Dodge Journey 2.4 Serpentine Belt Diagram
Looking for a reliable and efficient vehicle that can take you on all your adventures? The Dodge Journey 2.4 is a versatile and spacious SUV that’s perfect for families, road trips, and daily commutes. One important component of the Dodge Journey’s engine is the serpentine belt, which plays a crucial role in powering various engine components. Understanding the serpentine belt diagram is essential for maintaining and repairing your Dodge Journey, so let’s take a closer look at this important aspect of your vehicle’s engine system.

2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 Serpentine Belt Diagram
If you’re looking for a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 serpentine belt diagram, you’ve come to the right place. The serpentine belt plays a crucial role in the functioning of your vehicle’s engine, powering essential components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. A clear and accurate diagram is essential for proper installation and maintenance of the serpentine belt. By following the diagram, you can ensure that the belt is routed correctly and at the appropriate tension, ultimately contributing to the smooth operation of your Dodge Journey. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, having access to the correct serpentine belt diagram is essential for keeping your vehicle running smoothly.

abrieliaasrokah.blogspot.com
2013 Dodge Journey Belt Diagram
The 2013 Dodge Journey 2.4 serpentine belt diagram is an essential reference for DIY car maintenance. This diagram illustrates the routing of the belt around various pulleys, guiding the proper installation and tensioning of the serpentine belt. By following the belt diagram, car owners can ensure that the belt is correctly positioned, preventing slippage and potential damage to the engine components. Understanding and utilizing the belt diagram is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of the Dodge Journey’s engine.

diagramwiringschema.blogspot.com
2010 Dodge Journey Belt. Accessory Drive, Serpentine
If you’re looking for information about the 2010 Dodge Journey’s accessory drive and serpentine belt, you’ve come to the right place. The accessory drive system in the Dodge Journey 2.4L engine is powered by a serpentine belt, which is responsible for driving multiple components such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Understanding the serpentine belt diagram for the Dodge Journey 2.4L engine is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. By following the correct belt routing, tensioning, and inspection procedures, you can ensure the smooth operation of the accessory drive system in your Dodge Journey. If you’re in need of a visual guide, the serpentine belt diagram for the 2010 Dodge Journey can be a helpful resource.

www.moparpartsinc.com
Dodge Nitro Drive Belt. Serpentine Belt. Routing:crk, Idler, Tens, Comp
If you’re looking for information on the Dodge Journey 2.4 serpentine belt diagram, understanding the routing of the drive belt is essential. The serpentine belt, also known as the drive belt, plays a crucial role in powering various components of the engine, including the crankshaft, idler pulley, tensioner, and compressor. Proper routing of the drive belt ensures that these components function efficiently, allowing your Dodge Nitro to operate smoothly. Understanding the correct routing of the drive belt is important for maintenance and replacement, so be sure to consult the serpentine belt diagram to ensure proper installation and functionality of your Dodge Journey 2.4’s drive belt.

www.lindsaychryslerparts.com

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
2015 Dodge Journey 2 4 Serpentine Belt Diagram
If your 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L engine is experiencing issues, it's crucial to diagnose the problem accurately. One common culprit is a faulty serpentine belt, responsible for powering various accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Replacing the serpentine belt is a relatively straightforward task, but it's essential to follow the correct procedure to ensure proper operation and prevent further damage.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide a detailed diagram of the 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L serpentine belt routing, along with step-by-step instructions for its replacement. Whether you're a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and visuals necessary to tackle this repair confidently. By following the instructions carefully and using the provided diagram as a reference, you can restore your Journey's performance and ensure a smooth and reliable driving experience.
Symptoms of a Bad Serpentine Belt
The serpentine belt is a vital part of your car's engine. It drives the water pump, alternator, and power steering pump. If the serpentine belt breaks, your car will overheat and stall.
There are a few symptoms that can indicate that your serpentine belt is bad. These include:
- A squealing noise when you start your car
- A whining noise when you accelerate
- A burning smell
- A loss of power steering
- A loss of coolant
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to have your serpentine belt checked by a mechanic. A bad serpentine belt can cause serious damage to your engine, so it's important to replace it as soon as possible.
How to Replace a Serpentine Belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L
The serpentine belt is an essential part of your vehicle's engine. It drives the water pump, power steering pump, alternator, and air conditioning compressor. If the serpentine belt breaks, your engine will overheat and eventually seize up.
Replacing a serpentine belt is a relatively simple task that can be completed in about an hour. Here are the steps on how to do it:
- Gather your tools and materials. You will need a new serpentine belt, a 15mm socket wrench, a 13mm socket wrench, a breaker bar, and a jack.
- Park your vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. Allow the engine to cool down completely before beginning.
- Locate the serpentine belt. The serpentine belt is located on the front of the engine. It is a long, black belt that wraps around several pulleys.
- Loosen the tensioner pulley. Using the 15mm socket wrench, loosen the bolt that holds the tensioner pulley in place. The tensioner pulley is located on the top of the engine, near the front.
- Remove the old serpentine belt. Once the tensioner pulley is loose, you can remove the old serpentine belt. Simply pull the belt off of the pulleys.
- Install the new serpentine belt. Wrap the new serpentine belt around the pulleys, starting with the crankshaft pulley. Make sure that the belt is routed correctly, according to the diagram in your owner's manual.
- Tighten the tensioner pulley. Once the new serpentine belt is installed, tighten the bolt that holds the tensioner pulley in place. Use the 15mm socket wrench to tighten the bolt until the belt is tight.
- Check the belt tension. Using the 13mm socket wrench, turn the crankshaft pulley clockwise by hand. The belt should deflect about 1/2 inch when you press on it with your thumb. If the belt is too loose or too tight, adjust the tensioner pulley accordingly.
- Start your engine and check for leaks. Once the belt is properly tensioned, start your engine and let it run for a few minutes. Check for any leaks around the belt or pulleys. If you see any leaks, stop the engine and tighten the belt or pulleys as necessary.
Replacing a serpentine belt is a simple task that can be completed in about an hour. By following these steps, you can save yourself money and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Serpentine Belt Diagram for the 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L
The serpentine belt is an important part of your vehicle's engine. It drives the water pump, alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. If the serpentine belt breaks, your engine will overheat and you will lose power steering and air conditioning.
The serpentine belt diagram for the 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L is shown below. The diagram shows the routing of the belt around the various pulleys on the engine.
[Image of the serpentine belt diagram for the 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L]
To replace the serpentine belt on the 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L, follow these steps:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Loosen the tensioner pulley bolt.
- Remove the old serpentine belt.
- Install the new serpentine belt.
- Tighten the tensioner pulley bolt.
- Connect the negative battery terminal.
Here are some tips for replacing the serpentine belt on the 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L:
- Use a new serpentine belt.
- Inspect the pulleys for wear and tear.
- Replace the tensioner pulley if it is worn or damaged.
- Tighten the tensioner pulley bolt to the specified torque.
By following these steps, you can easily replace the serpentine belt on your 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L.
Causes of a Broken Serpentine Belt
A broken serpentine belt can cause a variety of problems for your car, including overheating, loss of power steering, and alternator failure. If you suspect that your serpentine belt is broken, it is important to have it checked out by a mechanic as soon as possible.
There are a number of things that can cause a serpentine belt to break, including:
- Wear and tear: Serpentine belts are made of rubber, and like all rubber products, they will eventually wear out. The average lifespan of a serpentine belt is 50,000 to 100,000 miles, but this can vary depending on the make and model of your car and your driving habits.
- Misalignment: If the serpentine belt is not properly aligned, it can cause premature wear and tear. Misalignment can be caused by a number of factors, including a loose belt tensioner, a worn pulley, or a bent crankshaft.
- Overheating: If your car is overheating, it can put extra stress on the serpentine belt, causing it to break. Overheating can be caused by a number of factors, including a faulty thermostat, a clogged radiator, or a blown head gasket.
- A seized pulley
- A loose belt tensioner
- A wornidler pulley
- A damaged crankshaft
If you suspect that your serpentine belt is broken, it is important to have it checked out by a mechanic as soon as possible. A broken serpentine belt can cause a number of serious problems for your car, and it is important to get it fixed before it causes further damage.
Maintenance Schedule for the Serpentine Belt
The serpentine belt is an essential part of your Dodge Journey's engine, as it drives multiple accessories, including the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Over time, the serpentine belt can wear out and need to be replaced. The recommended replacement interval for the serpentine belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L is every 60,000 miles.
Symptoms of a Worn Serpentine Belt
There are a few signs and symptoms that may indicate that your serpentine belt is worn and needs to be replaced. These include:
- A squealing or chirping noise when the engine is running
- Visible cracks or fraying on the belt
- The belt is loose and can be easily moved by hand
- The engine is overheating
- The power steering is not working properly
- The air conditioning is not working properly
Replacing the Serpentine Belt
If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, it is important to have your serpentine belt inspected and replaced as soon as possible. Replacing the serpentine belt is a relatively simple procedure that can be completed in about an hour.
Tools and Materials Needed
- New serpentine belt
- Socket wrench
- 1/2-inch drive ratchet
- 15-mm socket
- 18-mm socket
Step-by-Step Instructions
Note: Before you begin, allow the engine to cool down completely.
- Locate the serpentine belt. It will be located on the front of the engine, driving multiple accessories.
- Loosen the tensioner pulley bolt using the 15-mm socket and ratchet.
- Use the pry bar to pry the tensioner pulley away from the belt.
- Remove the old serpentine belt from the pulleys.
- Install the new serpentine belt on the pulleys, starting with the crankshaft pulley.
- Route the belt around the other pulleys, following the diagram in your owner's manual.
- Tighten the tensioner pulley bolt using the 18-mm socket and ratchet.
- Start the engine and check for any unusual noises or vibrations.
- If everything is working properly, turn off the engine and double-check the tension of the serpentine belt.
Replacing the serpentine belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L is a relatively simple procedure that can be completed in about an hour. By following the above instructions, you can save yourself the cost of having the belt replaced by a mechanic.
Tools Required for Serpentine Belt Replacement on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4
Replacing the serpentine belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 is a relatively simple task that can be completed in about 30 minutes. However, you will need the following tools to complete the job:
- 15mm socket
- 18mm socket
- Breaker bar
Once you have all of the necessary tools, you can follow these steps to replace the serpentine belt:
- Park the Journey on a level surface and engage the parking brake.
- Open the hood and locate the serpentine belt. It is the long, black belt that runs around the front of the engine.
- Use the 15mm socket and ratchet to loosen the tensioner pulley. The tensioner pulley is located on the top of the engine, near the front.
- Once the tensioner pulley is loose, you can remove the old serpentine belt.
- Wrap the new serpentine belt around the pulleys, starting with the crankshaft pulley.
- Use the 18mm socket and ratchet to tighten the tensioner pulley.
- Double-check that the serpentine belt is properly routed and tensioned.
- Close the hood and start the engine. Check for any leaks or unusual noises.
Replacing the serpentine belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L is a relatively simple task that can be completed in about an hour. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can save yourself the cost of having a mechanic do the job for you. Just be sure to take your time and double-check your work before starting the engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the serpentine belt diagram for a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4?
The serpentine belt diagram for a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 can be found in the owner's manual. It is also available online from various sources, such as the manufacturer's website or a parts store website.
How do I replace the serpentine belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4?
To replace the serpentine belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4, you will need to follow these steps:
- Locate the serpentine belt tensioner.
- Use a wrench to loosen the tensioner.
- Tighten the tensioner.
What are the symptoms of a bad serpentine belt?
The symptoms of a bad serpentine belt can include:
- Squealing noise
- Loss of power
- Overheating
- Battery not charging
How often should I replace the serpentine belt on my 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4?
The serpentine belt on a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 should be replaced every 60,000 miles.
Can I replace the serpentine belt on my 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 myself?
Yes, you can replace the serpentine belt on your 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 yourself. However, if you are not comfortable doing so, it is recommended that you take your vehicle to a mechanic.
Latest Posts

