

25 of the Best Words to Describe the Outer Space
By: Author Hiuyan Lam
Posted on Last updated: October 20, 2023
Categories Vocabulary Boosters

If you want to be a good or even great storyteller, you need to equip yourself with words to describe everything imaginable to paint vivid pictures for your readers.
In this post, we’re going to take a look at some words to describe space. Space can be a tricky thing to describe since most humans have never been there, and we can only base it on what we’ve seen in movies or read in books.
The good thing about being a writer is that even if you can’t draw on your memory to describe something such as outer space, you can use your imagination. If you want to create different settings for your readers in your description of what outer space feels like, you need to tap deep into your creativity.
Here are 25 of our favorite words to describe space and how you can use them to improve your writing:
10 words to describe space in a mystical way
Outer space isn’t just about what you can see. Sure, there are planets, stars and moons, but what about the way that it makes you feel, or in other words, the vibe? When writing, it’s important to set that tone for your readers to make your storytelling more effective. Here are 10 words to describe space in a mystical sense:

You May Also Like:
35 Words to Describe a Forest Well in a Novel

8 words to describe space when it is vast and infinite
Space is really big. It is so vast that it can be hard to describe to your readers just how huge it really is. Here are some words to describe space based on its size:

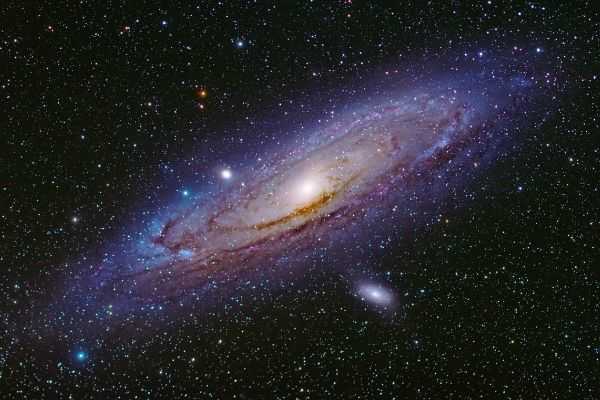
7 words to describe the starry Milky Way
Now, let’s talk about words to describe space that we live in, meaning the Milky Way galaxy:

20+ of the Best Words to Describe Night in a Story
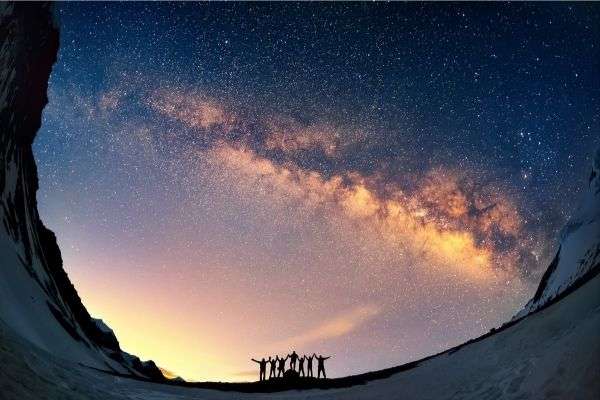

Finding the right words to describe space can improve your writing significantly and help you connect with your readers. You can even come up with other words to describe space once you start to think outside of the box.
20+ Best Words to Describe Space, Adjectives for Space
Space, in its simplest definition, is the limitless expanse that surrounds our planet and everything in the universe. It’s a vast canvas, stretching beyond imagination, harboring celestial wonders and mysteries that continue to captivate humanity. As we gaze up at the night sky, we find ourselves compelled to describe this enigmatic realm. From infinite to awe-inspiring, from mysterious to boundless, a plethora of words have been crafted to convey the profoundness and grandeur of space. Join us as we embark on a linguistic journey through the lexicon of words that paint the portrait of the cosmos in all its glory.
Adjectives for Space
Here are the 20 Most Popular adjectives for space:
- Astronomical
- Dimensional
- Interstellar
- Wide-ranging
Adjectives for Space Exploration:
- Adventurous
- Groundbreaking
Adjectives for Space Travel:
- Extraordinary
- Interplanetary
- Unprecedented
Adjectives for Space Shuttle:
- Cutting-edge
- Sophisticated
Adjectives for Space Station:
- International
- State-of-the-art
- Revolutionary
- Collaborative
Adjectives for Spaceship:
- Streamlined
Words to Describe Space with Meanings
- Astronomical: Related to celestial objects and phenomena.
- Boundless: Having no limits or boundaries.
- Celestial: Relating to the heavens or sky.
- Cosmic: Pertaining to the universe as a whole.
- Dimensional: Relating to spatial extent or dimensions.
- Expansive: Extending over a wide area.
- Galactic: Associated with galaxies or the Milky Way.
- Infinite: Endless or limitless in space.
- Interstellar: Occurring between stars or in space.
- Limitless: Having no boundaries or restrictions.
- Nebulous: Hazy or unclear, like a nebula.
- Open: Unobstructed or accessible.
- Planetary: Relating to planets or their characteristics.
- Vast: Extremely large or immense.
- Stellar: Pertaining to stars or outstanding excellence.
- Timeless: Not affected by time or age.
- Unbounded: Having no limits or bounds.
- Universal: Applying to all or the whole universe.
- Void: Empty or containing nothing.
- Wide-ranging: Extending over a broad scope.
Example Sentences for Space Adjectives
- The astronomical discoveries amazed the scientists.
- Boundless curiosity drives space exploration.
- The telescope captured stunning celestial images.
- We marveled at the cosmic mysteries.
- The dimensional analysis revealed intricate patterns.
- The spacecraft explored the expansive universe.
- The book delves into the wonders of galactic phenomena.
- The concept of infinity is truly infinite .
- They sent a message through interstellar space.
- Her imagination was limitless like the cosmos.
- The nebulous cloud took intriguing shapes.
- The open horizon invited exploration.
- Earth is just one of many planetary bodies.
- The observatory offered a view of the vast sky.
- The lecture highlighted the stellar lifecycle.
- The ancient monument stood as a timeless symbol.
- Their love for space was unbounded .
- The theory proposed a universal law.
- The spacecraft entered a void in space.
- The project had wide-ranging implications.
Explore More Words:
Words to Describe Sky
Words to Describe a Moon
Words to Describe Stars
How to describe space in writing?
In writing, space can be described as an infinite expanse that envelopes celestial bodies and fosters boundless exploration.
What is the adjective for a lot of space?
The adjective for a lot of space is “expansive.”
What is an adjective for outer space?
The adjective for outer space is “celestial.”
Related Posts

20+ Best Words to Describe Princess, Adjectives for Princess

20+ Best Words to Describe Japan, Adjectives for Japan

20+ Best Words to Describe Hunting, Adjectives for Hunting

20+ Best Words to Describe a Sport, Adjectives for Sport

20+ Best Words to Describe Island, Adjectives for Island

20+ Best Words to Describe Fitness, Adjectives for Fitness
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.

50 Words Associated With Space

Space is a vast and mysterious place, full of wonders and mysteries waiting to be discovered. From the distant reaches of the universe to the planets and moons in our solar system, there are many words associated with space that help us describe and understand this incredible frontier.
From terms for different celestial bodies and phenomena to words that describe the history and exploration of space, this list of 50 words will give you a greater appreciation for the vastness and beauty of the cosmos.

Subscribe to our mailing list to receive FREE exclusive content and offers!
50 Words Associated With Space Meanings
Cosmos : Refers to the universe as an ordered, harmonious and holistic entity. It encompasses everything that exists: space, time, matter, energy, and the physical laws and constants that describe them.
Universe : The totality of all space, time, matter, and energy that exist, including all planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space.
Galaxy : A large system of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter gravitationally bound together. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is just one of billions in the universe.
Solar system : The Sun and all the celestial bodies that are held by the Sun’s gravity and orbit it. This includes eight planets, their moons, and other objects like asteroids and comets.
Planet : A celestial body that orbits around the Sun or another star, is spherical in shape, and has cleared its orbit of other debris. In our solar system, there are eight recognized planets.
Star : A luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity, generating heat and light through nuclear fusion. Our Sun is an example of a star.
Asteroid : A small, rocky object that orbits the sun. While similar to planets, they are much smaller in size.
Comet : A celestial body composed of ice and rock that orbits the Sun. As a comet gets closer to the Sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize and create a glowing coma or tail.
Nebula : A cloud of gas and dust in space, often acting as a nursery for new stars and planets.
Supernova : The explosion of a star at the end of its life cycle, which causes an incredibly bright burst of light and radiation.
Astronomy : The scientific study of celestial objects, such as stars and galaxies, and the phenomena that occur outside Earth’s atmosphere.
Astrophysics : A branch of astronomy that deals with the physical properties of celestial bodies and the underlying physics of the universe.
Cosmology : The scientific study of the large scale properties of the universe as a whole, including its origins and evolution.
Space exploration : The investigation of physical conditions in space and on stars, planets, and other celestial bodies through the use of artificial satellites (spacecraft), telescopes, and other observational techniques.
Rocket : A vehicle designed to propel itself through the air, and into space, by ejecting exhaust gas from a rocket engine.
Shuttle : Refers to the Space Shuttle, a reusable space vehicle that was used by NASA to carry astronauts and payloads to and from Earth’s orbit.
Spaceship : A vehicle designed for space travel or operation in outer space.
Satellite : An object in space that orbits or revolves around another object. There are natural satellites, like moons, and artificial satellites, like the ones used for communication or weather monitoring.
Probe : An unmanned spacecraft designed to explore outer space and send data back to Earth. Probes have been used to explore the moon, other planets, and beyond.
Space station : A large spacecraft that remains in low Earth orbit for extended periods of time. It is a home where astronauts live and work.
International Space Station (ISS) : A habitable artificial satellite in low Earth orbit that serves as a space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted.
Moon : Earth’s only natural satellite. It’s also a term used to describe any natural satellite that orbits another body.
Mars : The fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system, often called the “Red Planet” because of its reddish appearance. It is a potential target for future human space exploration.
Venus : The second planet from the Sun in our solar system. It is the hottest planet and is characterized by its bright, cloudy appearance.
Earth : The third planet from the Sun in our solar system. Earth is the only known celestial body to support life.
Mercury : The smallest and innermost planet in our solar system. It orbits the Sun quickly, making a full orbit every 88 Earth days.
Jupiter : The largest planet in our solar system. It is a gas giant, known for its Great Red Spot, a storm that has been raging on the planet for at least 300 years.
Saturn : The second-largest planet in our solar system, known for its extensive ring system. It is a gas giant like Jupiter.
Uranus : The seventh planet from the Sun, known for its blue color caused by the methane in its atmosphere. It is a gas giant and has a set of thin rings.
Neptune : The eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun in the solar system. It is a gas giant and is known for its deep blue color.
Pluto : A dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of bodies beyond Neptune. It was the first Kuiper belt object to be discovered and is the largest known plutoid.
Chandra : The Chandra X-ray Observatory, a NASA satellite that observes the universe in the X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Hubble : The Hubble Space Telescope, a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. It has provided some of the most dramatic and detailed photos of our universe.
Spitzer : The Spitzer Space Telescope, an infrared space telescope launched by NASA, used to observe astronomical objects in the infrared spectrum.
Kepler : A space observatory launched by NASA to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars.
Gravity : The force by which a planet or other body draws objects towards its center. The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun.
Atmosphere : The layer of gases that surrounds a planet or other celestial body.
Oxygen : A chemical element that is a gas at room temperature and is necessary for most forms of life on Earth. In space travel, oxygen must be provided for astronauts to breathe.
Weightlessness : The condition that occurs in free fall when the weight of an object or person is effectively zero. This is experienced by astronauts in orbit.
Microgravity : A state of very weak gravity, much weaker than that on Earth, as experienced by astronauts in space.
Zero gravity : Another term for weightlessness, often used to describe the condition of astronauts in orbit.
Spacewalk : Also known as extravehicular activity, it refers to any activity done by an astronaut or cosmonaut outside a spacecraft beyond the Earth’s appreciable atmosphere.
Extravehicular activity (EVA) : Any activity done by an astronaut or cosmonaut outside a spacecraft beyond the Earth’s appreciable atmosphere. It includes spacewalks from the International Space Station or shuttle, or surface activities on the Moon or Mars.
Space suit : A garment worn by astronauts to keep them alive in the harsh environment of outer space, vacuum and temperature extremes.
Moonwalk : A type of spacewalk that occurs on the surface of the Moon. It was first performed by astronaut Neil Armstrong during the Apollo 11 mission in 1969.
Lunar rover : A vehicle designed for moving across the surface of the Moon. Some rovers have been designed to transport members of a crew, others have been partially or fully autonomous robots.
Asteroid mining : The exploitation of raw materials from asteroids and other minor planets, including near-Earth objects. These materials could be used for in-space manufacturing or brought back to Earth for use.
Exoplanet : A planet that orbits a star outside the solar system.
Dark matter : A form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe and about a quarter of its total mass–energy density. Its presence is implied by the effects of its gravity on visible matter and radiation.
Black hole : A region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation can escape. They are thought to form from the remnants of large stars after their final collapse.
Share or print this page:
More Word Lists

List Of 100 French Origin Words Used In English

List Of Words With The Suffix “on”

List Of Words Ending In “nder”

List Of Adjectives Ending In “D”

List Of Words With The Prefix “extra”

List Of Nouns Ending In “S”
Spotted an error on this page? Please let us know! [email protected] .
Remember to bookmark this page to use it regularly!
Subscribe to our mailing list to receive FREE exclusive guides, tips and offers!

