purpose of visit and alternative forms of tourism. Tourism can be categorized as international and domestic tourism .
Tourism has two types and various forms. Based on the movement of people, tourism is categorized into two kinds. These are the following:
International Tourism
When people visit a foreign country, it is referred to as International Tourism . To travel to a foreign country, one needs a valid passport, visa, health documents, foreign exchange, etc.
International tourism is divided into two types; Inbound Tourism & Outbound Tourism.
This refers to tourists of outside origin entering a particular country. Traveling outside their host/native country to another country is called inbound tourism for the country where they are traveling. For example, when a tourist of Indian origin travels to Japan, it is Inbound tourism for Japan because foreign tourists come to Japan.
This refers to tourists traveling from the country of their origin to another country. When tourists travel to a foreign region, it is outbound tourism for their own country because they are going outside their country. For example, when a tourist from India travels to Japan, it is outbound tourism for India and Inbound tourism for Japan.
The tourism activity of the people within their own country is known as domestic tourism . Traveling within the same country is easier because it does not require formal travel documents and tedious formalities like compulsory health checks and foreign exchange. A traveler generally does not face many language problems or currency exchange issues in domestic tourism.
Tourism has various forms based on the purpose of the visit and alternative forms. These are further divided into many types according to their nature. Forms of tourism are the following:
Some most basic forms of tourism are the following:
- Adventure Tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Beach Tourism
- Cultural Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Medical Tourism
- Religious Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Sex Tourism
- Space Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
- Virtual Tourism
- War Tourism
- Wildlife Tourism
Tourism can be classified into six distinct categories according to the purpose of travel. These are the following:
1) Recreational : Recreational or leisure tourism takes a person away from the humdrum of everyday life. In this case, people spend their leisure time in the hills, sea beaches, etc.
2) Cultural tourism satisfies cultural and intellectual curiosity and involves visits to ancient monuments, places of historical or religious importance, etc.
3) Sports/Adventure : Trips taken by people with a view to playing golf, skiing and hiking, fall within this category.
4) Health : Under this category, people travel for medical, treatment or visit places where there are curative possibilities, for example, hot springs, spa yoga, etc.
5) Convention Tourism : It is becoming an increasingly important component of travel. People travel within a country or overseas to attend conventions relating to their business, profession, or interest.
6) Incentive Tourism : Holiday trips are offered as incentives by major companies to dealers and salesmen who achieve high targets in sales. This is a new and expanding phenomenon in tourism, These are in lieu of cash incentives or gifts, Today incentive tourism is a 3 billion dollar business in the USA alone.
Tourism as a socio-economic phenomenon comprises the activities and experiences of tourists and visitors away from their home environment and are serviced by the travel and tourism industry and host destination. The sum total of this activity experience and services can be seen as a tourism product.
The tourism system can be described in terms of supply and demand. Tourism planning should strive for a balance between demands and supply. This requires an understanding not only of market characteristics and trends but also of the planning process to meet the market needs.
Often tourists from core generating markets are identified as the demand side; the supply side includes all facilities, programs, attractions, and land uses designed and managed for the visitors. These supply-side factors may be under the control of private enterprises, non-profit organizations, and the government. New and innovative forms of partnerships are also evolving to ensure the sustainable development and management of tourism-related resources.
The supply and demand side can be seen to be linked by flows of resources such as capital, labor, goods, and tourist expenditures into the destination, and flows of marketing, promotion, tourist artifacts, and experiences from the destination back into the tourist generating region.
In addition, some tourist expenditures may leak back into the visitors generating areas through repatriation of profits of foreign tourism investors and payment for improved goods and services provided to tourists at the destination. Transportation provides an important linkage both to and from the destination.
For planning purposes, the major components that comprise the supply side are:
- Various modes of transportation and other tourism-related infrastructure.
- Tourist information.
- Marketing and promotion.
- The community of communities within the visitor’s destination area.
- The political and institutional frameworks for enabling tourism.
The tourism system is both dynamic and complex due to many factors linked to it and because of the existence of many sectors contributing to its success. These factors and sectors are linked to the provision of the tourist experience and the generation of tourism revenue and markets .
The dynamic nature of the tourism system makes it imperative to scan the external and internal environment of the destinations on a regular basis so as to make changes when necessary to ensure a healthy and viable tourism industry.
Thus, it is now an accepted fact that tourism development can no longer work in isolation of the environment and the local communities, nor can it ignore the social and cultural consequences of tourism.
Tourism and hospitality , which are inextricably linked to each other, are among the major revenue-earning enterprises in the world. They happen to be among the top employers too. There has been an upmarket trend in tourism over the last few decades as travel has become quite common. People travel for business, vacation, pleasure, adventure, or even medical treatments.
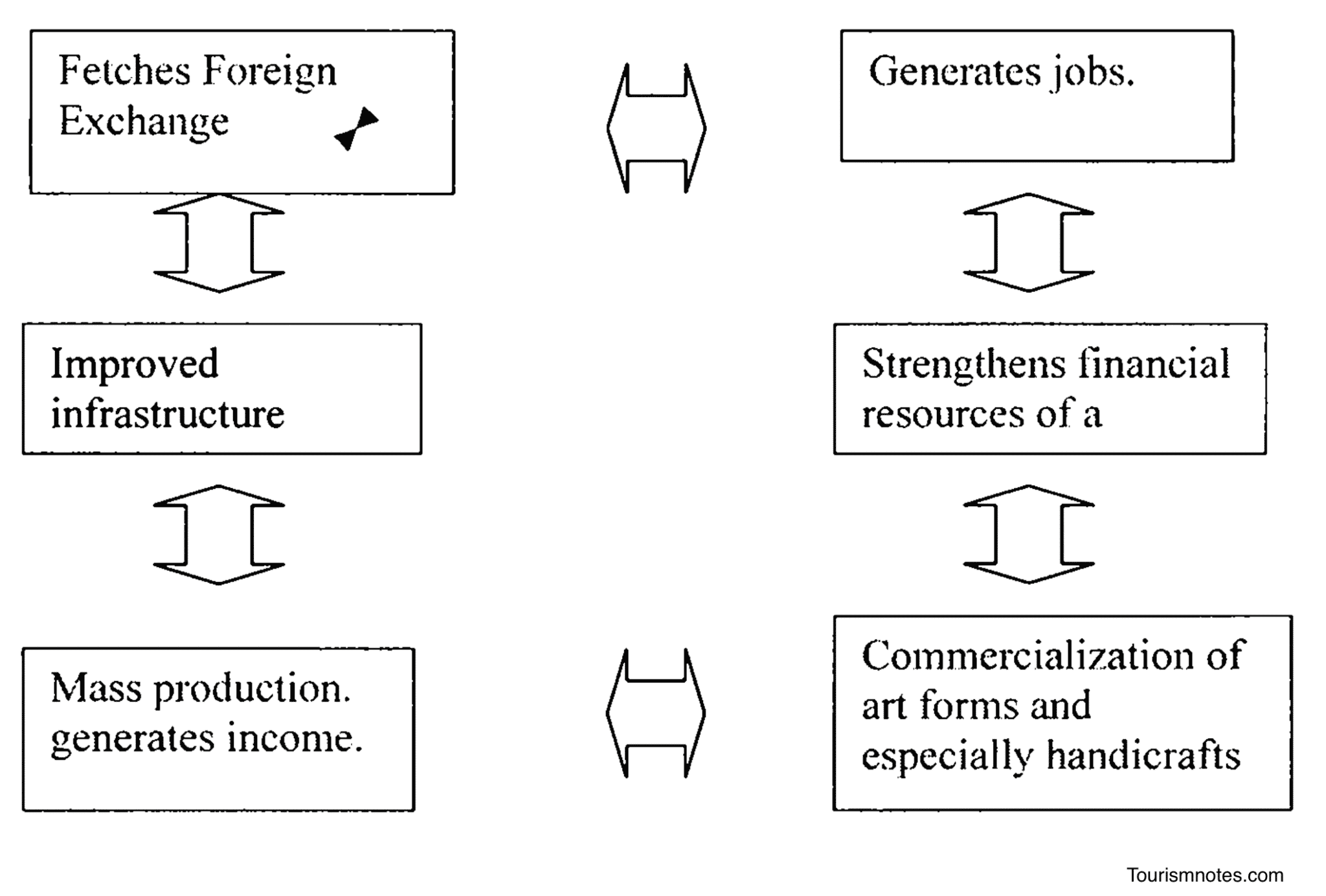
Tourism constitutes an important industry today. It has opened up new vistas for the play of economic emancipation. It provides a very potent contribution by strengthening and developing the financial resources of a country. Moreover, it is a process in which mutual material and mental benefits occur. Furthermore,
- Tourism fetches foreign exchange in the form of invisible exports, which results in the manifold progress of the nation.
- Tourism generates jobs. These employments are the main contribution of tourism to generating national income. But one should remember that employment in the tourism industry is often seasonal.
- Tourism often leads to the commercialization of art forms and especially handicrafts. Art items with cultural or religious meaning are sought by tourists as souvenirs. As more and more tourists visit a destination, souvenir production has increased, often leading to mass production. This production also generates income.
With several business-related activities associated with tourism, the industry has a tremendous potential to generate employment as well as earn foreign exchange. Many countries, such as Mauritius, Malaysia, Singapore, Fiji, and the Caribbean, whose economies are primarily driven by tourism. Tourism can contribute to the economic growth of a country in the followings ways:
Employment Generation
It creates a large number of jobs among direct services providers (such as hotels , restaurants, travel agencies , tour operators , guide and tour escorts, etc.) and among indirect services providers (such as suppliers to the hotels and restaurants, supplementary accommodation, etc.)