- Forum Listing
- Marketplace
- Advanced Search
- Dodge Dart Garage - The Mopar Zone
- Dodge Dart 2.4L Tigershark
2.4L serpentine belt replacement
- Add to quote
Does anyone have a video or how-to? I'm surprised I couldn't find one on youtube. I'm sure it's not too hard to figure it out but I don't want to reinvent the wheel. Thanks
dgdart said: Does anyone have a video or how-to? I'm surprised I couldn't find one on youtube. I'm sure it's not too hard to figure it out but I don't want to reinvent the wheel. Thanks Click to expand...
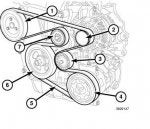
Thanks, I don't need the belt routing, I can just look at it. More interested in knowing in advance what's involved in getting the belt in and out. Does the engine mount need to come out? Can it be done from the top or do I need to go through the wheelwell? Also, are the idler and tensioner pulleys normally replaced with the belt or are they good for the long run?
That question might be answered in the link I provided. The process should just be to use socket and loosen then tension pulley and pull it off. Unless you suspect any pulleys failing, then they should be good. I believe you will need to do it from the wheel well to access all the locations for belt routing. Take it off the crank pulley first, and then everything else should slide back off. Just like most serpentine belts, it can be a royal pain to get back on.
I needed to replace my belt at 136,500+ miles. There was a split right in the middle. This simple job was a pain especially while it's cold outside. I ended up doing it from the bottom with no ramps or jack. I had a hole already in my bumper with the splash shield missing which made access easy. I ended up having to route the belt like normal then slip on #7 last while holding down the tensioner as far down as possible. I had issues with trying to hold it down while slipping the rest of the belt on as it's easy for the offset wrench to slip which ruins your progress. I wish they would have a lock or toggle of some sort to keep it in place without having to hold it down. It took me a couple hours of trying.
- ?
- 528.5K posts
- 31.2K members
Top Contributors this Month

Dodge Journey: Bad Serpentine Belt
One of the most common issues with a vehicle is a bad serpentine belt. If you suspect that your Dodge Journey has this problem, we’ll give you the common symptoms below, as well as how to replace it.
The good news is that serpentine belts are cheap , and in the grand scheme of things, relatively easy to replace. The sound that a bad serpentine belt makes is a squealing sound. It has a higher pitch than an engine rattling .

Bad Serpentine Belt Symptoms: Dodge Journey
Here are the most common symptoms of a bad serpentine belt in the Dodge Journey:
Squealing Belt
Often, the first sign of a bad serpentine belt in your Journey is squealing. The squealing should match the engine RPM. That is to say, that when you rev the engine, the squeal changes pitch accordingly.
It might also go away entirely if you rev your engine a few times. This happens because the serpentine belt gets heat in it and is able to grab ahold of the pulleys. At this point it is no longer slipping. It’s a matter of time before revving the engine no longer corrects the problem.
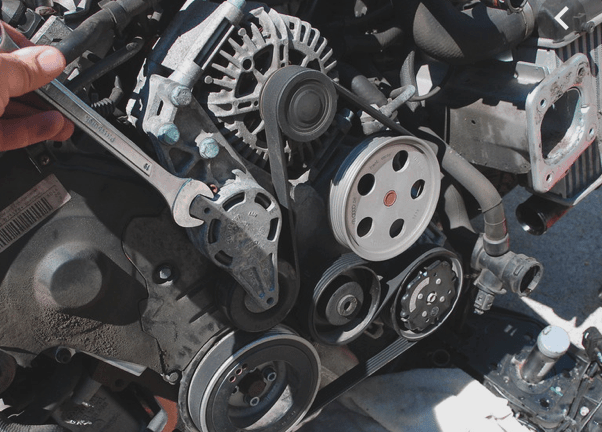
Visible Wear and Cracking on the Belt
As your serpentine belt ages, it will begin to show visible signs of wear. These belts are not designed to last the life of an engine. A bad serpentine belt may have:
- Smooth Surface
- Missing Pieces
- Uneven Wear
- Missing/Damaged Ribs
Any of these items are enough to replace the belt.
Engine Accessories Not Working
The serpentine belt powers your engine accessories, such as the power steering pump and air conditioning compressor. If these accessories are not working, that’s an indication that the serpentine belt is shot or missing entirely. Get a new belt immediately.
Overheating
The serpentine belt is responsible for turning the water pump in your Journey. If it fails, water can no longer circulate throughout the engine. You also shouldn’t have power steering (although some vehicles now have electric power steering so be careful).
If the belt is off all the way, or the engine is overheating, do not drive it somewhere to have it looked at. Overheating the engine and blowing a head gasket will cost way more than a new serpentine belt.

Dodge Journey Serpentine Belt Replacement
Replacing a serpentine belt is a straightforward process. Your Journey uses a tensioner to keep the serpentine belt tight.
The first thing you are going to need to do is find the tensioner and apply force to it in order to loosen the serpentine belt. Once you’ve applied force you can pull the belt off of a pulley. Now, let off the tensioner slowly.
We recommend taking a picture of the belt route, and making sure that you have a diagram of the route before taking the belt off. The last thing you want is to not remember how to get the belt back on. You should see a sticker under your Journey’s hood with serpentine belt route information.
Here’s a great video from Scotty Kilmer on how to change a serpentine belt:
Conclusion: Bad Serpentine Belt Diagnosis – Journey
Serpentine belt replacement is something that any shade tree mechanic can do with very few tools. So if you have reason to believe that a bad serpentine belt is causing your Dodge Journey’s engine to squeal, replacing it might be exactly what you need to do.
If there is anything that you would like to add, please leave a comment below. Good luck!
Share this:

Mopar.com National eStore
- Login / Register
- Order Status
- 1-800-399-2668
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
Shipping Policy
Mopar ® Authentic Parts & Accessories
- Store Policies
Cart is Empty
- Sign in or Create Account
- Track Order
- Select Vehicle
Accessories
- Sign In or Create Account
- Audio & Video
- Bed Products
- Branded Goods
- Cargo Management
- Chemical Guys
- Electronics
- EV Chargers
- Exterior Appearance
- Exterior Security
- Interior Appearance
- Interior Convenience
- Interior Protection
- Interior Security
- Performance
- Vehicle Care
- AC & Heater Controls
- AC & Heater Plumbing
- AC & Heater Units
- AC Compressor and Mounting
- Drive Shaft
- Front Axle Assembly
- Front Axle Disconnect
- Front Axle Shafts
- Front Axle: Housing, Differential and Vent
- Rear Axle Assembly
- Rear Axle Shafts
- Rear Axle: Housing, Differential and Vent
- Aperture Panel, Pillar Supports and Cab Back
- Bed Liner, Tonneau Cover, and Boot
- Body Structure Welds, Weatherstrips, Seals, Sealers and Adhesives
- Cowl and Dash Panel
- Hood and Hood Release
- Pickup Box and Fuel Filler Door
- Shelf Panel
- Sport Bar or Luggage Rack
- Body Hold Down
- Front Bumper and Fascia
- Rear Bumper and Fascia
- Trailer Tow and Tow Hooks
- Under Body Protection
- Dual and Single Cargo Door
- Exterior Mirror
- Liftgates and Tailgates
- Sliding Cargo Door
- Weatherstrips and Seals
- Brake Master Cylinder
- Brake Pedals
- Front Brakes
- Hydraulic Control Unit, Brake Tubes and Hoses
- Parking Brake Level, Cables, and Rear Disc Park Brake Assembly
- Power Brake Booster
- Rear Brakes
- Exerior Conversion and Upfit Packages
- Exterior Appearance, Exterior Protection, Decals and Tape Stripes
- Axle Cooling
- Axle Cooling and Diesel Fluid Injector Coolant Pump
- Battery Cooling
- Drive Belts
- EGR Cooling System
- Engine Coolant Reservoir (Bottle)
- Engine Oil Cooler and Lines
- Pulleys and Related Parts
- Radiator and Related Parts; Charge Air Cooler
- Transmission Heater
- Transmission Oil Cooler and Lines
- Turbo Charger Cooling System
- Water Pump and Related Parts
- Battery, Battery Tray and Cables
- Convertible Top - Electric
- Generators / Alternators
- Instrument Panel Cluster
- Keys, Modules and Engine Controllers
- Lamps, Interior and Exterior
- Park Assist
- Power Distribution, Fuse Block, Junction Block, Relays and Fuses
- Radio, Antenna, Speakers, DVD and Video systems
- Spark Plugs, Cables, Coils and Glow Plugs
- Speed Control
- Telecommunication
- Wiper and Washer System
- Wiring and Repair
- Wiring, Body and Accessories
- Wiring, Headlamp to Dash
- Wiring, Instrument Panel
- Wiring, Powertrain
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid System
- Emission Controls
- Emission Harness
- Vacuum Canister
- Vacuum Canister/Leak Detection Pump
- Camshaft and Valve
- Crankcase Ventilation
- Crankshaft, Piston, Drive Plate, Flywheel, and Damper
- Cylinder Block
- Cylinder Head
- Engine Identification, Service Engines & Engine Service Kits
- Engine Mounting
- Engine Oil Cooler
- Engine Oiling, Oil Pan and Indicator (Dipstick)
- Manifolds and Vacuum Fittings
- Timing Belt/Chain and Cover and Balance Shaft
- Turbo and Super Chargers
- Electric Motor
- Decals and Tape Strips
- Grilles, Moldings and Ornamentation
- Moldings and Ornamentation
- Running Boards and Side Steps
- Accelerator Pedal
- Air Cleaner
- Air Inlet Components
- Fuel Lines and Tubes
- Fuel Pump and Sending Unit
- Fuel Rail and Injectors
- Fuel Tank Filler Tube
- Throttle Body
- Exhaust System
- Glass and Interior Rearview Mirror
- Adjusters, Recliners, Shields and Risers
- Carpets, Floor Mats, Load Floor and Silencers
- Door Trim Panels
- Front Seats
- Headliners - Visors - Assist Straps
- Instrument Panel
- Liftgate Panel and Scuff Plate
- Panels - Moldings - Scuff Plates, Pillar, Cowl, 1/4 Panel Trim and Cargo Covers
- Power Steering Hoses
- Power Steering Pump and Reservoir
- Steering Column and Intermediate Shaft
- Steering Gear
- Steering Linkage and Steering Shock
- Steering Wheel
- Air Suspension
- Front Stabilizer Bar
- Front Suspension, Strut and Cradle
- Rear Stabilizer Bar
- Rear Suspension and Cradle
- Clutch Controls
- Clutch Housing
- Clutch Pedals
- Case, Extension and Indicator (Dipstick)
- Differential
- Fork and Rails
- Gearshift Controls and Related Parts
- Mounting and Skid Plate
- Seal and Shim Packages
- Transmission and Transfer Case Assembly
- Valve Body, Accumulator, Solenoid and Parking Sprag
- Emergency Roadside Tools
- Jack Stowage
- Tire Monitoring System
- Wheel Covers and Center Caps
- Wheel Spare
- Wheels, Tires and Hardware
- Town & Country
- Grand Caravan
- Grand Cherokee
- Ram ProMaster 1500
- Ram ProMaster 2500
- Ram ProMaster 3500
- Ram ProMaster City
- Grand Wagoneer
- Air & Fuel Delivery
- Driveline & Axles
- Electrical, Charging & Starting
- Tire & Wheel
- Wiper & Washer
- Schedule Maintenance
Shop Models
- Shop Accessories
- Shop bproauto
- Air Conditioning & Heating
- Axle & Drive Shaft
- Body Components
- Conversion & Upfit Packages
- Emissions & Exhaust
- Exterior Ornamentation
- Fuel & Air Intake
- Glass & Mirrors
- Transmission & Transfer Case
Serpentine Belt - Mopar (4891721AB)
2007-2020 Mopar - 4891721ab
Change ZIP Code ×
Also purchased.
- Additional Info
Vehicle Fitment
- Product Reviews
- Ask Our Team
- Warranty & Disclosures
- Interchange
- Installation Instructions

- SKU: 4891721AB
- Other Names: Accessory Drive Belt, 04891721ab, Belt
- Condition: New
- Notes: Engines: 1.8l i4 dohc 16v dual vvt engine. 2.0l i4 dohc 16v dual vvt engine. 2.0l i4 pzev 16v dual vvt engine. 2.4l i4 dohc 16v dual vvt engine. 2.4l i4 pzev 16v dual vvt engine. Transmissions: W/off-rd crawl ratio trans. 5-speed manual t355 transmission. Continuously variable transaxle ii.
- Applications: SE 4x4. SE FWD. 4x2 FWD. 4x4. 4x2. 4x4. 70th Anniversary 4x2. 70th Anniversary 4x4.
- Sold In Quantity: 1
Learn more about Warranty Details
California Proposition 65
Returns policy.
Khabarovsk ( Russian : Хабаровск [ xɐˈbarəfsk ] ⓘ ) is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai , Russia , [3] located 30 kilometers (19 mi) from the China–Russia border , at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers , about 800 kilometers (500 mi) north of Vladivostok . As of the 2021 Russian census , it had a population of 617,441. [16] The city was the administrative center of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia from 2002 until December 2018, when the status was given to Vladivostok. [17] It is the largest city in the Russian Far East , having overtaken Vladivostok in 2015. [ citation needed ] It was known as Khabarovka until 1893. [5] As is typical of the interior of the Russian Far East, Khabarovsk has an extreme climate with strong seasonal swings resulting in strong, cold winters and relatively hot and humid summers.
Earliest record
17th-century russian exploration, qing empire, from khabarovka to khabarovsk, russian federation, administrative and municipal status, demographics, economy and infrastructure, transportation, international events, notable people, twin towns – sister cities, external links.

Historical records indicate that a city was founded on the site in the eighth century. The Tungusic peoples are indigenous to the city's vicinity. The city was named Boli ( 伯力 ; Bólì ) in Chinese when it was part of the Chinese empire. During the Tang dynasty, Boli was the capital of Heishui Protectorate, called Heishui Duhufu. [18] In AD 722, Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (唐玄宗) established Heishui Protectorate and gave self-rule to Heishui Mohe tribes. The seat of this administrative region was then established near today's Khabarovsk. [19] [20]
In the mid-17th century, the Amur Valley became the scene of hostilities between the Russian Cossacks , who tried to expand into the region and collect tribute from the natives, and the rising Manchu Qing dynasty , who were intent on securing the region for themselves. [ citation needed ]
Khabarov's Achansk

