

What is mpox? A microbiologist explains what’s known about this smallpox cousin
Regents' Professor & Chair, Medical Laboratory Science, Texas State University
Disclosure statement
Rodney E. Rohde has received funding from the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP), American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science (ASCLS), U.S. Department of Labor (OSHA), and Texas State University. Rohde is affiliated with ASCP, ASCLS, ASM, and serves on several scientific advisory boards.
Texas State University provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
On Aug. 14, 2024, the World Health Organization declared mpox a public health emergency of international concern . There have been over 15,600 cases and over 530 deaths reported in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and neighboring countries in Africa. The disease had previously caused a global outbreak from 2022 to 2023.
Mpox – previously called monkeypox – isn’t a new disease. The first confirmed human case was in 1970 , when the virus was isolated from a child suspected of having smallpox in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Though usually mild, mpox can still potentially cause severe illness. Health officials are concerned that more cases will arise with increased travel.
I’m a researcher who has worked in public health and medical laboratories for over three decades, especially in the realm of diseases with animal origins. What exactly is happening in the current outbreak, and what does history tell us about mpox?
A cousin of smallpox
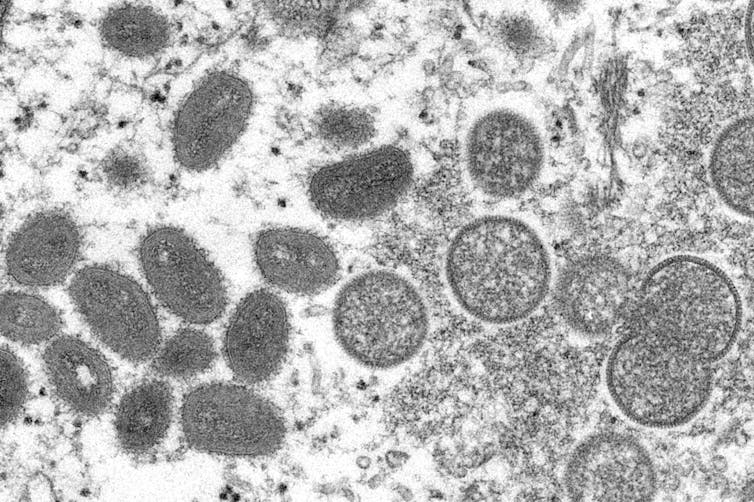
Mpox is caused by the monkeypox virus, which belongs to a subset of the Poxviridae family of viruses called Orthopoxvirus. This subset includes the smallpox, vaccinia and cowpox viruses. While an animal reservoir for monkeypox virus is unknown , African rodents are suspected to play a part in transmission. The monkeypox virus has only been isolated twice from an animal in nature. Diagnostic testing for mpox is currently only available at Laboratory Response Network labs in the U.S. and globally.
The name “monkeypox” comes from the first documented cases of the illness in animals in 1958, when two outbreaks occurred in monkeys kept for research. However, the virus did not jump from monkeys to humans, nor are monkeys major carriers of the disease.
Epidemiology
Since the first reported human case, mpox has been found in several other central and western African countries , with the majority of infections in the DRC. Cases outside of Africa have been linked to international travel or imported animals, including in the U.S. and elsewhere .
The first reported cases of mpox in the U.S. was in 2003, from an outbreak in Texas linked to a shipment of animals from Ghana. There were also travel-associated cases in July and November 2021 in Maryland. The outbreak of mpox that began May 2022 is ongoing .
Because mpox is closely related to smallpox, the smallpox vaccine can provide protection against infection from both viruses. Since smallpox was officially eradicated, however, routine smallpox vaccinations for the U.S. general population were stopped in 1972. Because of this, mpox has been appearing increasingly in unvaccinated people.

Transmission
The virus can be transmitted through contact with an infected person or animal or contaminated surfaces. Typically, the virus enters the body through broken skin, inhalation or the mucous membranes in the eyes, nose or mouth. Researchers believe that human-to-human transmission is mostly through inhalation of large respiratory droplets rather than direct contact with bodily fluids or indirect contact through clothes.
Health officials are worried that the virus may currently be spreading undetected through community transmission, possibly through a new mechanism or route. Where and how infections are occurring are still under investigation.
Signs and symptoms
After the virus enters the body, it starts to replicate and spread through the body via the bloodstream. Symptoms usually don’t appear until one to two weeks after infection.
Mpox produces smallpox-like skin lesions , but symptoms are usually milder than those of smallpox. Flu-like symptoms are common initially, ranging from fever and headache to shortness of breath. One to 10 days later, a rash can appear on the extremities, head or torso that eventually turns into blisters filled with pus. Overall, symptoms usually last two to four weeks, while skin lesions usually scab over in 14 to 21 days.
While mpox is rare and usually nonfatal, one version of the disease kills around 10% of infected people . The form of the virus currently circulating is thought to be milder, with a fatality rate of less than 1%.
Vaccines and treatments
Treatment for mpox is primarily focused on relieving symptoms. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, no treatments are available to cure mpox infection.
Evidence suggests that the smallpox vaccine can help prevent mpox infections and decrease the severity of the symptoms. One vaccine known as Imvamune or Imvanex is licensed in the U.S. to prevent mpox and smallpox.
Vaccination after exposure to the virus may also help decrease chances of severe illness. The CDC currently recommends smallpox vaccination only in people who have been or are likely to be exposed to mpox. Immunocompromised people are at high risk.
This is an updated version of an article originally published on May 20, 2022.
- Infectious diseases
- Smallpox vaccine

Head of Evidence to Action

Supply Chain - Assistant/Associate Professor (Tenure-Track)

Education Research Fellow

OzGrav Postdoctoral Research Fellow

Casual Facilitator: GERRIC Student Programs - Arts, Design and Architecture
What Travelers Need to Know About the Mpox Vaccine
The UN World Health Organization (WHO) declared on August 14, 2024, that the recent upsurge in mpox cases constitutes “a public health emergency of international concern," the organization's highest alert level. The next day, Sweden confirmed the first case of the new strain, mpox Clade 1, to be diagnosed outside Africa .
As of August 21, 2024, there have been more than 17,000 suspected cases of mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) reported in Africa since the beginning of the year—a significant increase in the total suspected cases in 2023. The current consensus states that the rise in cases is due to the new mpox Clade 1 strain. Mpox Clade 2 was the milder variant behind 2022's global outbreak of less severe infections. More than 99.9% of those infected with mpox Clade 2 survive. Compared to Clade 2, Clade 1 typically causes a higher percentage of people with mpox to get severely sick—it can also cause fatalities—per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); some outbreaks of Clade 1 were reported to have killed up to 10% of people who got sick.
The latest global health emergency declaration is the result of an IHR Emergency Committee decision, which met to review data presented by experts from WHO and affected countries. There are concerns that the disease could spread further across Africa and across continents, however, Mpox is “not the ‘new COVID,'” a top WHO official said on August 20. At the time of publication, no cases of Clade 1 mpox have been reported in the United States.
Following WHO's announcement, there have been instances of mpox misinformation and disinformation going viral on social media, as USA Today reported Tuesday. Platforms such as X , Meta , and TikTok have pages outlining their policies on combatting the spread of misinformation and misleading content, but the most reliable sources for information concerning mpox remain the official channels of public health organizations such as the WHO and the CDC.
Do I need the mpox vaccine to travel?
As of August 21, 2024, there is no official call for general travelers to be vaccinated against mpox ahead of their trips.
However, the CDC issued a Level 2 Travel Health Notice on August 7, 2024, regarding travel to DRC and neighboring countries. The notice advises travelers to “practice enhanced precautions,” which includes vaccinating with both doses of the JYNNEOS vaccine at least 28 days apart as soon as possible if you visit DRC or its neighboring countries (Burundi, Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, and Uganda). While there is currently no official recommendation for how far in advance travelers should receive the second dose prior to their trip, the CDC notes that “it takes two weeks after the second dose to be the most protected.” Research on how long protection lasts is ongoing, with studies being conducted on data from the most recent outbreak. All of the CDC's advisories on travel to those countries can be found on their respective Travel Health Notice pages , and updates on the effectiveness of the JYNNEOS vaccine can be found on their mpox vaccination recommendations page .
In 2022, the United States launched its Mpox Vaccine Equity Pilot Program (MVEPP) in response to the Clade 2 outbreak. The CDC, which administered the program, offered the JYNNEOS vaccine as, "free and available to everyone, regardless of immigration status, gender identity, or sexual orientation.” MVEPP rolled out in two phases: the first involved outreach in public events attended largely by gay, bisexual, and other MSM (men who have sex with men) populations such as Pride festivals, and its second phase was mpox vaccination proposals designed by health departments to mitigate medical racial prejudices.
The current CDC guidance recommends vaccinations for those who are gay, bisexual, MSM, transgender, gender non-binary, or gender-diverse AND in the last six months have had, or expect to have:
- One or more sexually transmitted infections
- More than one sexual partner, or anonymous sexual or intimate contact
- Sex at a commercial sex venue
- Sex in association with a large public event in a geographic area where mpox transmission is occurring
Additionally, the vaccine is recommended for those who have had sexual or intimate contact with a person who is at risk of mpox as described above, those who have had sexual or intimate contact with someone who may have mpox, and those with occupational exposure to orthopoxviruses (e.g. healthcare, laboratory, and wildlife professionals) regardless of sexual or gender identity. For the most up-to-date information on the CDC's vaccination recommendations, visit their page , and the US Government's official health recommendations for travelers can be found on their Travelers' Health page on mpox .
A version of this article was originally published on Condé Nast Traveller UK. Condé Nast Traveler does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any information published on this website or by this brand is not intended as a substitute for medical advice, and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional.
The Latest Travel News and Advice
Want to be the first to know? Sign up to our newsletters for travel inspiration and tips
Southwest Ends Its Open Seating Policy —Could More Changes Be on the Way?
Why You Should Never Check a Bag
Why Travelers Should Start Preparing for the Next Airline Scheduling Meltdown
Hotels Are Now Offering Dedicated Butlers for Destination Proposals
By signing up you agree to our User Agreement (including the class action waiver and arbitration provisions ), our Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement and to receive marketing and account-related emails from Traveller. You can unsubscribe at any time. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

The Embassy of The Republic of Indonesia in Berlin

- Layanan WNI
- Our Embassy
- Consular Service
- Honorary Consul
- Visit B211A
- Diplomatic/Service visa
- Visa on Arrival (VoA)
- Calling Visa
- Visa Exemption
- Invest in Indonesia
- Trade with Indonesia
- Wonderful Indonesia
- Information
- Tips and tricks
- Testimonials
Current Health Regulations at Entry
All entrants to Indonesia are currently required to follow the following health protocol on entry, in accordance with the latest Circular Letter No. 25 /2022 issued by the National Taskforce to Combat COVID-19 ( Satgas COVID-19 ) dated 01.09.2022 :
- Indonesian Nationals:
- Obligation to provide proof of having received three doses of COVID-19 vaccination (= booster ) for all entrants aged 18 years and above via the PeduliLindungi app (see below);
The obligation for providing proof of complete vaccination (printed (recommended) or digital) does not apply for:
- Entrants who have not yet received a third dose of vaccination (= booster ) and have finished carrying out COVID-19 isolation or treatment and have been declared no longer actively transmitting COVID-19, with the requirement that they show a doctor’s certificate from the Government Hospital of the country of origin or from the Ministry that administers Government affairs in the health sector on the country of origin, stating that the person concerned is no longer actively transmitting COVID-19, or COVID-19 recovery certificate;
- Entrants with special health conditions or comorbid diseases that prevent them to get vaccinated, with the requirement that they show a doctor’s certificate from the Government hospital of the country of origin stating that the person concerned has not and/or cannot receive COVID-19 vaccine (with letterhead and stamp).
2. Proof of having the PeduliLindungi app installed and registered with your personal data and your vaccination (see below).
B. Foreign Nationals:
- Obligation to provide proof of complete having received two doses of COVID-19 vaccination (=2 times) for all entrants aged 18 years and above;
The obligation for providing proof of full complete vaccination (printed (recommended) or digital) does not apply for:
- Entrants under 18 years of age;
- Entrants who have not yet received a complete second dose of vaccination and have finished carrying out COVID-19 isolation or treatment and have been declared no longer actively transmitting COVID-19, with the requirement that they show a doctor’s certificate from the Government Hospital of the country of origin or from the Ministry that administers Government affairs in the health sector on the country of origin, stating that the person concerned is no longer actively transmitting COVID-19, or COVID-19 recovery certificate;
2. Proof of having the PeduliLindungi app installed , and registered with your personal data and your vaccination as follows:

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Vaccines for Travelers
Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places.
Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you’re traveling. It will also help make sure that you don’t bring any serious diseases home to your family, friends, and community.
On this page, you'll find answers to common questions about vaccines for travelers.
Which vaccines do I need before traveling?
The vaccines you need to get before traveling will depend on few things, including:
- Where you plan to travel . Some countries require proof of vaccination for certain diseases, like yellow fever or polio. And traveling in developing countries and rural areas may bring you into contact with more diseases, which means you might need more vaccines before you visit.
- Your health . If you’re pregnant or have an ongoing illness or weakened immune system, you may need additional vaccines.
- The vaccinations you’ve already had . It’s important to be up to date on your routine vaccinations. While diseases like measles are rare in the United States, they are more common in other countries. Learn more about routine vaccines for specific age groups .
How far in advance should I get vaccinated before traveling?
It’s important to get vaccinated at least 4 to 6 weeks before you travel. This will give the vaccines time to start working, so you’re protected while you’re traveling. It will also usually make sure there’s enough time for you to get vaccines that require more than 1 dose.
Where can I go to get travel vaccines?
Start by finding a:
- Travel clinic
- Health department
- Yellow fever vaccination clinic
Learn more about where you can get vaccines .
What resources can I use to prepare for my trip?
Here are some resources that may come in handy as you’re planning your trip:
- Visit CDC’s travel website to find out which vaccines you may need based on where you plan to travel, what you’ll be doing, and any health conditions you have.
- Download CDC's TravWell app to get recommended vaccines, a checklist to help prepare for travel, and a personalized packing list. You can also use it to store travel documents and keep a record of your medicines and vaccinations.
- Read the current travel notices to learn about any new disease outbreaks in or vaccine recommendations for the areas where you plan to travel.
- Visit the State Department’s website to learn about vaccinations, insurance, and medical emergencies while traveling.
Traveling with a child? Make sure they get the measles vaccine.
Measles is still common in some countries. Getting your child vaccinated will protect them from getting measles — and from bringing it back to the United States where it can spread to others. Learn more about the measles vaccine.
Find out which vaccines you need
CDC’s Adult Vaccine Quiz helps you create a list of vaccines you may need based on your age, health conditions, and more.
Take the quiz now !
Get Immunized
Getting immunized is easy. Vaccines and preventive antibodies are available at the doctor’s office or pharmacies — and are usually covered by insurance.
Find out how to get protected .
Disclaimer Policy: Links with this icon ( ) mean that you are leaving the HHS website.
- The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) cannot guarantee the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not mean that HHS or its employees endorse the sponsors, information, or products presented on the website. HHS links outside of itself to provide you with further information.
- You will be bound by the destination website's privacy policy and/or terms of service when you follow the link.
- HHS is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on private websites.
For more information on HHS's web notification policies, see Website Disclaimers .
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Indonesia Travel Advisory
Travel advisory july 24, 2023, indonesia - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise increased caution in Indonesia due to terrorism and natural disasters. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do Not travel to:
- The provinces of Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and Highland Papua (Papua Pegunungan) due to civil unrest.
Terrorists continue plotting possible attacks in Indonesia. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, targeting police stations, places of worship, hotels, bars, nightclubs, markets/shopping malls, and restaurants.
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis or volcanic eruptions may result in disruptions to transportation, infrastructure, sanitation, and the availability of health services.
Demonstrations occur frequently and have the potential to become violent. Avoid demonstrations and crowds.
Indonesia’s revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. It is unclear how Indonesian authorities will implement the revised criminal code.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Indonesia.
If you decide to travel to Indonesia:
- Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to adjust your plans.
- Visit the websites for Badan Geologi (Indonesian Geological Agency, Indonesian language only) for the latest information from the Government of Indonesia on current natural disasters.
- Review the CDC’s suggestions on how to prepare for natural disasters.
- Be aware of your personal safety and security at all times.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Ensure your passport is valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay.
- Follow the Department of State Facebook and Twitter . Follow the U.S. Embassy Jakarta on Facebook , Instagram , and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Indonesia.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Central Papua and Highland Papua– Level 4: Do Not Travel
In Central Papua and Highland Papua, violent demonstrations and conflict could result in injury or death to U.S. citizens. Avoid demonstrations and crowds. Armed separatists may kidnap foreign nationals.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in Central Papua and Highland Papua as U.S. government employees must obtain special authorization before traveling to those areas.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, indonesia map, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Indonesia Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status
Traveling from the United States to Indonesia
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces and enclosed environments.
Documents & Additional resources
Ready to travel, find flights to indonesia, find stays in indonesia, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Indonesia from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Indonesia.
Can I travel to Indonesia if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Indonesia without restrictions.
Can I travel to Indonesia without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Indonesia without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Indonesia?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Indonesia.
Can I travel to Indonesia without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Indonesia?
Mask usage in Indonesia is not required in public spaces and enclosed environments.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Indonesia?
Restaurants in Indonesia are open. Bars in Indonesia are .
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Uganda Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip

Be aware of current health issues in Uganda. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 2 Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Updated Global Polio August 20, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List: Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Guinea, Indonesia, Kenya, Liberia, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, including Zanzibar, The Gambia, Uganda, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe
- Clade I Mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Neighboring Countries August 07, 2024 There is an outbreak of clade I mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Countries sharing borders with DRC are considered at risk for spread. Destination List: Burundi, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Uganda
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
African sleeping sickness (african trypanosomiasis).
- Tsetse fly bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
African Trypanosomiasis
African Tick-Bite Fever
African Tick-bite fever
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic fever
- Tick bite
- Touching the body fluids of a person or animal infected with CCHF
- Mosquito bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
- Avoid animals
- Touching infected animals (including bats and primates) or their body fluids
- Touching body fluids (blood or sweat) from an infected person
- Touching objects contaminated with the body fluids of a person infected with Ebola or Marburg virus
- Avoid sick people
- Avoid animals and areas where they live
Ebola virus
Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever
Marburg virus
Rift Valley Fever
- Touching blood, body fluids, or tissue of infected livestock
Rift Valley fever
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Uganda, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Uganda. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Uganda include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Uganda. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Uganda’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in Uganda. Fill your malaria prescription before you leave and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Uganda may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Uganda, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Uganda.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Uganda for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Travel Vaccines and Advice for Indonesia

Indonesia is the largest island country in the world, spanning over 17,000 islands.
It is the world’s fourth most populous country and is one of the largest countries in land-size as well. Although Indonesia is densely populated, it also has a large amount of wilderness and an abundance of wildlife.
Indonesia is home to hundreds of different ethnic groups with the Javanese being the largest. Although the cultures are diverse, ethnic groups unify over a common language (Indonesian) and a majority Muslim religion.
This diversity allows for hundreds of different cultures, foods and wildlife to be explored. It is a popular tourist site for its beaches, nightlife, food and wildlife.
On This Page: Do I Need Vaccines for Indonesia? Other Ways to Stay Healthy in Indonesia Health Notices and Outbreaks in Indonesia Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Indonesia? What Is the Climate Like in Indonesia? Is It Safe to Travel to Indonesia? Komodo Dragons in Indonesia What Should I Take to Indonesia? U.S. Embassies and Consulates in Indonesia
Do I Need Vaccines for Indonesia?
Yes, some vaccines are recommended or required for Indonesia. The CDC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Indonesia: typhoid , hepatitis A , polio , yellow fever , Japanese encephalitis , chikungunya , rabies , hepatitis B , influenza , COVID-19 , pneumonia , meningitis , chickenpox , shingles , Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis) and measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) .
See the bullets below to learn more about some of these key immunizations:
- Typhoid – Food & Water – Shot lasts 2 years. Oral vaccine lasts 5 years, must be able to swallow pills. Oral doses must be kept in refrigerator.
- Hepatitis A – Food & Water – Recommended for most travelers.
- Polio – Food & Water – Active polio transmission has been documented in Indonesia. Single adult booster recommended.
- Yellow Fever – Mosquito – Required if traveling from a country with risk of yellow fever transmission.
- Japanese Encephalitis – Mosquito – Recommended for all regions. Most cases are in: Bali, Kalimantan, Java, Nusa Tenggara, Papua, and Sumatra.
- Chikungunya – Mosquito – Indonesia is a higher risk region. Vaccination is recommended.
- Rabies – Saliva of Infected Animals – High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-term travelers and those who may come in contact with animals.
- Hepatitis B – Blood & Body Fluids – Recommended for travelers to most regions.
- Influenza – Airborne – Vaccine components change annually.
- COVID-19 – Airborne – Recommended for travel to all regions, both foreign and domestic.
- Pneumonia – Airborne – Two vaccines given separately. All 65+ or immunocompromised should receive both.
- Meningitis – Direct Contact & Airborne – Given to anyone unvaccinated or at an increased risk, especially students.
- Chickenpox – Direct Contact & Airborne – Given to those unvaccinated that did not have chickenpox.
- Shingles – Direct Contact – Vaccine can still be given if you have had shingles.
- Polio – Food & Water – Considered a routine vaccination for most travel itineraries. Single adult booster recommended.
- TDAP (Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis) – Wounds & Airborne – Only one adult booster of pertussis required.
- Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR) – Various Vectors – Given to anyone unvaccinated and/or born after 1957. One time adult booster recommended.
See the table below for more information:
Specific Vaccine Information
- Typhoid – Salmonella Typhi causes typhoid, a potentially life-threatening illness spread through contaminated food and water. Vaccination is a critical preventive measure, especially for travelers heading to endemic regions or individuals with an increased risk of exposure.
- Hepatitis A – Hepatitis A is a contagious liver infection transmitted through contaminated food, water, or close personal contact. To prevent it, practicing good hygiene and getting vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine are crucial steps recommended by the CDC.
- Polio – Polio is a contagious virus that can cause paralysis and is mainly spread through feces. The best prevention method is vaccination. The vaccine triggers the immune system to produce antibodies, offering protection against polio and aiding in the worldwide campaign to eliminate the disease.
- Japanese Encephalitis – Japanese encephalitis is a mosquito-borne viral infection affecting the brain. It is found primarily in Asia. The Japanese encephalitis vaccine, administered through injections, effectively prevents the disease. It is recommended for travelers to endemic areas and residents in high-risk regions.
- Chikungunya – Chikungunya, transmitted via mosquito bites, poses a health threat. Prevention involves mosquito bite avoidance and vaccination against the disease.
- Rabies – Rabies is a lethal disease transmitted through the saliva of infected animals, and vaccination is the key to prevention. Pre-exposure vaccination is advised for individuals at risk, and immediate post-exposure vaccination is crucial if one encounters a potentially rabid animal.
- Hepatitis B – Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus, transmitted through blood, sexual contact, or from mother to child during birth. It can become chronic, leading to liver failure or cancer. The hepatitis B vaccine, given as a series of injections, effectively prevents this infection.
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) – Measles, mumps, and rubella are viral infections that can spread through close contact and respiratory droplets. Vaccination is the most effective way to halt their transmission. The MMR vaccine, given in two doses, strengthens immunity, reducing the chances of contracting and spreading these diseases.

