Warning notification: Warning
Unfortunately, you are using an outdated browser. Please, upgrade your browser to improve your experience with HSE. The list of supported browsers:

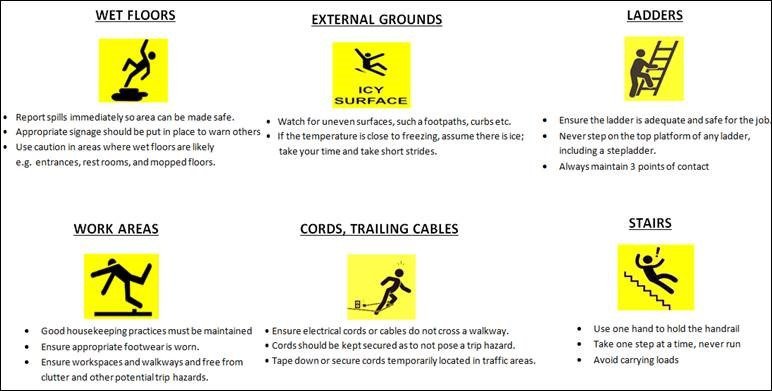
Slips, trips and falls
Slips, trips and falls are the main cause of accidents in the workplace that result in more than 3 days absence from work.
The main causes of slips, trips and falls includes:
- wet surfaces
- damaged flooring
- changes in level of floors
- slippery surfaces
- transition areas, for example, carpeted to tiled floor
- cables, mats and other floor obstructions
- overused warning or safety signs
- inadequate or inappropriate lighting
Fast facts - slips, trips and falls (PDF, 745 KB, 2 pages)
Check list - slips, trips and falls (Word, 43 KB, 4 pages)
- Safety guidance to prevent slips, trips, and falls (PDF, 424 KB)
Managers carrying out a risk assessment
You must ensure that slips, trips and falls are assessed as part of the risk assessment.
When carrying out the risk assessment, you should consider:
- the use of the premises
- the occupancy of the premises
- the services being supplied
- the activity that takes place
Related files
- Generic risk assessment form (Word, 33 KB, 2 pages)
- Generic risk assessment fillable form template (Word, 132 KB, 2 pages)
Contact HSE Health and Safety helpdesk
Use the Health and Safety self-service portal or
Phone: 1800 420 420
Monday to Friday 10.30am to 12 noon and 2.00pm to 3.30pm

Slips, Trips, And Falls Hazards | How To Prevent Them
Every year, countless individuals experience the unexpected mishap of a slip, trip, or fall. These incidents occur across all age groups and settings, from homes and public spaces to workplaces. While often brushed off as minor inconveniences or embarrassments, slips, trips, and falls can lead to serious injuries and significant financial and emotional costs.
The key to tackling this pervasive issue lies in understanding the factors contributing to these accidents and implementing effective prevention measures. In this blog, we delve into the causes of slips, trips, and falls, their impact, and, most importantly, how we can prevent them.
By understanding these risks, we empower ourselves to create safer environments, whether looking at the comfort of our homes, the safety of public spaces, or the well-being of employees in a workplace. This guide aims to heighten awareness, encourage preventive action, and highlight our shared responsibility in reducing the risks and consequences of slips, trips, and falls. Join us as we navigate through this important topic step by carefully step.
The Importance of Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls
The impact of slips, trips, and falls can be highly significant, from bruised shins to broken bones. These incidents aren’t just about physical injury. The repercussions can ripple outwards, affecting an individual’s quality of life, workability, and mental well-being. In the workplace, such accidents can lead to significant downtime, loss of productivity, and even legal implications for businesses. It’s estimated that the annual costs associated with occupational falls run into billions of dollars globally, impacting not just individuals but entire economies. Therefore, it’s clear that these everyday accidents are anything but trivial and that preventing them should be a top priority for everyone.
Basic Understanding of Slips, Trips, and Falls
To prevent these incidents, we first need to understand them. So, what exactly are slips, trips, and falls? A slip occurs when there is too little friction or traction between your footwear and the walking surface, leading to a loss of balance. A trip happens when your foot or lower leg hits an object, and your upper body continues moving, resulting in loss of balance. A fall can result from a slip or trip but can also occur due to other factors, like poor lighting, lack of handrails, or sudden illness.
Each of these incidents can occur under various circumstances. While some common causes include wet or uneven surfaces, poor footwear, and cluttered walkways, there can also be less obvious contributors, like insufficient training or awareness. This article aims to delve deeper into the world of slips, trips, and falls, elucidating their causes, impacts, and, most importantly, the strategies for prevention. The goal is not to instill fear but to inspire a culture of safety, vigilance, and proactive measures to keep everyone safe.

Definition and Differences: Slips, Trips, and Falls
While the terms ‘slips,’ ‘trips,’ and ‘falls’ are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct occurrences. As we’ve already discussed, a slip occurs when there is insufficient traction between your foot and the walking surface. This lack of grip may cause an imbalance, leading you to fall.
Trips, on the other hand, occur when your foot contacts an object in its path or drops unexpectedly, causing you to lose balance. A trip might occur due to clutter, an obstacle in the pathway, or an uneven walking surface.
Finally, a fall is a sudden, uncontrolled descent for various reasons, including slips, trips, loss of consciousness, or other health-related issues. Falls can occur on the same level (for example, falling on the floor) or from one level to another (like falling down the stairs or from a ladder).
Common Causes of Slips, Trips, and Falls
Understanding the common causes of these incidents is the first step toward prevention. Below are some major factors that often contribute to slips, trips, and falls.
- Wet or Oily Surfaces: One of the most common causes of slips is the presence of wet or oily surfaces. This might occur in areas prone to spills or leaks, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and certain industrial environments.
- Uneven Surfaces, Irregularities, and Obstacles: Uneven walking surfaces or irregularities such as potholes, cracks, or abrupt transitions can cause trips. Obstacles might include clutter, cords, open drawers, and other items that haven’t been stored properly.
- Poor Lighting Conditions: Inadequate lighting can make it difficult to see and avoid potential hazards like spills, obstacles, or changes in level. This can lead to both trips and falls.
- Weather Hazards: Outdoor slips and falls often increase during bad weather conditions such as rain, snow, or ice, which make surfaces slippery and vision less clear.
- Human Factors: Rushing, distraction, fatigue, or lack of proper training can also contribute to slips, trips, and falls. These can often be mitigated through awareness and training.
- Improper Footwear: Footwear unsuitable for the work environment or the current weather conditions can increase the risk of slips, trips, and falls. For example, smooth-soled shoes might not provide enough traction on a wet or oily surface, leading to slips.
- Loose or Unsecured Mats or Rugs: Unsecured mats, rugs, or carpets can shift underfoot or present tripping hazards with their edges.