The Russian explorers and raiders of the 1650s set up a number of more or less fortified camps ( ostrogs ) on the Amur. Most of them were in use for only a few months and later destroyed. It is usually thought that the first such camp in the general area of today's Khabarovsk was the fortified winter camp named Achansk ( Ачанск ) or Achansky gorodok ( Ачанский городок ), built by the Cossacks of Yerofey Khabarov in September 1651 after they had sailed to the area from the upper Amur. The fort was named after the local tribe whom Khabarov's people called "Achans". [21] [22] On October 8 the fort was unsuccessfully attacked by joint forces of Achans and Duchers (who had good reasons to hate the Cossacks, due to their rather heavy-handed tribute -extraction tactics [23] ), while many Russians were away fishing. [22] In late November, Khabarov's people undertook a three-day campaign against the local chief Zhakshur (Жакшур) (whose name is also known in a more Russian version, Zaksor (Заксор)), collecting a large amount of tribute and announcing that the locals were now subjects of the Russian Czar. A similar campaign was waged later in winter against the Ducher chief Nechiga (Нечига), farther away from Achansk. [22]
On March 24 (or 26), 1652, Fort Achansk was attacked by Manchu cavalry, led by Ninguta 's commander Haise, reinforced by Ducher auxiliaries, but the Cossacks stood their ground in a day-long battle and even managed to seize the attackers' supply train . [22] Once the ice on the Amur broke in the spring of 1652, Khabarov's people destroyed their fort and sailed away. [22]
The exact location of Khabarov's Achansk has long been a subject for debate among Russian historians and geographers. [23] [24] A number of locations, both upstream and downstream of today's Khabarovsk, have been proposed since Richard Maack , one of the first Russian scholars to visit the region, identified Achansk in 1859 with the ruins on Cape Kyrma, which is located on the southern (Chinese) shore of the Amur, upstream of Khabarovsk. [23] The most widely accepted point of view is probably that of Boris Polevoy , who believed that Khabarov's Achansk was located in the Nanai village later known as Odzhal- Bolon ( Russian : Оджал-Болонь ), located on the left bank of the Amur, closer to Amursk than to Khabarovsk. One of his arguments was that both Khabarov's Achan (sometimes also spelt by the explorer as Otshchan, Отщан), and Wuzhala (乌扎拉) of the Chinese records of the 1652 engagement are based on the name of the Nanai clan "Odzhal" (Оджал), corresponding to the 20th-century name of the village as well. (The name of the clan was also written as "Uzala", as in the name of its best-known member, Dersu Uzala ). [23]
Polevoy's view appeared to gain wide support among the Russian geographer community; petitioned by the Amur Branch of the Russian Geographical Society , the Russian Government renamed the village of Odzhal to Achan in 1977, to celebrate its connection with Khabarov's raid. [23]
As to the Cape Kyrma ruins, thought by Maack to be the remains of Achansk, B.P. Polevoy identified them as the remains of another ostrog – namely, Kosogorsky Ostrog, where Onufriy Stepanov stayed a few years later. [24]
After the Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689) between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing Empire , the area became an uncontested part of China for the next century and a half. Modern historical maps of the Qing period published in China mark the site of future Khabarovsk as Bólì ( Chinese : 伯力 ). All of the middle and lower Amur region was nominally part of the Jilin Province, run first out of Ninguta and later out of Jilin City . [25]
French Jesuits who sailed along the Ussuri and the Amur Rivers in 1709 prepared the first more or less precise map of the region. According to them, the indigenous Nanai people were living on the Ussuri and on the Amur down to the mouth of the Dondon River (i.e., in the region including the site of the future Khabarovsk). These people were known to the Chinese as Yupi Dazi ("Fish skin Tartars"). [26]

In 1858, the area was ceded to Russia under the Treaty of Aigun . The Russians founded the military outpost of Khabarovka ( Хаба́ровка ), [27] named after Yerofey Khabarov . The post later became an important industrial center for the region. Town status was granted in 1880. In 1893, it was given its present name: Khabarovsk . [5]
In 1894, a department of the Russian Geographical Society was formed in Khabarovsk and to found libraries, theatres and museums in the city. Since then, Khabarovsk's cultural life has flourished. Much of the local indigenous history has been well preserved in the Regional Lore Museum and Natural History Museum and in places like near the Nanai settlement of Sikachi-Alyan , where cliff drawings from more than 13,000 years ago can be found. The Khabarovsk Art Museum exhibits a rare collection of old Russian icons. [25]
In 1916, the Khabarovsk Bridge across the Amur was completed, allowing Trans-Siberian trains to cross the river without using ferries (or temporary rail tracks over the frozen river in winter). During the Russian Civil War , Khabarovsk was occupied by Japan in September 1918. [28]

After the defeat of Japan in World War II , Khabarovsk was the site of the Khabarovsk War Crime Trials , in which twelve former members of the Japanese Kwantung Army and Unit 731 were put on trial for the manufacture and use of biological weapons during World War II. [25]
Chinese Emperor Puyi , captured by Soviet troops in Manchuria , was relocated to Khabarovsk and lived there from 1945 up to 1950, when he was returned to China. [29]
When Japan fell in September 1945 the United States reached an agreement with Stalin to build two U.S. Naval Advance Bases (Fleet Weather Centrals) in the USSR. [30] The U.S. built one 10 miles (16 km) outside Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky on the Kamchatka Peninsula with the code name TAMA. [31] The other was 20 miles (32 km) outside Khabarovsk in buildings provided by the Soviets, code-named MOKO. [31] For mail Khabarovsk was assigned U.S.Navy number 1168, FPO San Francisco. [32] The American use of these two bases was short-lived. [ citation needed ]
On 5 November 1956, the first phase of the city tram was commissioned. The Khabarovsk television studio began broadcasting in 1960. On 1 September 1967, the Khabarovsk Institute of Physical Education, now the Far Eastern State Academy of Physical Culture , opened. On 14 January 1971 Khabarovsk was awarded the Order of October Revolution . In 1975 the first stage of the urban trolley opened. In 1976 the city hosted an international ice hockey tournament with the ball for the prize of the newspaper Sovietskaya Rossia . In 1981 the Bandy World Championship was played in the city. [25]
In 1996, Khabarovsk held its first mayoral elections . Paul D. Filippov, whose candidacy was supported by Governor Viktor Ishayev , was defeated. In 1998, reconstruction of the central square of Khabarovsk was completed. In May 2000, President of Russia , Vladimir Putin , decreed that new federal districts be formed, and Khabarovsk became the center of the Far Eastern Federal District . [25]
In 2006, the Center for Cardiovascular Surgery, a high-tech medical center, was constructed according to a Russian national health project . In 2008, the train station was completely renovated, and the adjacent square was reconstructed to include fountains and an underground passage. In 2009, Khabarovsk hosted the EU-Russia summit . In 2010, the city hosted a meeting of the Great Circle of Ussuri Cossacks . On 3 November 2012, Khabarovsk was awarded the honorary title of " City of Military Glory ". [25]
On 9 July 2020, the governor of the region, Sergei Furgal , was arrested and flown to Moscow. The 2020 Khabarovsk Krai protests began on 11 July 2020 in support of Furgal. [33]
The flag of Khabarovsk displays a bear on the right (Red side) and a Siberian tiger on the left (blue side), holding a yellow shield with a blue reversed pall and a red fish . The flag is a representation of the coat of arms of Khabarovsk. [34] The flag was adopted on 30 October 2007 and is 2:3 in ratio. [25]
The city is located 30 kilometers (19 mi) from the China–Russia border, at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers, about 800 kilometers (500 mi) north of Vladivostok . [25]
Khabarovsk experiences a monsoonal dry-winter humid continental climate ( Köppen climate classification Dwb borders on Dwa ). [25]
The average annual precipitation is 696 millimeters (27.4 in) , mainly concentrated in the summer. In a few years, November to March hardly receive any precipitation. The driest year was 2001 with only 381 millimeters (15.0 in) of precipitation and the wettest was 1981 when 1,105 millimeters (43.5 in) of precipitation fell. The wettest month was August 1981 with a total precipitation of 434 millimeters (17.1 in) . Due to high summer humidity , overnight lows remain mild to warm during several months. Snowfall is common, though light, with an average maximum snow height of 16 centimeters (6.3 in) . During peak winter, highs above freezing are very rare. [25]
The city's extreme climate sees daily average high and low temperatures vary by around 50 °C (90 °F) over the course of the year. The average temperature in January is −19.2 °C (−2.6 °F) and the average for July is +21.4 °C (70.5 °F) . Extremes have ranged from −40 °C (−40 °F) in January 2011 to +36.4 °C (97.5 °F) in June 2010. [35]

Khabarovsk is the administrative center of the krai [3] and, within the framework of administrative divisions , it also serves as the administrative center of Khabarovsky District , [37] even though it is not a part of it. [1] As an administrative division, it is incorporated separately as the city of krai significance of Khabarovsk —an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts . [1] As a municipal division , the city of krai significance of Khabarovsk is incorporated as Khabarovsk Urban Okrug . [12]
Ethnic composition (2010): [38]
- Russians – 92.6%
- Ukrainians – 1.8%
- Koreans – 1.1%
- Chinese – 0.6%
- Tatars – 0.5%
- Uzbeks – 0.5%
- Others – 2.9%

Primary industries include iron processing, steel milling, Khabarovsk shipyard, Daldizel, machinery, petroleum refining, flour milling, pharmaceutical industry, meatpacking and manufacturing of various types of heavy and light machinery. [25]
A high-speed international fiber-optic cable connects the city of Khabarovsk with the city of Fuyuan in China. [ citation needed ]
On March 28, 2024, a person reported radiation reading to the city's authorities. [39] In April 2024, the city declared a state of emergency because of the radiation leak. [40] The source of the radiation was "removed and placed in a protective container" and taken to a radioactive waste storage facility. [41]

The city is a principal railway center and is located along the Trans-Siberian Railway ; the rail distance of Khabarovsk railway station from Moscow is 8,523 kilometers (5,296 mi) .
Khabarovsk is served by the Khabarovsk Novy Airport with international flights to East Asia , Southeast Asia , European Russia , and Central Asia .
Road links include the Trans-Siberian Highway ( M58 and M60 Highways), and water transport links are provided by the Amur River and Ussuri River .
Public transport includes: tram (8 routes); trolleybus (4 routes); bus and fixed-route taxi ( marshrutka , approximately 100 routes).
Transborder travel to China in winter ice road in summer boat on Amur river to Fuyuan (and train to Harbin )
In 2021, the construction of a paid high-speed bypass of the city was completed.
There are the following institutions of higher education in Khabarovsk: [42] [43]
- Pacific National University (former Khabarovsk State University of Technology or Polytechnic Institute )
- Far Eastern State University of Humanities (former Khabarovsk State Teachers Training University)
- Far Eastern State Medical University
- Khabarovsk State Academy of Economics and Law
- Far Eastern State Transport University
- Far Eastern Academy of Public Service
- Far Eastern State Physical Education University
- Khabarovsk State Institute of Arts and Culture