Infrastructure Development
Tourism spurs infrastructure development. In order to become an important commercial or pleasure destination, any location would require all the necessary infrastructure, like good connectivity via rail, road, and air transport , adequate accommodation, restaurants, a well-developed telecommunication network, and, medical facilities, among others.
Foreign Exchange
The people who travel to other countries spend a large amount of money on accommodation, transportation, sightseeing, shopping, etc. Thus, an inbound tourist is an important source of foreign exchange for any country.
The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) predict in 1997 that the twenty-first-century economy would be dominated by three industries: telecommunications, information technology, and tourism. The travel and tourism industry has grown by 500 percent in the last 25 years.
Now withstanding this bright outlook and prospects, the tourism and hospitality industries are very vulnerable to the fluctuations of national economies and happenings in the world, especially terrorist attacks that have at times dealt severe blows to business.
In recent years, there have been a few setbacks in tourism, such as the terrorist siege of the Taj and Oberoi in Mumbai, India (26 November 2008); the attack on the World Trade Centre in the United States of America (11 September 2001); bombing in a hotel on the Indonesian island of Bali (12 October 2002); tsunami in Southeast Asia and South Asia on 26 December 2004, in which thousands of the lives where lost and consequently tourism was hit. Nonetheless, the sector is now getting back to business.
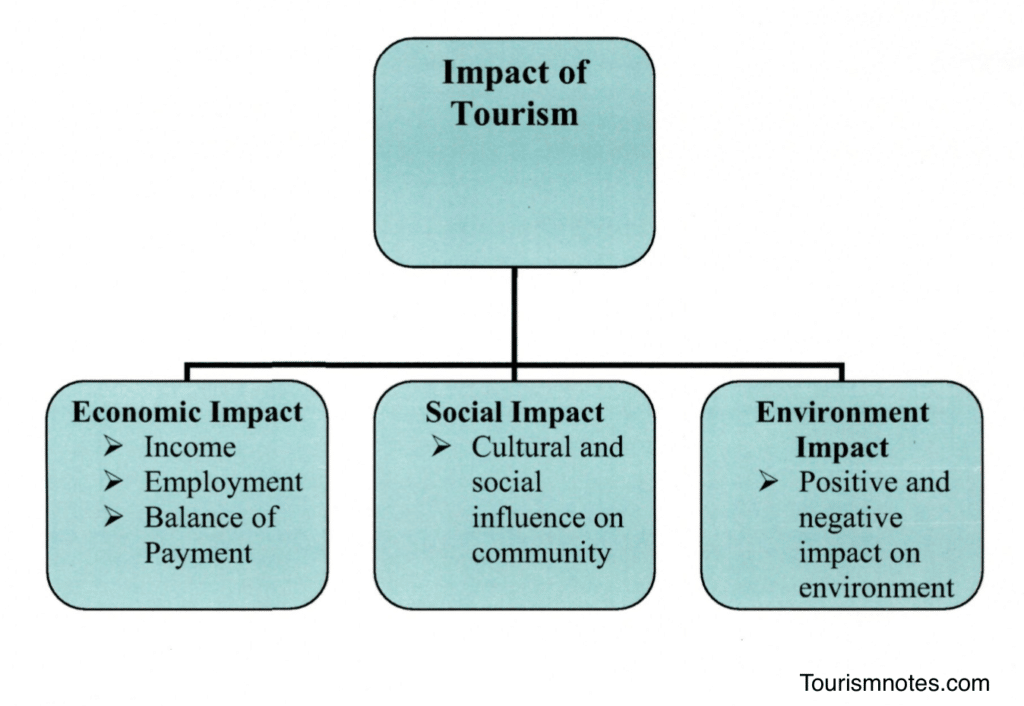
Impacts of Tourism
Tourism is a multi-dimensional activity. The scope of tourism activities is so wide and varied that it cannot be restricted to any particular field of activity. Tourism has ramifications in almost all sectors and is influenced by the performance of each of these sectors directly or indirectly. Tourism in any country can be an apt reflection of the nation’s economic and social endowment apart from its natural wealth.
Tourism has vast potential to bring about changes in the country’s economic, environmental, societal, and cultural edifice. Tourism has two basics: the supply of facilities and the demand for participation. The twin market forces of supply and demand interact to produce tourism patterns. These patterns are associated with economic, social, cultural, environmental, and ecological impacts.
Establishing or developing a tourism industry involves expenditure, gains, costs, and benefits. If these impacts are considered from the outset of planning, strengths and opportunities can be maximized while weaknesses and threats can be minimized.
Each destination will be different in terms of tourism characteristics . The cost and benefits of tourism will vary in each destination and can change over time, depending on tourism and other activities in a destination’s local and regional context.
Tourism activities impact the economy of the country as well as the local economy of the destination.
Economics Benefits
- Tourism generates local employment, directly in the tourism sector and in the support and resource management sectors.
- Tourism stimulates profitable domestic industries, hotels and other lodging facilities, restaurants and food services, transportation systems, handicrafts, and guide services.
- Tourism generates foreign exchange for the country and injects capital and new money into the local economy.
- Tourism helps to diversify the local economy.
- Improved tourism infrastructure.
- Increase tax revenues from tourism.
Economic Costs
- Higher demand created by tourism activity may increase the price of land, housing, and a range of commodities necessary for daily life.
- Demands for health services provision and police service increase during the tourist seasons at the expense of the local tax base.
Tourism also affects the society of the destination in good as well as bad ways. It benefits and costs the local communities.
Social Benefits
- The quality of a community can be enhanced by economic diversification through tourism.
- Recreational and cultural facilities created for tourism can be used by local communities as well as domestic/international visitors.
- Public space may be developed and enhanced through tourism activity.
- Tourism Enhances the local community’s esteem and provides an opportunity for greater understanding and communication among people of diverse backgrounds.
Social Costs
- Rapid tourism growth can result in the inability of local amenities and institutions to meet service demands.
- Without proper planning and management, litter, vandalism, and crime often accompany tourism development.
- Tourism can bring overcrowding and traffic congestion.
- Visitors bring with them material wealth and apparent freedom. The youths of the host community are particularly susceptible to the economic expectations these tourists bring which can result in complete disruption of traditional community ways of life.
- The community structure may change, e.g. community bonds, demographics, and institutions.
- The authenticity of the social and cultural environment can be changed to meet tourism demands.
Tourism activities also affect the culture of the host country. There are many positive and negative cultural impacts of tourism.
Cultural Benefits
- Tourism can enhance local cultural awareness.
- Tourism can generate revenue to help pay for the preservation of archaeological sites, historic buildings, and districts.
- Despite criticism about the alteration of cultures to unacceptable levels, the sharing of cultural knowledge and experience can be beneficial for hosts and guests of tourism destinations and can result in the revival of local traditions and crafts.
Cultural Costs
- Youth in the community begin to emulate the speech and attire of tourists.
- Historic sites can be damaged through tourism development and pressures.
- There can be long-term damage to cultural traditions and the erosion of cultural values, resulting in cultural change beyond a level acceptable to the host destination.
Tourism impacts the environment in positive as well as negative ways. These impacts are following below.
Environmental Benefits
- Parks and nature preserves may be created and ecological preservation supported as a necessity for nature-based tourism.
- Improved waste management can be achieved.
- Increased awareness and concern for the environment can result from nature-based tourism activities and development.
Environmental Costs
- A negative change in the physical integrity of the area.
- Rapid development, over-development, and overcrowding can forever change the physical environment and ecosystems of an area.
- Degradation of parks and preserves.
Over the years, tourism has become a popular global activity. Depending upon the nature and purpose of their travel, tourists, need and demand certain facilities and services. This has given rise to a wide range of commercial activities that have acquired industry proportions. Thus travel and tourism nowadays represent a broad range of related industries.
Hotels are a commercial establishment that provides accommodation, meals, and other guest services. In the travel and tourism industry, the hotel industry plays a very significant role, as all tourists need a place to stay at their destinations, and require many more services and facilities to suit their specific needs and tastes.

Restaurants
Restaurants are retail establishments that serve prepared food and beverages to customers. In the travel and tourism industry, restaurants and other food and beverage outlets are very important as tourists like to experiment with the local cuisines of the places they are visiting.
Retail and Shopping
The retail industry is very important as tourists shop for their day-to-day necessities as well as look for mementos and souvenirs. In recent years, some cities in the world have been promoted as shopping destinations to attract people with a penchant for shopping by offering various products, such as garments, electronic goods, jewelry, and antiques. New York, Paris, London, and Milan in Italy are famous as fashion havens of the world.
Transportation
It is the movement of people and goods from one place to another. A well-developed transport industry, as well as infrastructure, is integral to the success of any travel and tourism enterprise.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a retailing business that sells travel-related products and services, particularly package tours, to customers on the behalf of suppliers such as airlines, car rentals, cruise liners, hotels, railways, and sightseeing.
Travel agencies play a very important role as they plan out the itinerary of their clients and make the necessary arrangements for their travel, stay, and sightseeing, besides facilitating their passport, visa, etc.
Tour Operators
A tour operator assembles the various elements of a tour. It typically combines tour and travel components to create a holiday. Tour operators play an important role in the travel and tourism industry.
Tourist Destinations
A tourist attraction is a place of interest for tourists, typically for its inherent or exhibited cultural value, historical significance, nature or building beauty or amusement opportunities. These are the basic fundamentals of the tourism industry.
Cultural Industries
Cultural or creative industries are responsible for the creation, production, and distribution of goods and services that are cultural in nature and usually protected by intellectual property rights. As tourists like to visit places of cultural significance and soak in the culture of the area, the cultural industry is very important to travel and tourism.