- Improper Use of Equipment: This might involve using chairs instead of ladders, climbing on shelves, or not using safety equipment correctly, all of which can lead to falls.
- Poor Housekeeping: If work and walkway areas are not kept clean and orderly, they can contribute significantly to slips, trips, and falls. Examples include cluttered workspaces, cables across walkways, or spills not promptly cleaned up.
- Lack of Safety Training: Employees not properly trained on the correct job procedures, including safety equipment, can be at higher risk for accidents.
- Inadequate Maintenance: Neglecting maintenance can lead to hazards such as leaky pipes (leading to wet surfaces), potholes, or uneven flooring, which can cause slips, trips, and falls.
- Poorly Designed Walkways: Walkways with sudden drops, absence of handrails, sharp turns, or inadequate space can increase the risk of falls.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions like poor vision, balance disorders, or mobility problems can also increase the risk of slips, trips, and falls.
- Age: Both the very young and the elderly are at an increased risk for falls, partly due to factors such as lack of coordination, decreased strength, or reduced balance.
Remember, while this list of causes is extensive, it is not exhaustive. There may be other contributing factors depending on the specific circumstances or environment. That’s why it’s crucial to carry out regular risk assessments to promptly identify and address potential hazards.

Impact and Consequences Of Slips, Trips, And Falls
The impacts of slips, trips, and falls extend beyond the immediate event and can have lasting effects on the individuals involved and the organizations they belong to. These incidents can result in physical injuries, financial costs, and psychological distress.
Physical Injuries: From Minor to Severe
Physical injuries resulting from slips, trips, and falls can range from minor to severe. Minor injuries may include bruises, abrasions, or sprains. At the same time, more severe cases can lead to fractures, concussions, or even life-threatening injuries such as traumatic brain injuries or spinal cord damage.
In some cases, these incidents can lead to chronic pain or long-term disability, affecting the individual’s ability to perform daily activities or return to work. Falls, in particular, can be especially dangerous for older adults, leading to hip fractures or other serious injuries that significantly impact their independence and quality of life.
Financial Implications: Costs of Accidents
The financial implications of these incidents are also considerable. For individuals, this can include medical expenses, rehabilitation costs, and lost wages during recovery. Additionally, they might face expenses related to modifying their home for accessibility if the fall leads to a long-term disability.
For businesses, the financial costs can be substantial. There are indirect costs besides direct costs like medical expenses and workers’ compensation claims. These can include lost productivity due to employee absence, costs related to training replacement employees, and potential increases in insurance premiums. In severe cases, businesses may also face legal fees if they are negligent in providing a safe environment.
Psychological Implications: Fear and Anxiety After a Fall
The psychological impacts of slips, trips, and falls should not be underestimated. People who have experienced such an incident may develop a fear of falling again. This fear can limit their activities, reduce their independence, and decrease their quality of life.
Anxiety, depression, and social isolation can also result from the fear of falling or the consequences of an injury, such as disability. Employees may experience stress or anxiety about returning to work, especially if they feel the environment is unsafe.
Understanding these impacts highlights the importance of preventive measures to ensure safe environments, reducing the risk of slips, trips, and falls. The following sections will explore strategies to identify potential hazards and implement effective control measures.

Slips, Trips, And Falls Hazards Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is critical in preventing slips, trips, and falls. It involves identifying potential hazards, evaluating their risks, and determining appropriate control measures. A thorough risk assessment should consider all areas and activities in a given environment, from the home to the workplace.
Identifying High-Risk Areas in the Home or Workplace
High-risk areas vary depending on the setting. These might include staircases, bathrooms, and kitchens in the home, where wet surfaces are common. Outdoor areas like driveways or walkways can also present risks, especially in adverse weather conditions. Any area without sufficient support structures could be risky for older adults or those with mobility issues.
In the workplace, high-risk areas could be those with heavy foot traffic, wet or uneven surfaces, or places with lots of equipment and machinery. Industrial kitchens, construction sites , warehouses, and healthcare facilities are examples of workplace environments that often have high-risk areas.
Key Considerations for Risk Assessment
A comprehensive risk assessment should consider various factors. These include:
- The Environment: Assess the condition of the floors, lighting, staircases, and walkways. Look for hazards like wet surfaces, uneven floors, poor lighting, or lack of handrails.
- Human Factors: Consider the behavior and health of individuals in the environment. Are they rushing? Are they carrying heavy items that may obstruct their view? Do they have any health conditions that increase their risk?
- Tasks: Evaluate the tasks being performed. Does the job involve working at height, handling hazardous substances, or heavy physical labor? Are workers exposed to distractions or time pressure?
- Footwear and Clothing: Assess whether appropriate footwear and clothing are worn for specific environments and tasks.
- Previous Incidents: Look at the history of slips, trips, and falls in the environment. A pattern might indicate a persistent problem that needs addressing.
Importance of Regular Safety Audits
Regular safety audits are essential to maintain a safe environment. These audits involve routinely inspecting the environment and practices to ensure that safety measures are up-to-date and effectively implemented. They help identify new or overlooked hazards and assess the effectiveness of current control measures.
Regular audits also demonstrate a commitment to safety, which can encourage individuals to take responsibility for their safety and that of others. This fosters a proactive safety culture where hazards are promptly reported and addressed, further reducing the risk of slips, trips, and falls.

Prevention and Control Measures For Slips, Trips, And Falls
Once potential hazards have been identified through risk assessment, it’s crucial to implement prevention and control measures to mitigate these risks. This involves a range of strategies, from good housekeeping practices to installing safety features.
Housekeeping Best Practices
Proper housekeeping is one of the most effective ways to prevent slips, trips, and falls. Here are some best practices:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean floors regularly and immediately clean up any spills. Ensure to put up “wet floor” signs until the area is dry.
- Declutter: Keep walkways and work areas clear of clutter and obstacles.
- Proper Storage: Store materials and equipment properly when not in use.
- Maintenance: Promptly repair any damages to walkways and work areas, like cracks or uneven surfaces.
Installing Safety Features (Handrails, Non-Slip Mats, etc.)
Installing safety features can greatly reduce the risk of accidents. Here are a few examples:
- Handrails: Install sturdy handrails on all staircases and other areas where individuals may need extra support.
- Non-slip Mats: Use non-slip mats in areas prone to wet or slippery conditions.
- Guard Rails: Install guardrails around elevated platforms, mezzanines, and other fall hazards.
- Visible Markings: Use reflective tape or other visible markings to highlight changes in floor level or other hazards.

Appropriate Footwear for Different Surfaces
Wearing the right footwear can significantly reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls. Choose shoes with good traction, especially for wet or slippery surfaces. Protective footwear should be worn in workplaces where specific hazards are present, such as construction sites.