SPACE TRAVEL DESCRIBE WORDS
Found 817 words to describe [space travel] . You can click on each words to see its definition.
- Spaceflight
- Spacefaring
- Space Medicine
- Space Vehicle
- Space Probe
- Interplanetary Space
- Outer Space
- Astronavigation
- Intergalactic Space
- Space Station
- Space Shuttle
- Space Opera
- Last Frontier
- Interplanetary Medium
- Space Capsule
- Interplanetary
- Extraterrestrial
- Astrophobia
- Science Fiction
- Inner Planet
- Orbital Plane
- Space Rocket
- Event Horizon
- Intergalactic
- Space Biology
- Circumjovial
- Nuclear Rocket
- Interstellar
- Lunar Module
- Giant Planet
- Rocket Engine
- Cape Canaveral
- Outer Planet
- Solar System
- Astronautical
- Minor Planet
- Major Planet
- Circumterrestrial
- Microgravity
- Intersidereal
- Radio Astronomy
- Cosmic Background Radiation
- Launch Vehicle
- Terrestrial Telescope
- Ultramundane
- Strategic Defense Initiative
- Superterrestrial
- Launch Window
- Terraforming
- Inferior Planet
- Circumterraneous
- Nuclear Fusion
- Aeronautics
- Biomedicine
- Bioastronautics
- Yuri Gagarin
- Retrorocket
- Reservation
- Accommodation
- Aeromedicine
- Biotelemetry
- Change Of Location
- Controlling
- Cosmic Rays
- Electromagnetic Radiation
- Homomorphism
- Indentation
- Interferometer
- Lumbar Puncture
- Magnetic Field
- Marketplace
- Mediastinum
- Neighborhood
- Orientation
- Pseudosphere
- Telecommunication
- Telecommunications
- Teleportation
- Transmission
- Umbilical Cord
- Underground
- Unidirectional
- Ventilation
- Caterpillar
- Displacement
- Intercourse
- Move Around
- Peregrination
- Thoroughfare
- Transportation
Adjectives For Space Travel
[space travel] implies to a voyage outside the earth's atmosphere, the process of travelling in or into outer space. or travel through space in order to visit and explore other worlds
As you can see in the list above, top common adjectives for space travel are: Spaceflight, Spacefaring, Spaceship, Space Medicine, Space Vehicle, Space Probe, Interplanetary Space, Space Walk, Outer Space, Astronavigation. Based on our algorithm, there are 817 words to decribe space travel. I hope list of words to describe space travel could help you in improving your vocabulary and enhance your writing skills.
Recent Searches

Describing Words
This tool helps you find adjectives for things that you're trying to describe. Also check out ReverseDictionary.org and RelatedWords.org . Here are some adjectives for space travel : . You can get the definitions of these space travel adjectives by clicking on them. You might also like some words related to space travel (and find more here ).
Sort By Usage Frequency
Click words for definitions.
Loading you some adjectives... Won't be much longer! :)
Words to Describe space travel
Below is a list of describing words for space travel . You can sort the descriptive words by uniqueness or commonness using the button above. Sorry if there's a few unusual suggestions! The algorithm isn't perfect, but it does a pretty good job for most common nouns. Here's the list of words that can be used to describe space travel :
- travel-real
- travel�real
- practical deep
- travel--real
- practical interstellar
- crisp, convincing
- cheap and easy
- months-long
- interstellar
- long-distance
- discretionary
- interplanetary
- rudimentary
- unauthorized
- conventional
- inexhaustible
- instantaneous
- spontaneous
- independent
Popular Searches
As you've probably noticed, adjectives for " space travel " are listed above. Hopefully the above generated list of words to describe space travel suits your needs.
If you're getting strange results, it may be that your query isn't quite in the right format. The search box should be a simple word or phrase, like "tiger" or "blue eyes". A search for words to describe "people who have blue eyes" will likely return zero results. So if you're not getting ideal results, check that your search term, " space travel " isn't confusing the engine in this manner.
Note also that if there aren't many space travel adjectives, or if there are none at all, it could be that your search term has an abiguous part-of-speech. For example, the word "blue" can be an noun and an adjective. This confuses the engine and so you might not get many adjectives describing it. I may look into fixing this in the future. You might also be wondering: What type of word is space travel ?
The idea for the Describing Words engine came when I was building the engine for Related Words (it's like a thesaurus, but gives you a much broader set of related words, rather than just synonyms). While playing around with word vectors and the " HasProperty " API of conceptnet, I had a bit of fun trying to get the adjectives which commonly describe a word. Eventually I realised that there's a much better way of doing this: parse books!
Project Gutenberg was the initial corpus, but the parser got greedier and greedier and I ended up feeding it somewhere around 100 gigabytes of text files - mostly fiction, including many contemporary works. The parser simply looks through each book and pulls out the various descriptions of nouns.
Hopefully it's more than just a novelty and some people will actually find it useful for their writing and brainstorming, but one neat little thing to try is to compare two nouns which are similar, but different in some significant way - for example, gender is interesting: " woman " versus " man " and " boy " versus " girl ". On an inital quick analysis it seems that authors of fiction are at least 4x more likely to describe women (as opposed to men) with beauty-related terms (regarding their weight, features and general attractiveness). In fact, "beautiful" is possibly the most widely used adjective for women in all of the world's literature, which is quite in line with the general unidimensional representation of women in many other media forms . If anyone wants to do further research into this, let me know and I can give you a lot more data (for example, there are about 25000 different entries for "woman" - too many to show here).
The blueness of the results represents their relative frequency. You can hover over an item for a second and the frequency score should pop up. The "uniqueness" sorting is default, and thanks to my Complicated Algorithm™, it orders them by the adjectives' uniqueness to that particular noun relative to other nouns (it's actually pretty simple). As you'd expect, you can click the "Sort By Usage Frequency" button to adjectives by their usage frequency for that noun.
Special thanks to the contributors of the open-source mongodb which was used in this project.
Please note that Describing Words uses third party scripts (such as Google Analytics and advertisements) which use cookies. To learn more, see the privacy policy .

Recent Queries

- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
Adjectives for Space: Examples & Descriptions

Hey there! If you’re looking to spruce up your writing or expand your vocabulary, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, I’ll be diving into the fascinating world of adjectives for space. Whether you’re describing the vastness of the universe or the coziness of a room, these words will help you paint a vivid picture in your readers’ minds.
Space is an infinite expanse that has captivated humans for centuries. From the twinkling stars in the night sky to the vastness of the cosmos, there’s no shortage of descriptive words to bring this awe-inspiring subject to life. I’ll be sharing some popular adjectives that will help you add depth and detail to your writing. So, get ready to elevate your descriptions and take your readers on an unforgettable journey through space.
Table of Contents
How to Describe space? – Different Scenarios
When it comes to describing space, there are various scenarios to consider. Each scenario presents a unique opportunity to use different adjectives that can bring your writing to life. Let’s explore some of these scenarios and the adjectives you can use to describe them.
- Outer Space:
- Vast : Outer space is a vast expanse of emptiness.
- Mysterious : It’s a mysterious realm that holds many secrets.
- Infinite : The possibilities in outer space are infinite.
- Distant : Planets are distant, celestial bodies.
- Colorful : They come in various colors like the red of Mars and the blue of Neptune.
- Ethereal : The planets have an ethereal beauty that captivates the imagination.
- Dazzling : The stars in the night sky are dazzling and mesmerizing.
- Radiant : They emit a radiant glow that lights up the darkness.
- Twinkling : Stars appear to twinkle like diamonds in the sky.
- Luminous : The moon’s gentle glow is luminous and calming.
- Majestic : Its presence in the night sky is majestic and awe-inspiring.
- Reflective : The moon reflects the sun’s light, casting a soft glow on Earth.
- Sprawling : Galaxies are sprawling structures that stretch across vast distances.
- Spectacular : They are a spectacular sight to behold, with their swirling colors and patterns.
- Unfathomable : The complexity of galaxies is unfathomable, making them a subject of great intrigue.
As you can see, describing space offers a plethora of opportunities to use vivid adjectives. By choosing the right adjectives for different scenarios, you can transport your readers on an unforgettable journey through the cosmos.
Adjectives for Space
Describing Words for space in English
When it comes to describing space, there are countless words that can help bring the vastness and wonder of the cosmos to life. Here are some descriptive words that can paint a vivid picture of space:
- Vast : Space is incredibly vast, with no known boundaries. Its expanse is beyond measure, making it a perfect word to capture the sheer size and scale of the universe.
- Mysterious : Space holds many mysteries that continue to captivate scientists and astronomers. Its secrets and unknown phenomena make it a place of intrigue and fascination.
- Infinite : Space is often described as infinite, indicating its boundless nature and endless possibilities. This word conveys the idea that space goes on forever, with no definite end.
- Distant : Space is far beyond our reach, with stars and galaxies located millions or even billions of light-years away. The word “distant” emphasizes the immense distance that separates celestial objects.
- Colorful : While space may seem mostly dark and empty, it is surprisingly filled with vibrant colors. Nebulas, planets, and galaxies exhibit a stunning range of hues, from deep blues to fiery oranges.
- Ethereal : Space has a quality that is otherworldly and ethereal. Its intangible nature and heavenly appearance make the word “ethereal” a fitting choice to describe the enchanting beauty of the cosmos.
- Dazzling : Stars and celestial bodies in space emit a dazzling light that can illuminate the darkness of the universe. This word captures the brilliance and radiance of these luminous objects.
- Radiant : The word “radiant” conveys the idea that space is filled with radiant energy and light. It emphasizes the glowing, radiant nature of stars and brings to mind the spectacular phenomena like supernovae.
- Twinkling : Stars in space appear to twinkle from a distance, creating a sense of magic and twinkling lights. The word “twinkling” adds a touch of whimsy and wonder to descriptions of celestial bodies.
- Luminous : Just like the word suggests, space is luminous, filled with glowing objects that emit light throughout the cosmos. It conveys the radiance and luminosity of stars, planets, and galaxies.
Adjectives for space
Positive adjectives for space with 12 example sentences.
When it comes to describing space, there are many positive adjectives that can help us convey its wonder and grandeur. Here are some examples of positive adjectives for space, along with sentences to illustrate their usage:
- Vast : Space is a vast expanse that stretches beyond our imagination.
- Mysterious : There is something mysterious and unknown about the depths of space.
- Infinite : The universe is believed to be infinite in its size and scope.
- Distant : The stars and galaxies in space seem so distant from our earthly perspective.
- Colorful : Space is not just black and white. It is filled with colorful cosmic phenomena.
- Ethereal : The beauty of space can be described as ethereal and otherworldly.
- Dazzling : The dazzling light of stars fills the night sky with awe-inspiring beauty.
- Radiant : The sun’s rays illuminating space create a radiant spectacle.
- Twinkling : The stars in the night sky appear as tiny twinkling lights.
- Luminous : The moon’s gentle glow adds a luminous touch to the night.
These positive adjectives capture the size, intrigue, boundlessness, distance, vibrant colors, ethereal beauty, brilliance, radiance, magic, and luminosity of space.
Negative Adjectives for Space with 5 Example Sentences
While space is often associated with wonder and beauty, there are negative adjectives that can be used to describe certain aspects of the cosmos. Here are some examples of negative adjectives for space, along with sentences to demonstrate their usage:
- Void : Outer space is often depicted as a void devoid of life and sound.
- Cold : Space is an extremely cold and inhospitable place.
- Vacuum : The absence of air or atmosphere in space creates a vacuum environment.
- Harsh : The conditions in space can be harsh and unforgiving to living organisms.
- Unfathomable : The vastness of space can be overwhelming and unfathomable to comprehend.
These negative adjectives highlight the emptiness, chilling temperatures, lack of atmosphere, challenging conditions, and incomprehensibility of space.
Adjectives play a crucial role in bringing the vastness and wonder of space to life. Using descriptive words like “vast,” “mysterious,” “infinite,” “distant,” “colorful,” “ethereal,” “dazzling,” “radiant,” “twinkling,” and “luminous” allows us to capture the beauty and magnitude of the cosmos. However, it’s important to also recognize the negative aspects of space, such as its void, coldness, vacuum, harshness, and unfathomable nature. Together, the positive and negative adjectives paint a more complete picture of the enigmatic and awe-inspiring realm that is space.
Synonyms and Antonyms with Example Sentences
Synonyms for space.
When it comes to describing space, there are several synonyms that can help us capture its infinite wonder and vastness. Here are some examples:
By using these synonyms, we can paint a more vivid and complete picture of the beauty and magnitude of space.
Antonyms for space
However, space is not always filled with positive attributes. There are also antonyms or opposite words that describe the negative aspects of space. Here are some examples:
While these antonyms may describe the challenging and unforgiving nature of space, they are equally important in capturing the complete picture of our universe.
Using a combination of both synonyms and antonyms, we can create a more well-rounded understanding of space, from its breathtaking beauty to its vast emptiness.
Describing space can be a daunting task, but with the help of adjectives, we can bring the wonders of the cosmos to life. Throughout this article, we have explored a range of adjectives that capture the vastness, mystery, and infinite beauty of space.
By using words like “vast,” “mysterious,” “infinite,” and “colorful,” we can paint a more vivid and complete picture of the cosmos. These adjectives allow us to convey the awe-inspiring magnitude of space and its countless wonders.
On the other hand, we have also explored antonyms such as “void,” “cold,” and “unfathomable.” These words help us acknowledge the negative aspects of space, reminding us of its immense power and the challenges it poses.
Adjectives play a crucial role in describing space. They allow us to capture the essence of the universe, both in its grandeur and its complexities. So, whether you’re writing a scientific article or simply marveling at the night sky, remember to choose your adjectives wisely to truly convey the beauty and magnitude of space.
Related Posts

Describing Blood: Adjectives with Examples
Blood is a vital element of our existence, coursing through… Read More » Describing Blood: Adjectives with Examples

Adjectives for Age: Describing Words & Examples
As we navigate through life, one thing that remains constant… Read More » Adjectives for Age: Describing Words & Examples