Leisure, Recreation, and Sport
Leisure or free time is a period of time spent out of work and essential domestic activity. Recreation or fun is spending time in a manner designed for therapeutic refreshment of the body or mind. While leisure is more like a form of entertainment or rest, recreation requires active participation in a refreshing and diverting manner.
As people in the world’s wealthier regions lead an increasingly sedentary lifestyle, the need for recreation has increased. These play a significant role in the travel and tourism sector.
A tourism/tourist product can be defined as the sum of the physical and psychological satisfaction it provides to tourists, during their ‘traveling and sojourn’ en route at the destinations.
Since the travel and tourism industry is an agglomeration of too many sectors that promote travel-related services. These sectors are referred to as travel vendors and their services and goods are called ‘travel products’. A tourism product includes five main components such as physical plant, services, hospitality, freedom of choice, and a sense of involvement.
Thus, whatever the natural and man-made resources and services brought about the consumption of tourists are called tourism products .
Charecterstatics Of Tourism Products
By now, you must have understood what a tourism product is. Now let us look at some of its characteristics:-
1) Intangible : Tourism is an intangible product means tourism is such a kind of product that can not be touched or seen and there is no transfer of ownership, But the facilities are available for a specified time and for a specified use. For e.g. a room in the hotel is available for a specified time.
2) Psychological : The main motive to purchase a tourism products is to satisfy the psychological need after using the product, by getting an experience while interacting with a new environment. And experiences also motivate others to purchase that product.
3) Highly Perishable : Tourism product is highly perishable in nature means one can not store the product for a long time. Production and consumption take place while a tourist is available. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not purchase it.
A travel agent or tour operator who sells a tourism product cannot store it. Production can only take place if the customer is actually present. And once consumption begins, it cannot be stopped, interrupted, or modified. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not visit a particular place, the opportunity at that time is lost. It is due to tourism reason that heavy discount is offered by hotels and transport-generating organizations during the offseason.
4) Composite Product : Tourist product is a combination of different products. It has not a single entity in itself. In the experience of a visit to a particular place, various service providers contribute like transportation The tourist product cannot be provided by a single enterprise, unlike a manufactured product.
The tourist product covers the complete experience of a visit to a particular place. And many providers contribute to the tourism experience. For instance, the airline supplies seats, a hotel provides rooms and restaurants, travel agents make bookings for stay and sightseeing, etc.
5) Unstable Demand : Tourism demand is influenced by seasonal, economic political, and other factors. There are certain times of the year that see greater demand than others. At these times there is a greater strain on services like hotel bookings, employment, the transport system, etc.
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
Global tourism industry - statistics & facts
What are the leading global tourism destinations, digitalization of the global tourism industry, how important is sustainable tourism, key insights.
Detailed statistics
Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP worldwide 2019-2034
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
Global leisure travel spend 2019-2023
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2023
Travel and tourism employment worldwide 2019-2034
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
Further recommended statistics
- Basic Statistic Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP worldwide 2019-2034
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2034
- Basic Statistic Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2023
- Basic Statistic Global leisure travel spend 2019-2023
- Premium Statistic Global business travel spending 2001-2024
- Premium Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
- Basic Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism employment worldwide 2019-2034
Total contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) worldwide in 2019 and 2023, with a forecast for 2024 and 2034 (in trillion U.S. dollars)
Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2034
Share of travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP worldwide in 2019 and 2023, with a forecast for 2024 and 2034
Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in leading travel markets worldwide in 2019 and 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leisure tourism spending worldwide from 2019 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Global business travel spending 2001-2024
Expenditure of business tourists worldwide from 2001 to 2024 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 1950 to 2023 (in millions)
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 2005 to 2023, by region (in millions)
Number of travel and tourism jobs worldwide from 2019 to 2023, with a forecast for 2024 and 2034 (in millions)
- Premium Statistic Global hotel and resort industry market size worldwide 2022-2023
- Premium Statistic Most valuable hotel brands worldwide 2023, by brand value
- Basic Statistic Leading hotel companies worldwide 2023, by number of properties
- Premium Statistic Number of hotels in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
- Premium Statistic Number of hotel rooms in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
- Premium Statistic Countries with the most hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide 2024
Global hotel and resort industry market size worldwide 2022-2023
Market size of the hotel and resort industry worldwide in 2022 and 2023 (in trillion U.S. dollars)
Most valuable hotel brands worldwide 2023, by brand value
Leading hotel brands based on brand value worldwide in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leading hotel companies worldwide 2023, by number of properties
Leading hotel companies worldwide as of June 2023, by number of properties
Number of hotels in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
Number of hotels in the construction pipeline worldwide as of the first quarter of 2024
Number of hotel rooms in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
Number of hotel rooms in the construction pipeline worldwide as of the first quarter of 2024
Countries with the most hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide 2024
Countries with the highest number of hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide as of the first quarter of 2024
- Premium Statistic Airports with the most international air passenger traffic worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Market value of selected airlines worldwide 2024
- Premium Statistic Global passenger rail users forecast 2017-2028
- Premium Statistic Daily ridership of bus rapid transit systems worldwide by region 2023
- Premium Statistic Number of users of car rentals worldwide 2020-2029
- Premium Statistic Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023
- Premium Statistic Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Airports with the most international air passenger traffic worldwide 2023
Leading airports for international air passenger traffic in 2023 (in million international passengers)
Market value of selected airlines worldwide 2024
Market value of selected airlines worldwide as of May 2024 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Global passenger rail users forecast 2017-2028
Worldwide number of passenger rail users from 2017 to 2023, with a forecast through 2028 (in billion users)
Daily ridership of bus rapid transit systems worldwide by region 2023
Number of daily passengers using bus rapid transit (BRT) systems as of April 2023, by region
Number of users of car rentals worldwide 2020-2029
Number of users of car rentals worldwide from 2020 to 2029 (in millions)
Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023
Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023 (in million)
Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Transport-related emissions from international tourist arrivals worldwide in 2005 and 2016, with a forecast for 2030, by mode of transport (in million metric tons of carbon dioxide)
Attractions
- Premium Statistic Most visited museums worldwide 2019-2023
- Basic Statistic Most visited amusement and theme parks worldwide 2023
- Basic Statistic Monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list 2023, by type
- Basic Statistic Selected countries with the most Michelin-starred restaurants worldwide 2024
Most visited museums worldwide 2019-2023
Museums with the highest attendance worldwide from 2019 to 2023 (in millions)
Most visited amusement and theme parks worldwide 2023
Leading amusement and theme parks worldwide 2023, by attendance (in millions)
Monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list 2023, by type
Number of monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list as of September 2023, by type
Selected countries with the most Michelin-starred restaurants worldwide 2024
Number of Michelin-starred restaurants in selected countries and territories worldwide as of August 2024
Online travel market
- Premium Statistic Online travel market size worldwide 2017-2028
- Premium Statistic Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading OTAs worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Number of aggregated downloads of leading online travel agency apps worldwide 2023
- Basic Statistic Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Estimated EV/Revenue ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
- Premium Statistic Estimated EV/EBITDA ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Online travel market size worldwide 2017-2028
Online travel market size worldwide from 2017 to 2023, with a forecast until 2028 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading OTAs worldwide 2023
Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading online travel agencies (OTAs) worldwide in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Number of aggregated downloads of leading online travel agency apps worldwide 2023
Number of aggregated downloads of selected leading online travel agency apps worldwide in 2023 (in millions)
Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide 2023
Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide as of September 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Estimated EV/Revenue ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Estimated enterprise value to revenue (EV/Revenue) ratio in the online travel market worldwide as of April 2024, by segment
Estimated EV/EBITDA ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Estimated enterprise value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) ratio in the online travel market worldwide as of April 2024, by segment
Selected trends
- Premium Statistic Share of tech investments by travel and mobility corporations worldwide 2018-2024
- Premium Statistic Use of mobile devices to plan travel with an AI chatbot worldwide 2023, by country
- Premium Statistic Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2024
- Premium Statistic Reasons for traveling sustainably worldwide 2024
- Premium Statistic Airbnb revenue worldwide 2017-2023
- Premium Statistic Airbnb nights and experiences booked worldwide 2017-2023
Share of tech investments by travel and mobility corporations worldwide 2018-2024
Distribution of tech investment deals by travel and mobility corporations worldwide between 2018 and 2024, by area of investment
Use of mobile devices to plan travel with an AI chatbot worldwide 2023, by country
Share of travelers who used a mobile device to plan or research travel with an AI chatbot worldwide as of October 2023, by country
Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2024
Share of travelers that believe sustainable travel is important worldwide in 2024
Reasons for traveling sustainably worldwide 2024
Factors that inspire eco-friendly travel worldwide as of February 2024
Airbnb revenue worldwide 2017-2023
Revenue of Airbnb worldwide from 2017 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Airbnb nights and experiences booked worldwide 2017-2023
Nights and experiences booked with Airbnb from 2017 to 2023 (in millions)
- Premium Statistic Travel and tourism revenue worldwide 2020-2029, by segment
- Premium Statistic Distribution of sales channels in the travel and tourism market worldwide 2019-2029
- Premium Statistic Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
- Premium Statistic Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Travel and tourism revenue worldwide 2020-2029, by segment
Revenue of the travel and tourism market worldwide from 2020 to 2029, by segment (in billion U.S. dollars)
Distribution of sales channels in the travel and tourism market worldwide 2019-2029
Revenue share of sales channels of the travel and tourism market worldwide from 2019 to 2029
Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide from 2020 to 2022, with a forecast until 2025, by region
Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide from 2020 to 2022, with a forecast until 2025, by region

- Brand Resources
- Economic Impact
- WTTC Research Hub
- Insights & Publications
- Knowledge Partners
- Data Enquiries
- Sustainability Hub
- Hotel Sustainability Basics
- Nature Positive Travel & Tourism
- Social Impact
- Community Conscious Travel
- Security & Travel Facilitation
- Women Empowerment
- Destination Spotlight - SLO CAL
- SafeTravels: Global Protocols & Stamp
- SafeTravels Stamp Application
- Governments
- Global Summit
- Upcoming Events
- Event Photography
- Hosting a Summit
- Event Enquiries
- Our Members
- Our Associates Community
- Membership Benefits
- Enquire About Membership
- Sponsors & Partners
- Press Releases
- Press Enquiries
- Consumer Travel Blog
- ONEin330Million Campaign
- Reunite Campaign

Economic Impact Research
- In 2023, the Travel & Tourism sector contributed 9.1% to the global GDP; an increase of 23.2% from 2022 and only 4.1% below the 2019 level.