Prompt Removal or Correction of Identified Hazards
Address identified hazards as quickly as possible to prevent accidents. If a hazard cannot be immediately removed or corrected, ensure it is clearly marked, and individuals are informed about it until it can be addressed.
Adequate Lighting
Ensure all areas have sufficient lighting to allow individuals to see and avoid potential hazards. This is particularly important for stairways, hallways, and outdoor paths. Replace burnt-out bulbs promptly and consider installing automatic lights in often-used areas.
By implementing these prevention and control measures, you can greatly reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls, promoting a safer environment for everyone. In the next section, we’ll explore additional strategies and considerations specific to the workplace.

Workplace-Specific Considerations
While many of the principles of slips, trips, and falls prevention apply universally, certain considerations are particularly relevant to workplaces. These involve safety training, employer responsibilities, and industry-specific hazards.
Importance of Safety Training and Awareness Programs
Safety training is vital to workplace safety . Regular training sessions can ensure that employees are aware of potential hazards and the best practices for avoiding them. Training should cover topics such as proper use of equipment, safe handling of materials, and emergency procedures.
Awareness programs, too, can play a crucial role in maintaining a safe work environment. These programs could include regular safety reminders via bulletins, emails, or meetings, encouraging employees to be vigilant and proactive about safety.
Employer Responsibilities and Employee Rights
Employers have a responsibility to provide a safe work environment. This involves conducting regular risk assessments, addressing identified hazards promptly, and providing necessary safety training and equipment. They should also have procedures in place for reporting accidents or hazards and ensure that employees feel comfortable using these procedures without fear of retaliation.
Employees, on the other hand, have the right to a safe workplace and the right to speak up about safety concerns. They also have a role in maintaining safety by following established procedures, using provided safety equipment, and promptly reporting any hazards or incidents.
Industry-Specific Hazards and Control Measures
Every industry has its unique set of hazards, so it’s important to consider these when planning prevention and control measures. For example, spills and hot surfaces might be major hazards in a restaurant kitchen. Measures could include non-slip mats, appropriate footwear, and caution signs. In a construction site, falls from a height might be the primary concern, necessitating guardrails, safety harnesses, and fall arrest systems.
In conclusion, slips, trips, and falls are common but preventable incidents. By understanding their causes and impacts, conducting regular risk assessments, and implementing effective prevention and control measures, we can significantly reduce these accidents, fostering safer homes, workplaces, and communities.

The Role of Training in Preventing Slips, Trips , and Falls
Proper training programs are essential to educate employees on recognising hazards and taking preventive measures. Key training includes:
- Slips, Trips , and Falls Training: This program focuses on identifying potential slip, trip, and fall hazards, understanding the causes and learning preventive measures. Through online slips, trips, and falls training , employees can learn how to recognize and mitigate these risks effectively and promptly report such incidents.
- Hazard Awareness Training: General hazard awareness training helps employees recognize various workplace hazards, including those that could lead to slips, trips and falls. It promotes a culture of safety and vigilance.
- Housekeeping and Workplace Organi z ation: Training on maintaining a clean and organized workplace can prevent many trip hazards. This includes proper material storage, cable management and clear walkways.
- Emergency Response Training: Knowing how to respond in the event of a slip, trip or fall is crucial. This training covers first aid, emergency procedures and reporting protocols to ensure quick and effective response to incidents.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Training: Employees must know how to select, use and maintain their PPE. PPE training includes instructions on wearing non-slip footwear, gloves and other protective gear to minimize the risk of slips, trips and falls.
- Work at Height Training: Work at height course educates employees on the risks of working at heights and teaches safe practices for performing such tasks. This specialized training helps prevent severe injuries resulting from fall incidents.
Preventing slips, trips, and falls is no small task, but it is a crucial one. As we’ve explored in this guide, these incidents are far from trivial, carrying the potential for serious physical injuries, significant financial costs, and profound psychological impacts. Yet, armed with the knowledge of what causes these incidents and understanding their impacts, we’re already halfway towards prevention.
The steps to creating safer environments—at home, in public spaces, or at workplaces—aren’t overly complex. They begin with recognizing the potential hazards and involve a thoughtful blend of risk assessment, implementing practical measures, and fostering a culture of safety awareness. From basic housekeeping to installing safety features, each action reduces the risk.
It’s important to remember that the responsibility of preventing slips, trips, and falls doesn’t rest on a single individual or group—it’s a collective effort. Employers, employees, homeowners, and public facility managers all have roles to play. And in our various roles, we all contribute to a larger, shared goal: creating safer environments for everyone.
Preparing for and preventing these incidents can seem daunting in a world where the unexpected is expected. But, as we’ve seen, it’s not only possible; it’s a critical part of our commitment to safety for ourselves and others. Let this guide serve as a reminder and resource for that commitment, helping us make each step we take a safer one. Thank you for joining us on this journey towards safer environments and greater awareness. Let’s continue to take steps, big and small, toward a safer tomorrow.
- Workplace guidance
Slips, trips and falls
Common slip, trip and fall hazards.
Information on the common slip, trip and fall hazards in the workplace
People must be able to move around the workplace safely. Slips, trips and falls are among the most common causes of accidents and injury at work.
Visitors may also be at risk, both inside and outside premises under your control.
Most slips and trips are caused by:
- poor lighting
- trailing cables
- unsuitable floor coverings
- uneven or damaged floor surfaces
- contaminated floor surfaces, for example liquid or grease
- poor housekeeping, for example tripping or falling over something left in a walk way
When considering areas in your workplace that could cause a hazard, remember to take into account:
- any outdoor areas
- differing weather conditions
- working activities carried out off your premises
Carry out a risk assessment
The best way to identify slip, trip and fall hazards and ways to control them in your workplace is to discuss the issue with staff and carry out a risk assessment.
Object reference not set to an instance of an object.
Use the Slips Assessment Tool (SAT)
The SAT is a useful tool developed by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) that helps you assess the slip potential of pedestrian walkway surfaces.
- Next page: Slips, trips and falls - Slip, trip and fall safety precautions
We use cookies on this website which are essential for it to work. We also use non-essential cookies to help us improve our websites, which you can opt out of in cookie settings. Any data collected is anonymised. By continuing to use this site, you agree to our use of cookies.
Healthy, safe and productive lives and enterprises
- Accident and Dangerous Occurrence Reporting
- Accreditation
- Introduction
- Justification
- Irish Legislation, EU Directives & Standards
- Delivery Guide
- Design-Construction-Handover
- Functional Safety
- EPD Guidance
- International/European Committees
- National Projects
- Useful Links
- Useful Tools
- ATEX Regulations - Frequently Asked Questions
- What are Biological Agents?