Malaria in Indonesia
Malaria is less common in many of the popular tourist destinations in Indonesia. No transmission is reported in Jakarta or Ubud; malaria is also not found in resort areas of Bali, Java, the Gili Islands or Pulau Seribu. Rural areas of most other regions have at least low levels of malaria spread. All areas of eastern Indonesia, including Labuan Bajo and Komodo have widespread malaria transmission.
Atovaquone, doxycycline, mefloquine and tafenoquine are suggested as antimalarials if traveling to the region. Consult with a travel health specialist on which antimalarial will best fit your needs.
Health officials have reported several cases of measles in travelers coming from Bali. You should get the measles vaccine and be extra-vigilant of washing your hands.
Although healthcare conditions are low, medical care is readily available in all major cities, including limited psychiatric services.
Medicare does not cover costs overseas. Make sure that you have international coverage on your health care plan. Most hospitals expect payment upfront before a procedure is done.
Visit our vaccinations page to learn more. Travel safely with Passport Health and schedule your appointment today by calling or book online now .
Other Ways to Stay Healthy in Indonesia
Prevent bug bites in indonesia.
To fend off bug bites, follow CDC advice: cover up with long clothing, use repellents containing DEET or picaridin, and avoid bug-heavy areas during dawn and dusk. Protect your sleep with insect-repellent-treated bed nets.
Food and Water Safety in Indonesia
When traveling, ensure food safety by adhering to CDC recommendations, which include eating fully cooked foods, avoiding raw seafood, and selecting reputable dining places. Safely drink bottled beverages, avoiding ice in uncertain water sources, and consume alcohol in moderation. Prevent travelers’ diarrhea through hand hygiene and avoiding street food in unsanitary areas.
Altitude Sickness in Indonesia
Altitude sickness, or acute mountain sickness (AMS), stems from inadequate oxygen at high elevations, causing symptoms like headaches and nausea. Preventing AMS involves gradual ascent, hydration, and potential medication use. Should AMS symptoms develop, swift descent to lower altitudes, rest, and medical evaluation are essential for recovery and safety.
Infections To Be Aware of in Indonesia
- Avian/Bird Flu – Avian flu, a highly contagious virus, can infect both birds and humans. Prevention strategies include vaccinating poultry, implementing robust biosecurity measures, ensuring safe poultry handling and cooking, monitoring for outbreaks, and educating the public about the risks.
- Dengue – The threat of dengue fever, carried by Aedes mosquitoes, looms large worldwide, with millions infected each year. Prevention through nettings and repellents is a must.
- Schistosomiasis – Schistosomiasis, a parasitic disease transmitted through contaminated water, poses a health risk. Prevention strategies include avoiding freshwater activities and wearing protective clothing. Prompt medical attention is necessary if symptoms like fever or abdominal pain occur.
- Zika – Zika, a mosquito-borne virus, can cause mild to severe symptoms and poses significant risks during pregnancy. Prevention strategies include using insect repellent, safe sex practices, and avoiding travel to affected areas.
Health Notices and Outbreaks in Indonesia
- Polio – At least one case of polio was reported in Indonesia over the last 12 months. The CDC and WHO advise all travelers to ensure their polio vaccination history is up-to-date. Adults who previously received a full set of polio vaccinations may need a single, lifetime booster dose.
Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Indonesia?
A passport that will remain valid for at least six months is required to enter Indonesia. A visa is required for entry to Indonesia.
Sources: Embassy of Indonesia and U.S. State Department
If you are not a tourist, you need to purchase a visa before arriving in Indonesia.
What Is the Climate Like in Indonesia?
Indonesia has a tropical climate with high temperatures and high humidity (between 70-90%).
The average temperature ranges between the mountain region and the coast, varying from 74 degrees Fahrenheit to 82 degrees Fahrenheit.
Precipitation is heavy in Indonesia, with the Western and Northern regions experiencing the most rainfall. The wet region of Indonesia receive 80 inches of rain a year.
Typhoon season in Indonesia is between September and December.
Is It Safe to Travel to Indonesia?
Terrorist activity has been present in Indonesia since 2002. Extremists have attacked in the nightclub district of Bali and in Central Jakarta. On May 24, 2017, there was another explosion in Jakarta near a bus station.
ISIL has claimed responsibility for this attack and others in Indonesia.
Currently, travel by U.S government officials to the provinces of Central Sulawesi and Papua is restricted.
Avoid traveling by yourself late at night as petty crime is common in urban areas.
Credit card fraud is common in Indonesia. Use ATMs in secure locations only and keep track of your account.
If you are at a nightclub, be aware of your surroundings as drink poisonings have been on the rise.
Report crimes to the local police at 112 and contact the U.S. Embassy at +(62)(21) 3435-9000 ext. 0
Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime.
Komodo Dragons in Indonesia
Avoid an embarrassing stop, over 70% of travelers will have diarrhea., get protected with passport health’s travelers’ diarrhea kit .
Komodo National Park was names a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1991. It holds three large islands and 26 smaller ones and is rich in natural and marine biological diversity.
This park provides refuge for a large number of animals and plants including the komodo dragon, the Timor deer, dolphins and turtles.
Due to its rich marine life, diving is a common activity in Komodo National Park, with over 40 different unique diving sites available.
Villages span throughout the park, many with few resources and access to clean water.
The cities of Labaun Bajo and Bima act as gateway cities to the park.
What Should I Take to Indonesia?
If you’re going to Indonesia, it’s important to pack the right things. Indonesia is hot, so bring light clothes made of cotton or linen. Pack a mix of short-sleeved and long-sleeved shirts, pants, shorts and a rain jacket or poncho because it rains a lot in some places. Bring comfortable shoes like sandals or closed-toe shoes. You’ll also need sun protection like sunscreen, sunglasses, and a hat.
Mosquitoes are common, so bring insect repellent to avoid bites. Don’t forget your travel documents, power adapter, medications, and some cash and cards. Indonesia is a Muslim country, it’s important to dress modestly and respect local customs, especially when visiting religious sites. If you’re staying in rural areas, consider bringing a mosquito net.
Remember to pack smart and light, keeping in mind the climate and activities you plan to do to make your trip fun and comfortable.
U.S. Embassies and Consulates in Indonesia
All Americans visiting Indonesia should register online with the U.S. Department of State before departure. This will inform the office of your travel plans within the country and will allow them to reach out in the case of an emergency or evacuation.
Once in Indonesia, the information for the U.S. Embassy is:
U.S. Embassy Jakarta Jl. Medan Merdeka Selatan No. 3 – 5 Jakarta 10110, Indonesia Telephone: +(62)(21) 5083-1000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(62)(21) 5083-1000 ext. 0 (operator) Fax: +(62)(21) 385-7189 Email: [email protected]
Visit the Embassy to Indonesia website before departure to confirm correct contact details for the office.
If you have any questions about traveling to Indonesia or are wondering what shots you may need for your trip, schedule an appointment with your local Passport Health travel medicine clinic. Call us at or book online now! and protect yourself today.
Customer Reviews
Passport health – travel vaccines for indonesia.