- In 2023, there were 27 million new jobs, representing a 9.1% increase compared to 2022, and only 1.4% below the 2019 level.
- Domestic visitor spending rose by 18.1% in 2023, surpassing the 2019 level.
- International visitor spending registered a 33.1% jump in 2023 but remained 14.4% below the 2019 total.
Click here for links to the different economy/country and regional reports
Why conduct research?
From the outset, our Members realised that hard economic facts were needed to help governments and policymakers truly understand the potential of Travel & Tourism. Measuring the size and growth of Travel & Tourism and its contribution to society, therefore, plays a vital part in underpinning WTTC’s work.
What research does WTTC carry out?
Each year, WTTC and Oxford Economics produce reports covering the economic contribution of our sector in 185 countries, for 26 economic and geographic regions, and for more than 70 cities. We also benchmark Travel & Tourism against other economic sectors and analyse the impact of government policies affecting the sector such as jobs and visa facilitation.
Visit our Research Hub via the button below to find all our Economic Impact Reports, as well as other reports on Travel and Tourism.

Now boarding: Faces, places, and trends shaping tourism in 2024
After falling by 75 percent in 2020, travel is on its way to a full recovery by the end of 2024. Domestic travel is expected to grow 3 percent annually and reach 19 billion lodging nights per year by 2030. 1 Unless otherwise noted, the source for all data and projections is Oxford Economics. Over the same time frame, international travel should likewise ramp up to its historical average of nine billion nights. Spending on travel is expected to follow a similar trajectory, with an estimated $8.6 trillion in traveler outlays in 2024, representing roughly 9 percent of this year’s global GDP.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Caroline Tufft , Margaux Constantin , Matteo Pacca , and Ryan Mann , with Ivan Gladstone and Jasperina de Vries, representing views from McKinsey’s Travel, Logistics & Infrastructure Practice.
There’s no doubt people still love to travel and will continue to seek new experiences in new places. But where will travelers come from, and where will they go? We developed a snapshot of current traveler flows, along with estimates for growth through 2030. For the purposes of this report, we have divided the world into four regions—the Americas, Asia, Europe, and the Middle East and Africa.
Our analysis identifies three major themes for industry stakeholders to consider:
- The bulk of travel spending is close to home. Stakeholders should ensure they capture the full potential of domestic travel before shifting their focus to international travelers. And they should start with international travelers who visit nearby countries—as intraregional trips represent the largest travel segment after domestic trips.
- Source markets are shifting. Although established source markets continue to anchor global travel, Eastern Europe, India, and Southeast Asia are all becoming fast-growing sources of outbound tourism.
- The destinations of the future may not be the ones you imagine. Alongside enduring favorites, places that weren’t on many tourists’ maps are finding clever ways to lure international travelers and establish themselves as desirable destinations.
The bulk of travel spending is close to home
International travel might feel more glamorous, but tourism players should not forget that domestic travel still represents the bulk of the market, accounting for 75 percent of global travel spending (Exhibit 1). Domestic travel recovered from the COVID-19 pandemic faster than international travel, as is typical coming out of downturns. And although there has been a recent boom in “revenge travel,” with travelers prioritizing international trips that were delayed by the pandemic, a return to prepandemic norms, in which domestic travel represents 70 percent of spending, is expected by 2030.
The United States is the world’s largest domestic travel market at $1 trillion in annual spending. Sixty-eight percent of all trips that start in the United States remain within its borders. Domestic demand has softened slightly, as American travelers return abroad. 2 Dawit Habtemariam, “Domestic U.S. tourism growth levels off as Americans head overseas,” Skift, August 18, 2023. But tourism players with the right offerings are still thriving: five national parks broke attendance records in 2023 (including Joshua Tree National Park, which capitalized on growing interest from stargazers indulging in “dark sky” tourism 3 Scott McConkey, “5 national parks set attendance records in 2023, and the reasons may surprise you,” Wealth of Geeks, April 16, 2024. ).
China’s $744 billion domestic travel market is currently the world’s second largest. Chinese travelers spent the pandemic learning to appreciate the diversity of experiences on offer within their own country. Even as borders open back up, Chinese travelers are staying close to home. And domestic destinations are benefiting: for example, Changchun (home to the Changchun Ice and Snow Festival) realized 160 percent year-on-year growth in visitors in 2023. 4 Shi Xiaoji, “Why don’t Chinese people like to travel abroad anymore? The global tourism industry has lost 900 billion yuan. What is the situation?,” NetEase, February 12, 2024. In 2024, domestic travel during Lunar New Year exceeded prepandemic levels by 19 percent.
China’s domestic travel market is expected to grow 12 percent annually and overtake the United States’ to become the world’s largest by 2030. Hotel construction reflects this expectation: 30 percent of the global hotel construction pipeline is currently concentrated in China. The pipeline is heavily skewed toward luxury properties, with more than twice as many luxury hotels under construction in China as in the United States.
India, currently the world’s sixth-largest domestic travel market by spending, is another thriving area for domestic travel. With the subcontinent’s growing middle class powering travel spending growth of roughly 9 percent per year, India’s domestic market could overtake Japan’s and Mexico’s to become the world’s fourth largest by 2030. Domestic air passenger traffic in India is projected to double by 2030, 5 Murali Krishnan, “Can India’s airports cope with rapid passenger growth?,” Deutsche Welle, February 7, 2024. boosted in part by a state-subsidized initiative that aims to connect underserved domestic airports. 6 “India is seeing a massive aviation boom,” Economist , November 23, 2023.
When travelers do go abroad, they often stay close to home (Exhibit 2).
Europe and Asia, in particular, demonstrate strong and growing intraregional travel markets.
Recognizing this general trend, stakeholders have been funneling investment toward regional tourism destinations. An Emirati wealth fund, for instance, has announced its intent to invest roughly $35 billion into established hospitality properties and development opportunities in Egypt. 7 Michael Gunn and Mirette Magdy, “UAE’s $35 billion Egypt deal marks Gulf powers’ buying spree,” Bloomberg, April 27, 2024.
Europe has long played host to a high share of intraregional travel. Seventy percent of its travelers’ international trips stay within the region. Europe’s most popular destinations for intraregional travelers are perennial warm-weather favorites—Spain (18 percent), Italy (10 percent), and France (8 percent)—with limited change to these preferences expected between now and 2030.
Despite longer travel distances between Asian countries, Asia’s intraregional travel market is beginning to resemble Europe’s. Intraregional travel currently accounts for about 60 percent of international trips in Asia—a share expected to climb to 64 percent by 2030. As in Europe in past decades, Asian intraregional travel is benefiting from diminishing visa barriers and the development of a low-cost, regional flight network.
Thailand is projected to enjoy continued, growing popularity with Asian travelers. Thailand waived visa requirements for Chinese tourists in 2023 and plans to do the same for Indian tourists starting in 2024. It has aggressively targeted the fast-growing Indian traveler segment, launching more than 50 marketing campaigns directed at Indians over the past decade. The investment may be paying off: Bangkok recently overtook Dubai as the most popular city destination for Indian tourists. 8 “Bangkok overtakes Dubai as top destination for Indians post visa relaxation, reveals Agoda,” PR Newswire, January 18, 2024.
A McKinsey ConsumerWise survey on consumer sentiment, conducted in February 2024, suggests that Chinese travelers are also exhibiting high interest in international travel, with 36 percent of survey respondents indicating that they intend to spend more on international travel in the next three months. 9 Daniel Zipser, “ China brief: Consumers are spending again (outside of China) ,” McKinsey, April 8, 2024. Much of this interest is directed toward regional destinations such as Southeast Asia and Japan, with interest in travel to Europe down from previous years. 10 Guang Chen, Zi Chen, Steve Saxon, and Jackey Yu, “ Outlook for China tourism 2023: Light at the end of the tunnel ,” McKinsey, May 9, 2023.
Given travelers’ preference for proximity, how can tourism stakeholders further capitalize on domestic and intraregional travel demand? Here are a few strategies:
- Craft offerings that encourage domestic tourists to rediscover local gems. Destinations, hotels, and transportation providers can encourage domestic tourists to integrate lesser-known cultural landmarks into their trips to visit friends and relatives. In France, the upscale hotel chain Relais & Châteaux markets historic properties that lie far from classic tourist sights—such as Château Saint-Jean in rural Auvergne—as a welcome escape from the bustle of Paris. In Mexico, the Pueblos Mágicos program has successfully boosted domestic tourist visits to a set of “magical towns” that showcase Mexican heritage.
- Fold one-off domestic destinations into fuller itineraries. Route 66 in the United States is a classic road trip pathway, which spurs visits to attractions all along the highway’s length. Tourism stakeholders can collaborate to create similar types of domestic itineraries around the world. For instance, Mexico has expanded on its Pueblos Mágicos concept by branding coordinated visits to multiple villages as “magical routes.” In France, local tourism boards and vineyards have collaborated to promote bucket list “wine routes” around the country.