A key street in Khabarovsk is the broad Amursky Boulevard with its many shops and a local market. The city's five districts stretch for 45 kilometers (28 mi) along the Amur River. The similar boulevard – Ussuryisky is located between the two main streets Muravyov-Amursky and Lenin street and runs to the city's artificial lakes (Gorodskie Prudi) with the sport complex Platinum Arena. The lakes are famous for their fountains with the light show. The Military History Museum of the Far Eastern Military District is located in the city, the only such museum in the Russian Far East. [44]
Recently, [ when? ] there have been renovations in the city's central part, rebuilding with historical perspective. There is a walking tour from the Lenin Square to Utyos on Amur via Muravyov-Amursky Street, where visitors find traditional Russian cuisine restaurants and shops with souvenirs. [ citation needed ] There are a number of night clubs and pubs in this area. In Wintertime ice sculptures are on display on the cities squares and parks. Artists come from as far as Harbin in China.
Unlike Vladivostok , the city has never been closed to foreigners, despite it being the headquarters of the Far East Military District , and retains its historically international flavor. Once the capital of the Soviet Far East (from 1926 to 1938), since the demise of the Soviet Union , it has experienced an increased Asian presence. It is estimated that over one million Chinese travel to and through Khabarovsk yearly, and foreign investment by Japanese and Korean corporations have grown in recent years. The city has a multi-story shopping mall and about a dozen hotels.
Aleksandr Fedosov, the Khabarovsk Krai Minister of Culture, estimates that the city became more attractive to tourists following the 2015 Bandy World Championship . [45]
Khabarovsk is the closest major city to Birobidzhan , which is the administrative center of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast , Russia , located on the Trans-Siberian Railway , close to the border with China . The Jewish Autonomous Oblast is a federal subject of Russia in the Russian Far East , bordering Khabarovsk Krai and Amur Oblast in Russia and Heilongjiang province in China . Its administrative center is the town of Birobidzhan , and it is the only region in the world in which Yiddish is the official language. Khabarovsk provides the closest major airport to Birobidzhan , which is Khabarovsk Novy Airport (KHV / UHHH), 198 km from the center of Birobidzhan . [ citation needed ]

The headquarters of the Russian Ground Forces 's Eastern Military District is located at 15 Serysheva Street. The district was preceded by the Far Eastern Military District , which was located in the same location. The following component units of the district are stationed in the city:
- 104th Chuj Headquarters Brigade
- Honour Guard Company of the Khabarovsk Garrison [46] [47]
- 17th Independent Electronic Warfare Brigade
- 118th Independent Pontoon-Bridge Railway Battalion
- 392nd Pacific Training Center for Junior Specialists
- 11th Air and Air Defence Forces Army
- Military Band of the Eastern Military District
All 5 of these units make up the Khabarovsk Garrison. The Russian Navy 's Pacific Fleet maintains a presence in the city as well. There is also an airbase located 3 km (1.9 mi) to the east of the city. The main public relations asset for the military in the city is the Military History Museum of the Far Eastern Military District and the district military band . [ citation needed ]

- Amur Khabarovsk , a professional ice hockey club of the international Kontinental Hockey League and plays its home games at the Platinum Arena . It used to be the furthest team from the European-based teams in the league until Admiral Vladivostok joined the KHL in 2013 as an expansion team.
- FC SKA-Khabarovsk , a professional association football team playing in the Russian First League , the second tier of Russian association football.
- SKA-Neftyanik , a professional bandy club which plays in the top-tier Russian Bandy Super League at its own indoor venue Arena Yerofey . It is both the easternmost and southernmost team in the top division. In the 2016–17 season the club became Russian champion for the first time. [48] As of 2019 the team has won the title three years in a row. [49]
The city was a host to the 1981 Bandy World Championship . It also hosted the 2015 Bandy World Championship , which was visited by Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev . [50] 21 teams were expected, [51] which would have been 4 more than the then record-making 17 (now it's 18) from the 2014 tournament . In the end, China was the only newcomer, while Canada and Ukraine withdrew, the latter for political reasons . Khabarovsk organised the 2018 tournament as well, but not Division B that time around, which was held in Chinese Harbin . [52] The event was named by the Federal Agency for Tourism as one of the best 200 events of the year. [45]
A delegation from the 2022 Winter Olympics organising committee visited Khabarovsk to watch matches in the bandy league to study the plans if the sport was to be added to the Games program. [53]
- Kristina Akheeva , actress and model
- Oleksandr Aliyev , association football player
- Nikita Balakhontsev , association football player
- Sergei Bodrov , filmmaker
- Evgeny Grachev , ice hockey player
- Mikhail Grigorenko , ice hockey player
- Alexandra Ivanovskaya , 2005 Miss Russia winner
- Denis Kenzo , music producer
- Ivan Koumaev , dancer
- Alexander Mogilny , ice hockey player
- Evgeni Plushenko , Olympic figure skater
- Vita Sidorkina , model
- Ivan Skobrev , speed skater
- Andrei Tchmil , professional cyclist
- Evgeny Tsaregorodtsev , professional ice hockey player
- Daria Usacheva , figure skater
- Vladimir Volegov , painter
- Andrey Zamkovoy , boxer
- Efim Zelmanov , mathematician
- Artem Zub , ice hockey player
Khabarovsk is twinned with: [54]
- Khabarovsk placed first in different categories of "Most Developed and Comfortable City of Russia" in 2006, [56] 2008 [57] and 2009.
- In 2010, Khabarovsk won the second place in the Forbes list of most suitable cities for private business in Russia. [58] First place went to Krasnodar .
- Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island
- 2020 Khabarovsk Krai protests
Related Research Articles
Khabarovsk Krai is a federal subject of Russia. It is located in the Russian Far East and is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The administrative centre of the krai is the city of Khabarovsk, which is home to roughly half of the krai's population and the largest city in the Russian Far East. Khabarovsk Krai is the fourth-largest federal subject by area, and had a population of 1,343,869 as of 2010.

Komsomolsk-on-Amur is a city in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located on the west bank of the Amur River in the Russian Far East. It is located on the Baikal-Amur Mainline, 356 kilometers (221 mi) northeast of Khabarovsk. Population: 238,505 (2021 Census) ; 263,906 (2010 Russian census) ; 281,035 (2002 Census) ; 315,325 (1989 Soviet census) .

Nikolayevsk-on-Amur is a town in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia located on the Amur River close to its liman in the Pacific Ocean. Population: 22,752 (2010 Russian census) ; 28,492 (2002 Census) ; 36,296 (1989 Soviet census) .

Sovetskaya Gavan is a town in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, and a port on the Strait of Tartary which connects the Sea of Okhotsk in the north with the Sea of Japan in the south. Population: 27,712 (2010 Russian census) ; 30,480 (2002 Census) ; 34,915 (1989 Soviet census) .

Amursk is a town in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located on the left bank of the Amur River 45 kilometers (28 mi) south of Komsomolsk-on-Amur. Population: 42,970 (2010 Russian census) ; 47,759 (2002 Census) ; 58,395 (1989 Soviet census) .

Bikin is a town in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located on the river Bikin 230 kilometers (140 mi) southwest of Khabarovsk. Population: 17,154 (2010 Russian census) ; 19,641 (2002 Census) ; 19,129 (1989 Soviet census) ; 19,000 (1967).

Khabarovsky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the seventeen in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It consists of two unconnected segments separated by the territory of Amursky District, which are located in the southwest of the krai. The area of the district is 30,014 square kilometers (11,588 sq mi). Its administrative center is the city of Khabarovsk. Population: 85,404 (2010 Russian census) ; 90,179 (2002 Census) ; 85,218 (1989 Soviet census) .

Komsomolsky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the seventeen in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It is located in the southern central part of the krai. The area of the district is 25,167 square kilometers (9,717 sq mi). Its administrative center is the city of Komsomolsk-on-Amur. Population: 29,072 (2010 Russian census) ; 31,563 (2002 Census) ; 33,649 (1989 Soviet census) .

Nikolayevsky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the seventeen in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It is located in the east of the krai. The area of the district is 17,188 square kilometers (6,636 sq mi). Its administrative center is the town of Nikolayevsk-on-Amur. Population: 9,942 (2010 Russian census) ; 13,850 (2002 Census) ; 19,683 (1989 Soviet census) .

Solnechny District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the seventeen in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It is located in the center of the krai. The area of the district is 31,085 square kilometers (12,002 sq mi). Its administrative center is the urban locality of Solnechny. Population: 33,701 (2010 Russian census) ; 36,006 (2002 Census) ; 46,772 (1989 Soviet census) . The population of the administrative center accounts for 39.5% of the district's total population.

Sovetsko-Gavansky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the seventeen in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It is located in the southeast of the krai. The area of the district is 15,534 square kilometers (5,998 sq mi). Its administrative center is the town of Sovetskaya Gavan. Population: 15,794 (2010 Russian census) ; 16,602 (2002 Census) ; 24,302 (1989 Soviet census) .