- Records Requests
- Passport Health App
- Privacy Center
- Online Store
Mpox: What you need to know about the latest public health emergency
Facebook Twitter Print Email
The swift spread of a new virulent strain of the mpox virus across Africa triggered the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare it once again a public health emergency of international concern last week.
But, what is it, where did it come from and how can the world deal with the threat, which inevitably raises the spectre of pandemics past such as COVID-19 and the early spread of HIV infections?
Here’s what you need to know:
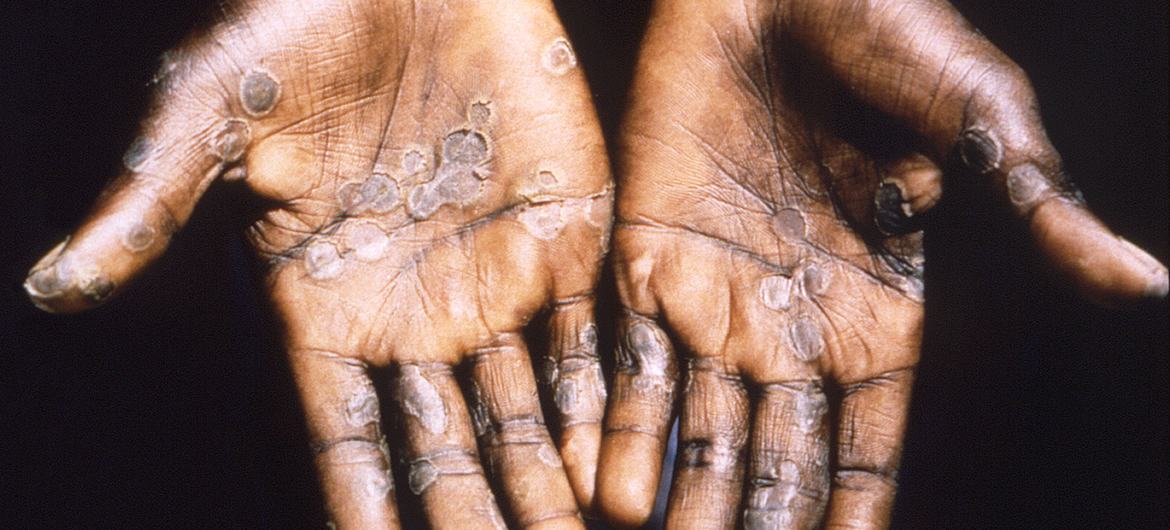
What is mpox?
Formerly known as monkeypox, the viral disease can spread between people, mainly through close contact, and occasionally from the environment to people via objects and surfaces that have been touched by a person with mpox.
Originating in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970, mpox was neglected there, according to WHO .
“It is time to act decisively to prevent history from repeating itself,” said Dimie Ogoina, who chairs the International Health Regulations’ Emergency Committee , which advises WHO on such matters.
Endemic in central and West Africa, the infectious disease later caused a global outbreak in 2022, leading to a WHO public health emergency in July as it became a multi-country outbreak.
Following a series of consultations with global experts, WHO has begun using a new preferred term “mpox” as a synonym for monkeypox. Find out more about that decision here .
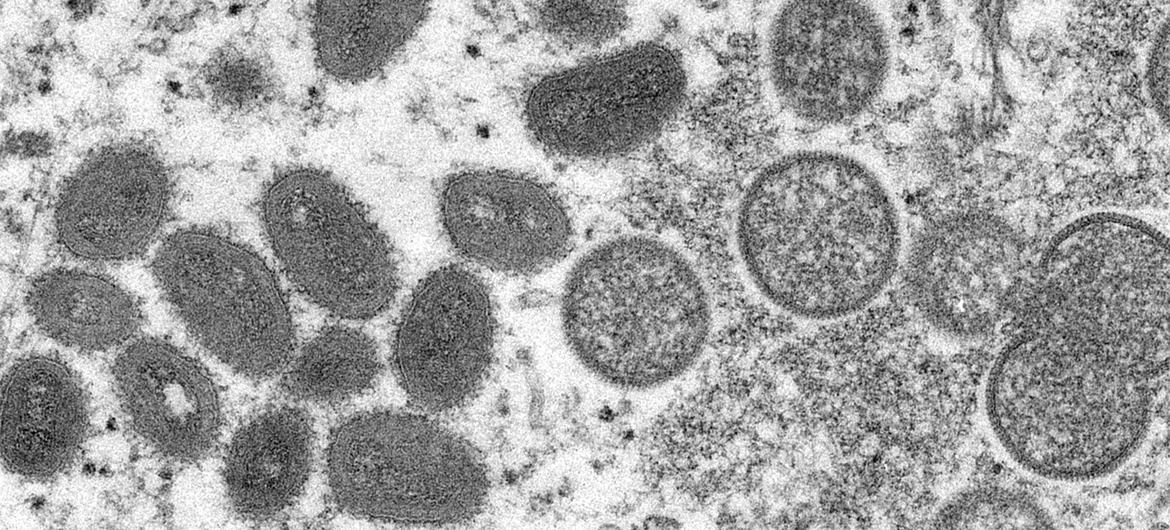
What are the symptoms?
Common symptoms of mpox include a rash lasting for two to four weeks, which may be started with or followed by fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, low energy and swollen lymph nodes.
The rash looks like blisters and can affect the face, palms of the hands, soles of the feet, groin, genital and/or anal regions, mouth, throat or the eyes. The number of sores can range from one to several thousand.
People with mpox are considered infectious at least until all their blisters have crusted over, the scabs have fallen off and a new layer of skin has formed underneath, and all lesions on the eyes and in the body have healed. Typically this takes two to four weeks. Reports show that people can be re-infected after they’ve had mpox.
People with severe mpox may require hospitalisation, supportive care and antiviral medicines to reduce the severity of lesions and shorten time to recovery.
How does mpox spread?
Human to human: Touching, sex and talking or breathing close to someone with mpox can generate infectious respiratory particles, but more research is needed on how the virus spreads during outbreaks in different settings and conditions, says WHO.
What scientists do know is that it is also possible for the virus to persist for some time on clothing, bedding, towels, objects, electronics and surfaces that have been touched by a person with mpox. Someone else who is in contact with these items may become infected without first washing their hands before touching their eyes, nose and mouth.
The virus can also spread during pregnancy to the fetus, during or after birth through skin-to-skin contact, or from a parent with mpox to an infant or child during close contact.
Although getting mpox from someone who is asymptomatic has been reported, there is still limited information on whether the virus can be transmitted from someone with the virus before they get symptoms or after their lesions have healed.
Humans to animals: Since many species of animals are known to be susceptible to the virus, there is the potential for spillback of the virus from humans to animals in different settings.
People who have confirmed or suspected mpox should avoid close physical contact with animals, including such pets as cats, dogs, hamsters and gerbils, as well as livestock and wildlife.
Animals to humans: Someone who comes into physical contact with an animal which carries the virus, such as some species of monkey - or a terrestrial rodent like a tree squirrel - may also develop mpox. Such exposure can occur through bites or scratches, or during activities such as hunting, skinning, trapping or preparing a meal. The virus can also be caught through eating contaminated meat which is not cooked thoroughly.
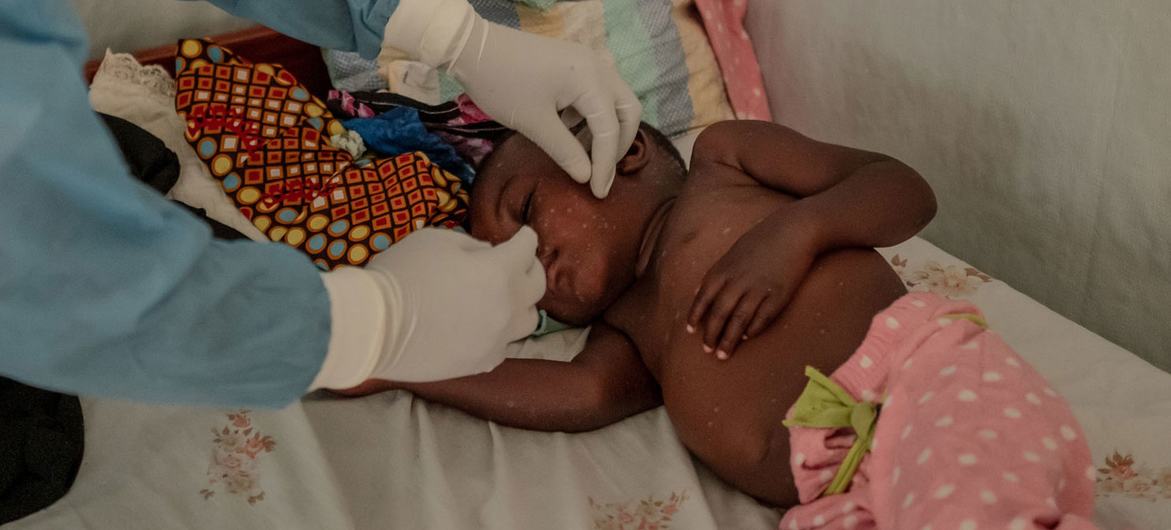
Can it be fatal?
Yes, for a small minority. Between 0.1 per cent and 10 per cent of people who have become infected with mpox, have died.
It is important to note that death rates in different settings may differ due to several factors, such as access to health care and underlying immunosuppression, including because of undiagnosed HIV or advanced HIV, according to the UN health agency.
In most cases, the symptoms of mpox go away on their own within a few weeks with supportive care, such as medication for pain or fever, but, in some people, the illness can be severe or lead to complications and eventual death.
Newborn babies, children, people who are pregnant and people with underlying immune deficiencies - such as from advanced HIV - may be at higher risk of more serious mpox disease and death.
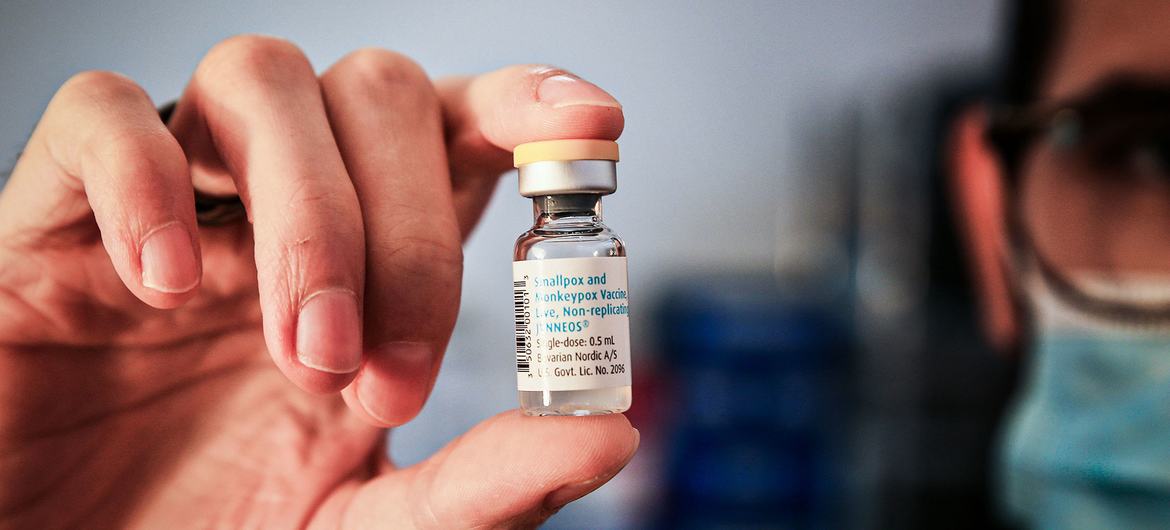
Is there a vaccine?
Yes. The UN health agency recommends several vaccines for use against mpox. However, mass vaccination, which rolled out during the COVID-19 global pandemic, is not currently recommended.
Many years of research have led to the development of newer and safer vaccines for the now eradicated disease smallpox. Some of these vaccines have been approved in various countries for use against mpox.
At present, WHO recommends use of MVA-BN or LC16 vaccines, or the ACAM2000 vaccine when the others are not available.
Only people who are at risk of exposure to mpox should be considered for vaccination, according to WHO. Travellers who may be at risk based on an individual risk assessment with their healthcare provider, may wish to consider vaccination.

How can you prevent mpox?
Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces or objects and cleaning your hands after touching surfaces or objects that may be contaminated can help prevent transmission.
The risk of getting mpox from animals can be reduced by avoiding unprotected contact with wild animals, especially those that are sick or dead, including their meat and blood.
In countries where animals carry the virus, any food containing animal parts or meat should be cooked thoroughly before eating.
Learn more about mpox here .
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Call 118 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance company quickly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccine recommendations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip:
- check the latest vaccine recommendations for Indonesia
- see where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
See what health risks you’ll face in Indonesia , including:
- poor air quality
Air pollution
Air quality in Indonesia’s major cities can reach levels classed as ‘unhealthy for sensitive groups’ or ‘unhealthy’. You can check current air quality data for Jakarta on the Air Quality Index website .
Ash plumes from volcanoes can have an impact on health, particularly for anyone with pre-existing respiratory conditions. If you’re affected, get advice on how to prepare and cope with ash fall .
During the dry season from May to November, widespread wildfires cause smoke haze, which drifts across parts of Indonesia, particularly Riau Islands, central Sumatra and Kalimantan. The haze can cause disruption to local and regional air travel, and the air pollution has an impact on public health. Keep up to date with local information and seek medical advice on appropriate precautions. A regional haze map is available from the Singapore Meteorological Service .
Tap water is not safe to drink in Indonesia.
Altitude sickness
Altitude sickness is a risk in parts of Indonesia. Read more about altitude sickness on TravelHealthPro .
There are many street dogs in Bali and elsewhere, and monkeys around temples and tourist areas. Rabies exists in both wild and domestic animals, including pets. Seek immediate medical assistance if you’re bitten or scratched.
Medication
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
TravelHealthPro explains best practice when travelling with medicines .
Healthcare in Indonesia
The standard of local medical care can be poor and some medical tests cannot be performed reliably. Psychological and psychiatric services are also limited.
Good medical care can be expensive. In remote areas, you may not be able to get treatment for serious injuries or illness. Medical evacuation can cost tens of thousands of pounds. Make sure you have adequate travel health insurance and accessible funds to cover the cost of any medical treatment abroad and repatriation.
FCDO has a list of medical providers in Indonesia where some staff will speak English.
See guidance on healthcare if you’re living in Indonesia .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also guidance on TravelHealthPro .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Advertisement
Supported by
How Did Mpox Become a Global Emergency? What’s Next?
The virus is evolving, and the newest version spreads more often through heterosexual populations. Sweden reported the first case outside Africa.
- Share full article