Adjectives for Fight: Examples and Describing Words
When it comes to describing a fight, finding the right… Read More » Adjectives for Fight: Examples and Describing Words
Make Your Vocabulary Skyrocket With These Space Words
- Space Words
- Take The Quiz
Our universe is unfathomably huge and getting bigger all of the time, according to the Big Bang model and the theory of universe expansion . That’s a pretty cool concept and term, right? As the theory goes, dark energy (more on this later) is causing the universe to continually stretch itself.
Studying the universe introduces us to some fascinating concepts in general: black holes , rogue planets , Oort clouds— and white holes , too? If you are a casual space explorer, you probably already know stellar objects like comets , asteroids , meteors , and galaxies . But there is so much more out there for you to discover! Jump in our (word) rocket ship as we boldly discover some awesome intergalactic words.
From Earth, a pulsar resembles a flickering star. In reality, a pulsar is a neutron star —a really dense object left over when a big star dies—that radiates beams of light in two directions. The pulsar rotates as it shines light beams, which makes it appear to blink or pulse as it spins away from Earth and points its lights in other directions.
Asterism is a fancy word that means “a group of stars.” So, what makes an asterism different from a constellation ? The 88 constellations in the sky have officially recognized names and shapes. Asterisms are those other groups of stars that aren’t officially recognized but still have popular names. The Big Dipper (part of Ursa Major ) and Orion’s Belt (part of Orion ) are two examples of commonly known asterisms.
Just like the Earth, the Sun has an atmosphere surrounding it. The outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere is called the corona . Because the Sun is so bright, you can only see the corona during a total solar eclipse . The Sun’s corona is very dense and, mysteriously, has a much higher temperature than the Sun itself.
A facula (plural faculae ) is an unusually bright spot on the surface of the sun. A facula is smaller and harder to see than the more well known sunspots . Both faculae and sunspots are caused by bubbles of hot gas and both are used to keep track of the solar cycle. As one last bit of trivia, the word facula is Latin for “little torch.”
A nebula is a cloud of dust and gas in outer space. While that may not sound terribly exciting, nebulae act as star nurseries as they have the perfect conditions that new stars need to form. The word nebula comes from Latin and means “mist,” “vapor,” or “cloud.”
planetesimal
A planetesimal is a small celestial object formed from dust, rocks, and other materials. According to one theory, planetesimals may be the building blocks that combined together to form the early planets of the universe. Planetesimals may have also played a part in the formation of the Earth’s moon and some of the other moons in our solar system as well.
Do you know the difference between a meteor, comet, and asteroid?
rogue planet
A rogue planet is a planet that doesn’t orbit a star. Many planets, like Earth, are part of a solar system and orbit around a central star. Rogue planets, on the other hand, are not confined to drift around a star and roam wherever they want across space. Because they aren’t next to a star and don’t emit light themselves, rogue planets are very hard for astronomers to find. Despite their lack of starry friends, evidence suggests that it may be possible for life to exist on rogue planets.
As you likely know, a black hole is a region of space where the gravity is so intense that not even light can escape. We often imagine black holes as terrifying objects that suck in all the matter around them.
A white hole is the theoretical opposite of a black hole, a celestial object that would endlessly expel matter out of it. According to Albert Einstein’s theories, black holes and white holes serve as the entrance and exits of wormholes that would allow travel through time and space. Other modern theories propose that a white hole could theoretically exist as the final stage of a black hole, where all of the mass sucked into a black hole is released back out again.
A quasar is a celestial object located very far away from us in distant galaxies. Quasars are a result of gas and stars accumulating into a disk around a gigantic black hole. This disk emits a huge amount of heat, making quasars some of the brightest objects in all of the known universe. Quasars also emit radiation (and in some cases, radio waves ) into space, which is how we have been able to find them. In fact, the name quasar is short for “quasi-stellar radio source,” which refers to the radio telescopes that were first used to detect them.
A blazar is basically identical to a quasar except for one quality: its angle toward Earth. Typically, a quasar is angled slightly toward Earth; that means we can detect its light and radio wave emissions. A blazar is angled directly toward the Earth so that the light and radiation shoots directly toward us. This difference in angle makes a blazar appear even brighter than an already absurdly luminous quasar.
Go Behind The Words!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
The Oort Cloud is the furthest outer region of our solar system, being more than a thousand times away from the Sun than Pluto is. The Oort Cloud is often imagined as a bubble of icy objects that exists around our solar system. The Oort Cloud could possibly contain trillions of celestial objects and is the source of many comets that pass through our solar system. The Oort Cloud is named for astronomer Jan Oort, who originally theorized its existence.
dark matter
Dark matter is a theoretical, invisible form of matter that exists in space. The word matter is used to refer to all of the stuff that takes up space as we know it. In outer space, everything is positioned where it is because of gravity. We can see what is going on in outer space because of light. However, there are areas of outer space where astronomers can detect mass (due to gravity) but nothing in that area is emitting or absorbing light. Because something must be there, this invisible “missing mass” is known as dark matter .
According to scientific estimates, dark matter makes up about 27 percent of space. This may not sound like much, but the “regular matter” that makes up our Earth and all the suns and planets accounts for less than 5 percent of the universe! But wait, we are only at about 32 percent of the universe. What is the rest of it made of?
dark energy
The answer, according to modern science, is dark energy. Dark energy is a theoretical form of energy that exerts negative, repulsive pressure. In the simplest sense, dark energy is basically “reverse gravity” that causes things to repel away from each other rather than attract each other as is the case with gravity. Dark energy is thought to be responsible for the expansion of our universe and is what the “empty space” of outer space is believed to be made out of.
No, a cat didn’t just walk across the keyboard. In astronomy, a syzygy is an alignment of three celestial objects. For example, when the Earth, sun, and moon are all positioned in a line to cause an eclipse, they are aligned in syzygy . This incredibly cruel word to use in a game of Hangman comes from the Greek word syzygía , meaning “union” or “pair.” In addition to syzygy , other cool words that astronomers use to refer to space observations include azimuth , parsec , ephemeris , and albedo .
Hyperjump over to take the quiz!
Did this list of cosmic words launch you into the stratosphere? You can jump into the void and review this expansive list of terms and their meanings with our word list here . Or, demonstrate your new grasp of space by heading to our short quiz on these words.
Take another outer space word trip right from your home with these words.
Science & Technology

Hobbies & Passions
Word Origins
Current Events
[ fawr- sooth ]
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

A-F G-M N-R S-Z
Asteroid: Rocks floating around in space. Some are the size of a pick-up truck. Others are hundreds of miles across.
Atmosphere: The gases held by gravity around Earth and around other planets. "Atmosphere" can also be used to talk about gases around stars.
Atom: The basic building block of matter. It is made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. There are many different kinds of atoms. For example, the simplest atom with one proton and one electron is a hydrogen atom. An atom with six protons, six neutrons, and six electrons is a carbon atom.
Aurora australis: Bright glows and bands of light that appear in the skies at night near the South Pole. They are also called the southern lights.
Aurora borealis: Bright glows and bands of light that appear in the skies at night near the North Pole. They are also called the northern lights.
Black hole: A place in space where matter and light cannot escape if they fall in.
Comet: An icy rock that lets off gas and dust, which may form tails when it is flying close to a sun.

Constellation: A group of stars in the sky. They're often named after an animal, object, or person. The stars form certain patterns based on where you are. We have one view of stars here on Earth, but from another solar system or galaxy, the constellations would look different.
Corona: The outer atmosphere of a star.
Cosmos: The universe seen as an orderly, harmonious whole.

Crater: A large, bowl-shaped dent in the ground. They can be caused by an explosion or the impact of a meteorite.
Dwarf planet: Objects that are round and orbit the sun, just like planets do. But unlike planets, dwarf planets are not able to clear their path around the sun. That means there are other objects orbiting at roughly the same distance from the sun. A dwarf planet is much smaller than a planet (smaller even than Earth's moon), but it is not a moon. Pluto is the best known of the dwarf planets.
El Niño: A weather condition that sometimes occurs in the Pacific Ocean. It is so big that it affects weather all over the world. It starts with unusually warm water in the Pacific Ocean near the equator.
Electromagnetic Spectrum: The name for all the different kinds of light and energy in the universe. This includes radio waves , microwaves , infrared radiation , visible light , ultraviolet light , X-rays , and gamma rays .
Equator: The circle around a planet or moon that is the same distance from its north pole and its south pole.
Exoplanet: A planet that freely floats between stars or one that orbits a star outside our solar system.

Galaxy: A collection of thousands to billions of stars held together by gravity. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way.
Gamma rays: Part of the electromagnetic spectrum , also called gamma radiation. These waves have lots of energy. They come from big events like solar flares and exploding stars.
Gas: A loose collection of atoms moving around each other.
GPS: This stands for Global Positioning System. It’s a system that uses satellites, ground stations, and receivers to tell you exactly where you are on Earth.
Gravity: A force that pulls matter together.
Greenhouse gas: Gases in the atmosphere that trap heat from the sun. Some greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxide.
Infrared: Part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we cannot see with our eyes but can feel as heat. It is made of waves released by hot objects, such as stars. We call it infrared because these waves are just a little longer than the wavelengths of red light we can see.
Kuiper Belt: A donut-shaped ring of icy objects beyond the orbit of Neptune. Pluto is the best known of these icy worlds.
La Niña: The opposite of El Niño . La Niña happens because of unusually cold sea surface temperatures across the east-central Equatorial Pacific. During a La Niña year, winter temperatures are warmer than normal in the Southeast and cooler than normal in the Northwest United States.
Light year: It’s not a year, or an amount of time at all. It’s the distance light travels in one year. It’s the same as 5,878,499,810,000 miles (or 9,460,538,400,000,000 meters). When things are very far away, it’s easier to talk about their distance in light years than millions or billions or trillions of miles.
Magnetic field: The space around a magnet where the magnetic force is active. Earth has a magnetic field and its extension into space helps protect us from space weather .
Mass: The amount of matter something is made of.
Matter: The stuff that everything is made of. Atoms are a tiny bit of matter. Big planets have lots of matter. Even you are made of matter!
Meteor: The streak of light caused when a meteoroid enters a planet’s atmosphere and starts to burn from the heat of friction.
Meteorite: A meteoroid that lands on the surface of a planet.

Meteoroid: A little chunk of rock in space smaller than a pick up truck. If it were bigger, it would be an asteroid .
Microwaves: Part of the electromagnetic spectrum . These waves of energy are made by stars, the clouds of gas between stars, and supernovae. There is also something called “cosmic microwave background radiation.” It’s all over the universe, and scientists study it to learn how the universe began.
Molecule: The smallest unit of a substance that still acts like the main substance. A molecule can be a single atom or a group of atoms. Water is a substance, and one molecule of water is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, which we write as H2O. That molecule of water still has the same properties as a glass of water. But if you split it into hydrogen and oxygen, it’s not water any more.
Moon: A natural object that travels around a bigger natural object. Planets can have moons. Dwarf planets can have moons. Even some asteroids have moons! Astronomers usually call them satellites or natural satellites.
Nebula: A cloud of dust or gas found between stars.
Neutron star: A very dense star made mostly of neutrons. It has very powerful gravitational force nearby because the whole mass of a star is pulled into one object just a few miles across.
Oort Cloud: A spherical shell around our solar system. It may contain more than a trillion icy bodies. Long-period comets (which take more than 200 years to orbit the sun) come from the Oort Cloud.

Orbit: The curved path that a planet, satellite, or spacecraft moves as it circles around another object.
Ozone layer: A part of Earth’s atmosphere that absorbs lots of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. It is made of a gas called ozone, which is a molecule of three oxygen atoms.
Particle: A tiny amount or small piece of something.
Planet: A large body in outer space that circles around the sun or another star.
Pulsar: An object, thought to be a rapidly rotating neutron star. It releases short pulses of radio waves and other electromagnetic radiation.
Quasar: Compact area in the center of a massive galaxy that is around a supermassive black hole. They are some of the brightest objects in the universe and can be observed across the entire electromagnetic spectrum .

Radiation: The energy or particles released from sources like radioactive materials, explosions, and chemical reactions. This includes energy waves on the electromagnetic spectrum .
Radio waves: Part of the electromagnetic spectrum . Radio waves are around us here on Earth, and they’re out in space too. These waves are low energy. We use them every time we listen to the radio. They’re used to talk to satellites, too. They are also common in outer space, since they are sent out by forming stars, pulsars, supernovae, the sun, and even colliding galaxies.
Radioactive: How we describe some atoms that are unstable. They change into different kinds of atoms and release lots of energy.
Satellite: An object that orbits another object. A moon is actually a satellite. We also say satellite to refer to spacecraft people build that orbit Earth, other planets, moons, asteroids, or other objects out in space.
Solar flare: A burst of energy and particles from the sun. It releases gases, radiation waves, and magnetic storms.
Solar Panel: A piece of material that can capture sunlight and turn it into electricity.
Solar system: A set that includes a star and all of the matter that orbits it, including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects.
Solar wind: The constant stream of particles and energy emitted by the sun.
Space weather: The conditions in space that can affect Earth, satellites, and space travel. Space weather is mostly the result of solar wind and solar storms.
Spacecraft: A vehicle used for traveling in space.
Speed of Light: Light is the fastest thing in the universe. It travels 186,282 miles (299,792,458 meters) every second.
Star: A ball of shining gas, made mostly of hydrogen and helium, held together by its own gravity. Turning hydrogen into helium creates the energy that makes stars shine.
Sun: The star in the center of our solar system.
Supermassive: How we describe objects that have a million times (or more!) mass than our sun.
Supernova: The explosion of a star that makes it as bright as a whole galaxy.
Tectonics: Big movements of Earth’s crust. Tectonics creates mountain ranges, deep sea trenches, volcanoes, and earthquakes that can cause destructive tsunami waves that can cross oceans.
Ultraviolet: Part of the electromagnetic spectrum . It’s called ultraviolet because the waves are shorter than violet light. We can’t see ultraviolet light with our eyes, but some birds and insects can. Our sun emits ultraviolet radiation, and it can give you a sunburn if you’re outside without sunblock for too long.

Universe: All of space and time, and everything in it. It’s everything ever!
Vacuum: An empty space that doesn't have any matter .

Volcano: A mountain or hill that has an opening where lava, rock fragments, or gas erupt from deep inside a planet or moon.
Visible light: The part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can see with our eyes. It’s all the colors of the rainbow.
Wave: A way energy moves from one place to another. Sometimes waves move materials the way water ripples in a pond move the water. Other times, waves don’t move anything around when they transfer energy. For example, X-rays and other waves on the electromagnetic spectrum don’t make any ripples when they move energy from place to place. We classify waves based on how long their wavelengths are. A wavelength is the distance from peak to peak (or valley to valley) of the wave.
X-Rays: Radiation with lots of energy made by very hot gases, stars, neutron stars, and gas around black holes. X-rays have so much energy they can pass though solid materials. They are part of the electromagnetic spectrum .
Explore Some Big Questions about Earth and Space!

What is the Big Bang?

Where does the sun get its energy?

What causes the seasons?