- Classification of Biological Agents
- Biological Agents Frequently Asked Questions
- Good Occupational Hygiene
- Disinfectants
- Vaccination - Frequently Asked Questions
- Transporting Biological Agents
- Biological Agents and Reproductive Health
- Relevant Legislation
- Code of Practice
- Notification
- Accident, Incident and Disease Reporting
- Avian Influenza
- Blood Borne Viruses
- SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19
- Legionellosis
- Leptospirosis
- Lyme Disease
- Tuberculosis
- Microbiological Safety Cabinets
- Health Surveillance
- Occupational Exposure Lists
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Useful Resources
- Brexit and Access of Products to the EU Market
- Chemicals Export / Import Regulation
- Market Surveillance – Industrial Products
- Selling Goods on the EU Single Market after Brexit
- Transportable Pressure Equipment
- Further information
- Employer Policy
- Are You Being Bullied
- Codes of Practice
- Bullying Employer Perspective
- Bullying Employee Perspective
- Accident/Incident Reporting
- ADR and TPED
- Biological Agents
- Construction
- Other Licensing Agencies
- All Notification Forms
- Classification and Labelling
- Confined Spaces
- Consultation
- Display Screen Equipment
- Managing Safety in Schools
- Teacher Support and Resources
- Teacher Training
- Initiatives in Education
- Electrical Fatality Statistics
- Electricity in the Workplace
- Overhead Power Lines
- Underground Cables
- Video - Dangers from Power Lines on Farms
- Role of the Commission for Regulation of Utilities
- HSA & Other Organisations
- IS 10101 National Rules for Electrical Installation
- Works Needing Certification
- Employees Duties
- Fire Detection and Warning
- Emergency Escape and Fire Fighting
- Fire Prevention
- First Aid Frequently Asked Questions
- Electricity
- Pedestrian safety
- Manual Handling Hazards
Slips, Trips and Falls
- Working at Height
- Lone Workers
- Myth 1: Inspections and Fines
- Myth 2: Health and Safety is Expensive
- Myth 3: Red Tape Hindering Business
- Myth 4: Manual Handling Training
- Myth 5: Everything Banned
- Horticulture
- Human Factors
- Illness Reports
- HSA Inspections
- Recording Inspections
- What to Expect When the Inspector Calls
- Actions of Inspectors
- Powers of Inspectors
- Workplace Fatalities
- The Appeals Process
- Prosecutions 2018
- Prosecutions 2017
- Prosecutions 2016
- Prosecutions 2015
- Prosecutions 2014
- Prosecutions 2013
- Prosecutions 2012
- Prosecutions 2011
- Prosecutions 2010
- Prosecutions 2009
- Prosecutions 2008
- Prosecutions 2007
- On Indictment
- Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG)
- Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act 2005
- Safety and Health Management Systems
- Safety Representatives and Consultation
- Safety Statement and Risk Assessment
- Manual Handling Guidance Documents
- Manual Handling Case Study Video Series 1
- Manual Handling Case Study Video Series 2
- Manual Handling FAQ's
- Manual Handling Research reports
- Selling Goods on the EU Single Market
- Joint Market Surveillance Action on HARmonised Products 2021 Omnibus (JAHARP2021 Omnibus)
- Motor Factors
- Respiratory Protective Equipment
- Noise at Work
- Noise - Frequently Asked Questions
- Safe Maintenance - Reducing Noise
- Health Surveillance – Noise
- Vibration at Work
- HAV Risk Assessment
- Optical Radiation at Work
- Electromagnetic Fields
- Agency Roles
- Posted Workers
- Prosecutions
- Public Consultation
- Remote Working
- Safety Alerts
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Safety Signs
- General Simple Safety
- Simple Safety in Food and Drink
- Simple Safety in Retailing
- Simple Safety in other Languages
- STF Online Courses
- Further Information
- Mapping Hazards
- Stairs and Steps
- Slippery Surfaces
- Identify Risks
- Measuring Slip Resistance
- Selecting Surfaces
- Information with Flooring
- Metal and Profiled Surfaces
- Communicate
- Housekeeping
Shoes, Footwear
- Communication
- Sample Risk Assessment
Over-used Signs
- Fatal Injury
- Non-Fatal Injury and Illness
- Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing
- Mining and Quarrying
- Manufacturing
- Electricity; Gas, Steam and Air Conditioning Supply
- Water Supply, Sewerage, Waste Management and Remediation Activities
- Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Personal Goods
- Transportation and Storage
- Accommodation and Food Service Activities
- Information and Communication
- Financial and Insurance Activities
- Real Estate Activities
- Professional, Scientific and Technical Activities
- Administrative and Support Service Activities
- Public Administration and Defence; Compulsory Social Security
- Human Health and Social Work Activities
- Arts, Entertainment and Recreation
- Other Service Activities
- Annual Review of Workplace Injury, Illness and Fatality Statistics
- Other Statistical Reports
- European Statistics on Accidents at Work
- CSO Labour Force Survey Data
- Sun Protection
- Ventilation
- Guidance on Managing the Risk of Work-Related Violence and Aggression
- Overview / Introduction
- Risk Assessment
- What We See
- Control Measures for Workplace Violence and Aggression
- Reporting of Incidents and Legislative Requirements
- Additional Information
- Vulnerable Workers
- Welfare Payments
- Winter Readiness
- Work at Height
- Work Positive Project 2008/2009
- Work Positive Project 2005-2007
- Stress in the Workplace
- Legal Requirements
- Work Related Vehicle Statistics
- Vehicle Risks
- Forklift Trucks
- Transport of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR)
- Managing Health and Safety
- Liabilities of Directors
- Protecting your Workplace's Reputation and Assets
- Benefits of Creating a Positive Safety Culture
- Organising Safety and Health in your Workplace
- Safety and Health Monitoring
- Roles and Responsibilities for Directors
- Precautions & Risk Assessment
- Legislation & Enforcement
- Agriculture Code of Practice
- Online Risk Assessment FAQs
- Updated Agriculture Safety Videos
- Farm Safety Partnership Advisory Committee
- ATVs / Quad Bikes
- Guidance on the Safe Handling of Cattle on Farms
- Safe Handling of Cattle on Farms Information Sheet
- Cattle Handling in Marts and Lairages
- Children's Book 'Stay Safe on the Farm with Jessy'
- Farm Safety During Lambing
- Sábháilteacht Feirme le linn Breith Uain
- Farm Safety During Calving
- Sábháilteacht Feirme le linn Breith Lao
- Using Petrol Driven Chainsaws
- Chainsaw Felling of Large trees
- Selecting & Monitoring of Contractors
- Mechanical Harvesting
- Extraction by Forwarders
- Electricity at Work
- Chainsaw Snedding
- Cross Cutting & Manual Stacking
- Chainsaw Clearance of Windblow
- Felling & Manual Takedown
- Chainsaw Safety Training Advice
- Forest Owners & Managers who intend to fell trees - Info Sheet
- Code of Practice for Managing Safety & Health in Forestry Operations
- Child Tractor Safety
- Farmers over 65 Years
- Farm Safety Video for Post Primary Schools
- Falls & Collapses
- Farmer Health
- Fire Electricity & Chemicals
- Manual Handling Slips & Trips
- Timber Work
- Video Index
- Online Farm Safety Course
- FarmFamilyCPD.ie
- Hospitality General
- Leisure Areas
- Larger Machinery
- Simple Safety
- Role Finder Tool
- Chemicals A-Z
- BeSmart Risk Assessment Tool
- Chemicals Act Guidance
- ECHA Guidance & FAQs
- ECHA Website
- ECHA Webinars
- E-Bulletin Archive
- Helpdesk Information
- Pesticides Control
- Poison Centre
- ADR - Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- What is Asbestos
- Asbestos Surveys
- Latest News
- Safety Alert
- Asbestos FAQs
- Asbestos risks in safes and fire resistant cabinets
- E-Learning Course
- Asbestos Legislation
- Restrictions and Exemptions
- Guidance Document
- Asbestos Removal
- Analysts and Laboratories
- Asbestos Notifications
- Asbestos Waivers
- Other Agencies with Responsibility for Asbestos
- The Chemicals Act
- What are Chemicals Agents?