Vyazemsky is a town and the administrative center of Vyazemsky District in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located 130 kilometers (81 mi) southwest of Khabarovsk, the administrative center of the krai, close to the Ussuri River and the border with China. Population: 14,555 (2010 Russian census) ; 15,760 (2002 Census) ; 18,426 (1989 Soviet census) .
Vysokogorny is an urban-type settlement in Vaninsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 3,376 (2010 Russian census) ; 4,044 (2002 Census) ; 4,244 (1989 Soviet census) .
Mukhen is an urban-type settlement in Imeni Lazo District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 4,068 (2010 Russian census) ; 4,756 (2002 Census) ; 6,142 (1989 Soviet census) .
Khor is an urban-type settlement in Imeni Lazo District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 10,346 (2010 Russian census) ; 11,850 (2002 Census) ; 13,227 (1989 Soviet census) .
Zavety Ilyicha is an urban-type settlement in Sovetsko-Gavansky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 9,162 (2010 Russian census) ; 9,429 (2002 Census) ; 13,141 (1989 Soviet census) .
Lososina is an urban-type settlement in Sovetsko-Gavansky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 3,224 (2010 Russian census) ; 3,246 (2002 Census) ; 5,687 (1989 Soviet census) .
Korfovsky is an urban-type settlement in Khabarovsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 5,733 (2010 Russian census) ; 5,823 (2002 Census) ; 5,193 (1989 Soviet census) .
Gorny is an urban-type settlement in Solnechny District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 1,523 (2010 Russian census) ; 1,674 (2002 Census) ; 2,893 (1989 Soviet census) .
Solnechny is an urban-type settlement and the administrative center of Solnechny District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 13,306 (2010 Russian census) ; 14,415 (2002 Census) ; 17,331 (1989 Soviet census) .
- 1 2 3 4 Resolution #143-pr
- ↑ Decision #856
- 1 2 3 4 Law #109
- 1 2 Charter of Khabarovsk, Article 2
- 1 2 Charter of Khabarovsk, Article 19
- ↑ Official website of Khabarovsk. Sergei Anatolyevich Kravchuk Archived December 10, 2020, at the Wayback Machine , Mayor of Khabarovsk (in Russian)
- ↑ Official website of Khabarovsk. Brief Reference Archived March 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine (in Russian)
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1 [ 2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1 ] . Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service .
- ↑ Khabarovsk Krai Territorial Branch of the Federal State Statistics Service . Численность населения Хабаровского края по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2015 года Archived March 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine (in Russian)
- ↑ Государственный комитет Российской Федерации по статистике. Комитет Российской Федерации по стандартизации, метрологии и сертификации. №ОК 019-95 1 января 1997 г. « Общероссийский классификатор объектов административно-территориального деления. Код 08 401 », в ред. изменения №278/2015 от 1 января 2016 г.. (State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation. Committee of the Russian Federation on Standardization, Metrology, and Certification. # OK 019-95 January 1, 1997 Russian Classification of Objects of Administrative Division (OKATO). Code 08 401 , as amended by the Amendment # 278/2015 of January 1, 2016. ).
- 1 2 3 Law #177
- ↑ Law #264
- ↑ "Об исчислении времени" . Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011 . Retrieved January 19, 2019 .
- ↑ Почта России. Информационно-вычислительный центр ОАСУ РПО. ( Russian Post ). Поиск объектов почтовой связи ( Postal Objects Search ) (in Russian)
- ↑ "Оценка численности постоянного населения по субъектам Российской Федерации" . Federal State Statistics Service . Retrieved September 1, 2022 .
- ↑ "Путин перенес столицу Дальневосточного федерального округа во Владивосток" . meduza.io . Retrieved December 13, 2018 .
- ↑ hellotravel, https://www.hellotravel.com/russia/khabarovsk
- ↑ 《新唐書·北狄傳》記載:「黑水西北又有思慕部,益北行十日得郡利部,東北行十日得窟說部,亦號屈設,稍東南行十日得莫曳皆部。」。(The "New Tang Dynasty Book of Beidi" records: "There is also a tribe called "Dream Tribe" in the northwest of Heishui, Yibei travels on the 10th days to the "County Tribe", and the northeast travels on the 10th days to the "Cave Tribe". 10th days to the "Mo Mo Tribe")
- ↑ 黑龙江古代道路交通史 (in Chinese). 人民交通出版社出版, 发行. 1988. ISBN 978-7-114-00315-8 .
- ↑ Археологи обнаружили на Амуре таинственный городок. Возможно, это первое русское поселение в данном регионе Archived May 25, 2006, at the Wayback Machine (Mysterious fort found by archaeologists on the Amur. Possibly, this is the first Russian settlement in this region) (in Russian)
- 1 2 3 4 5 Оксана Гайнутдинова (Oksana Gaynutdinova) Загадка Ачанского городка Archived August 13, 2007, at the Wayback Machine (The mystery of Fort Achansk)
- 1 2 3 4 5 B.P. Polevoy (Б.П. Полевой), Изветная челобитная С. В. Полякова 1653 г. и ее значение для археологов Приамурья (S.V. Polyakov's denouncing letter (1653), and its significance for the archaeologists of the Amur Valley), in: Русские первопроходцы на Дальнем Востоке в XVII-XIX вв. (Историко-археологические исследования) ( First Russian explorers in the Far East in the 17th–19th centuries: Historical and archaeological research – B.P.Polevoy's preface to the document), vol. 2, Vladivostok, Russian Academy of Sciences, 1995. (This article also contains references to Polevoy's earlier publications) (in Russian)
- 1 2 Б.П. Полевой (B.P. Polevoy) О подлинном местоположении Косогорского острога 50-х гг. XVII века (About the true location of the Kosogorsky Ostrog of the 1650s) (in Russian)
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "Tang Prize | Laureates | Yoshinobu Shiba" . www.tang-prize.org . Retrieved January 12, 2024 .
- ↑ Du Halde, Jean-Baptiste (1735). Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise . Vol. IV. Paris: P.G. Lemercier. p. 7. Numerous later editions are available as well, including one on Google Books
- ↑ Campbell, Heather. "Khabarovsk" . britannica.com . The Encyclopedia Britannica . Retrieved October 6, 2022 .
- ↑ "Campaign in Far East: Japanese Occupy Kharbarovsk" . The Northern Star . Reuters . September 9, 1918 . Retrieved February 23, 2021 – via National Library of Australia.
- ↑ http://khv9923.narod.ru/His_last_translator.pdf [ bare URL PDF ]
- ↑ The 114th CB cruise book, 1946, U.S.Navy Seabee Museum Archives, Port Hueneme, Ca, p.123-125
- 1 2 Yanks in Siberia: U.S. Navy Weather Stations in Soviet East Asia, 1945, G. Patrick March, Pacific Historical Review, Vol. 57, No. 3 (Aug., 1988), pp. 327–342, Published by: University of California Press.
- ↑ US Navy Abbreviations of World War II, the Navy Department Library, U.S. Navy web site, Published:Thu Jul 23 14:45:40 EDT 2015
- ↑ "Anti-Putin Protests in Russia's Far East Gather Steam" . VOA News . July 25, 2020.
- ↑ "флаг хабаровска" . www.vexillographia.ru .
- 1 2 "Pogoda.ru.net" (in Russian) . Retrieved November 8, 2021 .
- ↑ "Habarovsk/Novy (Khabarovsk) Climate Normals 1961–1990" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved November 2, 2021 .
- ↑ Государственный комитет Российской Федерации по статистике. Комитет Российской Федерации по стандартизации, метрологии и сертификации. №ОК 019-95 1 января 1997 г. « Общероссийский классификатор объектов административно-территориального деления. Код 08 255 », в ред. изменения №278/2015 от 1 января 2016 г.. (State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation. Committee of the Russian Federation on Standardization, Metrology, and Certification. # OK 019-95 January 1, 1997 Russian Classification of Objects of Administrative Division (OKATO). Code 08 255 , as amended by the Amendment # 278/2015 of January 1, 2016. ).
- ↑ "НАЦИОНАЛЬНЫЙ СОСТАВ И ВЛАДЕНИЕ ЯЗЫКАМИ, ГРАЖДАНСТВО НАСЕЛЕНИЯ" (PDF) . Habstat . Retrieved September 24, 2020 .
- ↑ Siberia.Realities, RFE/RL's. "High Radiation Levels Prompt State Of Emergency In Russia's Khabarovsk" . RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty . Retrieved April 6, 2024 .
- ↑ "Radiation Leak In Russia's Khabarovsk: What We Know So Far" . NDTV.com . Retrieved April 6, 2024 .
- ↑ The Institutions of Higher Education in Khabarovsk Krai Archived December 28, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Independent Russian and Ukrainian Interpreters" . RusMoose.com .
- ↑ Kokurin, Boris (February 25, 2014). "Военный музей в Хабаровске готовится к открытию" . Komsomolskaya Pravda . Retrieved November 1, 2017 .
- 1 2 "Добро пожаловать на сайт Bandy World Championship 2018 | Bandy World Championship 2018" . bandy-vm2018.ru .
- ↑ "Рота почетного караула | Лучшее в Хабаровске" .
- ↑ "Законодательство Хабаровского края: Постановление Администрации города Хабаровска от 09.10.2015 N 3490" .
- ↑ " "СКА-Нефтяник" — новый чемпион!" . Archived from the original on March 28, 2017.
- ↑ "Threefold Russian Bandy Championship winners! | ХК СКА Нефтяник" . skabandy.ru .
- ↑ "23-кратные! Как это было - Архив новостей - Федерация хоккея с мячом России" . rusbandy.ru .
- ↑ "Губернатор Хабаровского края: хоккей с мячом может попасть в программу Игр после ЧМ-2015 - ТАСС" . TACC .
- ↑ "Финская адаптация - Архив новостей - Федерация хоккея с мячом России" . rusbandy.ru .
- ↑ "Новости Хабаровска" .
- ↑ "Города-побратимы" . khabarovskadm.ru (in Russian). Khabarovsk. Archived from the original on April 15, 2020 . Retrieved February 3, 2020 .
- ↑ "Victoria pauses relationship with Russian 'twin city,' urges mayor to push back on invasion" . Vancouver Island . March 4, 2022 . Retrieved August 10, 2022 .
- ↑ "В Москве наградили призеров Всероссийского конкурса "Самый благоустроенный город России" — Российская газета — Сегодня в Москве на ВВЦ прошла церемония награждения призеров Всероссийского конкурса на звание "Самый благоустроенный город России" за 2006 год" . Rg.ru. October 26, 2007 . Retrieved March 26, 2013 .
- ↑ "Хабаровск вновь признан самым благоустроенным городом России — Нина Доронина — Российская газета — Хабаровск вновь признан самым благоустроенным городом России" . Rg.ru. June 21, 2012 . Retrieved March 26, 2013 .
- ↑ "Хабаровск занял II место в рейтинге Forbes – Новости" . Hbr.moigorod.ru. Archived from the original on August 17, 2011 . Retrieved March 26, 2013 .
- Хабаровская городская Дума. Решение №856 от 28 января 2014 г. «О гимне городского округа "Город Хабаровск"». Вступил в силу 28 января 2014 г. Опубликован: "Сборник нормативных актов администрации города Хабаровска и Хабаровской городской Думы", No. 1, январь 2014 г. (Khabarovsk City Duma. Decision # 856 of January 28, 2014 On the Anthem of the Urban Okrug of "the City of Khabarovsk" . Effective as of January 28, 2014.).
- Хабаровская городская Дума. Решение №509 от 13 июля 2004 г. «Устав городского округа "Город Хабаровск"», в ред. Решения №167 от 22 сентября 2015 г. «О внесении изменений и дополнений в Устав городского округа "Город Хабаровск"». Вступил в силу 8 октября 2004 г. (за исключением отдельных положений). Опубликован: "Хабаровские вести", №152, 8 октября 2004 г. (Khabarovsk City Duma. Decision # 509 of July 13, 2004 Charter of the Urban Okrug of "the City of Khabarovsk" , as amended by the Decision # 167 of September 22, 2015 On Amending and Supplementing the Charter of the Urban Okrug of "the City of Khabarovsk" . Effective as of October 8, 2004 (with the exception of several clauses).).
- Законодательная Дума Хабаровского края. Закон №109 от 28 марта 2007 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Хабаровского края», в ред. Закона №155 от 23 декабря 2015 г. «О внесении изменений в отдельные законодательные акты Хабаровского края». Вступил в силу через 10 дней после официального опубликования (28 апреля 2007 г.). Опубликован: "Приамурские ведомости", №52, 17 апреля 2007 г. (Legislative Duma of Khabarovsk Krai. Law # 109 of March 28, 2007 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Khabarovsk Krai , as amended by the Law # 155 of December 23, 2015 On Amending Various Legislative Acts of Khabarovsk Krai . Effective as of after 10 days from the official publication day (April 28, 2007).).
- Правительство Хабаровского края. Постановление №143-пр от 18 июля 2007 г. «Об утверждении реестра административно-территориальных и территориальных единиц Хабаровского края», в ред. Постановления №273-пр от 28 августа 2015 г. «О внесении изменений в Постановление Правительства Хабаровского края от 18 июля 2007 г. №143-пр "Об утверждении реестра административно-территориальных и территориальных единиц Хабаровского края"». Вступил в силу 13 августа 2007 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства Хабаровского края", №7(60), 12 августа 2007 г. (Government of Khabarovsk Krai. Resolution # 143-pr of July 18, 2007 On the Adoption of the Registry of the Administrative-Territorial and Territorial Units of Khabarovsk Krai , as amended by the Resolution # 273-pr of August 28, 2015 On Amending the Resolution #143-pr of the Government of Khabarovsk Krai of July 18, 2007 "On the Adoption of the Registry of the Administrative-Territorial and Territorial Units of Khabarovsk Krai" . Effective as of August 13, 2007.).
- Законодательная Дума Хабаровского края. Закон №177 от 28 апреля 2004 г. «О наделении муниципального образования города Хабаровска статусом городского округа и об установлении его границы». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования (28 мая 2004 г.). Опубликован: "Приамурские ведомости", №95, 28 мая 2004 г. (Legislative Duma of Khabarovsk Krai. Law # 177 of April 28, 2004 On Granting Urban Okrug Status to the Municipal Formation of the City of Khabarovsk and on Establishing Its Border . Effective as of the day of the official publication (May 28, 2004).).
- Законодательная Дума Хабаровского края. Закон №264 от 14 марта 2005 г «Об административных центрах сельских поселений и муниципальных районов Хабаровского края», в ред. Закона №239 от 28 ноября 2012 г. «О преобразовании городского населённого пункта рабочий посёлок Тырма, находящегося на территории Верхнебуреинского района Хабаровского края, путём изменения его статуса в сельский населённый пункт — посёлок Тырма и о внесении изменений в отдельные Законы Хабаровского края». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Приамурские ведомости", №57, 1 апреля 2005 г. (Legislative Duma of Khabarovsk Krai. Law # 264 of March 14, 2005 On the Administrative Centers of the Rural Settlements and the Municipal Districts of Khabarovsk Krai , as amended by the Law # 239 of November 28, 2012 On the Transformation of the Urban Locality the Work Settlement of Tyrma, Located on the Territory of Verkhnebureinsky District of Khabarovsk Krai, by Changing Its Status to That of a Rural Locality—the Settlement of Tyrma, and on Amending Various Laws of Khabarovsk Krai . Effective as of the day of the official publication.).
- Nikolay P. Kradin. It Is Protected by the State: the Monuments of Architecture in Khabarovsk . Khabarovsk: Chastnaya kollektsiya, 1999. 192 p. ISBN 5-7875-0011-3
- (in Russian) Official website of Khabarovsk Archived October 10, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- (in Russian) Khabarovsk Business Directory
- (in Korean) Manchu-Korean expedition against Russian expansion (나선정벌 (羅禪征伐)
- (in Korean) map of the Manchu-Korean expedition against Russian expansion (나선정벌 (羅禪征伐)
- (in Russian) Major problems of Russian-Korean relationship
- (in Russian) China and Russia relationship and history
- Website of Khabarovsk