- Make crossing borders into neighboring countries seamless. Removing logistical barriers to travel can nudge tourists to upgrade a one-off trip to a single attraction into a bucket list journey across multiple, less-trodden destinations. In Africa, for example, Ethiopian Airlines is facilitating cross-border travel to major regional tourist sites through improved air connectivity. In Asia, Thailand has announced its intent to create a joint visa easing travel among Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Source markets are shifting
The United States, Germany, the United Kingdom, China, and France remain the world’s five largest sources of travelers, in that order. These countries collectively accounted for 38 percent of international travel spending in 2023 and are expected to remain the top five source markets through 2030. But interest in travel is blossoming in other parts of the world—causing a shift in the balance of outbound travel flows (Exhibit 3).
North Americans’ travel spending is projected to hold steady at roughly 3 percent annual growth. US consumers voice growing concerns about inflation, and the most cost-constrained traveler segments are reducing travel, which is affecting ultra-low-cost airlines and budget hotels. Most travelers, however, plan to continue traveling: McKinsey research suggests that American consumers rank international and domestic travel as their highest-priority areas for discretionary spending. Instead of canceling their trips, these consumers are adapting their behavior by traveling during off-peak periods or booking travel further in advance. Travel spending by Europeans paints a slightly rosier picture, with roughly 5 percent projected annual growth. Meanwhile, the projected 12 percent annual growth in Chinese travelers’ spending should anchor substantial increases in travel spending across Northeast Asia.
Alongside these enduring traveler segments, new groups of travelers are emerging. Eastern Europe, India, and Southeast Asia are still comparatively small source markets, but they are developing fast-growing pools of first-time tourists (Exhibit 4).
India’s breakneck GDP growth of 6 percent year over year is bolstering a new generation of travelers, 11 Benjamin Laker, “India will grow to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2027,” Forbes , February 23, 2024. resulting in a projected annual growth in travel spending of 9 percent between now and 2030. Indian air carriers and lodging companies are making substantial investments to meet projected demand. Budget airline IndiGo placed the largest aircraft order in commercial aviation history in 2023, when it pledged to buy 500 Airbus A320 planes 12 Anna Cooban, “Biggest plane deal in history: Airbus clinches massive order from India’s IndiGo,” CNN, June 19, 2023. ; that same week, Air India nearly equaled IndiGo’s order size with purchase agreements for 250 Airbus and 220 Boeing jets. IndiGo later added an order for 30 additional Airbus A350 planes, well suited to serving both domestic and international routes. 13 “Airbus confirms IndiGo's A350 aircraft order,” Economic Times , May 6, 2024. The Indian Hotels Company Limited is ramping up its hotel pipeline, aiming to open two new hotels per month in the near future. International players are not sitting on the sidelines: seven hotel chains are launching new brands in India in 2024, 14 Peden Doma Bhutia, “Indian Hotels expansion plans: 2 new brands launching, 2 hotels opening every month,” Skift, February 2, 2024. including Marriott’s first Moxy- and Tribute-branded hotels in India and entrants from Hilton’s Curio and Tapestry brands. 15 Forum Gandhi, “Check-in frenzy: International hotel giants unleash fresh brands in India’s booming hospitality landscape,” Hindu Businessline , February 13, 2024. Development focus has shifted away from major metropolises such as Mumbai and Delhi and toward fast-developing, smaller cities such as Chandigarh and Hyderabad.
Southeast Asian travel spending is projected to grow at roughly 7 percent per year. Pockets of particularly high growth exist in Cambodia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. To capitalize on this blossoming source market, neighboring countries are rolling out attractive visa arrangements: for example, China has agreed to reciprocal visa waivers for short-term travelers from Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand. 16 Julienna Law, “China launches ‘visa-free era’ with Southeast Asia. Will travel retail boom?,” Jing Daily , January 30, 2024.
Travel spending by Eastern Europeans is expected to grow at 7 percent per year until 2030—two percentage points higher than spending by Western Europeans. Areas of especially high growth include the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland, where middle-class travelers are increasingly venturing farther afield. Major tourism players, including the TUI Group, have tapped into these new source markets by offering charter flights to warm-weather destinations such as Egypt. 17 Hildbrandt von Klaus, “TUI develops Czech Republic as a new source market,” FVW, December 22, 2023.
Although the number of travelers from these new source markets is growing, their purchasing power remains relatively limited. Compared with Western European travelers (who average $159 per night in total travel spending), South Asians spend 20 percent less, Eastern Europeans spend 40 percent less, and Southeast Asians spend 55 percent less. Only 3 percent of the current Asian hotel construction pipeline caters to economy travelers, suggesting a potential supply gap of rooms that could appeal to budget-constrained tourists.
While acknowledging that historical source markets will continue to constitute the bulk of travel spending, tourism players can consider actions such as these to capitalize on growing travel demand from newer markets:
- Reduce obstacles to travel. Countries can look for ways to strategically invest in simplifying travel for visitors from growing source markets. In 2017, for example, Azerbaijan introduced express processing of electronic visas for Indian visitors; annual arrivals from India increased fivefold in two years. Requirements regarding passport photocopies or in-person check-ins can similarly be assessed with an eye toward reducing red tape for travelers.
- Use culturally relevant marketing channels to reach new demographics. Unique, thoughtful marketing strategies can help destinations place themselves on first-time travelers’ bucket lists. For example, after the release of Zindagi Na Milegi Dobara , a popular Bollywood movie shot in Spain with support from the Spanish Ministry of Tourism, Indian tourism to Spain increased by 65 percent. 18 “ Zindagi Na Milegi Dobara part of syllabus in Spain colleges,” India Today , June 6, 2004.
- Give new travelers the tech they expect. Travelers from newer source markets often have access to tech-forward travel offerings. For example, Indian travelers can travel anywhere within their country without physical identification, thanks to the Digi Yatra app. The Southeast Asian rideshare app Grab has several helpful travel features that competitors lack, such as automated menu translation and currency conversion. Tourism stakeholders should consider how to adapt to the tech expectations of newer travelers, integrating relevant offerings that ease journeys.
- Create vibrant experiences tailored to different price points. Crafting lower-budget offerings for more cost-constrained travelers doesn’t need to result in giving them a subpar experience. Capsule hotels, in which guests sleep in small cubbies, began as a response to the high cost of accommodations in Japan, but they have become an attraction in their own right—appearing on many must-do lists. 19 Philip Tang, “24 of the best experiences in Japan,” Lonely Planet, March 23, 2024.
The places you’ll go: The destinations of the future may not be the ones you imagine
The world’s top ten destination countries (the United States, Spain, China, France, Saudi Arabia, Türkiye, Italy, Thailand, Japan, and India, in that order) currently receive 45 percent of all travel spending, including for domestic travel. But some new locales are gaining traction (Exhibit 5).
A significant number of travelers are expanding their horizons, booking journeys to less visited countries that are near to old standbys. For instance, Laos and Malaysia, which both border Thailand—an established destination that is home to Bangkok, the world’s most visited city 20 Katherine LaGrave, “This is the world’s most visited city,” AFAR , January 31, 2024. —are up a respective 20 percent and 17 percent, respectively, in year-over-year international travel spending.
The world’s top ten destination countries currently receive 45 percent of all travel spending, including domestic-travel spending. But some new locales are gaining traction.
Several other countries that have crafted thoughtful tourism demand generation strategies—such as Peru, the Philippines, Rwanda, and Vietnam—are also expected to reap benefits in the coming years. Vietnam logged a remarkable 40 percent increase in tourism spending in the five years before the pandemic. Postpandemic, it has rebounded in part by waiving visa requirements for European travelers (while indicating intent to offer similar exemptions in the future for Chinese and Indian travelers). 21 Ashvita Singh, “Vietnam looks to offer visa-free entry to Indians: India report,” Skift, November 20, 2023. The Philippines has made a concerted effort to shift its sun-and-beach branding toward a more well-rounded image, replacing its long-standing “It’s more fun in the Philippines” tourism slogan with “Love the Philippines.” Peru is highlighting less visited archeological sites while also marketing itself as a top-notch culinary destination through the promotion of Peruvian restaurants abroad. Rwanda is investing in infrastructure to become a major African transit hub, facilitated by Qatar Airways’ purchase of a 60 percent stake in the country’s major airport. 22 Dylan Cresswell, “Rwanda plots ambitious tourism recovery,” African Business , July 28, 2022. Rwanda has also successfully capitalized on sustainable tourism: by charging $1,500 per gorilla trekking permit, for instance, it has maximized revenue while reducing environmental impact.
Tourism players might consider taking some of these actions to lure tourists to less familiar destinations:
- Collaborate across the tourism ecosystem. Promotion is not solely the domain of destination marketing organizations. Accommodation, transportation, and experience providers can also play important roles. In Singapore, for instance, the luxury resort Marina Bay Sands partners extensively with Singapore Airlines and the Singapore Tourism Board to offer compelling tourism offerings. Past collaborations have included flight and stay packages built around culinary festivals. 23 “Singapore Tourism Board, Marina Bay Sands & UOB partner to enliven Marina Bay precinct,” Singapore Tourism Board news release, January 25, 2024.
- Use infrastructure linkage to promote new destinations. By extending route options, transportation providers can encourage visitors to create itineraries that combine familiar destinations with new attractions. In Asia, Thailand’s tourism authority has attempted to nudge visitors away from the most heavily trafficked parts of the country, such as Bangkok and Phuket, and toward less popular destinations.
- Deploy social media to reach different demographics. Innovative social media campaigns can help put a destination on the map. Australia launched its “Ruby the kangaroo” campaign in China to coincide with the return of postpandemic air capacity between the two places. A video adapted for Chinese context (with appropriate gestures and a hashtag in Mandarin) garnered more than 20 million views in a single day on one of China’s largest social media platforms. 24 Nicole Gong, “Can Ruby the kangaroo bring Chinese tourists hopping back to Australia?,” SBS, June 5, 2023.