By Apoorva Mandavilli
Apoorva Mandavilli covered the 2022 mpox outbreak and the Covid-19 pandemic.
Faced once again with a rapidly spreading epidemic of mpox, the World Health Organization on Wednesday declared a global health emergency. The last time the W.H.O. made that call was in 2022, when the disease was still called monkeypox.
Ultimately the outbreak affected nearly 100,000 people worldwide, primarily gay and bisexual men, including more than 32,000 in the United States.
The W.H.O.’s decision this time was prompted by an escalating crisis of mpox concentrated in the Democratic Republic of Congo. It recently spread to a dozen other African countries. If it is not contained, the virus again may rampage all over the world, experts warned.
On Thursday, Sweden reported the first case of a deadlier form of mpox outside Africa , in a person who had traveled to the continent. “Occasional imported cases like the current one may continue to occur,” the country’s public health agency warned.
“There’s a need for concerted effort by all stakeholders, not only in Africa, but everywhere else,” Dr. Dimie Ogoina, a Nigerian scientist and chair of the W.H.O.’s mpox emergency committee, said on Wednesday.
Congo alone has reported 15,600 mpox cases and 537 deaths, most of them among children under 15, indicating that the nature of the disease and its mode of spread may have changed.
Here’s what to know.
Is this the virus we saw in 2022?
This is a different version of the mpox virus.
Mpox is a close relative of the smallpox virus. There are two main types: Clade I, the version that is dominant in Congo, and Clade II, a form of which caused the 2022 global outbreak. (A clade is a genetically and clinically distinct group of viruses.)
Clade I mpox is generally thought to cause more severe illness and to have a much higher mortality rate, which is one reason the W.H.O. is sounding the alarm now. Officials hope to contain this outbreak before it spreads to other continents.
The infection may resemble an ordinary respiratory illness at first but later blooms into a raised rash in the mouth, hands, feet or genitals. The virus spreads mainly through close contact — directly with the skin or fluids of an infected person, or with contaminated bed linens and other items.
Scientists learned during the 2022 outbreak that mpox can spread even in the absence of symptoms. And the rash may be mistaken for other diseases such as measles or chickenpox, particularly in young children.
Who is getting infected this time?
In the 2022 outbreak, mpox spread globally mainly among gay and bisexual men. Behavioral changes in that community helped to contain the virus, and vaccination at the time, or now, will help protect them.
Until recently, most cases in Congo resulted from consumption of contaminated meat or close contact with infected animals and people. But last year, scientists discovered a new subtype of mpox, Clade Ib, which appears to spread from person to person primarily through heterosexual transmission .
Most cases have been observed in prostitutes, truckers and other transient workers.
“Sex is probably the primary driver, and then the secondary driver is close contact and households,” said Dr. Jay Varma, the chief medical officer at SIGA Technologies, which manufactures tecovirimat, a drug used to treat mpox infection.
As with many other infections, most people with healthy immune systems are unlikely to become severely ill with mpox. Those who have weakened immune systems, including those living with H.I.V., are at highest risk of severe illness and death .
Older adults, who are typically more susceptible to infections, may be at least somewhat protected by their childhood vaccinations for smallpox, which ended in the United States in 1972.
Most of the deaths in Congo have been in children under 15, perhaps because their health may already be compromised by poor medical care, malnutrition and the many other pathogens they face.
Has the outbreak spread to the United States or Europe?
Many countries worldwide, including the United States, have continued to see patients with Clade IIb mpox, the version that caused the 2022 outbreak.
So far this year, there have been about 1,657 cases of mpox in the United States, more than double the number at this time last year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Just one case of the more severe Clade I infection has been reported in Europe — in Sweden, in a person who had traveled to Africa. Other so-called “imported” cases seem likely. But experts tend to worry more about community transmission.
“I don’t think the risk right now for Americans is high at all, but what this is telling us is that we have to be vigilant,” said Dr. Trish Perl, an infectious disease physician at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
But previous epidemics, including of mpox, illustrate that an uncontrolled outbreak anywhere in the world may eventually turn up everywhere, Dr. Varma said. Since December, the C.D.C. has twice warned clinicians and the general public to remain alert for signs of mpox.
“I really think it’s only a matter of time before North America, Europe, etc., start to see cases,” he said, referring to the deadlier viral subtype. “Unless we invest in disease control everywhere, we’re going to remain always at risk.”
Will the vaccine still protect against mpox?
Two doses of the mpox vaccine Jynneos should protect against all versions of the virus, experts said.
Jynneos, made by Bavarian Nordic, was used in 2022 in the United States and Europe. The vaccine, initially developed against smallpox, should protect against mpox and all other members of that virus family, said Dr. Boghuma Titanji, an infectious diseases physician at Emory University in Atlanta.
Several studies have shown that antibodies prompted by the Jynneos vaccine wane and may be undetectable within a year. But other research has found that two doses effectively prevent severe illness , Dr. Titanji said.
In the United States, however, fewer than one in four people for whom vaccination was recommended got two doses.
“People were less interested in coming back and getting that second dose, or even starting the course of their vaccination,” Dr. Titanji said. “Maybe we will see an increase in uptick in vaccination, and this will serve as a reminder for people to come in and get vaccinated.”
In 2022, the federal government provided the shots at no cost. Jynneos is now commercially available, and some insurance companies may cover the cost.
For some patients, the shots may prove too expensive , Dr. Perl said. If mpox cases were to escalate, the U.S. government may again make the shots available free of charge, according to a federal official with knowledge of the situation.
Is the U.S. prepared for another bout with mpox?
Yes and no.
Scientists learned a lot about the virus in 2022 and have identified vaccines and treatments. But they do not fully understand how the deadlier virus is spreading in Africa, especially among children, or who is most at risk.
“This is very, very crucial when you think about designing a response strategy,” Dr. Titanji said.
There are few resources allocated to fighting sexually transmitted infections in the United States, said David Harvey, the executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors.
Officials have not solved the problems that hobbled the response in 2022, including poor uptake of the vaccine and “a shockingly underfunded S.T.I. public health system,” Mr. Harvey said.
“Today, we worry about an mpox outbreak,” he added. “We’re already dealing with syphilis, and tomorrow there will be another outbreak of an S.T.I.”
An earlier version of this article misstated the number of U.S. mpox cases so far in 2024. It is 1,657, not 740.
How we handle corrections
Apoorva Mandavilli is a reporter focused on science and global health. She was a part of the team that won the 2021 Pulitzer Prize for Public Service for coverage of the pandemic. More about Apoorva Mandavilli
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia overall due to security risks.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
Indonesia has a bit of everything for everyone. Whether you’re looking to experience the palm-fringed beaches and nightlife in Bali, climb the volcanoes in Java, or brave a trek in the deep jungles of Sumatra, Indonesia truly is a hidden gem.
If you’ve ever planned a holiday in Indonesia, you’ve probably been drawn to Bali. In fact, TripAdvisor awarded Bali as “best destination” winner of the 2017 Travelers’ Choice Awards, and that’s no surprise as Bali has so much to offer its visitors. For starters, there’s plenty of nightlife (if that’s your scene), beautiful white-sand beaches, lush jungles filled with amazing wildlife, not to mention the hard-to-beat culinary scene.
If you’re looking to take the road less travelled (and a little less touristy), visit the island of Sumatra. Sumatra is the wild, rugged hotspot for adventure and one of the only places in Indonesia where you can still see wild orangutans. If wildlife is on your list, you can’t miss exploring Gunung Leuser National Park, which is home to an abundance of wildlife, including monkeys, variety of bird species and most importantly, orangutans.
Whatever activities you have planned on your trip to Indonesia, it’s important to consider your travel health and ensure you come home with nothing but the best of memories.
Speak with your healthcare professional about how you can best protect yourself from contracting any disease or illness prior to your departure.
Before you go to Indonesia
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that all travellers are up-to-date with their routine vaccinations; measles, mumps, rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, polio, influenza and pneumococcal. These vaccinations are given as part of the National Immunisation Program (NIP). For a full list please refer to the NIP schedule, available here . In some cases, you may need a booster or re-vaccination against a disease to ensure you still have immunity.
Travellers to Indonesia who are aged 5 years or older should also ensure they are fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
Other diseases that are considered a risk in Indonesia include hepatitis A, hepatitis B, typhoid, Japanese encephalitis, malaria and rabies. Your doctor will be able to let you know which vaccinations or medications are recommended for you, based on the time of year, destination/s, activities planned and the duration of your stay.
Sources & Citations
It is best to consult with your doctor or travel health clinic at least a month prior to your departure. They will be able to advise you about any vaccinations that you may need for your trip well before you leave, based on your specific travel plans.
What your doctor will need to know:
- When you plan to travel (time of year/season)
- The duration of your trip
- The regions of Indonesia you are visiting
- Your planned activities (i.e. if you are going trekking or visiting remote and/or wilderness areas)
- If you will be in contact with animals
- If you are up-to-date with your routine vaccinations
Your doctor may also conduct a general health check-up. This may be needed for your travel insurance if you have a pre-existing medical condition.
If you are not up-to-date with your routine vaccinations or if the doctor believes you may be at an increased risk of contracting a vaccine-preventable disease, then they may recommend you get a booster or be revaccinated against a particular disease.
4. Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. Travelers Health – Indonesia. Available at: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/destinations/traveler/none/indonesia [accessed 07 February 2022].
MAT-AU-2200165 Date of preparation March 2022
In some circumstances, your private healthcare may cover the cost of the vaccination.
This will however depend on the specifics of your policy with your provider – the type of cover you have (hospital, hospital + extra) and the specifics of your extras cover.
Contact your provider to find out if vaccinations are included as part of your cover.
7. finder.com.au. Are travel vaccinations covered by health insurance? Available at: https://www.finder.com.au/travel-vaccinations (accessed 15 February 2022).
MAT-AU-2201296 Date of preparation May 2022
If you are trekking in Bali, you should consider vaccination against hepatitis A and typhoid, as these diseases occur in Indonesia. Other vaccines which might be considered include vaccination against Japanese encephalitis, hepatitis B and rabies.
It is also important to ensure that your routine and COVID-19 vaccinations are up-to-date including measles, mumps, rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, polio, influenza and pneumococcal disease.
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Travelers Health – Indonesia. Available at: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/destinations/traveler/none/indonesia [Accessed 21 February 2022].
MAT-AU-2200220 Date of preparation March 2022
The standard of healthcare facilities in Indonesia is generally lower than in Australia, so it is important you a prepared before heading off on your trip.
Before travelling
- Register your trip with Smart Traveller
- Make sure you have enough of your regular prescription medicines;
- Ensure you’re up-to-date with your routine vaccinations
- Take out travel insurance - to cover you and your family for medical and other costs resulting from unexpected incidents and accidents, or COVID-19
- Put together a travel kit with medication for pain, diarrhoeal medicine, oral rehydration salts, antiseptic lotion or ointment, adhesive bandages and other wound dressings, insect repellent, sunscreen, latex gloves, thermometer, motion sickness medicine, water purification tablets and compression stockings
During travel
- The tap water is Indonesia is not safe to drink.
- Only drink bottled or filtered water and check the seal on water bottles (some stores sell boiled water in recycled bottles). Avoid ice in your drinks, and check that salad and fruit have been washed with filtered water prior to eating.
- Drink spiking/poisoning from alcoholic drinks is common in parts of Indonesia. Alcoholic drinks have been known to have been contaminated with harmful substances (e.g. methanol). To protect yourself from poisoning, never leave your drink unattended while you are out, avoid home-made alcoholic drinks and drink only at reputable, licensed premises.
- ensure you wash your hands regularly.
- where possible opt for fully cooked fresh food and only eat fruit that you peel yourself.
- Avoid mosquito bites, as you may be at risk of contracting illnesses such as malaria. Malaria transmitting mosquitoes bite predominantly between dusk and dawn. There is no vaccination for malaria available in Australia. Preventative medication is available and needs to be taken before, during and after visiting the area where malaria occurs. Other mosquito borne illnesses which travellers need to be concerned about include dengue, zika, and Japanese encephalitis.
- Rabies is a deadly disease and considered a risk in Indonesia, particularly in Bali. It is spread by the bite, lick or scratch of an infected animal, such as a dog or a monkey. Avoid close contact with wild and domestic animals, this is especially important for children. Do not carry food around, or feed/play with monkeys or other animals. Vaccinations for rabies are available– your doctor can advise whether vaccinations are required for your trip.
- Use condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea, human papillomavirus (HPV), herpes, syphilis, hepatitis B and HIV/AIDS.
- Diseases such as HIV and hepatitis B can also be spread through fluids such as blood and semen. To protect yourself, do not inject drugs, do not share needles or devices that can break the skin including those used for tattooing, piercings or acupuncture. Vaccinations are available for hepatitis B.
Make sure you see a doctor for a travel health consult at least 6 weeks before leaving. If this is not possible, see your doctor as soon as you can.