- What are Carcinogens, Mutagens and Reprotoxic Substances ?
- Hazardous Medicinal Products (HMPs)
- Roadmap on Carcinogens
- REACH Restriction
- Information for Suppliers and Retailers
- Training Requirements
- Posters (Available in Several Languages)
- Health Surveillance and Monitoring
- Introduction to Welding
- Welding Risk Assessment
- Case Studies
- Chemical Agents Legislation
- Carcinogens, Mutagens and Reprotoxic Substances Legislation
- Chemical Weapons
- Classification
- Introductory Guidance on the CLP Regulation
- CLP Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
- Understanding CLP
- Publications and Guidelines
- External Resources
- Health Hazards
- Environmental Hazards
- Notification to NPIC
- Notification to the C&L Inventory
- Roles and Duties
- Introduction to COMAH
- Legislation
- Inspections
- Useful Links on Major Accidents
- Notifications
- MAPP and Safety Management
- Safety Report
- Timelines for Submission of COMAH Documentation
- Significant Modifications
- Reporting COMAH Accidents
- Information to the Public Overview
- List of all Establishments by Tier
- Lower Tier Establishments by County
- Upper Tier Establishments by County
- Objectives of Emergency Plans
- Testing and Review of Emergency Plans
- Local Competent Authority Annual Report
- Internal Emergency Planning
- External Emergency Planning
- Role of the HSA in Land-use Planning
- Consultation Distance
- Societal Risk
- Request for Technical Advice
- HSA Approach to Land Use Planning
- COMAH Regulations 2015
- Guidance on Technical Land-use Planning Advice
- Intermediate Temporary Storage
- LCA Annual Report on Activities
- Electronic Notification
- Request for TLUP Advice
- Schedule 7 Notifiable Incident
- LCA Annual Report of Activities
- News Updates
- What are Detergents
- Detergent Regulations
- Detergent Labelling & Packaging requirements
- Using and Storing Detergents
- Ingredient Data Sheets
- Liquid Laundry Detergent Capsules
- Biocidal detergent products
- EU Derogation for Surfactants
- DNAs in Ireland
- Obligations of EU Exporters
- Obligations of EU Importers
- Chemicals Subject to Export/Import Notification
- The Role of the Authority
- Nanomaterials
- Roles and duties under REACH
- SVHCs and Authorisation
- How does a chemical get onto Annex XVII of REACH
- Annex XVII Updates of REACH
- Information in the Supply Chain
- Notification of Substances in Articles
- The registration process
- Only representative
- Duty to inquire
- Downstream users
- Questions and Answers
- European Commission adopts EU wide restriction on cyclosiloxanes (D4, D5 and D6)
- Inspectors will check classification and labelling of mixtures in products
- ECHA adds another substance to the Candidate List
- European Commission updates REACH Restrictions Roadmap
- ECHA publishes fact sheet for candle makers
- PFAS restriction proposal
- HSA information sheet on regulatory obligations of EU candle and reed diffuser producers
- Mandatory Training requirements for Professional and industrial users of Diisocyanates
- Selling chemical products online
- Poison Centre Notification
- Obligations for producers of candles/diffusers
- Safety Data Sheets
- Keep your registration up to date
- Chemical Risk Assessment
- Read the back
- REACH Authorisation List
- REACH Candidate List
- Paint containing MEKO
- Candles and reed diffusers containing LILIAL
- ECHA & EU Consultations
- HSA Consultations
- Project Supervisor Design Process (PSDP)
- Project Supervisor Construction Stage (PSCS)
- Contractors
- Create a Site Specific Safety Statement
- Create a Construction Stage Safety and Health Plan
- Risk Assessment Method Statement (RAMS) Template and Guidance
- Create a Construction Site Traffic Management Plan
- Information for Employees
- Other Useful Resources
- hsalearning.ie for Construction
- Construction Skills Certification Scheme (CSCS)
- Duties as a Designer
- Good Design Practice
- Construction Site Traffic Management Plan
- Safe use of Dumpers
- The Lighthouse Club
- Construction Workers Health Trust
- CAIRDE On Site. In Mind.