- Embrace unknown status. “Off the beaten path” messaging can appeal to widely traveled tourists seeking fresh experiences. Saudi Arabia’s “#WhereInTheWorld” campaign promoted the country’s tourist spots by acknowledging that they are less familiar to travelers, using a series of images that compared these spots with better-known destinations.
As tourism stakeholders look to the future, they can take steps to ensure that they continue to delight existing travelers while also embracing new ones. Domestic and intraregional tourism remain major opportunities—catering to local tourists’ preferences while building infrastructure that makes travel more seamless within a region could help capture them. Creative collaboration among tourism stakeholders can help put lesser-known destinations on the map. Travel tides are shifting. Expertly navigating these currents could yield rich rewards.
Caroline Tufft is a senior partner in McKinsey’s London office, Margaux Constantin is a partner in the Dubai office, Matteo Pacca is a senior partner in the Paris office, Ryan Mann is a partner in the Chicago office, Ivan Gladstone is an associate partner in the Riyadh office, and Jasperina de Vries is an associate partner in the Amsterdam office.
The authors wish to thank Abdulhadi Alghamdi, Alessandra Powell, Alex Dichter, Cedric Tsai, Diane Vu, Elisa Wallwitz, Lily Miller, Maggie Coffey, Nadya Snezhkova, Nick Meronyk, Paulina Baum, Peimin Suo, Rebecca Stone, Sarah Fellay, Sarah Sahel, Steffen Fuchs, Steffen Köpke, Steve Saxon, Sophia Wang, and Urs Binggeli for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Seth Stevenson, a senior editor in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The future of tourism: Bridging the labor gap, enhancing customer experience

The promise of travel in the age of AI

From India to the world: Unleashing the potential of India’s tourists
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
The first global dashboard for tourism insights.
- UN Tourism Tourism Dashboard
- Language Services
- Publications
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN Tourism Data Dashboard
The UN Tourism Data Dashboard – provides statistics and insights on key indicators for inbound and outbound tourism at the global, regional and national levels. Data covers tourist arrivals, tourism share of exports and contribution to GDP, source markets, seasonality and accommodation (data on number of rooms, guest and nights)
Two special modules present data on the impact of COVID 19 on tourism as well as a Policy Tracker on Measures to Support Tourism
The UN Tourism/IATA Destination Tracker
Un tourism tracker.
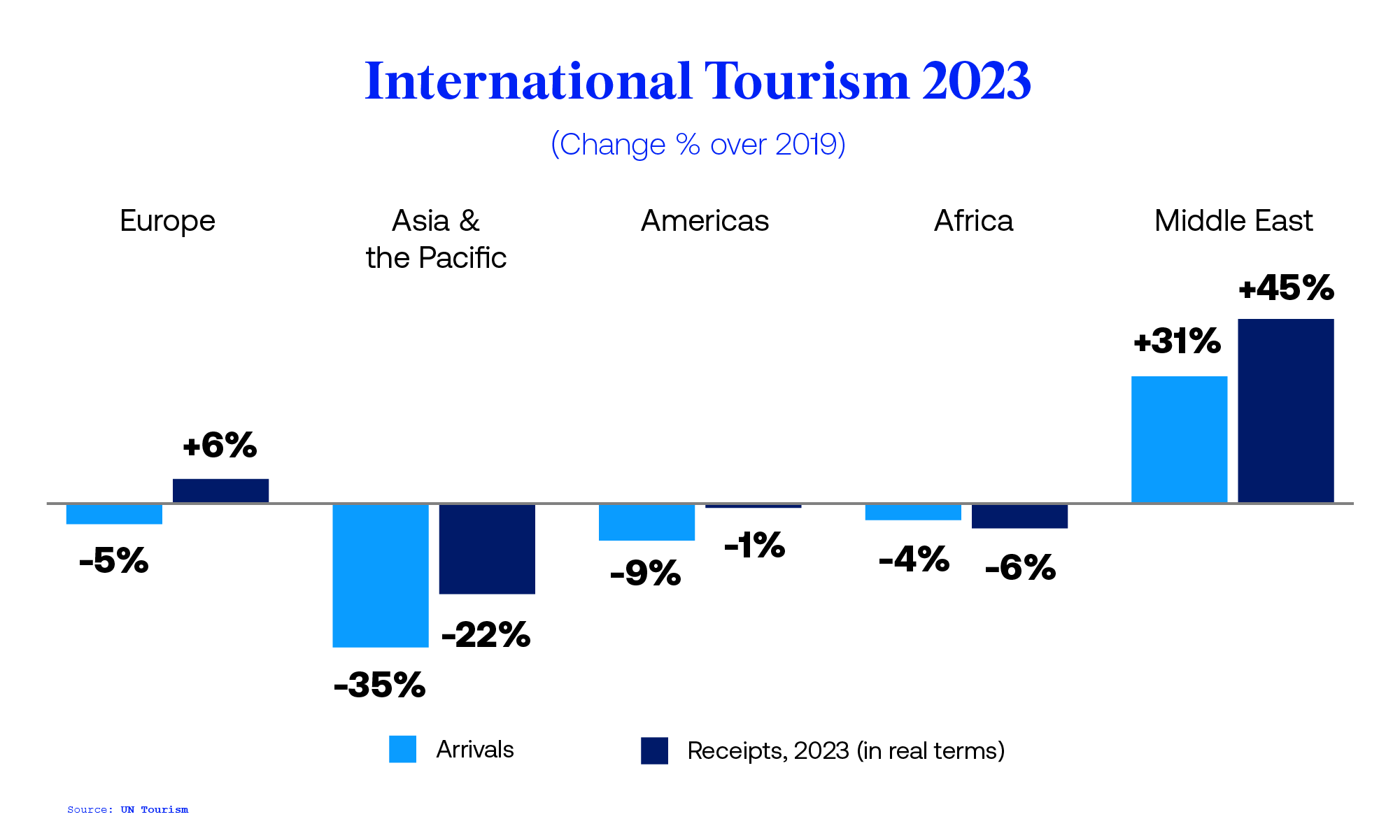
- International tourist arrivals and receipts and export revenues
- International tourism expenditure and departures
- Seasonality
- Tourism Flows
- Accommodation
- Tourism GDP and Employment
- Domestic Tourism
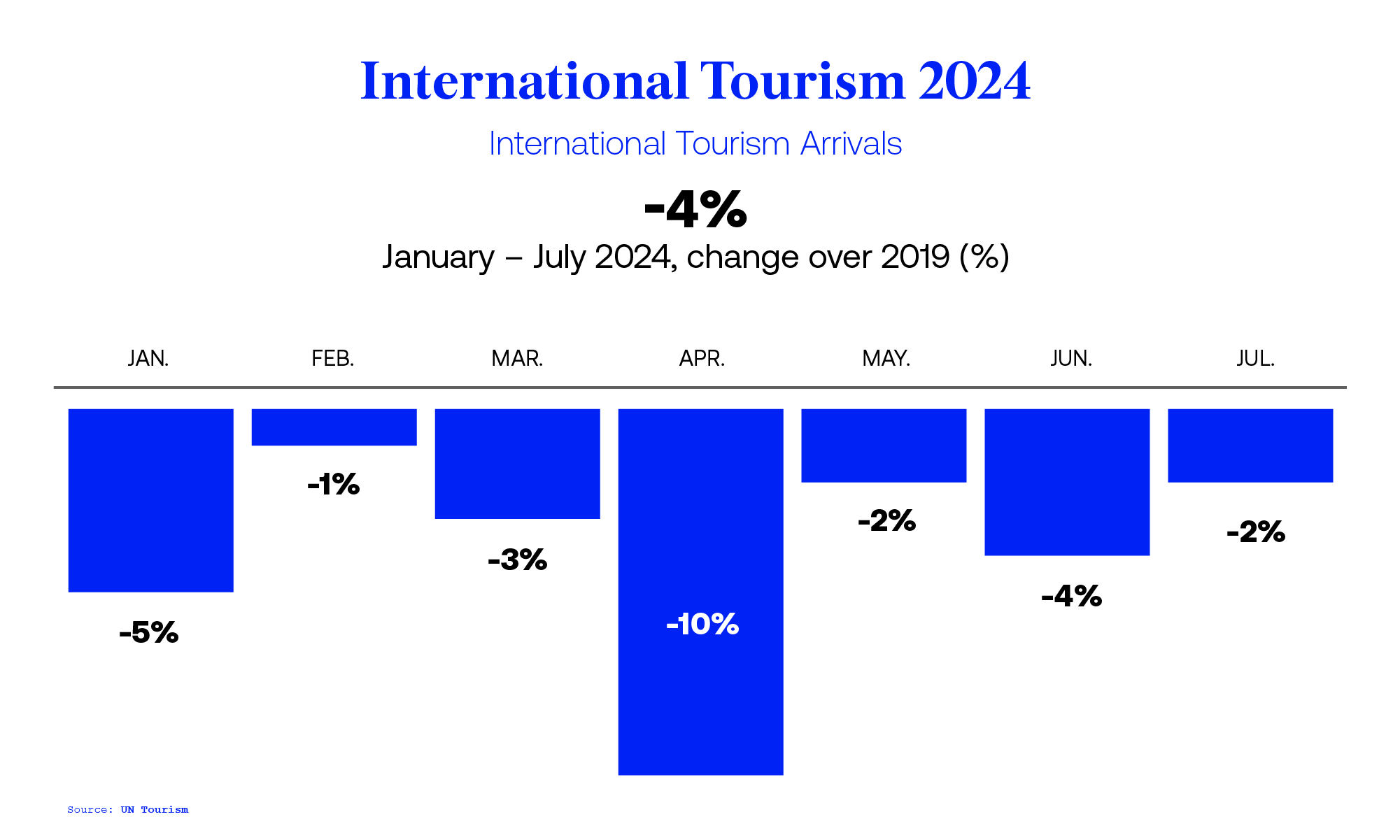
International Tourism and COVID-19
- The pandemic generated a loss of 2.7 billion international arrivals in 2020, 2021 and 2022 combined.