Launch interactive map
- Worldometer, Indonesia Population (live). Available at: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/indonesia-population/ [accessed 31 August 2023].
- Lonely Planet. Destination Indonesia. Available at: http://media.lonelyplanet.com/shop/pdfs/indonesia-9-getting-started.pdf [accessed 07 February 2022].
- Travel Guide, The Jakarta Post. TripAdvisor presents Bali with the 2017 Travelers’ Choice Awards. Available at: http://www.thejakartapost.com/travel/2017/04/21/tripadvisor-presents-bali-with-2017-travelers-choice-awards.html [accessed 07 February 2022].
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. Travelers Health – Indonesia. Available at: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/destinations/traveler/none/indonesia [accessed 07 February 2022].
- Australian Government, Department of Health. National Immunisation Program Schedule. Available at: https://www.health.gov.au/health-topics/immunisation/immunisation-throughout-life/national-immunisation-program-schedule [accessed 07 February 2022].
- Finder, Travel Vaccinations – Can I claim travel vaccinations on my private health insurance? Available at: https://www.finder.com.au/travel-vaccinations [accessed 07 February 2022].
- Australian Government. Smart Traveller – Indonesia. Available at: https://www.smartraveller.gov.au/destinations/asia/indonesia#health [accessed 07 February 2022].
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. Traveler’s Health Pack Smart. Available at: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/pack-smart [accessed 07 February 2022].
- NSW Government. Mosquitoes are a health hazard fact sheet. Available at: https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/Infectious/factsheets/Pages/mosquito.aspx [accessed 07 February 2022].
- Australian Government. Smart Traveller – Infectious Diseases. Available at: https://www.smartraveller.gov.au/before-you-go/health/diseases [accessed 07 February 2022].
By clicking on this link, you will be leaving this Sanofi hosted website, and depending on the link, will be redirected to either another Sanofi website (for example, to view the Sanofi Privacy Policy) or an independent third party website which is typically not a Sanofi controlled website and may not be located in Australia (“Third Party Website”). Use of and access to any Third Party Site is subject to the terms, limitations and conditions set by the Third Party Site producer and applicable laws. Sanofi does not generally develop or maintain Third Party Sites, nor does it necessarily control those sites availability or what information is contained on those sites in any given instance and makes no representation in relation to those sites to the maximum extent permitted under any applicable laws, regulations or codes. Any information that you access via a Third Party Site, may not comply with the Australian regulatory requirements. Further information relevant to the Australian environment is available from Sanofi or via the Product Information.