- Construction Safety Partnership Advisory Committee
- Construction Regulations Amendment 2019
- Auxiliary Devices
- Safety File
- Excavations
- Diving at Work
- Hiring Diving Contractors
- Diving Methods
- Dive Team Size
- Diving Training
- Compression Chambers
- Emergency Equipment
- Diving Medicals
- Fitness to Dive
- Mutual Recognition
- Diving and Pregnancy
- Reporting Accidents and Dangerous Occurrences
- Underwater Heritage Orders
- Health and Safety Management
- Emergency Plans
- Docks Code of Practice
- Common Hazards
- Container Terminals
- Dry Bulk Terminals
- Roll On Roll Off (Ro-Ro) Terminals
- Useful Websites & Publications
- Legislation and Enforcement
- Who's Who in Fishing Safety
- Maritime Legislation
- Top 10 Tips
- Management of Health and Safety
- Emergency Contacts
- The Safety Statement
- Safe Systems of Work
- Instruction, Training and Supervision
- Injuries and Ill Health
- Slips and Trips
- Manual Handling
- Dangerous Chemicals
- Instability
- Publications and Useful Websites
- Lifejackets
- Regulations
- Information and Guidance
- The Health and Social Care Sector
- Health and Social Care Regulators
- Health and Social Care Illness and Injury Statistics
- Sharps Directive and Regulations
- Healthcare Waste
- Specific Biological Agents
- Chemical Agents
- Electricity and Healthcare
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Slips Trips and Falls in Healthcare
- Work Related Stress
- Violence and Aggression
- Work Equipment
- Emergency Department
- Ambulance Services
- Outpatients
- Stores / Warehouse
- Technical Services
- Maintenance Workshop
- Lounge / Activity Room
- Sluice Room
- Garden / Grounds
- Nurse's Station
- Hallway / Corridor
- Mining Legislation and Notifications
- Promotional Activities
- Disused Mines and Shafts
- Mines Rescue
- Mining in Ireland
- Mining Techniques Used in Ireland
- Managing for Health and Safety
- Health and Safety in Education Sector
- Health and Safety in Central Government
- Health and Safety in Local Government
- Heath and Safety in Healthcare Sector
- HSALearning
- Healthy Ireland
- State Claims Agency
- Chemical Exposure
- Dust Including Silica Dust
- Noise in Quarries
- Whole Body Vibration
- Muscoskeletal injury
- Quarry Accident and Inspection Statistics
- What to Expect from an Inspection
- HSA Quarry Sector Resources
- Safe Quarry Guidance
- Statutory Notifications
- Quarries Legislation and Guidance
- Quarry Workers Guide
- Other Quarry Industry Groups
- Publications and Videos
- Quarry Safety Week
- All Island Seminar 2018 Exhibitors Info
- All Island Seminar 2018 Delegates
- Vehicle Access
- Driver Selection and Training
- Construction of Haul Roads
- Reversing and One-way Systems
- Selection of Equipment
- Inspection of the Working Face
- Significant Hazards
- Overburden Stripping
- Trespass, Boundary Fencing and Prevention of Drowning
- Drilling of Shotholes
- Danger Zones
- Disposal of Surplus Explosives
- Blast Specification
- Duties of Shotfirer
- Face Profiling and Drill Hole Logging
- Edge Protection during drilling and loading
- Management of Lagoons and settling ponds
- Management of Tips and Stockpiles
- Inspection, Appraisal and Geotechnical assessment
- Asphalt Plant Safety
- Machinery and Conveyor Initiative 2020
- Work Permits and Isolation of Equipment
- Tyre Changing and Repair
- Workshop Safety
- Maintenance Work at Height
- Guarding Return Idler Rollers
- Mobile Crushing and Sizing
- Conveyor Guarding and stops - pull wires
- Clearing Blocked Crushers
- Batching Concrete, Block and Asphalt Plants
- Renewable Energy
- Taking Care of Business
- Getting Started
- Safety Statement
- Recommended Publications
- Micro Business
- Vehicle Incident Trends
- Work Related Vehicle Safety
- Workplace Transport Safety
- Working on or near a road
- Driving for work
- Vehicle Maintenance
- Chemical Agents and Carcinogens
- Information to the Public
- Export / Import
- Nanotechnology
- Chemicals Acts 2008 and 2010
- Chemical Weapons Act 1997
- Organisation of Working Time Act 1997
- Safety Health and Welfare (Offshore Installations) Act 1987
- Safety in Industry Act 1980
- Dangerous Substances Act 1972
- European Communities Act 1972
- Factories Act 1955
- Code of Practice for the Chemical Agents Regulations
- Code of Practice for Preventing Injury and Ill health in Agriculture
- Farm Safety Code of Practice - Risk Assessment document
- Code of Practice for the Design and Installation of Anchors
- Code of Practice for Working in Confined Spaces
- Working on Roads Code of Practice - for contractors with three or less employees
- Code of Practice for Avoiding Danger from Underground Services
- Code of Practice for Safety in Roofwork
- Code Of Practice for Biological Agents
- More Codes of Practice
- Online Complaint Form
- Agriculture
- Chemical and Hazardous Substances
- Docks and Ports
- General Application Regulations
- Health and Social Care Sector
- Information Sheets
- Latest Publications
- Machinery and Work Equipment
- Manual Handling and Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Mines and Quarries
- Occupational Health
- Physical Agents
- Research Publications
- Safe System of Work Plan (SSWP)
- Safety and Health Management
- Slips Trips and Falls
- Work Related Vehicles
- EU Weekly RAPEX Alerts
- The Benefits
- Risk Assessments Made Easy
- Safety Statements Made Simple
- hsalearning.ie
- Work Positive
- Small Business Courses
- Managing Hazards in the Workplace
- Publications, Top Tips and Videos
- Workplace Health Toolkit for Businesses
- Simple Safety Series
- Safety Representatives
- New Publications and Resources
- Resources in Different Languages
- Post-Primary Guidelines
- Post-Primary Guidelines - Safety Statement Checklist Word Documents
- Post-Primary Guidelines - Safety Statement Checklist PDFs
- Post-Primary Guidelines - Part B - FAQs
- Post-Primary Guidelines - Part C - Risk Assessment Templates
- Primary Schools Guidelines - Short Guide
- Primary Schools Guidelines
- BeSMART.ie Primary Schools
- Video on Primary School Guidelines
- Interactive Risk Assessments – Primary
- Treoirlínte ar Bhainistiú Sábháilteachta, Sláinte agus Leasa i mBunscoileanna
- Treoirlínte maidir le Bainistiú Sábháilteachta, Sláinte agus Leasa in Iar-Bhunscoileanna
- 'What's Under the Sink?' Household Chemicals SPHE Presentation – Primary students
- 'What's Under the Sink?' – Primary teacher guidelines
- Farm Safety Presentation - Primary teachers
- On the Farm Videos - Primary students
- Choose Safety / Get Safe Work Safe - Transition Year teachers / students
- Choose Safety – Post Primary / Further Education
- Keep Safe on the Farm – Post Primary students
- Graduate.ie – Post Primary students
- Roghnaigh an tSábháilteacht
- Post Primary
- Choose Safety
- Courses for Apprentices on hsalearning
- Workplace Health and Safety Induction hsalearning course
- Get Safe Work Safe hsalearning course
- Mainstreaming
- Only a Giant can Lift a Bull
- Too Cold for Sharks
- Health and Safety Training Providers
- Online Course for Schools
- Online Courses for Students
- Your Safety, Health and Welfare in Healthcare - Online Course
- Online Course Information Leaflets
- Safety, Health and Welfare Induction
- New Resources
- Translated Resources
- Work Related Vehicles Safety Program Plan and Priorities for 2016-2018
- Public Consultation on new Code of Practice - Safe Industrial Truck Operation
- Vehicle Related Accident Trends
- Falls from Vehicles
- Vehicle Overturns
- How to Manage Work Related Road Risks
- Online Vehicle Risk Management Resource (EU Commission)
- Winter Driving Tips
- Grey Fleet Driver Declaration Form
- Managing Grey Fleet Information Sheet
- HSA and UCD joint webinar on Work Related Road Fatalities
- Employer Responsibilities
- Online Course
- Driver Health
- Driver Handbook
- Road Safety Law
- Managing Your Employees
- How to Manage Driving for Work
- Evaluating Road Safety Risks Movie
- Benefits for the Community
- Vehicle Safety Pre-Checks
- Vehicle Risk Management Business Case Studies
- New Guidance – Safe and Efficient Goods Reception for Road Freight
- Managing Workplace Priority Risks
- Workplace Transport E-Learning Courses
- Managing Pedestrians at Work
- Warehousing Safety
- Guidance and Publications
- Load Securing Videos
- Working on Roads Guidelines
- Safety in Road Work Zones - PRAISE Report 2011
- Guidance and Information
- Transport & Storage Sector Incident Trends
- Behaviour Based Safety Guide Part 1
- Behaviour Based Safety Guide Part 2
- Top Ten Tips for Behavioual Safety - Factsheet
- Are you being Bullied ?