- Export revenues from international tourism (including receipts and passenger transport) dropped 62% in 2020 and 59% in 2021, versus 2019 (real terms) and then rebounded in 2022, remaining 23% below pre-pandemic levels.
- The total loss in export revenues from tourism amounts to USD 2.5 trillion for that three-year period.
- International tourist arrivals reached 89% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023 and 96% in January-July 2024.
- Revised data for 2023 shows export revenues from international tourism reaching USD 1.8 trillion virtually the same as before the pandemic (-1% in real terms compared to 2019). Tourism direct GDP also recovered pre-pandemic levels in 2023, reaching an estimated USD 3.4 trillion, equivalent to 3% of global GDP.
COVID-19: Measures to Support Travel and Tourism

Shelley Zumwalt announces retirement as director of Oklahoma Tourism and Recreation Department
Oklahoma State Capitol
OKLAHOMA CITY — The executive director of the Oklahoma Tourism and Recreation Department (OTRD), Shelley Zumwalt, announced her retirement from the public sector on Thursday.
Zumwalt has served in her role at the department since October 2022.
The OTRD said Zumwalt has retired to pursue the next phase of her career in the private sector.
Zumwalt started her career with the state in an entry-level position before taking on leadership roles such as her time at the Oklahoma Employment Security Commission during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Other accomplishments during her career included welcoming more than 18 million visitors to the state and leading the agency to a Heartland Emmy for the “Imagine That” campaign, according to the OTRD.
Zumwalt’s last day in office is October 11 as she will stay to help with the transition and training for the person who will be taking over her position.
“Spending over a quarter of my life as a state servant has shaped my life in ways I will forever be grateful for. It’s been the honor of a lifetime to dedicate so much of my professional career to the people of Oklahoma,” said Shelley Zumwalt. “I will always look back on my time in service with a deep appreciation and admiration for the dedicated employees I have had the privilege to work alongside over my time with the State of Oklahoma. I will continue to serve as I remain in my position until October 11 to ensure the next leader of OTRD has a seamless transition into their new role. To wake up each day and roll up your sleeves for something you believe in is a beautiful thing. It’s been a great honor to serve the citizens of Oklahoma.”
In April 2024 , Oklahoma Attorney General Gentner Drummond called for the resignation Zumwalt following an audit alleging misuse of millions of tax dollars.
The audit alleged that Zumwalt, who was appointed as the executive director of the Oklahoma Employment Security Commission (OSEC) in May 2020, used her position to approve millions of dollars in contracts for a software company, Phase 2 Development (P2), where her husband was employed as the vice president.
©2024 Cox Media Group
Your browser does not support HTML5 audio.
More From KRMG
:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/cmg/2E2KXO2QK5HTTG5ABJYFAJ6H4A.jpg)
KRMG Celebrates Veterans Through The Oklahoma Warriors Honor Flight
:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/cmg/BY5Q5EUP55A3NBU6AQNWFJQCO4.jpg)
You Could Win $1,000 With The KRMG Potter’s Payroll Payout
:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/cmg/2BS7RBPN4ZHZLABJTVPI5VXH7A.jpg)
The 2024 Tulsa State Fair is Almost Here!
Sign up below to be added to our mailing list for the latest news updates, access to exclusive contests, and more!
mobile apps
Everything you love about krmg.com and more! Tap on any of the buttons below to download our app.
amazon alexa
Enable our Skill today to listen live at home on your Alexa Devices!
Audio Temporarily Unavailable
You may be offline. Please check your connection and try again using the Retry button.


THE POWER OF PEOPLE, PLACES & FIRMS

Tourism stewardship: how destination organisations are driving change
Tourism has found itself at a crossroads. The sector faces renewed challenges that are undermining the post-COVID “build-back-better” promise – with many destinations stretched by growing visitor numbers and overcrowding, environmental pressures, and communities once again questioning the value of tourism.
To meet these challenges, forward-thinking destinations are embracing destination stewardship to balance tourism promotion activities with efforts to preserve and enhance the natural, cultural, and social assets that make each destination unique. It’s no longer just about maximising visitor numbers and dollars; it’s about ensuring tourism delivers long-term value to communities.
Destination organisations: Leading the charge in the new era of tourism
Destination organisations can be structured as government entities, private organisations, or public-private partnerships, funded by a mix of sources. Traditionally they are responsible for promoting their destination at national, regional and local levels.
As the OECD has highlighted , tourism’s future depends on local action, and destination organisations are uniquely positioned to drive this change. A number have evolved into Destination Management Organisations (DMOs), assuming a stewardship role that shapes a tourism industry focused on resilience, inclusivity, and sustainability.
These DMOs are now focussing on building strong partnerships, developing capabilities, enhancing visitor experiences, attracting investment, and delivering sharp marketing that aligns with sustainable growth. However, this can be without clear mandates, or alignment of national, regional or local strategies.
This expanded DMO remit requires a shift in mindset and transformation in how they are structured and operate, as well as how they are supported by governments and industry. They are the glue that unites stakeholders around a shared vision and have an objective view across the destination’s eco-system. They must be empowered with the authority and resources to drive meaningful change.
Tourism doesn’t exist in isolation; the impact of visitation is felt across wider economic, environmental and social systems. DMOs must be thought leaders “at the table”, aligning visitor strategies with broader policy goals, addressing challenges and capitalising on opportunities.
The DMO’s ability to lead in this evolving landscape depends on building new skills — particularly in leadership, advocacy, stakeholder engagement, systems thinking, and understanding of regulatory frameworks.

New Zealand’s approach to building destination stewardship
New Zealand is a long way from many international markets. We are a country of 5 million people where tourism is a major contributor to our prosperity. It’s also deeply connected to our environment, communities, and our national identity.
Over the last few decades New Zealand’s visitor economy has grown steadily. We also suffer from seasonal fluctuations, labour shortages, and inadequate infrastructure in popular destinations. As a small island nation, New Zealand is particularly vulnerable to climate change and is heavily reliant on aviation for international tourism and trade connections. And, with continued growth, tourism’s social license is being tested, and overtourism is starting to creep into some key locations.
Prior to COVID-19, the government at the time, recognised the importance of destination management in their National Tourism Strategy, and subsequently, Destination Management Guidelines were developed to guide regions to adopt a more holistic approach in an effort to address emerging challenges.
While borders were closed, government-funded Destination Management Plans (DMPs) were developed across 30 regions, led by Regional Tourism Organisations (RTOs – equivalent of DMOs) in collaboration with mana whenua (indigenous Māori people), industry and community. Regional Tourism New Zealand (RTNZ – industry body) provided oversight, benchmarking and monitoring.
Recognising the need for support to meet the expanding RTO role, RTNZ undertook a skills assessment of RTOs, which led to a comprehensive national capability-building programme, Te Ūnga Mai (“to arrive at a deeper place of knowledge”).
Over three years, Te Ūnga Mai provided RTOs with the best practice knowledge, resources, and mentoring to succeed. The result? A stronger, more capable network of RTOs better equipped to lead a destination stewardship approach.
Examples of this transition include New Zealand’s most southern region fully integrating tourism within their economic development strategy , and the Great South RTO adding new skills focused on sustainability and climate change.
The Taitokerau Northland region has co-created a DMP with mana whenua, placing people, culture and environment at the centre. New Zealand’s hero destinations Queenstown and Lake Wanaka have collaborated on a regenerative tourism plan, centred on the community with a bold ambition of achieving net zero by 2030.

Lessons learned: Key contributors for success
Destinations thrive when there is an agreed vision and strategy, co-created by both public and private sectors, indigenous peoples and communities.
Tourism needs to be embedded in broader macroeconomic strategies, acknowledging the impact visitors have across society and systems. This requires enabling policies or legislation which activates responsibilities across the system. The recent groundbreaking legislation for Hawaii is embedding regenerative tourism, thereby creating lasting change.
DMOs require a clear mandate to act in a broader stewardship capacity. They must also be fit for purpose, with sufficient capacity, resources, and the right mix of skills to enable effective stewardship that supports a regenerative future.
In summary
Tourism must shift from growth-driven promotion to stewardship for the sector to effectively navigate the challenges ahead.
A stewardship approach must also be embedded into the system to sustain the long-term commitment needed to ensure tourism delivers enduring value and resilience for destinations.
DMOs play a pivotal role in this transformation. As critical change agents, they can drive and shape destinations so that they thrive not only economically, but also socially, culturally, and environmentally.

Kiri Goulter
Kiri Goulter is a highly accomplished tourism and economic development professional with an extensive, multi-faceted career.
Kiri has held significant leadership roles at regional and national levels, including the New Zealand Government, Tourism New Zealand and Hamilton & Waikato Tourism, where as CEO spearheaded the region’s tourism renaissance.
She has played a pivotal role in reshaping New Zealand’s tourism landscape, authoring the Destination Management Guidelines (Ministry of Business Innovation & Employment, 2019) and guiding all 30 Regional Tourism Organisations (RTOs) in their planning and capability building.