What is a planet?
If you liked this, you may like:
Outer Space Vocabulary
one of thousands of rocky objects that move in orbits mostly between those of Mars and Jupiter and have diameters from a fraction of a mile to nearly 500 miles (800 kilometers)
a heavenly body with such strong gravity that light cannot escape it and that is thought to be caused by the collapse of a massive star
a small bright heavenly body that develops a cloudy tail as it moves in an orbit around the sun
a heavenly body similar to a planet but too small to clear other objects from its orbit
Dwarf Planets in our solar system:
Ceres : a dwarf planet that orbits within the asteroid belt with a mean distance from the sun of 2.7 astronomical units (260 million miles) and a diameter of 590 miles (950 kilometers)
Eris : a dwarf planet with a mean distance from the sun of 67 astronomical units (6.2 billion miles) and a diameter of 1500 miles (2400 kilometers)
Haumea : a dwarf planet that orbits within the Kuiper belt with a mean distance from the sun of 43 astronomical units (6.45 billion kilometers) and a diameter of approximately 890 miles (1,430 kilometers)
Makemake : a dwarf planet that orbits within the Kuiper belt with a mean distance from the sun of 46 astronomical units (6.85 billion kilometers) and a diameter of approximately 930 miles (1,500 kilometers)
Pluto : a celestial object that orbits the sun at an average distance of 3.7 million miles (5.9 million kilometers) and has a diameter of about 1500 miles (2300 kilometers) and is often considered one of the planets
any one of the very large groups of stars that make up the universe
a unit of length in astronomy equal to the distance that light travels in one year or about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers)
one of the small pieces of matter in the solar system that enter the earth's atmosphere where friction may cause them to glow and form a streak of light
a broad band of light that stretches across the sky and is caused by the light of a very great number of faint stars
a smaller body that revolves around a planet
any large heavenly body that orbits a star (as the sun)
Planets in our solar system:
Mercury : the planet that is nearest the sun and has a diameter of about 3000 miles (4700 kilometers)
Venus : the planet that is second in order of distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 7,500 miles (12,100 kilometers)
Earth : the planet that is thirds in distance from the sun. The planet that we live on.
Mars : the planet that is fourth in order of distance from the sun, is known for its redness, and has a diameter of about 4200 miles (6800 kilometers)
Jupiter : the planet that is fifth in order of distance from the sun and is the largest of the planets with a diameter of about 89,000 miles (140,000 kilometers)
Saturn : the planet that is sixth in distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 75,000 miles (120,000 kilometers)
Uranus : the planet that is seventh in order of distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 32,000 miles (51,000 kilometers)
Neptune : the planet that is eighth in order of distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 31,000 miles (50,000 kilometers)
the sun and the planets, asteroids, comets, and meteors that revolve around it
any of the heavenly bodies except planets which are visible at night and look like fixed points of light
the heavenly body in our solar system whose light makes our day and around which the planets revolve
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
Games & Quizzes


List of Space Words in English with Pictures
This reference aims to teach you English vocabulary related to the vast universe. By the end, you will have a solid grasp of key space words and their meanings. Expand your English vocabulary and discover the wonders of space at the same time.
List of Space Words

Space Words with Facts
Asteroids are floating pieces of space minerals and rock. Asteroids, unlike meteoroids, are greater than one meter in diameter.
Atmosphere refers to a layer of gas that surrounds a planet or other celestial body.
“Celestial” refers to objects and phenomena that are of the heavens or sky. Celestial bodies include things like stars, planets, moons, and comets.
Comets are large masses of rock, dirt, and ice that orbit a star (like our sun). When they approach a star, their ice melts and they break apart — forming a trail of dust and gas called a “tail”.
Cosmos is a term, ancient Greek in origin, that refers to the universe.
An eclipse is when a celestial body is blocked from view by another celestial body. A common type of eclipse is a solar eclipse, in which an object (like the moon) obscures the sun.
A galaxy is an entity that is bound by gravitational forces. Galaxies commonly consist of swirling masses of stars, planets, dust, gas, and dark matter. Our galaxy is known as the Milky Way.
Gravity is a force of the universe that attracts objects of mass to one another. On Earth, gravity pulls objects to its center; in our solar system, the sun’s gravity pulls the planets towards the sun’s mass.
A light-year is a measure of distance. It is the amount of distance light can travel in a vacuum. One light-year is 9.46 times 10^12 kilometers.
A meteor refers to the light and particle of matter that enters the Earth’s atmosphere (from a meteoroid).
A meteorite is the remains of a celestial body (a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid) that has collided with earth.
A meteoroid is a celestial body of rock or metal that is one meter in diameter or smaller.
A moon refers to a satellite that revolves around a planet (i.e. orbits the planet).
The orbit is a reference to the direction, acceleration, and speed one (celestial) object takes in relation to another.
A planet is a celestial mass that is large enough that it takes a round shape due to its own gravity. Planets are not large enough, however, to cause nuclear fusion reactions on their own.
A satellite is a natural or man-made object that typically orbits a planet.
A star is a round ball of plasma held together by its own gravity. Stars consist of burning gases and are luminous in nature.
A universe refers to everything within the Cosmos — including stars, planets, moons, and galaxies.
Learn more with natural words in English.
- Latest Posts
- Judgement vs. Judgment: A Look at Spelling Variations - January 9, 2024
- Crochet vs. Knit: Understanding the Differences - January 5, 2024
- Metric vs. Imperial: What’s the Difference? - December 28, 2023
Which Language Do You Want to Learn?
- Inside Babbel
- Babbel Bytes
ARTICLES ABOUT
Jargon watch: astronauts and the language of space travel.

“5-4-3-2-1-0 booster ignition and liftoff!” You’ve probably heard the familiar sounds of a spaceship launch countdown at some point, but there are plenty of other space-related words and phrases that may be totally unintelligible to you. Astronaut lingo has been around as long as NASA itself. In fact, some of the earliest space slang was pretty hilarious, like referring to Cape Canaveral as “Malfunction Junction” or an astronaut’s adjustable seat as a “barber chair.”
Astronaut lingo has toned down quite a bit since the 1960s, and now it largely comprises jargon words and acronyms to describe technical aspects of spaceships and interstellar travel. While most of it’s only really useful if you plan to join NASA or visit the International Space Station , there are a few pieces of slang that have made it into our general lexicon. What may have started in outer space eventually became popular among civilians down on Earth.
This list, which is by no means comprehensive, will introduce you to some of the most common or interesting astronaut lingo. And if you can’t get enough of outer space linguistics, check out this explanation of where some common space exploration terms originated.
A Brief Guide To Astronaut Lingo
abort — to cut short or cancel a mission, first used in reference to space-flight in 1946
airlock — a room with two doors that allows astronauts to enter and exit a spacecraft without letting air out
command module — the compartment of a spacecraft that carries the crew, communications equipment and controls
downlink — radio signal sent to Earth from a spacecraft
glitch — a hitch, snag or malfunction; now used universally
keyhole — a part of the sky where an antenna cannot track a spacecraft due to technical limitations
liftoff — when a rocket leaves the launch pad and begins its flight into space
L minus (L-) — refers to the days, hours and minutes left until launch (L-0). T minus (T-) refers to the time remaining until launch on the official countdown clock. L- time and T- time are usually synced .
LOX — stands for liquid oxygen , which, when combined with fuel, creates a propellant that can be used to launch a rocket
nadir — the downward direction from a spacecraft to the center of a planet below (opposite the zenith )
puffy head bird legs — the feeling of a congested head and wobbly legs astronauts get upon the loss of gravity, which allows the fluid in their bodies to move around
screw the pooch — to make an embarrassing mistake (and yes, this phrase did originally come from NASA)
some words — instructions or advice given between astronauts and ground control, as in “We have some words for you about the signal light issue”
Spacecraft Event Time (SCET) — local time for events that happen aboard the spacecraft (the time on Earth minus the elapsed time between Earth and the spacecraft)
uplink — radio signal sent to a spacecraft from Earth
zenith — the point on a planet directly above the spacecraft (opposite the nadir )
zero gravity — the weightlessness astronauts experience in space due to an apparent absence of gravity (though gravity is still technically in effect)
Header Photo by The New York Public Library on Unsplash
Space Words
Words related to space.
Below is a massive list of space words - that is, words related to space. The top 4 are: galaxy , stardust , universe and cosmos . You can get the definition(s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it. The words at the top of the list are the ones most associated with space, and as you go down the relatedness becomes more slight. By default, the words are sorted by relevance/relatedness, but you can also get the most common space terms by using the menu below, and there's also the option to sort the words alphabetically so you can get space words starting with a particular letter. You can also filter the word list so it only shows words that are also related to another word of your choosing. So for example, you could enter "galaxy" and click "filter", and it'd give you words that are related to space and galaxy.
You can highlight the terms by the frequency with which they occur in the written English language using the menu below. The frequency data is extracted from the English Wikipedia corpus, and updated regularly. If you just care about the words' direct semantic similarity to space, then there's probably no need for this.
There are already a bunch of websites on the net that help you find synonyms for various words, but only a handful that help you find related , or even loosely associated words. So although you might see some synonyms of space in the list below, many of the words below will have other relationships with space - you could see a word with the exact opposite meaning in the word list, for example. So it's the sort of list that would be useful for helping you build a space vocabulary list, or just a general space word list for whatever purpose, but it's not necessarily going to be useful if you're looking for words that mean the same thing as space (though it still might be handy for that).
If you're looking for names related to space (e.g. business names, or pet names), this page might help you come up with ideas. The results below obviously aren't all going to be applicable for the actual name of your pet/blog/startup/etc., but hopefully they get your mind working and help you see the links between various concepts. If your pet/blog/etc. has something to do with space, then it's obviously a good idea to use concepts or words to do with space.
If you don't find what you're looking for in the list below, or if there's some sort of bug and it's not displaying space related words, please send me feedback using this page. Thanks for using the site - I hope it is useful to you! 🐧
- constellation
- interstellar
- solar system
- extraterrestrial
- cosmic dust
- dark matter
- speed of light
- celestial body
- andromeda galaxy
- spacewalking
- gravitation
- asteroid belt
- light-years
- elliptical galaxy
- proxima centauri
- heliosphere
- spiral galaxy
- euclidean geometry
- zero gravity
- earth orbit
- space station
- nucleosynthesis
- celestial sphere
- alpha centauri
- morning star
- dark energy
- dwarf planet
- parallel universe
- astrophysical
- galaxy cluster
- spiral nebula
- yuri gagarin
- space-time continuum
- dwarf galaxy
- milky way galaxy
- globular cluster
- expansion of the universe
- kuiper belt
- epsilon aurigae
- trans neptunian
- electromagnetic spectrum
- general relativity
- omega centauri
- outer space
- supercluster
- ultimate fate of the universe
- orbiting outpost
- black dwarf
- fundamental interaction
- outer solar system
- celestial object
- goldilocks zone
- habitable zone
- space velocity
- spaceflight
- electromagnetism
- cepheid variable
- giant planet
- shuttle discovery
- metric expansion of space
- white dwarf
- star cluster
- astrophilia
- interstellar planet
- sub brown dwarf
- astrophysics
- luminosities
- cosmological principle
- quantum mechanics
- accelerating expansion of the universe
- nasa astronaut
- space shuttle
- big bang nucleosynthesis
- stellar nucleosynthesis
- theoretical physics
- shuttle missions
- thermal equilibrium
- neutron star
- astronomers
- extragalactic
- cosmic microwave background
- observable universe
- outer planet
- interplanetary space
- space debris
- planetary nebula
- structure formation
- elementary particle
- age of the universe
- human spaceflight
- galax urceolata
- international space station
- shuttle atlantis
- microgravity
- newton's law of universal gravitation
- atomic physics
- many-worlds interpretation
- weightlessness
- mission control
- planetary society
- minkowski space
- soyuz spacecraft
- shape of the universe
- open cluster
- interstellar medium
- magellanic cloud
- interstellar space
- brown dwarf
- subatomic particle
- aggregation
- galaxy filament
- subplanetary
- superplanet
- our solar system
- in universe
- planetary body
- space reconnaissance
- goldilocks planet
- inferior planet
- orbit earth
- photosphere
- cold dark matter
- hadron epoch
- square feet
- center of mass
- space agency
- strong nuclear force
- accommodate
- large magellanic cloud
- dimensional
- gravitational singularity
- messier object
- heliocentrism
- planetary system
- metallicity
- dwarf spheroidal galaxy
- interplanetary
- protoplanet
- circumjovial
- planetscape
- extraplanetary
- astronomical object
- many planet
- other planet
- planetary object
- lunar occultation
- judicial astrology
- silicate planet
- inner solar system
- inner planet
- space alien
- eclipsing binary
- gravitational attraction
- cosmological constant
- nicolaus copernicus
- angular momentum
- active galactic nucleus
- nuclear physics
- quantum physics
- space exploration
- blackbody spectrum
- macrocosmic
- superior planet
- major planet
- in outerspace
- islamic astronomy
- irregular galaxy
- lambda-cdm model
- transorbital
- photoevaporation
- minor planet
- nine planet
- satellite planet
- chemical element
- electromagnetic radiation
- lepton epoch
- weak nuclear force
- photon epoch
- harlow shapley
- heavenly body
- extragalactic nebula
- geoheliocentrism
- magmasphere
- jovian planet
- space communication
- planet strike
- proplanetary disk
- gravitational interaction
- physical cosmology
- physical constant
- electroweak
- accumulation
- physical law
- planetesimal
- recombination
- albert einstein
- spectral line
- cramped quarters
- electric charge
- large-scale structure of the cosmos
- russian soyuz
- comoving distance
- wander star
- carbon planet
- olympus mon
- heber curtis
- hydrogen atom
- annihilation
- local group
- thomas wright
- isaac newton
- universe of discourse
- william herschel
- portability
- environment
- standard model
- soap bubble
- immanuel kant
- square foot
- parking bays
- greek language
- homogeneity
- middle ages
- english language
- subpopulation
- ancient greece
- parking spaces
- friedmann–lemaître–robertson–walker metric
- indian philosophy
- netherlands
- kitchenette
That's about all the space related words we've got! I hope this list of space terms was useful to you in some way or another. The words down here at the bottom of the list will be in some way associated with space, but perhaps tenuously (if you've currenly got it sorted by relevance, that is). If you have any feedback for the site, please share it here , but please note this is only a hobby project, so I may not be able to make regular updates to the site. Have a nice day! 🐈
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Space travel
Smart vocabulary: related words and phrases.
The SMART Vocabulary cloud shows the related words and phrases you can find in the Cambridge Dictionary that make up this topic. Click on a word to go to the definition.