- Bullying - Employer Perspective
- Bullying - Employee Perspective
- Ergonomic Risk Assessment Tools
- Manual Handling Videos Series 1
- Manual Handling Videos Series 2
- BeSMART Videos
- Miscellaneous Videos
- Infographics
- Display Screen Equipment FAQs
- Manual Handling FAQs
- Manual Handling Training System FAQs
- Other Links
- Further Reading and Information
- Occupational Dermatitis Frequently Asked Questions
- Occupational Asthma Frequently Asked Questions
- Pregnant at Work Frequently Asked Questions
- Workplace Stress (AKA Work-Related Stress)
- The Role of the HSA
- What is WorkPositiveCI
- What Workplace Stressors does WorkPositiveCI Measure
- How to Implement WorkPositiveCI in your Workplace
- Guidance - Work-related Stress a Guide for Employers
- Guidance - Work-related Stress Information Sheet for Employees
- Managing Psychosocial Hazards in the Workplace Information Sheet
- Healthcare - Work-related Stress Webpage
- Homeworking - Managing Stress whilst Working from Home
- Podcast - Questions and Answers on Stress and Bullying at Work
- HSE (UK) Management Standards on Work-related Stress
- Job Stress and Working Conditions Report (2019) ERSI
- Healthcare - Work Related Stress Mental Health Promotion in the Healthcare Sector (EU OHSA)
- Practical Advice for Workers on Tackling Work-Related Stress and its Causes (EU OSHA)
- Critical Incident Stress Management Network Ireland
- Board Vacancies
- General Information for Applicants
- Working with the HSA
- Recruitment Policy
- About the HSA
- Social Media
- Webinar Recordings
- Previous Events
- Workers' Memorial Day
- Press Releases 2024
- Media Queries
- Newsletters & Bulletins
- Focal Point Network
- European Healthy Workplaces Campaign 2023-2025
- European Healthy Workplaces Campaign 2020-2022
- European Healthy Workplaces Campaign 2018-2019
- European Healthy Workplaces Campaign 2016-2017
- Good Practice Awards
- European Union Senior Labour Inspectors Committee (SLIC)
- HSA on Facebook
- HSA on YouTube
- HSA on LinkedIn
- HSA on Twitter
- Press Releases 2023
- Press Releases 2022
- Press Releases 2021
- Press Releases 2020
- Press Releases 2019
- Press Releases 2018
- Press Releases 2017
- Press Releases 2016
- Press Releases 2015
- Press Releases 2014
- Press Releases 2013
- Media Campaigns
- Board Member Profiles
- Organisational Structure
- Vision, Mission and Mandate
- Strategic Priorities
- Prompt Payment Details
- Purchase Orders in Excess of €20,000
- Financial Statements and Reports
- Why Contact the HSA Contact Centre
- HSA Contact Centre Service Levels
- Make a Complaint
- Protected Disclosures Annual Report
- HSA Contact Centre
- Protected Disclosures
Please Note
Our website uses cookies to enhance your browsing experience and to collect information about how you use this site to improve our service to you. By not accepting cookies some elements of the site, such as video, will not work. Please visit our Cookie Policy page for more information on how we use cookies.
- News, Events & Media
- Customer Service
- RSS News Feed
- Follow HSA on Twitter
- Subscribe to our newsletter
- Your Industry
- Publications and Forms
- Employer and Employee Supports
- Vehicles at Work
- Workplace Health
- Slips Trips Falls
Every working day seven people are hurt in work slips, trips and falls (STF)
- See a systematic approach to Slip Risk Assessment and Prevention
- See our online training on Slips, Trips and Falls and Safer Stairs and Steps
- See our Information Sheets on Preventing Work STF , Safer Work Stairs and Steps , Preventing Vehicles STF and Choosing Slip-resistant Footwear
- See our internet sections on STF Info , High-risk Areas , Spills , Pedestrian Surfaces , Environmental Cleanliness , Footwear , Ice and Over-used Signs
Submission completed, thank you!
Slips trips falls info, high-risk areas.
Pedestrian Surfaces
Environmental cleanliness.
- Floor Wet Cleaning
Snow and Ice
Subscribe to hsa publications, subscribe to hsa chemicals publications.

Slips, trips and falls Risk Assessment

A comprehensive Risk Assessment covering slips, trips and falls, highlights the potential risks and control measures to reduce the likelihood of injury
This document is:
- Recognised by local authorities
- Recognised by principal contractors
- Suitable for CDM sites
- Approved by H&S managers
It increases your chance of winning tenders and has been written by trained health and safety professionals.
If you want others to have confidence in your company, download and buy the proper documents today.
As with all our documents, our risk assessments are in Word™ format and available for instant download and use. You only need to buy them once.
Once you buy and download this document, it's yours for life to use repeatedly.
Download today's risk assessment, put your company details on, and use it immediately.
Give people confidence in you, your company, your products and services.
Some sample text from this document reads:
' Natural hazards'
• Staff and public members suffer various injuries from slips, trips and falls due to natural hazards.
• Natural hazards such as leaves, blossom, snow and hail to be cleaned up at regular intervals
• Natural occurrences such as lichen, moss and grass infringement on paths and walkways to be included in planned maintenance works
• Prevention remedies such as grit and salt to be used when relevant weather predictions are in place
GET THIS DOCUMENT
£8.99 +VAT
- Available in Word™
- Fully customisable
- Add your Company Logo
- UK & EU Compliant
What Our Customers Think
Direct links, our company, our quality, our policies.

© 2024 HSE Docs
Secure design by Webforward
Modal title
Fill in the box below now to receive your completely free document. your browser will then download it to your computer..