In Kiri’s current role as Director Destination Management at Regional Tourism New Zealand, she designed the award-winning Te Ūnga Mai programme, which upskilled RTOs as regional stewards, earning the 2022 New Zealand Tourism Award for Industry Collaboration. Her career reflects a deep commitment to ensuring tourism delivers enduring value to communities, businesses, and the environment.
Share this:
Discover more from cogito.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Skip to global NPS navigation
- Skip to the main content
- Skip to the footer section

Exiting nps.gov
News release, national park tourism in utah contributes $3 billion to state economy.
Date: September 4, 2024 Contact: IMR Public Affairs
DENVER, Colo. – The National Park Service (NPS) reports that 15.7 million visitors to Utah’s 13 national parks spent $1.9 billion in the state in 2023. That spending resulted in 26,507 jobs and had a cumulative benefit to the state economy of $3 billion. “I’m so proud that our parks and the stories we tell make a lasting impact on more than 300 million visitors a year,” said NPS Director Chuck Sams. “And I’m just as proud to see those visitors making positive impacts of their own, by supporting local economies and jobs in every state in the country.” “In 2023, visitors to national parks in Utah spent $3 billion and supported 26,507 jobs in local communities,” said NPS Intermountain Regional Director Kate Hammond. “Whether it’s science, adventure, history or scenery, Utah’s national parks leave the more than 15 million visitors marveling. Investments into Utah national parks give back to communities and these visitors support the state’s economy.” The National Park Service finds that visitors spent $26.4 billion in communities near national parks. Nationwide, this spending supported 415,400 jobs, provided $19.4 billion in labor income and $55.6 billion in economic output to the U.S. economy. The lodging sector had the highest direct contributions with $9.9 billion in economic output and 89,200 jobs. The restaurants received the next greatest direct contributions with $5.2 billion in economic output and 68,600 jobs. An interactive tool enables users to explore visitor spending, jobs, labor income, value added, and output effects by sector for national, state, and local economies. Users can also view year-by-year trend data. The interactive tool and report are available at nps.gov. To learn more about national parks in Utah and how the National Park Service works with Utah communities to help preserve local history, conserve the environment, and provide outdoor recreation, visit nps.gov .
Last updated: September 6, 2024

Ministry of Tourism announces Winners of Best Tourism Villages Competition-2024 36 villages recognized as winners across 8 categories
Ministry of Tourism, Government of India announced winners of the Best Tourism Villages Competition 2024, today, on 27 th September, 2024, on the occasion of World Tourism Day.
To promote tourism to the Soul of India (India’s villages), the Best Tourism Villages Competition was introduced in 2023. The focus was to identify and recognize villages which preserve and promote cultural and natural assets through community-based values and commitment to sustainability in all aspects.
The first edition of the Best Tourism Villages Competition in 2023 saw applications from 795 villages. In the second edition of the Best Tourism Villages Competition, a total of 991 applications were received from 30 States and UTs, out of which 36 villages were recognized as winners across 8 categories of the Best Tourism Villages competition 2024.
These 36 are as follows:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 6 A's of tourism provide a framework for understanding the different components that make up the industry. By focusing on these elements, tourism professionals can identify areas that need improvement and develop strategies to enhance the overall tourism experience. For example, a destination with limited accessibility may struggle to ...
The 6 A's of Tourism are: These are the primary reasons people visit a destination, including natural wonders, historical sites, cultural events, entertainment venues, and unique experiences. Easy access to a destination through well-developed transportation infrastructure, such as airports, highways, and public transit, is essential for ...
Tourism is a massive industry that encompasses various activities and services, including transportation, accommodation, and entertainment. To understand the different aspects of tourism, experts have identified six critical elements that make up the industry. These six elements are known as the 6 A's of tourism.
Conclusion. Apart from the classic five 'A's of tourism, we suggest a sixth 'A' which is vital to the tourism agency's success, Affordability. The travel expenses like transport costs, accommodation charges, entrance fees, and many more should be at an affordable price for travelers.
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
There are six major components of tourism, each with their own sub-components. These are: tourist boards, travel services, accommodation services, conferences and events, attractions and tourism services. There are many components of tourism that make up the industry.
In 2010, international tourism reached US$919B, growing 6.5% over 2009, corresponding to an increase in real terms of 4.7%. [30] In 2010, there were over 940 million international tourist arrivals worldwide. [31] By 2016 that number had risen to 1,235 million, producing 1,220 billion USD in destination spending. [32]
Tourism has massively increased in recent decades. Aviation has opened up travel from domestic to international. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of international visits had more than doubled since 2000. Tourism can be important for both the travelers and the people in the countries they visit. For visitors, traveling can increase their ...
Figure 1.2 The tourism supply chain. [Long Description] Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it's important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date. Long Descriptions. Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the ...
The contribution of tourism to economic well-being depends on the quality and the revenues of the tourism offer. UN Tourism assists destinations in their sustainable positioning in ever more complex national and international markets. As the UN agency dedicated to tourism, UN Tourism points out that particularly developing countries ...
6) Incentive Tourism: Holiday trips are offered as incentives by major companies to dealers and salesmen who achieve high targets in sales. This is a new and expanding phenomenon in tourism, These are in lieu of cash incentives or gifts, Today incentive tourism is a 3 billion dollar business in the USA alone.
Shaping the value offerings for tourism we need to consider -apart from the marketing strategy- the 5 A's of tourism: Attraction: It includes all those factors which attract a tourist. It could be a place, nature, lakes, beach, monuments etc. Accessibility: It is how to access or reach to that place of attraction. Ways to reach.
In 2023, travel and tourism's direct contribution to gross domestic product (GDP) was approximately 9.9 trillion U.S. dollars, making up a 9.1 percent share of the total global GDP. Show more ...
WTTC's latest annual research shows: In 2023, the Travel & Tourism sector contributed 9.1% to the global GDP; an increase of 23.2% from 2022 and only 4.1% below the 2019 level. In 2023, there were 27 million new jobs, representing a 9.1% increase compared to 2022, and only 1.4% below the 2019 level.
As travel resumes and builds momentum, it's becoming clear that tourism is resilient—there is an enduring desire to travel. Against all odds, international tourism rebounded in 2022: visitor numbers to Europe and the Middle East climbed to around 80 percent of 2019 levels, and the Americas recovered about 65 percent of prepandemic visitors 1 "Tourism set to return to pre-pandemic levels ...
Batu City is a place with many types of tourism and had many tourists in 2019. However, there was an imbalance of tourist attractions visited from the total number.
Global tourism is back and buzzing in 2024. We take a closer look at the top trends shaping consumer behavior and spending when it comes to travel. ... Spending on travel is expected to follow a similar trajectory, with an estimated $8.6 trillion in traveler outlays in 2024, representing roughly 9 percent of this year's global GDP.
International Tourism and COVID-19. The pandemic generated a loss of 2.7 billion international arrivals in 2020, 2021 and 2022 combined. Export revenues from international tourism (including receipts and passenger transport) dropped 62% in 2020 and 59% in 2021, versus 2019 (real terms) and then rebounded in 2022, remaining 23% below pre-pandemic levels.
The audit alleged that Zumwalt, who was appointed as the executive director of the Oklahoma Employment Security Commission (OSEC) in May 2020, used her position to approve millions of dollars in ...
Kiri Goulter is a highly accomplished tourism and economic development professional with an extensive, multi-faceted career. Kiri has held significant leadership roles at regional and national levels, including the New Zealand Government, Tourism New Zealand and Hamilton & Waikato Tourism, where as CEO spearheaded the region's tourism renaissance.
The Department of Tourism was then renamed Ministry of Tourism as a result of the shift in the form of government pursuant to the enforcement of the 1973 Constitution. In 1986, under Executive Orders 120 ... Pilipinas Kay Ganda (2010) [5] [6] It's More Fun in the Philippines! Experience the Philippines (2017) We Give the World our Best (2023 ...
Literature review and hypothesis development. Tourism is one of the sectors most affected by the pandemic. Tourism-related businesses (e.g., accommodation, transportation, travel agencies, and tour operators) experienced a massive loss (Habibi et al., Citation 2022; UNWTO, Citation 2021b).The pandemic caused an economic loss of approximately USD 2.0 trillion in 2020 and an unprecedented ...
John Percy, president and CEO of Destination Niagara USA, was recently honored with the 2024 New York State Tourism Excellence Award for Excellence in Leadership: Career/Lifetime Achievement by ...
Date: September 4, 2024 Contact: IMR Public Affairs DENVER, Colo. - The National Park Service (NPS) reports that 15.7 million visitors to Utah's 13 national parks spent $1.9 billion in the state in 2023. That spending resulted in 26,507 jobs and had a cumulative benefit to the state economy of $3 billion.
The executive director of the Oklahoma Tourism and Recreation Department (OTRD), Shelley Zumwalt, announced her retirement on Thursday.
Zumwalt has held several high-level positions in Gov. Kevin Stitt's administration, including director of the Oklahoma Employment Security Commission during the worst of the COVID-19 recession.
Overall, travel and tourism represent 9. 1% of global GDP, giving an inkling of what we could achieve, especially given our generous endowment of natural and cultural attractions, he said.
Ministry of Tourism, Government of India announced winners of the Best Tourism Villages Competition 2024, today, on 27 th September, 2024, on the occasion of World Tourism Day.. To promote tourism to the Soul of India (India's villages), the Best Tourism Villages Competition was introduced in 2023. The focus was to identify and recognize villages which preserve and promote cultural and ...
The value in sharing thousands of years of Indigenous knowledge inside the mountainous rainforest, home to ceremonial meeting places, now has a modern significance with Traditional Owners to play ...
6. The tourism event establishment making the taxable transaction connected with the tourism event mentioned in paragraph 5(1) is the operator of the hotel. Amount of cess: 7. The cess payable on a taxable transaction connected with the tourism event is as follows: (a)