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
to do something or go somewhere very slowly, taking more time than is necessary

Like a bull in a china shop: talking about people who are clumsy
Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists

If you ever wonder the meaning of an astronomical word, search no further and browse below to find the definition of the space term. The following are terms from A-Z related to space & astronomy:
Absolute magnitude – also known as absolute visual magnitude, relates to measuring a heavenly object’s brightness when viewed from 10 parsec or 32+ light years.
Absolute zero – The international community agreed to define absolute zero as equivalent to −273.15°C on the Celsius scale or−459.67°F on the Fahrenheit scale. It is the theoretical temperature entropy reaches its minimum value.
Absorption lines are a dark feature in the spectrum of a star formed by cooler gases in a star’s outer layer.
Accretion disks arise when material, usually gases, are transferred from one celestial object to another. There are two places astronomers find accretion disks, binary star systems and galactic nuclei.
Achromatic lens is a combination of lenses made of different glass. These bring two wavelengths into focus (normally red & blue) on the same plane. Achromatic lenses are used to take chromatic aberrations away from images.
Active galactic nuclei is a region in the center of a galaxy that has a higher than normal brightness. It is a class of galaxies that emit a large amount of energy from their center more than ordinary galaxies.
Active optics – Technology developed in the 80’s for reflecting telescopes. The construction enables telescopes to move 8 meter primary mirrors. As the name suggests, it works by “actively” adjusting the telescope mirrors.
Adaptive optics – technology used to improve performance of optical systems through the reduction of rapidly changing optical distortion. It is used to remove atmospheric distortion through the use of astronomical telescopes and laser communication.
Airy disk – Named after George Airy, it is the central spot in a diffraction pattern of a stars image in focus in a telescope.
Albedo is the ratio that light is reflected by a planet or satellite to that received by it. It is the ratio of total-reflected light.
Altazimuth mount is a two-axis mount used to support and rotate an instrument in two common perpendicular axes, vertical (altitude) and horizontal (azimuth).
Altitude is the height of anything above given a planetary reference plane. In astronomy the angular distance of a heavenly body above the horizon.
Anaglyph is a composite picture printed in two colors to produce a 3D image viewed through eye glasses having lenses of the same colors.
Andromeda galaxy is a spiral galaxy that is nearly two and a half million light years away in the constellation Andromeda.
Angular size is the angle between two lines of sight to its two opposite sides. It is a measure of how large an object actually appears to be.
Anisotropy is the state of being directionally dependent. The property of being anisotropic and having a different value when measured in different directions.
Annular eclipse , a solar eclipse in which the moon covers all but the bright ring around the circumference of the sun. When Sun and Moon are exactly in line, because the Moon is smaller, the Sun appears as a bright ring (annulus) surrounding the moon.
Antimatter is matter composed of anti-particles: antiprotons, antineutrons, and positrons. Hypothetically a type of matter identical to physical matter except that the atoms are made of: anti-electrons, anti-protons, and anti-neutrons.
Aperture is a hole, gap, or slit and any other small opening. Diameter of the objective of a telescope.
Aphelion is the point of orbit of a planet or comet which is farthest away from the sun.
Panchromatic – sensitive to light of all colors in the visible spectrum.
Apogee is the point in the orbit of an object (moon, satellite, etc…) orbiting the earth that is at the greatest distance from the center of the earth.
Apparent magnitude is the measure of brightness of a celestial body as seen from Earth as seen without atmosphere.
Apparition is the appearance or time when a comet is visible such as Halley’s Comet.
Archeoastronomy , the study of how people of the past “understand phenomena in the sky and how those phenomena affect their cultures.” Branch of archaeology that deals with use by prehistoric civilizations of astronomical techniques to establish seasons or cycle of the year, as evidenced in megaliths and other ritual structures.
ArcMinute is a unit of angular distance equal to a 60 th of a degree.
ArcSecond a 60 th part of a minute of an arcminute.
Asterism is a group of starts. Also a pattern of stars seen from earth which is not part of an established constellation.
Asteroids are any of thousands of smaller bodies or planetoids that orbit around the Sun. they range in size from 1.6 miles to 480 miles.
Asteroid belt is the region in space between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter where most asteroids are located.
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy dealing with the measurement of the positions and motions of heavenly bodies.
Astronomical unit (AU) a unit of length which is equal to the mean distance of the earth from the Sun.
Astronomy is the science that deals with the material universe beyond the earth’s atmosphere. Natural science engaged with the study of celestial objects.
Astrophotography a specialized branch of photography that captures images of astronomical objects and large portions of the night sky.
Aurora is a radiant emission from the upper atmosphere that occurs intermittently over the middle and high altitudes of both hemispheres. They appear in the form of luminous bands, streamers, or the like. This is caused by the constant bombardment of the atmosphere by charged particles attracted by earth’s magnetic lines.
Aurora Australis or Southern Lights are dynamic displays of light that appear in the Antarctic Skies in winter. They are nature’s light show. It is the name given to light emitted by atoms, molecules, and ions that have been excited by energetic charged particles. Common colors are pale green and pink in spiral curtains, arcs and streamers.
Aurora Borealis also know as Northern Polar lights are natural occurring light display in the heavens in the Northern hemisphere. They are nature’s light show. It is the name given to light emitted by atoms, molecules, and ions that have been excited by energetic charged particles. Common colors are pale green and pink in spiral curtains, arcs and streamers.
Auto guider is a tool used in astrophotography to track celestial objects that are photographed from drifting away from the field of view.
Autumnal equinox is the time that signals the end of the summer months and the beginning of winter. It is when the Sun passes the equator.
Averted vision – a technique to view faint objects using peripheral vision. You do not look at the object directly, but just off to the side, you do this while concentrating on the object.
Axis is the line which an object rotates. A straight line about which a body or geometric object rotates or may be conceived to rotate.
Azimuth is the arc of the horizon measured clockwise from the south point, in astronomy, or from the north point, in navigation, to the point where a vertical circle through a given heavenly body intersects the horizon.
Barlow lens named after its creator Peter Barlow, is a removable lens that can be attached to the eyepiece of a telescope and improves magnification.
Barnard’s Star is a red dwarf star that is six light years away from earth. It is also known as “Barnard’s Runaway Star”.
Barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy that has a centric bar-shaped configuration made-up of stars.
Baryon is a proton, neutron, or any elementary particle that decays into a set of particles that includes a proton.
Baseline is a line that serves as a basis for measurement, calculation, or location. A line between two points or telescopes of an interferometer.
Big Bang is a theory offered by cosmologists related to the early development of the universe.
Binary star is a star system composed of two stars that orbit a common center. The primary star is brightest; the secondary is referred to as the companion star.
Binoculars are optical devices providing good depth effect for both eyes. This consists of two small telescopes fitted side by side.
Black hole theoretically a massive object formed at the beginning of the universe or by a gravitational collapse of a star exploding as a supernova. The gravitational field is intense that no electromagnetic radiation can escape.
Blazar is a compact quasar. An active galaxy with very active and highly variable radio, electromagnetic, and optical emissions.
Blink comparator is used by astronomers, it is an optical instrument used to detect differences in two photographs of the same object by rapidly switching between the two, one picture at a time.
Blueshift is a shift toward shorter wavelengths on the spectral lines of a celestial object. This is caused by the movement of the object toward the object.
Bok globule is small interstellar clouds of very cold gas and dust that are thick. Because of the thickness, they are totally opaque to visible light; however, they can be studied using infrared and radio techniques.
Bolide is a fireball. A large brilliant meteor that explodes.
Bose-Einstein condensate also known as superatom . A phase of matter in which all bosons in a given physical system have been cooled to a temperature near absolute zero and enter the same quantum state.
Brown dwarf is a cold and dark star too small to initiate nuclear reactions that generate heat and light.
Buckyball is a natural occurring type of carbon recognized as C60. The molecular structure looks like the geodesic domes designed by Buckminster Fuller.
Bulge The generally spherical and central region of a spiral galaxy.
Cannibal coronal mass ejections are fast moving solar eruptions that overtake and often absorb their slower moving kin.
Carbon star is a cool, red giant having a spectrum with strong bands of carbon compounds.
Carbonaceous chondrites are recognized as a group of chondritic meteorites composed of at least 7 recognized groups.
Cassegrain telescope is a reflecting telescope in which the light, passing through a central opening in the primary mirror, is brought into focus a short distance behind it by a secondary mirror.
Cataclysmic variable are stars that invariably increase in brightness and decrease to a nearly dormant state.
Catadioptric telescope is a telescope that uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to increase the focal length of the telescope while allowing it to be folded into a more convenient and compact size.
Charge-coupled device (CCD) is a silicon chip used to detect light. A more efficient device at collecting light than regular film.
Celestial pole are two points in which the extended axis of the earth cuts the celestial sphere and about which the stars seem to revolve.
Celestial sphere is an imaginary spherical shell formed by the sky represented as an infinite sphere. The observer’s position is the given center of the sphere.
Cepheid variable is a variable star in which changes in brightness are due to alternate contractions and expansions in volume.
Chandrasekhar limit : named after Indian astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, is the mass limit above which a star has too much mass to become a white dwarf after gravitational collapse.
Charles Messier : French astronomer recognized for publishing the astronomical catalogue that consist of nebulae, star clusters that later become known as “103 Messier objects.”
Chondrite is a stony meteorite containing chodrules. Unchanged meteorites due to melting.
Chromosphere is a layer of the sun’s atmosphere. A gaseous envelope that surrounds the sun outside the photosphere from which large quantities of hydrogen and other gases erupt from.
Circumpolar : Circumpolar stars are permanently above the horizon from a given observing point on Earth; that is to say, they never set. At Earth’s Geographical North Pole (90° north latitude), all stars in the sky are circumpolar. On Earth’s equator, no stars are circumpolar.
Clock drive is a mechanism that causes an equatorial telescope to revolve about its polar axis so that it keeps the same star in its field of view.
Coated optics are optical elements that have refracting and reflecting surfaces coated with one or more coatings of dielectric or metallic material.
Collapsar is a gravitationally collapsed star.
Collimation : Perfectly aligning a telescope’s optics.
Coma : The shroud of gas surrounding a comet’s nucleus.
Coma Berenices is a constellation in the northern sky near Boötes and Leo that contains a prominent cluster of galaxies and the north pole of the Milky Way.
Comet is a celestial body moving about the sun consisting of a central mass surrounded by an envelope of dust and gas that may form a tail that streams away from the sun.
Comet nucleus : The solid, central part of a comet, also known as a “dirty snowball.” It is made of rock, dust, and frozen gases.
Conjunction : A moment when two or more objects appear close together in the sky.
Constellation is any of various groups of stars to which definite names have been given, as Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Boötes, Cancer, Orion.
Convection : The transfer of heat by the circulation or movement of heated parts of a liquid or gas.
Core : The central region of a planet, star, and galaxy.
Corona : A faintly colored luminous ring appearing to surround a celestial body visible through a haze or thin cloud, especially such a ring around the moon or sun, caused by diffraction of light from suspended matter in the intervening medium.
Coronagraph is an instrument for observing and photographing the sun’s corona, consisting of a telescope fitted with lenses, filters, and diaphragms that simulate an eclipse.
Coronagraph mask is a circular shaped instrument designed to block light from a star’s disk. This allows the area close to the target to be studied.
Coronal mass ejection (CME) is a large-scale solar event involving an ejection of hot plasma that may accelerate charged particles and travel as far as the Earth’s orbit, preceded by a shock front that may create a magnetic storm on Earth
Cosmic microwave background : Microwave radiation that permeates the universe and represents the still cooling heat generated in the universe.
Cosmic ray : A radiation of high penetrating power that originates in outer space and consists partly of high-energy atomic nuclei.
Cosmological constant is a term introduced by Einstein into his field equations of general relativity to permit a stationary, nonexpanding universe: it has since been abandoned in most models of the universe
Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that deals with the general structure and evolution of the universe.
Cosmos : The world or universe seen as an orderly, harmonious system.
Crescent : A lunar or planetary phase wherein less than half the surface is illuminated.
Critical density : The density of a pure element or compound at a critical point. Density of the universe that provide enough gravity to bring the expansion to halt.
Crust is the outermost geological thin layer of an asteroid, moon, or planet.
Cryovolcanism is an icy volcano. When water and other liquids or vapor-phase volatiles, together with gas-driven solid fragments, onto the surface of a planet or moon due to internal heating.
Damocloid – An elliptical shaped asteroid with a comet-like orbit. It is rare and named after asteroid 5335 Damocles, the first of its kind discovered.
Dark adaptation – The ability of the human eye to adjust seeing dim objects in the dark.
Dark energy – Negative gravity that plays a role in the acceleration in the expansion of the universe.
Dark matter – a term used to describe matter in the universe that cannot be seen, but can be detected by its gravitational effects on other bodies.
Dark nebula – Dust grains that appear as clouds and is thick enough to shade light from stars in the background.
Declination – Angular distance of an object in the sky, above or below the celestial equator.
Deep-sky objects – Objects that are located beyond the solar system, usually consisting of galaxies, nebulae, stars, and star clusters.
Degree angular Scale interferometer (DASI) – Used to measure temperature and polarization in the Cosmic Microwave background. This is located at NSF Amundsen-Scott South Pole station.
Denison Olmsted – American physicist and astronomer born in Hartford, Connecticut. He is attributed for founding meteor science. He demonstrated that meteors are cosmic in origin and not an atmospheric phenomenon.
Density – Amount of matter contained in a given volume. Usually measured in grams per cubic centimeter.
Deuterium – An isotope of hydrogen with one proton and one neutron in the nucleus having an atomic weight of 2.014.
Diffraction – Spreading out of light as it passes the edge of an obstacle.
Dobsonian telescope – A telescope with a stable altazimuth mount that rotates easily.
Doppler effect – The change in wavelength of sound or light emitted by an object in relation to an observer’s position. An object approaching the observer will have a shorter wavelength (blue) while an object moving away will have a longer (red) wavelength. The Doppler effect is used to estimate an object’s speed and direction.
Double Star – Grouping of two stars. The grouping may look distinct, where the stars appear close together, or physical, such as a binary system.
Double asteroid – Two asteroids that orbit around each other and linked by the gravity between them.
Dust – Minute particles floating in space.
Dwarf galaxy – Small galaxy that contain a few million stars, it is the most common kind of galaxy in the universe.
Dwarf star – A Smaller star. Any star of average to low brightness, mass, and size.
Eccentric – Deviation from a circle, applied when describing the shape of an orbit.
Eclipse – the total or partial blocking of one celestial body by another.
Eclipsing binary – binary star with an orbital plane oriented so that one star passes in front of the other, thus completely or partially blocking the light from the other star during each orbital period.
Ecliptic – the great circle formed by the intersection of the plane of the earth’s orbit with the celestial sphere; the apparent annual path of the sun in the heavens.
Edwin Hubble – American astronomer who pioneered the understanding of the universe. He showed that other galaxies existed, specifically the Milky Way. Born in Marshfield, Missouri then later moved to Chicago at the age of 9. Young Edwin Hubble had always been fascinated with science. He attended Oxford University on a Rhodes scholarship and studied law. He later realized that his true passion was astronomy; in 1917 Hubble received his doctorate in astronomy from the University of Chicago.
Ejecta – material from beneath the surface of a body such as a moon or planet that is ejected by an impact from a meteor and distributed on the surface. Ejecta usually appear lighter in color than the surrounding surface.
Electromagnetic radiation – Radiation that travels through space at the speed of light, and increases the interplay of oscillating and magnetic fields. The radiation has a wavelength and frequency.
Electromagnetic Spectrum – The range of all kinds of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. These include short to long wavelength gamma rays, x-rays, ultra-violet, optical, infrared and radio waves.
Electron – Negatively charged elementary particle found outside, but is attached to, the nucleus of an atom.
Electron Flux – Rate of flow of electrons through a reference surface.
Electron volt – A unit of energy equal to the energy gained by an electron that falls through a potential difference of one volt.
Element – Fundamental unit of matter consisting of fixed number of protons. Number of neutrons and electrons may vary.
Ellipse – An oval shape. Johannes Kepler discovered the orbits of planets are elliptical in shape and not circular.
Elliptical galaxy – A galaxy whose structure is shaped like an ellipse and is smooth and lacks complex structures such as spiral arms. Elongation – The angular separation of an object from the sun.
Emission – Discharge of electromagnetic radiation from an object.
Emission nebula – Cloud of hot gas being illumined from within by the radiation of energetic, young stars.
Ephemeris – Table that identifies the positions of astronomical objects at certain intervals.
Equatorial mount – a telescope mount in which one axis lies parallel to Earth’s rotational axis; the motion of the telescope about this axis compensates for Earth’s rotation.
Equinox – Two points in which the sun crosses the celestial equator in its yearly path in the sky. Equinoxes signal the start of spring and autumn seasons that occur on or near March 21 and September 22, respectively.
Escape velocity – Speed required for something or an object, to be free of the gravitational pull of a planet or other body.
Evening star – Venus, when it appears in the evening sky.
Event horizon – An invisible boundary around a black hole from which nothing can escape the gravitational pull, not even light.
Exit pupil – Image of the objective lens or primary mirror of a telescope formed on the eye side of the eyepiece.
Exobiologist – a person who studies the origin, development, and distribution of ‘living’ systems that may exist outside of Earth.
Extragalactic – Beyond the Milky Way galaxy.
Extrasolar – beyond the sun.
Extraterrestrial – beyond earth.
Eye relief – the distance between the eyeball and the lens nearest the eye of an eyepiece at which an observer can clearly see the entire field of view
Eyepiece – a magnifying lens used to view the image produced by a telescope’s primary lens or mirror.
Far ultraviolet – Ultraviolet radiation with the shortest wavelengths.
Field of view – The area of the sky visible through a telescope or binoculars.
Filter – A device that transmits light of only certain wavelengths. Used by astronomers to observe view specific wavelengths and to minimize the light of exceptionally bright objects.
Finder scope – a small, low-powered telescope attached to a larger telescope that helps the observer locate objects in the sky.
Fireball – A very bright meteor.
First quarter – Phase of the moon a quarter of the way around its orbit from new moon. Eastern portion is visibly bright during this phase.
Flare – The sudden, violent outburst of energy from a star’s surface.
Focus – Point at which rays of light passing through a lens meet.
Focal length – Distance from a lens or mirror to the point it draws light to a focus.
Focal ratio – The ratio of the focal length of a lens or mirror to its diameter.
Focuser – the device on a telescope that holds an eyepiece and moves to allow an observer to bring light to a sharp focus.
Fork mount – an equatorial mount in which the telescope swings in declination between the two prongs of a fork.
Frequency – the number of wave crests or troughs that pass a particular point in a given interval of time (usually one second); usually expressed in hertz (cycles per second)
Full moon – Phase of the moon when it is halfway around its orbit from new moon and opposite the sun in the sky; the full disk is illuminated.
Galactic disk – Disk of a spiral galaxy.
Galactic nucleus – central region of a galaxy. Contains a high density of stars and gas and a super massive black hole.
Galactic plane – Projection of the Milky Way’s disk on the sky.
Galaxy – an enormous gravitationally bound assemblage of millions or billions of stars.
Galaxy cluster – Gravitationally bound assemblage of dozens to thousands of galaxies.
Galilean moons/satellites – Jupiter’s four largest moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto as discovered by Galileo in 1610.
Gamma rays – the highest energy, shortest wavelength form of electromagnetic radiation.
Gamma-ray burst – Short and intense burst of high energy radiation emanating from the distant universe.
Gas giant – Planets made primarily of gas, these include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
General relativity – Theory of relativity governing accelerated motion that describes gravity as a curvature of space-time.
German equatorial mount – Mount in which the declination axis sits on top of the polar axis, with the telescope on one end of the declination axis and a counterweight on the other.
Giant molecular cloud – Interstellar clouds of cold gas and dust that contain tens or hundreds of thousands of solar masses.
Gibbous – The phase of the moon between first quarter and last quarter, when the moon appears more than half illuminated.
Globular cluster – A roughly spherical congregation of hundreds of thousands of stars; most globular clusters consist of old stars and exist in a galaxy’s halo.
Granulation – A pattern of small cells that can be seen on the surface of the Sun. They are caused by the convective motions of the hot gases inside the Sun.
Gravitational lens – A concentration of matter such as a galaxy or cluster of galaxies that bends light rays from a background object. Gravitational lensing results in duplicate images of distant objects.
Gravity – the attractive force that all objects exert on one another; the greater an object’s mass, the stronger its gravitational pull.
Gravity or Gravitational waves – Weak, wavelike disturbances which represent the radiation related to the gravitational force; produced when massive bodies are accelerated or otherwise disturbed.
Greenhouse Effect – An increase in temperature caused when incoming solar radiation is passed but outgoing thermal radiation is blocked by the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide and water vapor are two of the major gases responsible for this effect.
Habitable zone – Zone around a star in which a planet can maintain liquid on its surface.
Halo – Outer region of a galaxy, contains globular clusters, a few stray stars, and dark matter.
Heliacal rising – the period of time when an object, such as a star, is briefly seen in the eastern sky before dawn and is no longer hidden from the glare of the sun.
Heliopause – The point at which the solar wind meets the interstellar medium or solar wind from other stars.
Heliosphere – a vast region around the sun dominated by the solar wind.
Helium – Second lightest element, consists of two protons, two neutrons and two electrons. Eight percent of the atoms in the universe are helium.
Hertz – A unit of frequency equal to one cycle per second.
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram – a diagram that plots luminosity against temperature for a group of stars.
HII region – an area filled with clouds of ionized hydrogen; the ionization is usually caused by radiation from newborn stars.
Hubble law – the principle that a distant galaxy’s recessional velocity is proportional to its distance from Earth
Hubble space telescope (HST) – The Hubble Space Telescope makes its observations from above Earth’s atmosphere. The telescope orbits 600 kilometers (375 miles) above Earth, working around the clock. It was originally designed in the 1970s and launched in 1990. The telescope is named for astronomer Edwin Hubble.
Hydrazine – Colorless liquid which burns quickly and used as rocket and missile fuel.
Hydrogen – the simplest and lightest element; usually consists of just a single proton and electron; about 90 percent of the atoms in the universe are hydrogen.
Hypered film – Film that has been treated, usually with gas, to enhance its response to low light levels.
Hypergalaxy – A system consisting of a spiral galaxy surrounded by several dwarf white galaxies, often ellipticals. Our galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy are examples of hypergalaxies.
Igneous rock – Rock formed by the solidification of magma.
Inclination – Angle between a planet’s orbit and the ecliptic place; Angle between a satellite’s orbit and its host planet’s rotational plane.
Inferior conjunction – The configuration of an inferior planet when it lies between the sun and Earth.
Inferior planet – A planet that orbits the sun inside earth’s orbit, these would be Mercury and Venus.
Inflation – a brief and extraordinarily rapid period of expansion a fraction of a second after the Big Bang.
Infrared – a form of light with slightly lower energy than visible light but with greater energy than radio waves.
Interacting galaxies – galaxies caught in each other’s gravitational embrace, often results in galactic mergers or extreme star formation.
Interference or interferometric fringes – a wave-like pattern resulting from the successful combination of two beams of light which amplifies the light.
Interferometer – A system of two or more widely separated telescopes that achieves the resolving power of a much larger telescope.
Interferometry – The technique of using two or more widely separated telescopes to achieve the resolving power of a much larger telescope.
Intergalactic – Space between the galaxies.
International Space Station – A global cooperative program between the United States, Russia, Canada, Japan, and Europe, for the joint development, operation, and utilization of a permanently habitat in space close to low-Earth orbit.
Interplanetary – Space between the planets.
Interstellar – Space between the stars of a galaxy.
Interstellar medium – Gas and dust located between the stars.
Ion – an electrically charged atom due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
Ionization – Process an atom gains or loses electrons.
Ionized gas – Gas heated to a state where it contains ions and free-floating electrons. Also referred to as plasma.
Ionosphere – An atmospheric layer with a high concentration of ions and free electrons.
Irregular galaxy – Galaxy without a clearly defined spiral or elliptical shape.
Isotope – Forms of an element wherein all atoms have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Jet – a narrow stream of gas or particles ejected from an accretion disk surrounding a star or black hole.
JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory) – The lead U.S. center for robotic exploration of the solar system located in Pasadena, California; JPL spacecraft have visited recognized planets with the exception of Pluto.
Jet stream – a high-speed, wandering wind current in the upper troposphere that blows from west to east and affects weather