HSE Docs is strongly committed to protecting the personal data of our customers. Your name and email are your personal contact details and we protect that privacy and don't knowingly share your information with third parties. We comply with the EUs General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and will continue to do so. We don't currently send out marketing emails, but should we do in the future, you will always have the opportunity to opt out of any correspondence we send.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Prevent contamination getting on floor. Stop contamination getting on to the floor, remember a smooth, clean, dry floor, is rarely a slip risk. Review work activities - Contamination comes in various forms, fluids, swarf, saw dust, food and drink, polythene, cardboard. It is usually created by the work activity, so an assessment of the activity and way in which people work is essential if it ...
Vulnerability disclosure. All content is available under the Open Government Licence v3.0, except where otherwise stated. HSE explains how to prevent slips and trips in the workplace. Looks at the causes of slips and trips and discusses how to prevent them.
Slips, trips and falls. Preventing slips and trips at work: A brief guide ; Assessing the slip resistance of flooring ; Slips and trips: The importance of floor cleaning ; Virtual College: Slips, Trips and Falls Online Training ; Related content. Slips and trips guidance; HSE Books; Research reports; Operational guidance; Other languages; HSE ...
Check list - slips, trips and falls (Word, 43 KB, 4 pages) Safety guidance to prevent slips, trips, and falls (PDF, 424 KB) Managers carrying out a risk assessment. You must ensure that slips, trips and falls are assessed as part of the risk assessment. When carrying out the risk assessment, you should consider: the use of the premises
The risk assessments must be documented in line with existing HSE risk assessment and management procedures. The risk assessments must include any practice concerns and take into ... 19 12 16 SAGN: 002:02 Preventing Slips Trips and Falls Page 5 The Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act (General Application) Regulations, 2007 Chapter 1 of
The Costly Effects of Slips, Trips and Falls It's amazing what one small drip or one misplaced tool can lead to. When it comes to safety and compliance, a slip, trip or fall can lead to serious injuries, a variety of citations and costs, and an overall impact on the running of your facility. Let's explore the impact an incident can have
re many slip, trip and fall hazards in the workplace. This Guide is designed to help Managers to identify potential slip, trip and fall hazards found in the workplace, communicate the issues with colleagues, and to put in place the procedures, that. ill deal with the problem before an incidents occurs. The STF materials, as well as the infor.
Slips, trips and falls H High risk areas for slips, trips, and falls are identified and dealt with, e.g. walkways, stairs/steps, entrances/ exits 6 Floor areas inside and outside the entrance are slip resistant when wet Higher risk slip, trip or fall periods Slips, trips and falls H Higher risk identified (e.g. during break time/1pm to
Appropriate Footwear for Different Surfaces. Wearing the right footwear can significantly reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls. Choose shoes with good traction, especially for wet or slippery surfaces. Protective footwear should be worn in workplaces where specific hazards are present, such as construction sites.
Slips, trips, and falls cause nearly 700 fatalities per year and many more injurious accident in the workplace according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. There are three physical factors involved in slips, trips, and falls: friction, momentum, and gravity. Each one plays a role. Friction is the resistance between objects, momentum is affected ...
Your site should be kept in a clean and orderly condition so as to reduce the chance of injury through slips and trips. Everyone can make a contribution to reducing slips and trips on site. If you see a risk, sort it, or report it to someone who can. Key aspects of construction slips and trips include: Uneven surfaces. Obstacles. Trailing cables.
Carry out a risk assessment. The best way to identify slip, trip and fall hazards and ways to control them in your workplace is to discuss the issue with staff and carry out a risk assessment. Object reference not set to an instance of an object. Use the Slips Assessment Tool (SAT)
Hazards in the Workplace. In 2022, 865 workers died in falls, and hundreds of thousands were injured badly enough to require days off of work. A worker doesn't have fall from a high level to suffer fatal injuries; 144 workers were killed in falls on the same level in 2022, according to Injury Facts. Construction workers are most at risk for ...
Slips, Trips, and Falls Prevention. Some slip, trip, and fall prevention measures are permanent, including: Adequate lighting. Handrails. Slip-resistant surfaces in high-risk areas. Effective drainage, ventilation, and other methods to keep surfaces dry. Marking the edges of steps or elevation changes.
Every working day seven people are hurt in work slips, trips and falls (STF) If you wish to make a complaint about a workplace, please use our online complaints form to ensure your complaint is handled as efficiently as possible or email [email protected]. Call: 0818 289 389. 9:00am to 3:00pm, Monday to Friday.
It is a very important responsibility of every employer to reduce the risk of slips, trips and falls. Perform a slips, trips and falls risk assessment so that you can identify the dangers and then determine what types of safety measures are necessary for preventing harm. Related Courses. Accident Reporting and Near Miss training; Asbestos courses
An essential Risk Assessment covering slips, trips and falls. protect yourself and others and control your risks with this assessment from HSEDocs. Online Health & Safety Documents and E-Learning Centre -0800 933 61 61 HSE Docs is an approved supplier to central government and the public sector. ... A comprehensive Risk Assessment covering ...
Slips. Slip and trip accidents happen for a number of reasons. The following model will help you understand the factors that can contribute to slip accidents and the action to take to prevent them . It is called the slip potential model. One or more of these factors may play a part in any slip accident. Slip potential model
Footwear. Footwear plays an important role in reducing the risk of slips, trips and falls. Footwear should be: suitable for the type of work and work environment. comfortable with an adequate non-slip sole and appropriate tread pattern. checked regularly to ensure treads are not worn away or clogged with contaminants.
Last reviewed 6 April 2023. Risk assessment is central to any approach aimed at protecting people from the risk of slips, trips and falls, explains Andrew Christodoulou. Slips, trips and falls continue to be major players in the accident statistics released by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE). In 2021/22, slips and trips accounted for 30% ...
For employers, the key way of avoiding slips and trips is to carry out regular risk assessments, using HSE's five-step process: 1. Identify the hazards. 2. Consider who might be harmed and how. 3. Evaluate the risks and decide on precautions. 4. Record significant findings.
Identify the risks. You must control the risks in your workplace, this includes the risks of a slip, trip or fall and do everything reasonably practicable to protect people from harm. Your assessment should consider who has access, the physical and environmental factors that may give rise to a slip, trip or fall and how these can be minimised ...
ការ វាយប្រហារ ដ៏ គួរ ឱ្យ ភ្ញាក់ផ្អើល របស់ អ៊ុយក្រែន ចូល ...
Many factors can cause slips, trips and falls. These include: methods of cleaning, flooring type, footwear, levels of lighting, contrast between floors, walls and doors, and obstructions or other trip hazards. The practical measures you can take will vary in different situations; some measures will reduce the risk to both workers and non ...