- About the Handbook
Vaccination for international travellers
Ensure that travellers are up to date with routine vaccines. Also consider other vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and risk of disease exposure.
Recently added
This page was added on 09 June 2018 .
Updates made
This page was updated on 16 August 2024 . View history of updates
Millions of Australians travel overseas every year. More than half of these trips are to destinations other than New Zealand, North America and Europe. 1
This page helps with making decisions about travel vaccines. Also check the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for details about specific vaccines.
See also Infographic. Vaccination for international travellers .
Health risks of overseas travel
Health risks associated with international travel include exposure to:
- infective agents
- altitude and temperature extremes
- other physical, psychological and environmental hazards
- poor-quality or limited access to clean water, shelter, hygiene and sanitation facilities, and health and medical care
The level of health risks depends on factors such as:
- the traveller’s underlying physical and mental health and physiological state
- the itinerary and activities undertaken
- the duration of exposure to various hazards during travel
Travellers at increased risk of serious travel-associated infections include:
- young children and infants
- pregnant women
- people with underlying medical conditions, especially immunocompromising conditions due to disease or medical treatment
- people spending extended periods in multiple regions with poor resources or in remote areas
- people participating in events where large numbers of people will gather, such as major sporting, cultural, social or religious events
- migrant families travelling back to their region of origin to visit friends and relatives
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are more likely to: 2
- have closer contact with local populations
- stay in remote or rural areas
- consume higher-risk food and beverages
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are less likely to: 2,3
- recognise the health risks associated with travelling
- seek pre-travel health advice
- obtain the recommended vaccines or prophylaxis
Common infections acquired by travellers
Exposure to infectious diseases is one of the many health hazards of international travel. Some of these diseases are vaccine preventable. Although some of these diseases are present in Australia, the risk of acquiring them overseas may be higher because of:
- higher disease incidence in other countries
- increased risk of exposure from participating in certain activities while travelling
Foodborne and waterborne infections
It is common for travellers to ingest contaminated food or beverages, resulting in an illness. 4-6 Practicing safe eating and drinking habits is essential to minimise the risk of contracting food and waterborne diseases while travelling. These include treating water or only drinking bottled water, avoiding undercooked meat, and avoiding raw fruit and vegetables (unless they can be peeled or washed in safe water prior to eating). Most infections are diarrhoeal diseases due to enteric pathogens, but some are due to extra-intestinal microorganisms, such as hepatitis A virus and Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (causing typhoid).
Vaccines are available against hepatitis A, typhoid and cholera.
Vector-borne infections
Insect-borne — especially mosquito-borne — infections, such as malaria and dengue, are important causes of fever in Australian travellers returning from endemic areas, particularly Southeast Asia and Oceania. 4,6
A dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) is available for the prevention of secondary dengue infections (not primary prevention of initial dengue infection ) in select individuals. See Clinical advice: ATAGI statement on use of Dengvaxia® for Australians .
Japanese encephalitis occurs throughout much of Asia and the Western Pacific region, including eastern Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. 7 Yellow fever occurs only in parts of Africa and South America, 8 and tick-borne encephalitis occurs in parts of Europe and Asia. 9
Vaccines are available against Japanese encephalitis , yellow fever and tick-borne encephalitis .
Some other vector-borne diseases and parasitic (including protozoal and helminthic) diseases are also important for international travellers. Some are preventable through appropriate barrier precautions and chemoprophylaxis (for example, malaria). 9
Aerosol-borne infections
Vaccine-preventable infections transmitted by aerosols and/or droplets include: 9
- influenza (the most common vaccine-preventable infection among travellers) 10
- meningococcal disease
- varicella (chickenpox)
The incidence of measles and mumps is higher in many overseas countries, including some developed countries, than in Australia.
Tuberculosis is a rare infection in travellers. 11 Expatriates who live in endemic areas for a long time are more likely to acquire tuberculosis than short-term visitors. 12
Vaccines are available against all of these diseases.
Bloodborne and sexually transmitted infections
Some Australian travellers may be at risk from bloodborne and sexually transmissible infections, such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV and mpox (monkeypox). In some areas, healthcare workers using non-sterile medical equipment or other poor infection control practices may transmit these viruses and other bloodborne agents.
Vaccines are available against hepatitis B and mpox.
Exotic infectious agents
Travellers may be exposed to a variety of other exotic infections, such as:
- rabies from bites or scratches from rabid dogs, bats and other mammals in many countries
- schistosomiasis from exposure to water infested with the parasites, especially in Africa
- leptospirosis through activities such as rafting or wading in contaminated streams
Of these diseases, vaccines are available only against rabies.
Recommending travel vaccines
Although recommending appropriate vaccines is important, it is not the only part of a pre-travel medical consultation. Travel vaccines — those relevant for travelling — include all relevant vaccines, not just the ones that prevent diseases that most commonly occur overseas.
Do not recommend a vaccine based only on the destination country, because there is no single ‘correct’ list of vaccines for travel to any particular country.
There are 3 categories of travel vaccines:
- routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
- selected vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
- vaccines required by the International Health Regulations 2005 (IHR) or for entry into specific countries
Questions for a pre-travel medical consultation
During a pre-travel medical consultation, ask questions about the traveller’s:
- personal information, including age and whether they are pregnant or planning pregnancy
- underlying medical conditions, particularly immunocompromising conditions, and current medicines
- vaccination history (including adverse events following immunisation) and allergy history
- purpose of travel and intended activities, especially those associated with various environmental risks and hazards
- plans for travel insurance
Also ask about their itinerary in detail, including:
- date of departure and time available for vaccinations
- specific localities and routes
- rural versus urban stay
- duration of stay
- likely access to health care and other services
- likelihood of changing the planned itinerary
This information helps to tailor recommendations about preventive vaccination or chemoprophylaxis for exposure risks during the proposed trip. It also allows the clinician to advise about other appropriate preventive health measures (for example, food and water precautions, avoiding bites from mosquitoes or other arthropods) and about managing possible health conditions during travel.
Organisational requirements for vaccination
Some overseas organisations, such as schools, colleges and universities, require evidence of vaccination or immunity against some vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles and meningococcal disease. Consider these requirements when planning and scheduling vaccines before departure.
Routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
Vaccinate all prospective travellers according to the recommended vaccination schedule appropriate for their age, underlying health conditions, occupation and lifestyle. Vaccines might include, for example, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for an older person, or hepatitis B vaccine for a first aid officer.
Also ensure that all children are vaccinated according to the National Immunisation Program schedule. In exceptional circumstances, give the National Immunisation Program vaccines at the minimum age rather than the recommended age (see Table. Minimum acceptable age for the 1st dose of scheduled vaccines in infants in special circumstances ). Children vaccinated using the minimum age rather than the recommended age may need extra vaccine doses to ensure adequate protection. Observe the minimum interval requirements between doses (see Table. Minimum acceptable dose intervals for children <10 years of age ). The chances of being exposed to some diseases, such as measles and mumps, may be greater during overseas travel, even to other developed countries.
For some itineraries, it may be appropriate for the traveller to receive some booster doses earlier than the routine recommended time. An example may be diphtheria-tetanus booster.
Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis
Vaccinate adult travellers against tetanus before departure, particularly if:
- their risk of sustaining a tetanus-prone wound is high
- there could be delays in accessing health services where they can receive tetanus toxoid boosters safely, if required
Offer dTpa vaccine during a pre-travel consultation if the traveller has never received a dose of dTpa . This provides protection against pertussis (see Pertussis ).
For high-risk travel, consider giving a booster dose of either dTpa or dT vaccine if more than 5 years have passed (see Tetanus ).
Hepatitis B
Most Australian children born since 2000 have been vaccinated against hepatitis B under the National Immunisation Program or state and territory school-based vaccination programs.
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for long-term or frequent travellers to regions of intermediate or high endemicity of hepatitis B, including:
- Central and South America
This is because travellers may be exposed to hepatitis B virus through bloodborne routes (including during emergency medical or dental procedures) or sexual routes. According to 1 survey, about half of Australian travellers who spent at least 3 nights in Southeast or East Asia participated in at least 1 activity that had a risk of hepatitis B transmission. 13
See also Hepatitis B .
Influenza, pneumococcal disease, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Older travellers and those with any relevant underlying medical or behavioural risk factors should receive pneumococcal vaccine. See Pneumococcal disease for more details.
Older travellers and those with medical risk factors for severe RSV disease should receive RSV vaccine.
See also RSV for more details.
Consider influenza vaccine for all travellers, especially if they are travelling to a region during its influenza season. Influenza vaccine is particularly relevant if:
- there is an influenza epidemic at the traveller’s destination
- the person is travelling in a large tourist group, especially one that includes older people
- the person is travelling on cruises, where people are relatively confined for days to weeks
See also Influenza for more details.
Measles, mumps and rubella
Inadequately vaccinated young adult travellers are responsible for most current measles outbreaks in Australia. This occurs when they acquire the infection overseas and bring it back to Australia. Some countries, regions or communities — including developed countries — have a higher incidence of measles and mumps than Australia. 9
Australians born during or since 1966 who have not received the recommended 2 doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella)–containing vaccines are recommended to receive MMR vaccine before travelling. This also applies to infants 6–12 months old travelling to areas with measles outbreaks or where measles is endemic . The exception is for pregnant women, because MMR is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
People born before 1966 do not need to receive measles-containing vaccine (unless serological evidence indicates that they are not immune). This is because circulating measles virus and disease were prevalent before 1966, so most people would have acquired immunity from natural infection .
However, confirmed cases of measles have occurred in people born before 1966. 14 If in doubt about a person’s immunity, it may be faster and easier to vaccinate the person than conduct serological testing . See Serological testing for immunity to measles .
See also Measles .
Unvaccinated travellers are recommended to receive varicella vaccine if they either:
- have not had clinical disease, or
- have an uncertain history of clinical disease and serology shows a lack of immunity
The exception is for pregnant women, because varicella vaccine is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
See also Varicella .
Meningococcal disease
Vaccination against meningococcal serogroups A, C, W-135, Y and B is recommended for certain age and population groups who are at increased risk of meningococcal disease.
In addition, MenACWY (quadrivalent meningococcal) vaccine is recommended for people who are:
- planning travel to, or living in, parts of the world where epidemics of serogroup A, C, W-135 or Y meningococcal disease occur, particularly the ‘meningitis belt’ of sub-Saharan Africa 15
- planning travel to mass gatherings, such as pilgrims travelling to the Hajj in Saudi Arabia
Seek up-to-date epidemiological information to determine whether a traveller needs meningococcal vaccination. See Accessing up-to-date travel information.
The Saudi Arabian authorities require that all pilgrims travelling to Mecca (for the Hajj or Umra) have evidence of recent vaccination with the quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine. 16 See Requirements for travellers to Mecca and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
See also Meningococcal disease .
Poliomyelitis
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against polio (see Poliomyelitis ).
If the person is travelling to a country where wild poliovirus is still circulating, they should receive inactivated poliovirus ( IPV ) vaccine if they have not completed a 3-dose primary course of any polio vaccine. Travellers who have completed the primary course should receive a single booster dose.
The World Health Organization (WHO) Global Polio Eradication Initiative website website has an up-to-date list of polio-affected countries.
Documented evidence of polio vaccination is not routinely required for travellers under the International Health Regulations. However, documented evidence of vaccination may be temporarily required according to WHO recommendations in response to new evidence of the spread of wild poliovirus (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries and Documentation and certificates ).
International polio epidemiology and associated travel requirements can change. Check the Australian Government Department of Health website for current recommendations for Australian travellers .
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against COVID-19. Foreign governments may require evidence of COVID-19 vaccination before a traveller is allowed to enter. The Australian-issued International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate is a secure way to prove COVID-19 vaccination history that has been developed to meet agreed international travel standards. Parents and carers of children <14 years of age, adolescents ≥14 years of age and adults can get a copy of their COVID-19 vaccination certificate at any time:
- using their Medicare online account through myGov
- through the Medicare Express Plus mobile app
- by calling 1800 653 809 (free call)
See also COVID-19 .
Vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
Use a risk assessment approach when recommending travel vaccines. Weigh the potential risks of disease exposure and protective benefits from vaccination against potential adverse effects, and the non-financial and financial costs of vaccination.
Prioritise vaccines for diseases that are:
- common and of significant impact, such as influenza and hepatitis A
- less common, but have severe potential adverse outcomes, such as Japanese encephalitis and rabies
Consider booster doses, where appropriate (see disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations). If the person is departing for travel soon, consider an accelerated schedule, if appropriate, such as for hepatitis B vaccine or the combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccine (see Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B ). Although immunity may be established sooner with the accelerated schedule, people who receive an accelerated schedule need another dose about a year later to complete the course and ensure long-term protection.
Most travellers do not need cholera vaccine. 16,17 The risk of a traveller acquiring cholera is very low if they avoid contaminated food and water.
No country requires travellers to have certification of cholera vaccination. No country has official entry requirements for cholera vaccination
See also Cholera .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for all travellers ≥1 year of age travelling to moderately or highly endemic countries (including all developing countries). The exceptions are people who have evidence of natural immunity after previous infection .
Normal human immunoglobulin is no longer used to protect travellers against hepatitis A.
See also Hepatitis A .
Japanese encephalitis
While now considered an emerging disease in Australia, Japanese Encephalitis is more likely in travellers to endemic regions overseas. 18 Japanese encephalitis ( JE ) vaccine is recommended for travellers spending a month or more in endemic areas in Asia, Papua New Guinea or the outer islands of Torres Strait during the JE virus transmission season.
Consider JE vaccination for shorter-term travellers, particularly if:
- travel is during the wet season
- travel may be repeated
- the person will spend a lot of time outdoors
- the person’s accommodation has no air-conditioning, screens or bed nets
Check a reputable source before travel for information about JE virus activity — for example, Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’) . 19
A traveller’s overall risk of acquiring JE in these JE - endemic countries is likely to be low (<1 case per 1 million travellers). Determine the specific risk according to the: 17
- season of travel
- regions visited
- duration of travel
- extent of outdoor activity
- extent to which the person avoids mosquito bites
See also Japanese encephalitis .
Before travel to rabies- endemic regions, advise people about:
- the risk of rabies infection
- avoiding close contact with wild, stray and domestic animals — especially dogs, cats, monkeys and bats
- the importance of appropriate immediate wound care of all animal bites and scratches
See also Rabies and other lyssaviruses, including Australian bat lyssavirus .
Recommendations for rabies vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
When deciding whether to give a pre-travel prophylactic rabies vaccination, assess the:
- likelihood of exposure to potentially rabid animals
- access to appropriate health care and availability of post-exposure prophylaxis , including rabies immunoglobulin , should there be an at-risk exposure
- timeliness of access to health care after exposure
Use a lower threshold for recommending rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis for children travelling to endemic areas.
Benefits of vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
Pre-travel rabies vaccination:
- ensures that the traveller has received a safe and efficacious vaccine
- simplifies the management of a subsequent exposure because the person will need fewer doses of vaccine
- means that rabies immunoglobulin — which is often extremely expensive, and difficult or even impossible to obtain in many developing countries — is not needed
- reduces the urgency of post-exposure prophylaxis
Mpox is a viral zoonotic illness caused by monkeypox virus . Previously, mpox was endemic to rainforest areas of Central and West Africa. Since 2022, there has been a multi-country outbreak in regions that are not endemic for mpox, including Australia. Mpox is often transmitted through close, sustained physical contact, with cases in the global outbreak primarily involving sexual contact.
Vaccination is recommended only for specific population groups at risk of exposure (See Mpox ). If travellers are eligible for mpox vaccination, they should receive two doses of mpox MVA-BN vaccine (JYNNEOS) before travel.
Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is caused by a tick-borne RNA flavivirus. The disease may involve the central nervous system. TBE is prevalent in parts of central and northern European temperate regions, and across northern Asia. Travellers are at risk when hiking or camping in forested areas in endemic regions during the summer months.