Jovian planet – A planet with the same attributes of Jupiter (gas giant).
Kelvin – a unit of temperature equal to one degree on the Celsius scale and 1.8 degrees on the Fahrenheit scale; also the absolute temperature scale defined so that 0 kelvin is absolute zero.
Kuiper Belt – a region in the outer solar system beyond Neptune’s orbit that contains billions of small, icy bodies; Pluto is the largest known Kuiper Belt Object. -L-
L chondrite – a chondrite (a stony meteorite containing small, round, silicate granules called chondrules) that has a low amount of iron.
Lagrange point – One of five locations in space relative to two bodies where less massive body can maintain a stable orbit around a common center of mass.
Large magellanic cloud – Irregular galaxy that orbits the Milky Way Galaxy.
Last quarter – Phase of the moon three quarters of the way around its orbit from the new moon, the western side is lit.
Latitude – the angular distance north or south from the equator to a point on Earth’s surface, measured on the meridian of the point.
Lens – Curved piece of glass that brings light to a focus.
Lenticular galaxy – a galaxy possessing a large bulge and small disk.
Libration – the small oscillations in the moon’s motion that allow Earth-based observers to see slightly more than half the moon’s surface.
Light pollution – Light, typically from artificial sources, that reaches the night sky, obscuring the view of faint astronomical objects.
Light-gathering power – the ability of a telescope to collect light; the larger a telescope’s aperture, the greater its light-gathering power.
Light-year – the distance light travels in one year, equivalent to approximately 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
Limb – Edge of a celestial object.
Limiting magnitude – the apparent magnitude of the faintest objects that can be seen given the local observing conditions and any telescope, film, or other detector you may be using.
LINER galaxy – A low-ionization nuclear emission-line region galaxy belongs to a common class of otherwise normal galaxies that display low-ionization line emissions near their central regions.
Local Group – the galaxy cluster containing 35 galaxies to which the Milky Way Galaxy belongs.
Local supercluster – the galaxy supercluster to which the Local Group belongs; it spreads over 100 million light-years and boasts the Virgo Cluster as its dominant member.
Long-period comet – Comets that have orbital periods greater than 200 years.
Longitude – the angular distance of a particular place on Earth as measured east or west from the prime meridian running through Greenwich, England.
Luminosity – the total amount of light that an object radiates.
Lunar eclipse – a phenomenon caused by the Earth passing between the sun and moon.
Lunar month – the period of one complete revolution of the moon around Earth, 29.5 days.
Lunation – the time between two successive new moons; approximately 29.5 days.
Magnetograph – A recording magnetometer used for recording variations in the earth’s magnetic field.
Magnetometer – An instrument that measures the intensity of earth’s magnetic field.
Magnetopause – The boundary space between the earth’s magnetosphere and interplanetary space (40,000 miles / 65,000 km) above the earth, marked by an abrupt decrease in the earth’s magnetic induction.
Magnetosphere – The dynamic region around a planet where the magnetic field traps and controls the movement of charged particles from the solar wind.
Magnitude – The measurement of an object’s brightness; the lower the number, the brighter the object.
Main sequence – The band of stars on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram stretching from the upper left to the lower right; stars spend most of their lives in the main sequence phase, in which they are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores.
Maksutov telescope – A catadioptric telescope that uses a deeply curved meniscus lens as the correcting plate. (See Catadrioptric Telescope)
Mantle – The portion of a planet’s interior above the core but below the crust.
Mare – Dark and smooth area on the surface of the moon or on a planet.
Mass – A measure of the total amount of matter within an object.
Mass loss – The loss of mass by a star during its evolution; some of the causes of mass loss include stellar winds, bipolar outflows, and the ejection of material in a planetary nebula or supernova.
Megaparsec – One million parsecs, equivalent to 3.26 million light-years.
Meridian – Imaginary circle on the celestial sphere that connects the zenith to the north, or south, celestial pole.
Messier Catalog – A catalog of 107 bright deep-sky objects that belong to a catalog compiled by French astronomer Charles Messier in the 1700s.
Meteor – A flash of light that occurs when a meteoroid burns up in earth’s atmosphere, also known as shooting star.
Meteor showers – Period of meteor activity that occurs when Earth collides with many meteoroids; an individual shower happens at the same time each year and has all its meteors appearing to radiate from a common point.
Meteor storm – Rare events that occur when Earth encounters dense regions within a meteor stream. Such encounters can increase normal meteor rates by more than 1,000 meteors per minute.
Meteorite – Rock from space that survives as it passes through the earth’s atmosphere and falls to the ground.
Meteoroid – Small rock that orbits the sun.
Microgravity – A condition the force of gravity is very low, producing a near-weightless environment.
Microlensing – Effect of gravity from a small astronomical body focusing light rays, similar to lenses.
Micron – One millionth of a meter.
Microwaves – Most energetic form of radio waves.
Milky Way – Spiral galaxy containing our solar system. It can be observed by the naked eye as a faint luminous band stretching across the heavens, containing approximately a trillion stars, most of which are too distant to be seen individually.
Millisecond pulsar – Neutron star rotates hundreds of times per second, which typically accretes matter from a stellar companion.
Minor planet – Rocky body that orbits the sun; also recognized as an asteroid.
Mirror – Piece of glass coated with a highly reflective material.
Molecule – Combination of two or more atoms that represent the smallest part of a compound that has the chemical properties of that compound.
Moon – Smaller body orbiting a larger body; often refers to earth’s moon.
Morning star – Venus, when it appears in the morning sky.
Multicultural astronomy – the variety of ways cultures of the past and present have observed, recorded, interpreted, and made use of astronomy to structure their lives, and in some cases satisfy their curiosity about the universe.
Multiple star system – Gravity bound system in which two or more stars orbit a common center of mass.
MUSES-C – The MUSES-C Mission will investigate an asteroid known as an Earth-approaching type. Through this mission, the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) in Japan intends to establish the technology to bring back samples of an asteroid’s surface to Earth.
MUSES stands for a series of missions performed launched by the MU rocket and C means the third mission of this series.
Naked eye – something visible without the aid of binoculars or a telescope.
Near-infrared – light from the part of the infrared band of the electromagnetic spectrum closest to the visible range.
Nebula – a cloud of interstellar gas and dust; some nebulae represent stellar nurseries, others represent stellar graveyards.
Neutrino – a subatomic particle produced in nuclear reactions and in supernovae that very rarely interacts with matter; neutrinos have no electrical charge and travel at or very close to the speed of light.
Neutron – a subatomic particle with no electric charge that resides in an atomic nucleus; it has about the same mass as a proton.
Neutron star – the collapsed, extraordinarily dense, city-sized remnant of a high-mass star.
New moon – the phase in which the moon is in the same direction as the sun in Earth’s sky, so it is unilluminated and invisible.
Newtonian telescope – a reflecting telescope in which a flat secondary mirror (called the diagonal) in the center of the tube reflects light to a focus outside the tube.
NGC – New General Catalogue, a 19th-century compendium of deep-sky objects such as galaxies, globular clusters, and nebulae.
NGC Objects – deep-sky objects such as galaxies, globular clusters, and nebulae included in the New General Catalogue.
North Celestial Pole – the point in the sky to which Earth’s Geographical North Pole points.
Nova – An explosion on the surface of a white dwarf that is accreting matter from a companion star, which causes the system to temporarily brighten by a factor of several hundred to several thousand.
Nuclear fusion – The process by which two atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier atomic nucleus; this is the energy source that causes most stars to shine.
Nucleosynthesis – the creation of heavy elements from lighter ones by nuclear fusion.
Nucleus – the central region of an atom, comet, or galaxy.
O-type star – A hot, massive blue star that emits strongly at ultraviolet wavelengths and has a surface temperature of roughly between 28,000 to 40,000 Kelvin’s.
OB Association – Loose grouping of O and B stars, which are the most luminous, most massive, and shortest-lived stars.
Objective – Telescopes primary lens or mirror that gathers light and brings it to a focus.
Obliquity – the angle between the plane of the earth’s orbit and that of the earth’s equator, equal to 23°27′; the inclination of the earth’s equator.
Occultation – The passage of one object in front of a smaller one, temporarily obscuring all or part of the background object from view.
Omega – 1. The ratio of the density of the universe to the critical density 2. The 24th letter of the Greek alphabet.
Omega centauri – Massive globular cluster in the southern constellation Centaurus located about 17,000 light-years from Earth; also known as NGC 5139.
Omega nebula – Also known as the Swan Nebula, M17, NGC 6618, the Horseshoe Nebula, and the Lobster Nebula. One of the Milky Way’s numerous stellar nurseries; the Omega Nebula is about 5,000 light-years from Earth and can be seen in the constellation of Sagittarius the Archer.
Oort cloud – Cloud of cometary nuclei that surrounds the sun at a distance of many thousands of astronomical units.
Open cluster – System containing a few dozen to a few thousand stars that formed from the same stellar nursery.
Opposition – Best time to observe a planet. The moment a planet far from the sun than Earth appears opposite the sun in the sky.
Optical double – Two stars at different distances that lie along nearly the same line of sight and thus appear close together.
Optics – Study of light and its properties; Lenses or mirrors.
Orbit – Curved path, usually elliptical in shape, an object follows around a bigger object or a common center of mass.
Orbital period – The length of time it takes one body to orbit another.
Outgassing – Release of gas from rocky body.
PAHs – Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). A class of stable organic molecules. Flat molecules made of carbon and hydrogen atoms. These are common and highly carcinogenic. It is one of the by-products of combustion from automobiles and airplanes.
Parallax – Shift of a nearby object against a fixed background due to the movement of the observer. Astronomers observe the parallax of stars to measure the distances of these same stars.
Parsec – Distance an object would have to be from earth so that its parallax when seen from two points separated by 1 AU is equivalent to one arcsecond, equivalent to 3.26 light years.
Patera – A shallow crater with a scalloped and complex edge; saucer shaped volcanic structure.
Penumbra – Outer filament region of a sunspot. Lighter region of a sunspot surrounding the umbra (dark center).
Penumbral eclipse – When the moon passes into the outer ring of earth’s shadow, causing a slight shading in the moon’s appearance.
Periastron – Location in an objects orbit where it is closest to the star it orbits.
Perigree – Position of a satellite’s orbit when it is closest to earth.
Perihelion – Position of an object, or body, when it is closest to the sun.
Period – Measured interval a regular event takes place.
Periodic comet – Comet that has been observed to circle, orbit, the sun more than once.
Phase – Cycle of changes in the appearance of a moon or a planet.
Photometer – An instrument that measures light emitted by an object.
Photometry – Degree and measurement of light intensities.
Photons – Single waves of light.
Photosphere – Visible surface of the sun.
Photovoltaic – When light energy or emissions are converted into electricity.
Pixel – Short name for “picture element.” Individual light detectors on a CCD chip.
Planck scale – A unit of measurement scientists utilize to describe the universe. One unit (length) of Planck is 10^-33 centimeters.
Planet – A gaseous, rocky body that orbits a star.
Planetary nebula – Gas ejected by dying, low mass stars that appear as glowing shells.
Planetesimals – Asteroid sized bodies in a new planetary system that collide and form larger bodies.
Planisphere – Map of the sky in two-dimensions with an adjustable overlay and shows a part of the sky that is visible anytime of the night or year.
Plasma – Gas heated to a state wherein it contains ions and free floating electrons.
Plasmasphere – Area of cold and high density plasma above the ionosphere.
Plate tectonics – Theory describing the possibility on how earth’s crust is broken into plates, suggesting that those plates move thru and across earth’s surface.
Polar cap – Icy region of a planet, specifically the north and south pole.
Polarization – When the direction of electric or magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave changes in a regular pattern.
Position angle – Direction in the heavens one celestial object from another, measured eastward from due north.
Power – Capability of a telescope or binoculars to increase the size of an object that is far away.
Poynting-Robertson effect – Interplanetary particles that are dragged and is caused by its interaction with solar radiation. This causes particles to lose momentum in their orbit and is drawn towards the sun.
Precession – Periodic change in the direction of an objects axis caused by the gravitational influence from another body.
Primary lens – Main lens of a telescope that gathers light bringing the object into focus.
Primary mirror – Main mirror of a telescope that gathers and reflects light to bring the object in focus.
Prime meridian – The line of longitude that runs through Greenwich, England.
Prism – A piece of glass that breaks white light into it’s basic colors, it is wedge shaped.
Prograde – Same direction a planet rotates. An object that move, or looks like it moves in the same direction of solar system bodies or moons.
Prominence – A massive eruption of gas streaming off the surface of the sun towards the corona.
Proper motion – Annual movement of a star across the sky.
Proton – Subatomic particle that is found in an atom’s nucleus and possesses a positive electric charge.
Protoplanet – Gas, dust, and rocks that gradually becomes a whole planet.
Protoplanetary disk – Disk of gas and dust surrounding a new planet; planets that form through the collision of particles inside the disk.
Protostar – Cloud of hot, dense gas and dust that gravitationally collapses to form a star.
Proxima Centauri – Nearest star to the sun at 4.2 light years away.
Pulsar – A rotating neutron star that showers earth with regular pulses of electromagnetic radiation.
Quadrillion – a number represented in the U.S. with a 1 followed by 15 zeros, in the U.K., 1 followed by 24 zeros.
Quantum mechanics – Law in physics describing the behavior of matter at the atomic and subatomic level.
Quasar – Highly energetic core in a young galaxy believed to be powered by a big black hole; Short for quasi-stellar object.
Radial velocity – Acceleration of an object going away from or headed towards an observer.
Radiant – Location in the sky where meteors belonging to a meteor shower appear to come from. 2. Very bright and shining.
Radiation – Electromagnetic waves as it relates to astronomy.
Radiation pressure – Amount of pressure applied on a surface by electromagnetic radiation or light.
Radio galaxy – Galaxy that emanates a large amount of radio waves.
Radio telescope – Designed to observe radio waves coming from space.
Radio waves – Type of light with the longest wavelength with the least energy.
Radiometer – Instrument to measure total energy or power from an object in the form of radiation, especially infrared radiation.
Red dwarf – Smaller star with a low mass, cooler, and less luminous than the sun.
Red giant – Cool star nearing the end of its cycle. These have expanded up a hundred times the diameter of the sun.
Red supergiant – Cool star nearing the end of its cycle. These have expanded from a hundred to a thousand times the diameter of the sun.
Redshift – Multiplication of wavelength of light coming from an object due to its motion away from earth; expansion of the universe; strong gravitational field.
Reflection nebula – Gas and dust clouds made visible due to the dust reflection from the light of nearby star.
Reflector – Telescope using curved mirrors to gather light.
Refractor – Telescope using a glass lens to gather light.
Regolith – Soil from the moon produced meteorites hitting the surface.
Relativity – Theory in physics developed by Albert Eistein. Describes measurement made by two observers who are in relative motion.
Resolution (Resolving power) – A camera or a telescopes ability to capture fine details of a subject.
Reticle – Using two fine wires as part of a grid attached to part of the focal plane or a telescope eyepiece. This is used to locate the position and size of a celestial object.
Retrograde – Viewing objects that move or appear be moving in the opposite direction of a solar system bodies.
Reusable launch vehicle (RLV) – A spacecraft that may be reused on successive missions. A single stage to orbit spacecraft.
Revolution – Orbital motion of a body around a common center of mass or another body.
Ribonucleic acid – Nucleic acid containing genetic information.
Rich clusters – Galaxy clusters with high population densities.
Rich-field telescope – Designed to show a larger field of view at low magnification.
Right ascension – Angular Distance of a celestial object located east of the vernal equinox; outer space sphere equivalent to longitude.
Rotation – Spin of an asteroid, planet, star, moon, or galaxy on its central axis.
Rotation period – Measurable interval an asteroid, planet, star, moon, or galaxy completes one rotation.
Satellite – Small body or object that goes (orbit) around a planet or asteroid.
Scarp – Cliffs created by erosion and fault movement.
Schmidt camera – Catadioptric telescope used as a camera to photograph wide-angle pictures of the sky.
Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope – Small telescope wherein light passes through a correcting lens located at the front of the telescope; it then reflects off a primary mirror back to a secondary mirror, which then directs the light through a hole in the primary and out the back of the scope; this is a popular telescope for backyard observers.
Secondary mirror – A small mirror used in a telescope that redirects light gathered by a primary mirror.
Seeing – State of observing phenomena created by earth’s atmosphere that blurs images of astronomical objects.
Semimajor axis – Average distance an orbiting body has from its main body.
SETI – “search for extra-terrestrial intelligence”
Seyfert galaxy – Galaxy with a bright nucleus coupled with spectral emission lines, first discovered by Carl Seyfert in 1943.
Shock wave – Powerful wave emanating from a sudden change in density, temperature, or pressure traveling through a medium faster than sound travels on that same medium.
Short-period comet – A comet that orbits less than 200 years.
Sidereal – Relating to or measured in association with the stars.
Sidereal year – Amount of time a body revolves around another with respect to the stars.
Siderostat – A movable flat mirror that reflects light from a celestial object to a given location.
Singularity – An area wherein space and time are infinitely distorted.
Small Magellanic Cloud – An irregular and small galaxy orbiting the Milky Way galaxy.
Solar eclipse – When the moon passes between the earth and the sun.
Solar filter – A safety precaution, a filter used to block almost all the suns light when being viewed.
Solar irradiance – Radiant energy given by the sun over all wavelengths that falls each moment on one square meter of earth’s atmosphere.
Solar mass – Amount of mass contained in the sun, equivalent to 330,000 times to that of earth.
Solar system – System that includes the sun and the smaller bodies (planets, moons, etc…) that orbit the sun.
Solar wind – Stream of charged minute particles coming from the sun.
Solstice – Two points on the celestial sphere wherein the sun is farthest north or south of the equator.
South Celestial Pole – Point in the sky earth’s South Pole points.
Space weathering – Process of changing the surface of an object in space by impacts from small meteors, cosmic rays, and even the solar wind.
Space-time – When the three dimensions of space come together with one dimension of time wherein the events can be exactly calculated.
Special relativity – Theory of relativity applied concerning uniform motion. It proposes that the equivalence of mass and energy and differs from Newtonian physics only when speeds approach that of light.
Spectra – Plural of spectrum. Radiant source energy.
Spectral class – Classification of stars based on its spectrum as dictated by the surface temperature.
Spectral line – Specific wavelength of light that corresponds to the energy exchange of an atom or molecule.
Spectrograph/Spectrometer – Instrument coupled to a telescope that records the spectrum of an astronomical object.
Spectroheliograph – Instrument to photograph the sun on a single wavelength of light.
Spectroscope – An apparatus to explore spectra.
Spectroscopy – In astronomy, it is the study of astronomical subjects.
Spectrum – 1. Whole range of electromagnetic radiation, also known as light. 2. Energy created from a radiant source.
Speed of light – Light travels through a vacuum at 186,000 miles per second, or 300,000 km per second. Distance light travels in a unit of time through a specific substance.
Spicules – Supersonic jet about 300 miles(500 km) in diameter found in the chromosphere of the Sun.
Spiral arm – Concentration of young stars, gas and dust that are finds its way out of the nucleus of a spiral galaxy.
Spiral galaxy – Spiral shaped system composed of stars, gas clouds, and dust, numbering in the billions.
Standard candle – In astronomy, refers to an object known for its brightness and is sometimes used to determine distances.
Star – Sphere of hot gas held together by gravity and emanates brightness by itself; common stars utilize nuclear fusion from its core to generate energy.
Star atlas – Collection of maps using a coordinate system to mark positions of astronomical objects, stars, galaxies, and nebula.
Star hopping – Techniques using familiar patterns of stars to hop from one part of the sky to another; this is done through the use of a telescope and the naked eye.
Star party – Gathering of friends and other like-minded people to observe the night sky.
Starburst galaxy – Galaxy going through a high rate of star formation.
Stellar evolution – Process, that include changes a star goes through during its existence.
Stellar wind – Torrent of charged atomic particles emanating from stars. Release of gas from a star’s surface.
Sterocomparator – Device that allows astronomers to view two separate images of the same region in the sky at the same time.
Stone Meteorite – Meteorite resembling a terrestrial rock made of similar materials.
Sublimate – Transition of solid substance that is evaporated into a gas without reaching the liquid phase.
Summer – Season in the northern hemisphere that commences around June 21.
Sunspot – Dark, temporary cool spot found on the surface of the sun.
Sunspot cycle – Cycle that averages eleven years at which the number of sunspots decreases and increases.
Supercluster – Huge congregation of galaxy clusters that span hundreds and millions of light years away.
Superfluid – State of matter exhibiting frictionless flow. Liquid helium is the one element that produces this when cooled to absolute zero.
Superior conjunction – Constitution of an inferior planet when it lies on the far side of the sun.
Superior planet – Planets that are farther from the sun than earth: Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto.
Superluminal motion – Movement that looks to be faster than the speed of light.
Supermassive black hole – Black hole located at the center of a galaxy containing millions or billions of solar masses.
Supernova – Destructive explosion of a star.
Supernova remnant – Growing cloud of gas that is the outer layers of star that just exploded.
Synchronous rotation – Identical rate of rotation of a satellite or moon to the main and bigger object it orbits.
Synchrotron emission – Electromagnetic field from high-energy electrons that are moving in a given magnetic field.
Synodic Period – Interval between points of opposition in a superior planet. -T-
Telescope – Instrument used to brighten and magnify the view of astronomical objects.
Tera (trillion) – American use, one followed by 12 zeros
Terminator – Boundary of a planet or moon separating the lighted from the unlighted sides.
Terrestrial – Related to the earth.
Terrestrial planet – Small and rocky planet which includes Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Venus.
Thermal radiation – Electromagnetic radiation coming from an object that is not at absolute zero.
Tidal force – disparity in gravitational force between two points on an object caused by the gravity of another object; this leads to a deformation of an object.
Tides – Distortion of a body caused by the gravitational influence on another body.
Trans-Neptunion Object – Object in our solar system lying beyond the orbit of Neptune.
Transit – Passage of a smaller body in front of a larger body. Passage of a celestial body across an observer’s meridian.
Transparency – Clarity of the sky.
Trapezium – Open cluster of young stars, protostars, gas, and dust in the Orion Nebula that feature four stars forming a the trapezium.
Tremolite – Common mineral in metamorphic rocks, made up mainly of calcium and magnesium.
Trojan – Asteroid lying in or near the Lagrange points 60 degrees for or aft Jupiter along the planet’s orbit.
Tropical year – Time earth revolves around the sun in relation to the vernal equinox.
True field of view – Angle of sky viewed through an eyepiece attached to a telescope.
Type la supernova – the explosion of a white dwarf that occurs when it accretes enough mass from a companion star to go above the Chandrasekhar limit.
Type II quasars – a quasar enshrouded in gas and dust that emits very little visible light, however, is easily seen in the infrared and x-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum
Type II supernova – the explosion of a massive star that occurs when its core runs out of nuclear fuel; these explosions leave behind a neutron star or a black hole -U-
Ultraviolet light or radiation – Radiation with a higher amount of energy than visible light, not as much as x-rays.
Umbra – Perfect and whole shadow of an opaque body, like a planet, wherein direct light from the source of brightness is totally reduced. 2) Area of complete darkness on the shadow made by an eclipse.
UIB – unidentified infrared bands – Unknown objects in space that produce unidentifiable infrared emission patterns.
Universal time – Also recognized as Greenwich Mean Time, forming the basis in all civil time keeping. Local time centered in Greenwich, England.
Universe – All that exists
UT – short for Universal time
UV (ultraviolet) – short for Ultra Violet. -V-
Van Allen Belts – Dual belts of charged particles from a solar wind trapped in earth’s magnetic field above the atmosphere. Radiation zone of charged particles surrounding Earth. Shape of Van Allen belts is determined by Earth’s magnetic field.
Variable star – Star with varying luminosity.
Vernal equinox – Time of the year when the sun moves across the celestial equator towards the north, usually around March 21.
Vignetting – Decreased illumination over an image plane in a camera or in some cases a telescope, this causes a distortion close to the edge of an image.
Virgo Cluster – 2,500 known galaxies near the north galactic pole of the constellation Virgo that is 60 million light years from earth.
Visible light – Wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can see.
Voids – Big regions of empty space found amidst galaxy clusters and superclusters.
Volatiles – Chemical compounds that become gaseous at very low temperatures. -W-
Waning/Waxing – Interval between full and new moon
Wavelength – Distance between two wave crests.
Weight – Force applied on an object because of gravity.
White dwarf – Dense remains of an intermediate mass star like the sun that has collapsed and is the same size as earth.
Winter – Season in the Northern Hemisphere that begins December 21.
Wolf-Rayet star – Luminous and hot star having temperatures reaching 90,000 kelvins.
X-rays – Type of electromagnetic radiation that is like light but has a shorter wavelength capable of penetrating solid objects and ionizing gases.
X-class flares – Most energetic kind of solar flares and the brightest.
X ray star – Bright object emitting x rays as a primary component of its radiation.
Yellow dwarf – Ordinary star, like the sun and is at its stable point in its transformation.
Zenith – Point on the celestial sphere directly above an observer.
Zenith hourly rate – Meteorites expected to be viewed per hour during a meteor shower, where the meteor showers radiance is at an observer’s zenith.
Zodiac – Imaginary belt across the sky wherein the solar system can always be found.
Zodiacal light – Cone of light that can be observed above the horizon before sunrise or after sunset. This is caused by small particles of reflected sunlight.
- Português Br
- Journalist Pass
Profiling health in extraterrestrial space travel
Susan Buckles
Share this:

Mayo Clinic research is probing the effects of space travel on the health of citizens engaged in a new era of civilian spaceflights.
The team led by Andre Terzic, M.D., Ph.D. , studied health responses of the Axiom Mission (Ax-1) crew by monitoring the first all-civilian astronaut crew to fly to the International Space Station. The research data revealed that the health profiles of the civilian astronauts were maintained during and after the 17-day space mission.
The Ax-1 crew launched from the Kennedy Space Center in April 2022 with several research projects from Mayo Clinic. The research is published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings .
"As more civilians are poised to participate in space travel, understanding the impact of spaceflight on health in the general population is essential for safety, health risk mitigation and development of countermeasures," says Dr. Terzic, a Mayo Clinic Distinguished Investigator and senior author of the research. "The present clinical study provides an inaugural plasma health profile for the next generation of space travelers."
Dr. Terzic is the Marriott Family Director, Comprehensive Cardiac Regenerative Medicine for the Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics.
Space travel within reach of private citizens
For more than 50 years, NASA has studied the health of professional astronauts with a goal of making space travel safer. One of the main risks is exposure to space radiation particles once rocket ships leave the Earth's atmosphere. Radiation on Earth has been linked to risk of cancer , heart disease and degenerative conditions such as cataracts . Microgravity in space may also potentially trigger loss of bone density and muscle mass.
Currently little is known about how private citizens, who do not go through the same rigorous training as professional astronauts, may respond during or after space flights. In addition, much still needs to be learned about the long-term effects of extraterrestrial travel as NASA and private astro businesses set their sights on lengthy space travel to the moon or Mars.