- White Pages
- Reverse Phone
- Email Lookup
- Phone Books
- Country Codes
Russia Phone Number Lookup:
- Country List
- Khabarovsk Phone Numbers
Khabarovsk, Russia Reverse Phone Lookup +7-421
Russia area code 421.

Unforgettable Russia Journeys
Learn, choose and book trips at www.portbaikal.com
phone: +7 3952 48 87 87, +7 914 927 44 66 VIBER
E-mail: [email protected]
- Cruises on Siberian Rivers
- Transsiberian Railway Tours
- Excursions in Russian cities
Excursions in Khabarovsk
Tailormade holidays.
Let’s do it together! Tell us of your dreams and we will suggest a program and give a quotation.
Send a request
Features of Russian tours
Are you going to travel Russia? Learn more about visa, currency, weather, transport etc.
Photo Gallery

About Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk is the administrative center and the largest city of Khabarovsk Krai. It is located 30 km from the Chinese border. Khabarovsk is the second largest city in the Russian Far East, after Vladivostok.
The city became the administrative center of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia in 2002. Population: 577,345 (2008). The city lies at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers, about 800 kilometers north of Vladivostok and is accessible from there by an overnight train running along the Trans-Siberian railway. Rail distance from Moscow is 8,523 km.
The city was founded in 1858 as a military outpost named Khabarovka, after a Russian explorer Yerofei Khabarov who founded in 1649 first russian settlement on the Amur river. The post later became an important industrial center for the region. In 1880 Khabarovka received the status of city, and in 1884 it officially became the capital of the Priamurskoye General-Governorship. Only in 1893 the city was given its current name of Khabarovsk.
With very good situation at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri rivers and the construction of Transsiberian Railroad the city began to develop very quickly. In 1894, a department of Russian Geographical Society was formed in Khabarovsk and began initiating the foundation of libraries, theaters, and museums in the city. Since then, Khabarovsk's cultural life has flourished. Since 1938 Khabarovsk began the center of Khabarovsky Krai.
Now Khabarovsk is one of the largest and beautiful cities of Russian Far East. It is also an industrial, transport, cultural and scientific center of the Far East. The city has about 100 enterprises of mechanical engineering, metal working, food, easy industries and other branches. The city is the largest transport knot of Far East region. The Khabarovsk railway junction is the biggest in the region. River port is one of the largest on the Amur river. Khabarovsk is a cultural centre. There are 4 museums, 4 professional theatres, many creative organizations, the union of writers, of composers, of artists.
We invite you in Khabarovsk to enjoy walking tour at the broad Amursky Boulevard with its many vibrant shops and perhaps visit the local market or walking tour from the Lenin Square to Utes via Muravyov-Amursky Street, where you can find traditional Russian cuisine restaurants and shops with souvenirs. You can go to the Khetskir National Reserve where you can see the flora and fauna of the region or to the village Sikachi Alyan – ancient Nanaian village.
Khabarovsk Gallery