Safe and effective vaccines are available. Vaccination is recommended only for people with a high risk of exposure.
TBE vaccine is not registered in Australia, but a small stock of vaccine may be available for use under the Special Access Scheme .
Tuberculosis
Vaccination with BCG (bacille Calmette–Guérin) vaccine is generally recommended for tuberculin-negative children <5 years of age who will be staying in high-risk countries for an extended period (3 months or longer).
Vaccinating older children and adults appears to be less beneficial. However, consider vaccinating tuberculin-negative children aged ≥5 years but <16 years who may be living or travelling for long periods in high-risk countries.
A high-risk country is one that has a tuberculosis incidence of >40 per 100,000 population.
For travellers who need BCG vaccine, consider the following precautions when scheduling their vaccination visits:
- If possible, give BCG vaccine at least 3 months before the person will arrive in an endemic area.
- Give other live viral vaccines (for example, MMR , varicella, yellow fever) at the same time or with a minimum 4-week interval after BCG vaccination.
- A tuberculin skin test (TST; Mantoux), performed by trained and accredited healthcare practitioners, is recommended before receiving BCG vaccine for all individuals (except infants aged <6 months).
- People may suppress reactions to tuberculin for 4–6 weeks after viral infections or live viral vaccines, particularly measles infection and measles-containing vaccines.
State and territory tuberculosis services can provide tuberculin skin tests and BCG vaccine.
See also Tuberculosis .
Typhoid vaccine may be recommended for travellers ≥2 years of age travelling to endemic regions, including:
- the Indian subcontinent
- most Southeast Asian countries
- several South Pacific nations, including Papua New Guinea
This advice is also relevant for those travelling to endemic regions to visit friends and relatives.
Inactivated parenteral and live oral typhoid vaccine formulations are available.
See also Typhoid fever .
Yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccine is recommended for all people ≥9 months of age travelling to, or living in, an area with a risk of yellow fever virus transmission. 20
To minimise the risk of introducing yellow fever, some countries require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination for entry, in line with the International Health Regulations (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries ).
When assessing the need for yellow fever vaccination, consider:
- the risk of the person being infected with yellow fever virus
- country entry requirements
- individual factors such as age, pregnancy and underlying medical conditions
Vaccination is generally not recommended for travel to areas with a low probability of yellow fever virus exposure — that is:
- where human yellow fever cases have never been reported
- where evidence suggests only low levels of yellow fever virus transmission in the past
However, consider vaccination for a small subset of travellers to lower-risk areas who are at increased risk of exposure to mosquitoes or who are unable to avoid mosquito bites. 20
People aged ≥60 years are at increased risk of severe adverse events after primary yellow fever vaccination. Weigh the adverse effects of vaccinating people in this age group against the potential for yellow fever virus exposure and, in turn, the benefits of vaccination. 17
See also Yellow fever .
Booster doses
Most people do not need a booster dose of yellow fever vaccine. A single dose induces protective antibody levels that last for many decades. However, certain people are recommended to receive a booster if their last dose was more than 10 years ago and they are at ongoing risk of yellow fever virus infection . See Yellow fever .
Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries
Yellow fever requirements.
The International Health Regulations require yellow fever vaccination for travelling in certain circumstances. This is to:
- protect travellers who are likely to be exposed to yellow fever
- stop importation of the virus into countries that have the relevant vectors (see Yellow fever ).
Some countries may require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination as a condition of entry or exit (see Planning and documenting vaccines ). This includes countries that do not currently have yellow fever circulating.
Australia’s yellow fever travel requirements are detailed in the Australian Government Department of Health’s yellow fever fact sheet .
Contact the relevant embassies or consulates in Australia to confirm the entry requirements for yellow fever vaccination for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through.
Requirements for travellers to Mecca
Each year, Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Health publishes the requirements and recommendations for entry visas for travellers on pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj and Umra). 16
For pilgrims travelling directly from Australia, only evidence of MenACWY vaccination is currently mandatory. However, check the current requirements when advising prospective Hajj and Umra pilgrims (see Meningococcal disease and Accessing up-to-date travel information ).
Temporary requirements
The International Health Regulations may temporarily introduce requirements for other vaccine-preventable diseases in response to changes in disease epidemiology that are of international health concern. An example is for polio vaccination.
Because country vaccination requirements are subject to change at any time, confirm all current vaccination requirements for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through before travel. See Poliomyelitis and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Planning and documenting vaccines
Ideally, start vaccination courses early enough before departure to allow:
- monitoring of any possible adverse events
- time for adequate immunity to develop
Requirements for multiple vaccines
A traveller may need multiple vaccines before they depart. Apply the standard recommendations and precautions when giving multiple vaccines (see Administration of vaccines ).
A traveller may need more than 1 clinic visit if they need multiple vaccines or doses (for example, rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis or hepatitis B vaccine). Pay special attention to scheduling of these visits, and consider:
- dose interval precautions (for example, for multiple live vaccines)
- requirements for pre-vaccination tests (for example, tuberculin skin test)
- potential interference by some antimalarials, if relevant (for example, rabies vaccine)
Documentation and certificates
It is important to document travel vaccines:
- in the clinic’s record
- in the traveller’s record that they can carry with them
- on the Australian Immunisation Register
The record should also include all the other routinely recommended vaccines that the traveller has ever received.
For yellow fever vaccination, a traveller needs to have an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), which only Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres can provide under the International Health Regulations (see Yellow fever ).
Travellers may also need an ICVP for other vaccine-preventable diseases, such as polio, based on temporary recommendations.
See also Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Vaccinating travellers with special risk factors
See Vaccination for women who are planning pregnancy, pregnant or breastfeeding , Vaccination for people who are immunocompromised and the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations for travellers who are pregnant or immunocompromised.
Accessing up-to-date travel information
International travellers’ health risks constantly change. Up-to-date information, and knowledge of the changing epidemiology and current outbreaks of infectious and emerging diseases are essential. Reliable online information sources include:
- World Health Organization (WHO) for disease outbreak news, and its Travel and health section for specific advice on travel and health, including travel vaccination recommendations
- Travelers’ health , United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Travel health information , Australian Government Department of Health
- Smartraveller , the Australian Government’s travel advisory and consular information service, which provides up-to-date advice about health, safety and other risks of specific destinations for Australian travellers
The following resources have comprehensive technical advice on international travel and health, including vaccination:
- the latest edition of WHO’s International travel and health
- the CDC’s Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’)
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 3401.0 – Overseas arrivals and departures, Australia, Mar 2018 (accessed May 2018).
- Paudel P, Raina C, Zwar N, et al. Risk activities and pre-travel health seeking practices of notified cases of imported infectious diseases in Australia. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24(5):tax044.
- Heywood AE, Watkins RE, Iamsirithaworn S, Nilvarangkul K, MacIntyre CR. A cross-sectional study of pre-travel health-seeking practices among travelers departing Sydney and Bangkok airports. BMC Public Health 2012;12:321.
- Chen LH, Leder K, Barbre KA, et al. Business travel-associated illness: a GeoSentinel analysis. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Angelo KM, Kozarsky PE, Ryan ET, Chen LH, Sotir MJ. What proportion of international travellers acquire a travel-related illness? A review of the literature. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24.
- Freedman DO, Weld LH, Kozarsky PE, et al. Spectrum of disease and relation to place of exposure among ill returned travelers. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354:119-30.
- Halstead SB, Hills SL, Dubischar K. Japanese encephalitis vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- Staples JE , Monath TP, Gershman MD, Barrett AD. Yellow fever vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Chapter 6: Vaccine-preventable diseases and vaccines . In: International travel and health. Geneva: WHO; 2017.
- Steffen R. Travel vaccine preventable diseases-updated logarithmic scale with monthly incidence rates. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Denholm JT, Thevarajan I. Tuberculosis and the traveller: evaluating and reducing risk through travel consultation. Journal of Travel Medicine 2016;23.
- Lachish T, Tenenboim S, Schwartz E. 35 - Humanitarian Aid Workers. In: Keystone JS, Kozarsky PE, Connor BA, et al., eds. Travel Medicine (Fourth Edition). London: Elsevier; 2019. (Accessed 6 July 2023). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323546966000355
- Leggat PA, Zwar NA, Hudson BJ. Hepatitis B risks and immunisation coverage amongst Australians travelling to Southeast Asia and East Asia. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease 2009;7:344-9.
- Winkler NE, Dey A, Quinn HE, et al. Australian vaccine preventable disease epidemiological review series: measles, 2012-2019. Commun Dis Intell (2018) 2022;46.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Epidemic meningitis control in countries of the African meningitis belt, 2017. Weekly Epidemiological Record 2018;93:173-84.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health: health conditions for travellers to Saudi Arabia for the pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) . 2017 (accessed May 2018).
- Freedman DO, Chen LH. Vaccines for International Travel. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2019;94:2314-39.
- Furuya-Kanamori L, Gyawali N, Mills DJ, et al. The Emergence of Japanese Encephalitis in Australia and the Implications for a Vaccination Strategy. Trop Med Infect Dis 2022;7.
- Hills SL, Rabe IB, Fischer M. Infectious diseases related to travel: Japanese encephalitis . In: CDC yellow book 2018: health information for international travel. New York: Oxford University Press; 2017.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health (accessed Apr 2018).
Page history
Updates to reflect new recommendations for RSV vaccines, Abrysvo and Arexvy.
Updates to reflect availability of the mpox vaccine, JYNNEOS. Updates to include recommendations for use of JYNNEOS in specific populations, including travellers in risk groups.
Minor updates to clinical guidance around routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas), including the addition of advice regarding COVID-19.
Editorial update to reflect changes to pneumococcal vaccine recommendations for older adults and people with medical risk factors.
Guidance on vaccination of travellers against measles, mumps and rubella updated to reflect advice in the Measles chapter.
Help us improve the Australian Immunisation Handbook
Printed content may be out of date. For up to date information, always refer to the digital version:
Subscribe to receive notifications regarding updates to the Australian Immunisation Handbook and changes to immunisation policy.
Help us improve
We are always looking for ways to improve our website, the NICC and mobile app.
Provide feedback
Acknowledgement
The Department of Health and Aged Care acknowledges First Nations peoples as the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia, and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to them and their cultures, and to all Elders both past and present.
© Commonwealth of Australia | Department of Health and Aged Care
Link , share or bookmark directly to this section of the page.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6-11 months, according to CDC's measles vaccination recommendations for international travel. In Indonesia poliovirus has been identified in the past year.
Prevention modalities: vaccination, medication, consultation. Hepatitis A. Contaminated food & water. Vaccination (2-dose vaccine): Recommended for most travelers. --Administer 2 doses, at least 6 months apart. --At least 1 dose should be given before travel. Consultation: Advise patient to wash hands frequently and avoid unsafe food and water.
If yellow fever vaccine is recommended or required for your destination, you'll need to go to a vaccine center authorized to give yellow fever vaccinations. Many yellow fever vaccine centers also provide other pre-travel health care services. Find an authorized US yellow fever vaccine center. Examples of Vaccines. Here is a list of possible ...
More. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
CDC uses Travel Health Notices (THNs) to inform travelers about global health risks during outbreaks, special events or gatherings, and natural disasters, and to provide advice about protective actions travelers can take to prevent infection or adverse health effects. ... make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List ...
CDC supports the Government of Indonesia to strengthen country-wide vaccine-preventable disease detection, surveillance, outbreak response, and vaccine delivery. This work helps reduce the risk of vaccine preventable disease burden in Indonesia. It also helps reduce the risk of travelers carrying diseases to other countries.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
Travelers can protect themselves against infection by taking the following steps. If you are eligible to get vaccinated for mpox, get two doses of vaccine before you travel. Use the Mpox Vaccine Locator to find out where you can get vaccinated. Avoid close, skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash that looks like mpox.
Adults who are unvaccinated against polio should complete a primary vaccination series of 3 doses: The first dose at any time. The second dose 1 to 2 months later. A third dose 6 to 12 months after the second dose. If an adult cannot complete the above series before traveling, an accelerated schedule (3 doses of IPV administered at least 4 ...
CDC recommends YF vaccination for travel to areas classified as having endemic or transitional risk (Maps 5-10 and 5-11). Because of changes in YF virus circulation, however, recommendations can change; therefore, before departure, travelers and clinicians should check CDC's destination pages for up-to-date YF vaccine information.
CDC/ Cynthia S. Goldsmith ... the smallpox vaccine can provide protection against infection from both ... Indonesia began screening travelers after an mpox case was reported in Singapore in May ...
Those who have been vaccinated against mpox in the past might only need one-top up dose, rather than two shots. Booster vaccine doses are typically recommended every two to 10 years if a person ...
As of August 21, 2024, there is no official call for general travelers to be vaccinated against mpox ahead of their trips. In 2022, the United States launched its Mpox Vaccine Equity Pilot Program ...
CDC has issued an updated Health Alert Network advisory for clinicians and public health departments and partners, as well as an updated Travel Health Notice, recommending travelers to DRC and neighboring countries to practice enhanced precautions. Through the State Department, our embassies are working to keep U.S. citizens abroad informed of ...
All entrants to Indonesia are currently required to follow the following health protocol on entry, in accordance with the latest Circular Letter No. 25/2022 issued by the National Taskforce to Combat COVID-19 (Satgas COVID-19) dated 01.09.2022: Indonesian Nationals: Obligation to provide proof of having received three doses of COVID-19 vaccination (=booster) for all entrants aged 18 ...
Vaccines for Travelers. Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places. Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you're ...
Indonesia will reimpose a Covid-19 testing requirement for travelers who haven't received their booster vaccine in order to curb a resurgence in cases. Starting from July 17, domestic travelers ...
If you decide to travel to Indonesia: Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to adjust your plans. Visit the websites for Badan Geologi (Indonesian Geological Agency, Indonesian language only) for the latest information from the Government of Indonesia on current natural disasters. Review the CDC's suggestions on how to ...
Restaurants in Indonesia are open. Bars in Indonesia are . Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Indonesia such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6-11 months, according to CDC's measles vaccination recommendations for international travel. Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book. Meningitis (Meningococcal disease)
Most cases are in: Bali, Kalimantan, Java, Nusa Tenggara, Papua, and Sumatra. Indonesia is a higher risk region. Vaccination is recommended. High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-term travelers and those who may come in contact with animals. Recommended for travel to all regions, both foreign and domestic.
The organization has signed off on the Emergency Use Listing process for both mpox vaccines and developed a regional response plan requiring $15 million, with $1.5 million released from the WHO ...
On Aug. 9, the W.H.O. invited vaccine manufacturers to apply for an emergency use listing, a prerequisite for international groups such as Gavi, a global vaccine alliance, to purchase and ...
Many years of research have led to the development of newer and safer vaccines for the now eradicated disease smallpox. Some of these vaccines have been approved in various countries for use against mpox. At present, WHO recommends use of MVA-BN or LC16 vaccines, or the ACAM2000 vaccine when the others are not available.
Healthcare in Indonesia. The standard of local medical care can be poor and some medical tests cannot be performed reliably. Psychological and psychiatric services are also limited. Good medical ...
The vaccine, initially developed against smallpox, should protect against mpox and all other members of that virus family, said Dr. Boghuma Titanji, an infectious diseases physician at Emory ...
Summary Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary for Consular Affairs Douglas Benning and Chief of the Traveler's Health Branch for the Centers for Disease Control Dr. Cindy Friedman discuss the October 25 presidential proclamation and how it changes requirements for foreign national travelers starting November 8, as well as the implementation of CDC's orders regarding vaccines, testing, and ...
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that all travellers are up-to-date with their routine vaccinations; measles, mumps, rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, polio, influenza and pneumococcal. These vaccinations are given as part of the National Immunisation Program (NIP).
Vaccinate all prospective travellers according to the recommended vaccination schedule appropriate for their age, underlying health conditions, occupation and lifestyle. Vaccines might include, for example, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for an older person, or hepatitis B vaccine for a first aid officer.
Vaccines recommended for travel and some specific groups. People in certain research jobs and travel situations may be exposed to dangerous or deadly diseases that are no longer common in the U.S. Because of the increased risk of disease exposure in these instances, these 9 non-routine vaccines are available, listed below by disease.