Currently little is known about how private citizens, who do not go through the same rigorous training as professional astronauts, may respond during or after space flights.
Ax-1 crew image courtesy Axiom
The Mayo researchers took blood plasma samples from crew members one month before the launch, four days into the flight and upon landing. They studied the health of crew members. They evaluated 14 health blood biomarkers reflecting sugar and electrolyte levels, along with heart, liver and kidney status. A biomarker is a measurable indicator of disease or infection. Examples of biomarkers are blood pressure, body temperature and body mass index.
"This was a unique and exciting opportunity to be one of the first, if not the first, to study health response of common citizens in space. Previous studies have focused on the health and safety of professional astronauts who have extensive training to handle the rigors of space travel," says Armin Garmany, an M.D./Ph.D. student within the Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine and first author on the paper. "Our study points to the need for more research on various aspects of health as private space travel becomes more common." Garmany is a trainee in Dr. Terzic's cardiac protection and regeneration lab.
Additional research is needed to validate these findings in larger groups of civilian space travelers. The goal is to build a scientific database that would inform safety and wellbeing of space travel for private citizens.
The team is now focusing on regenerative sciences data acquired from experiments on heart cells conducted by the Ax-1 crew during its mission to the International Space Station.
Review the study for a complete list of authors, disclosures and funding.
Related articles:
Taking Mayo Clinic research beyond the lab and into space
Safer space travel is the goal of Mayo researchers
- Mayo researchers develop tool that measures health of a person’s gut microbiome Perimenopause, menopause and … weightlifting? Expert explains value for bone health
Related Articles


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
12 Boundless. The term boundless describes a space that is limitless or immense. In other words, there are no boundaries, which is true for outer space as it's constantly expanding. Example: "The boundless nature of outer space attracts hundreds of thousands of applicants to the academy each year!". 13 Endless.
From infinite to awe-inspiring, from mysterious to boundless, a plethora of words have been crafted to convey the profoundness and grandeur of space. Join us as we embark on a linguistic journey through the lexicon of words that paint the portrait of the cosmos in all its glory. Adjectives for Space. Here are the 20 Most Popular adjectives for ...
Let's explore some incredible adjectives that capture the wonder and beauty of outer space. 1. Breathtaking. Outer space is an awe-inspiring place, filled with breathtaking sights and wonders. From dazzling star clusters to radiant nebulae, the sheer magnificence of the universe is unparalleled. 2.
Space: vast, mysterious, and awe-inspiring. In this guide, discover a plethora of words that perfectly encapsulate its vastness, beauty, and sometimes its emptiness. Description of Space Space refers to the limitless expanse where stars, planets, and galaxies exist, as well as any unoccupied area or interval. List of Words to Describe Space Here are the ... <a title="Top 100 Adjectives for ...
50 Words Associated With Space Meanings. Cosmos: Refers to the universe as an ordered, harmonious and holistic entity. It encompasses everything that exists: space, time, matter, energy, and the physical laws and constants that describe them. Universe: The totality of all space, time, matter, and energy that exist, including all planets, stars ...
Found 817 words to describe [space travel].You can click on each words to see its definition.
Words to Describe space travel. Below is a list of describing words for space travel. You can sort the descriptive words by uniqueness or commonness using the button above. Sorry if there's a few unusual suggestions! The algorithm isn't perfect, but it does a pretty good job for most common nouns.
Ethereal: The beauty of space can be described as ethereal and otherworldly. Dazzling: The dazzling light of stars fills the night sky with awe-inspiring beauty. Radiant: The sun's rays illuminating space create a radiant spectacle. Twinkling: The stars in the night sky appear as tiny twinkling lights.
dark matter. Dark matter is a theoretical, invisible form of matter that exists in space. The word matter is used to refer to all of the stuff that takes up space as we know it. In outer space, everything is positioned where it is because of gravity. We can see what is going on in outer space because of light.
Start your own discovery of astronomy and outer space with some basic vocabulary words. Space words can be exciting and confusing! Start your own discovery of astronomy and outer space with some basic vocabulary words. ... intergalactic - travel between galaxies; interstellar - between stars; Oort cloud - shell around our solar system in the ...
List of Adjectives For Space | Words For Space. Some of the adjectives given below may be used to describe physical space, while others may describe more figurative or abstract space. ... Adjectives for Space Travel. 1. astronauts 2. space shuttle 3. space station 4. spacewalk 5. launch 6. re-entry 7. orbit 8. telescope 9. probe 10. satellite ...
Solar system: A set that includes a star and all of the matter that orbits it, including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects. Solar wind: The constant stream of particles and energy emitted by the sun. Space weather: The conditions in space that can affect Earth, satellites, and space travel.
a unit of length in astronomy equal to the distance that light travels in one year or about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers) meteor | see definition ». one of the small pieces of matter in the solar system that enter the earth's atmosphere where friction may cause them to glow and form a streak of light.
Space Words with Facts. Asteroid. Asteroids are floating pieces of space minerals and rock. Asteroids, unlike meteoroids, are greater than one meter in diameter. Atmosphere. Atmosphere refers to a layer of gas that surrounds a planet or other celestial body. Celestial.
Astronaut lingo has been around as long as NASA itself. In fact, some of the earliest space slang was pretty hilarious, like referring to Cape Canaveral as "Malfunction Junction" or an astronaut's adjustable seat as a "barber chair.". Astronaut lingo has toned down quite a bit since the 1960s, and now it largely comprises jargon words ...
Below is a massive list of space words - that is, words related to space. The top 4 are: galaxy , stardust , universe and cosmos . You can get the definition(s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it.
Space travel - related words and phrases | Cambridge SMART Vocabulary
Full moon - Phase of the moon when it is halfway around its orbit from new moon and opposite the sun in the sky; the full disk is illuminated. -G-. Galactic disk - Disk of a spiral galaxy. Galactic nucleus - central region of a galaxy. Contains a high density of stars and gas and a super massive black hole.
To discover and use lots more exciting English resources, create your own Twinkl account here. This out-of-this-world word mat features lots of ambitious adjectives and higher-level vocabulary words to describe space. It's the perfect visual aid to inspire your pupils when they're writing creatively and descriptively about a journey into space. The word mat splits the vocabulary under seven ...
What are space words? Increase your cosmic vocabulary using the list below and enrich your child's exploration of the universe. Space Words. Asteroid - Small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun. Asteroid belt - The region between Mars and Jupiter that contains the largest population of asteroids in our solar system.; Astronaut - A person trained to travel in a spacecraft.
What is this KS2 Descriptive Word Mat: Journey into Space? This out-of-this-world word mat features lots of ambitious adjectives and higher-level vocabulary words to describe space. It's the perfect visual aid to inspire your pupils when they're writing creatively and descriptively about a journey into space.
interstellar flight. orbital flight. cosmonautics. nasar. interplanetary journey. space assets. flying through outer space. Another way to say Space Travel? Synonyms for Space Travel (other words and phrases for Space Travel).
Mayo Clinic research is probing the effects of space travel on the health of citizens engaged in a new era of civilian spaceflights. The team led by Andre Terzic, M.D., Ph.D., studied health responses of the Axiom Mission (Ax-1) crew by monitoring the first all-civilian astronaut crew to fly to the International Space Station. The research data ...
At The Macallan, we believe whisky making is like time travel: what we bottle today was created many years in the past, and the spirit we lay down in casks now is destined for many years in the future. Through time travelling, we learn from the past and look to the future. ... SPACE Mastery. When chopped by the sickle, the energy turns these ...