City tour of Khabarovsk, 2,5 hours
During the city tour you`ll know history of Khabarovsk foundation and development, you`ll see old buildings and modern areas of the city, its monuments and memorial complexes. You`ll visit main sights of Khbarovsk walking at the oldest city area, in the historical downtown – Muravyev-Amursky street admiring the beautiful architecture that survived during the Civil War.
Visit to the Museum of Regional Studies after N.I. Grodekov, 1,5 hours
The Museum of Regional Studies was opened on the initiative of the Priamursky department of the Imperial Russian Geographical Society in 1894. After renovation Museum was re-opened in 1995. It was named after N.I. Grodekov – the honored citizen of Khabarovsk, the governor-general of the Priamursky Territory, the explorer and the active creator of the museum reserves. In 2000 the Khabarovsk Museum of Regional Studies has been given the status of the scientific institution and the title "The best museum of the year 2000".
Boat excursion, 1 hour
The main attraction of Khabarovsk has always been the Amur river, one of the longest rivers in Russia and the 8th longest river in the world. Its length is 4,440 km including 1,000 km within the Khabarovsky Krai, and 45 km within the city of Khabarovsk. The Amur river has become the symbol and the most popular post card object.
Excursion to the Khekhtsir Nature Reserve, 4 hours
Khekhtsir Nature Reserve was founded in 1963. It is located 48 km southwest of Khabarovsk, occupies territory of 451,25 square kilometers. The reserve is part of the Sikhote Alin Mountain Range stretching for 968 km with peaks up to 2,500-3,300 feet high. During excursion you`ll see the beautiful nature of the taiga. The guide will tell you about the local plants, trees, birds and animals of this Reserve.
Excursion to the Nanaj village Sikachi-Alyan, 7 hours
The history of the Far East is a part of the history of the native population in the area. Since the antiquity the lands of the river Amour, the coasts of the sea of Okhotsk and of the Peaceful Ocean were exploited by many ethnic groups: Nanaïtsi, Oultchi, Nivkhi, etc. Nowdays the Nanaïtsi live near Khabarovsk, in the village Cikatchi Alian. You will have the unique chance to visit a nanaï village, to know the Nanaj culture.
- Transsiberian Railway
- Lake Baikal Winter Tours
- Lake Baikal Summer Tours
- Excursions Around Baikal and Irkutsk
- Accomodation in Russian cities
Port Baikal travel company, tour operator from Irkutsk, Russia
More than 15 years of experience in hospitality
Expert in tour organization
+7 3952 48 87 87 +7 914 9274466 Viber|WhatsApp
№ MVT 009619 in Unified State Register of touroperators
Personal Data Processing and Protection Policy
- Booking Form
- Rent a ship on lake Baikal
- Cruises on Baikal
- Cruises on Yenisei river
- Cruises on Lena river
- Summer tours on Baikal
- Winter tours on Baikal
- Tours to cities along Trans Siberian railway

IMAGES
COMMENTS
simple and easiest way to replace Dodge Journey 2.4l 2008 to 2020 serpentine belt #dodgejourney #drivebelt #replacement #carmaintenancetips #dodge #2008
2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 Serpentine Belt Diagram. If you're looking for a 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4 serpentine belt diagram, you've come to the right place. The serpentine belt plays a crucial role in the functioning of your vehicle's engine, powering essential components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor.
The serpentine belt is an important part of your vehicle's engine. It drives the water pump, alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. If the serpentine belt breaks, your engine will overheat and you will lose power steering and air conditioning. The serpentine belt diagram for the 2015 Dodge Journey 2.4L is shown below.
To begin the process of replacing the serpentine belt on a 2.4 L engine, you first need to locate the tensioner pulley. This pulley is responsible for keeping the belt tight and in place. Determine the location of the tensioner pulley by referring to the diagram or the owner's manual for your specific vehicle.
DODGE JOURNEY SERPENTINE BELT REPLACEMENT DIAGRAM 3.6 V6 PENTASTAR FIAT FREEMONT Serpentine belt: https://amzn.to/2UZUFtAIf you need to replace the serpenti...
Step by step serpentine belt replacement demonstration video start to finish on a 2014 Dodge Grand Caravan. Also applies to 2011-2019 Dodge Journey, Chrysler...
07 - Cooling / Accessory Drive / BELT, Serpentine / Removal 2.0L/2.4L. 1.Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable. 2.Raise and support the vehicle. 3.Remove the belly pan. 4.Remove the right front wheel. 5.Remove the five push pins from the forward end of the right wheel liner.
Highest quality, direct fit replacement auto parts enforced to the strictest product standards. Exceeding customers' expectations, our team of passionate auto enthusiasts are here to help. Thousands of how-to auto repair videos to guide you step-by-step through your repair. This video shows you how to install a serpentine belt idler pulley on ...
Often, the first sign of a bad serpentine belt in your Journey is squealing. The squealing should match the engine RPM. That is to say, that when you rev the engine, the squeal changes pitch accordingly. It might also go away entirely if you rev your engine a few times. This happens because the serpentine belt gets heat in it and is able to ...
Step-by-Step Guide to Replace the Serpentine Belt in your 2016 Dodge Journey 2.4. Replacing the serpentine belt in your 2016 Dodge Journey 2.4 is a relatively simple task that can be done with basic tools. Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure a successful belt replacement. Step 1: Locate the Belt
Should be a sticker with a diagram on it located under the hood. SOURCE: serpentine belt diagram: The belt routing diagram is located on the top radiator cross member by the hood latch. You should see it when you open the hood. If it is not there, all Chrysler, Dodge, and Plymouth minivans, from 1993 to at least 1999, used the same 3.3L engine ...
Our service team is available 7 days a week, Monday - Friday from 6 AM to 5 PM PST, Saturday - Sunday 7 AM - 4 PM PST. 1 (855) 347-2779 · [email protected]. Dodge Journey Serpentine/Drive Belt Replacement costs starting from $179. The parts and labor required for this service are ...
47.63 mi. 3405 Rogers Road. Wake Forest, NC. Closed. Opens 9:00 AM Mon. Check Availability. See All 4 Location s. The average cost for a Serpentine Belt Replacement is between $122 and $138 but can vary from car to car. A Dodge Journey Serpentine Belt Replacement costs between $122 and $138 on average.
SKU: 4891721AB Other Names: Accessory Drive Belt, 04891721ab, Belt Condition: New Notes: Engines: 1.8l i4 dohc 16v dual vvt engine. 2.0l i4 dohc 16v dual vvt engine. 2.0l i4 pzev 16v dual vvt engine. 2.4l i4 dohc 16v dual vvt engine. 2.4l i4 pzev 16v dual vvt engine. Transmissions: W/off-rd crawl ratio trans. 5-speed manual t355 transmission. Continuously variable transaxle ii.
Shop for New Auto Parts at 1AAuto.com http://1aau.to/c/178/6/drive-belt-pulleysThis video shows you how to install a serpentine belt idler pulley on your 200...
The picture is for 2.4L. SOURCE: serpentine belt diagram: The belt routing diagram is located on the top radiator cross member by the hood latch. You should see it when you open the hood. If it is not there, all Chrysler, Dodge, and Plymouth minivans, from 1993 to at least 1999, used the same 3.3L engine setup, so find someone with one and look ...
Low prices on Serpentine Belt for your Dodge Journey at Advance Auto Parts. Find aftermarket and OEM parts online or at a local store near you. ... 2015 Journey Serpentine Belt. 2014 Journey Serpentine Belt. 2013 Journey Serpentine Belt. ... Order Replacement 1958 Ford F-100 Differential Clutch Pack. Lighting For A 1998 Ford F800.
Car is a 2014 2.4L SXT Dodge Journey. Old belt which I think is the original (130k miles) was squeaking like mad the past few days. New belt is a Dayco 5061015 from Advance Auto Parts. Tensioner is pushed as far as it will go. It matches the size of the old belt almost exactly minus a tiny bit I can only assume is due to stretching.
Khabarovsk (Russian: Хабаровск [xɐˈbarəfsk] ⓘ ) is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located 30 kilometers (19 mi) from the China-Russia border, at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers, about 800 kilometers (500 mi) north of Vladivostok. As of the 202
Russia Area Code 421 Khabarovsk, Russia 7-421 reverse phone lookup. Search for major cities, dialing codes, how to call between Russian cities, or abroad.
Khabarovsk Krai. Khabarovsk Krai is a region in the Russian Far East, which borders Amur Oblast to the west, Magadan Oblast to the north, Sakhalin Oblast across the Nevelsky Straits to the east, Primorsky Krai to the southeast, and the Jewish Autonomous Oblast and China to the southwest. Photo: 2001Viktorovi4, CC0. Photo: Andshel, CC BY-SA 3.0.
SERPENTINE BELT TENSIONER PULLEY REMOVAL REPLACEMENT 2.4 MULTIAIR DODGE DART CHRYSLER 200 JEEP CHEROKEE RENEGADE COMPASS, DODGE RAM PROMASTER CITY, FIAT 500X...
Khabarovsk is the administrative center and the largest city of Khabarovsk Krai. It is located 30 km from the Chinese border. Khabarovsk is the second largest city in the Russian Far East, after Vladivostok. The city became the administrative center of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia in 2002. Population: 577,345 (2008).