Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
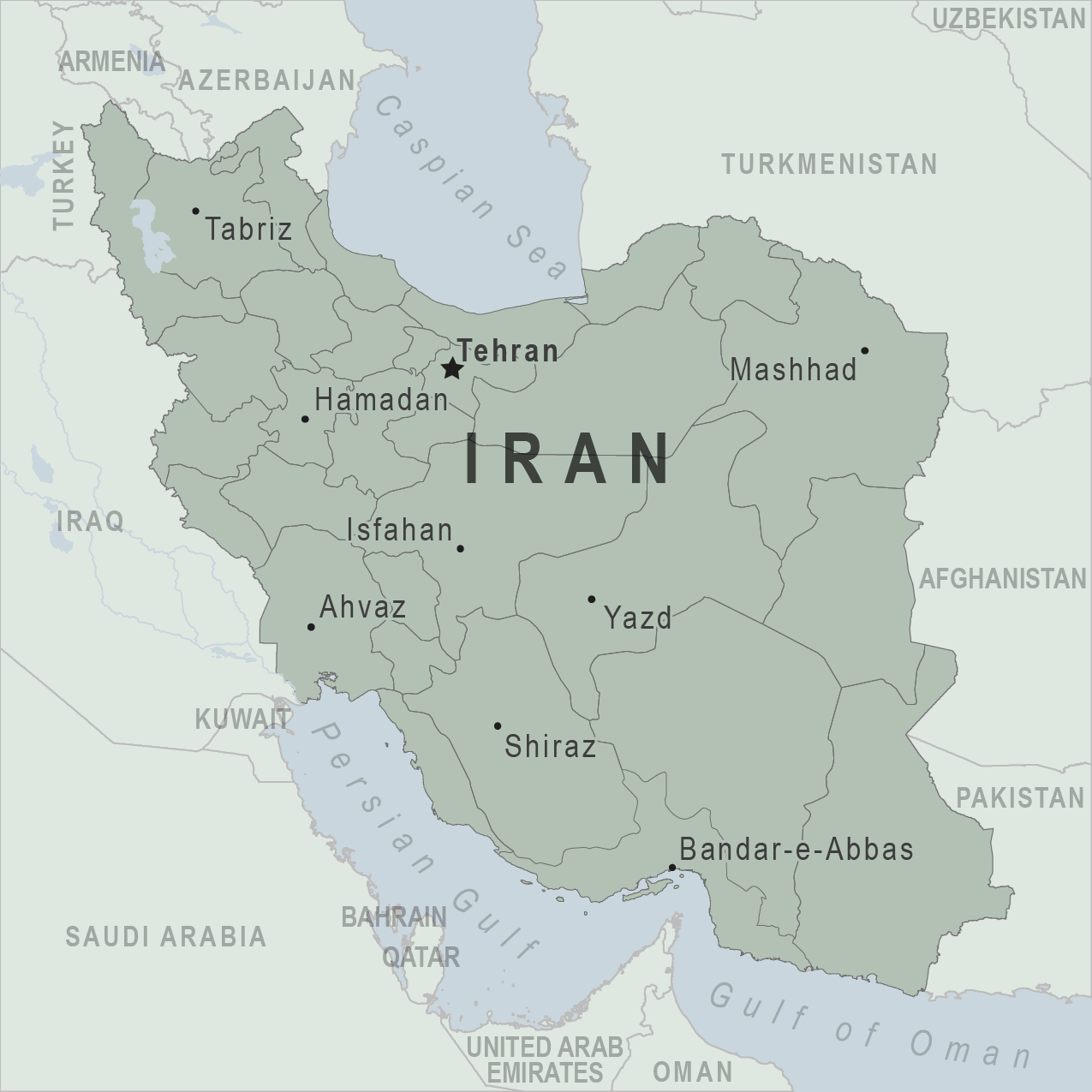
Iran Travel Advisory
Travel advisory august 14, 2024, iran - level 4: do not travel.
Reissued after periodic review with minor edits.
Do not travel to Iran due to the risk of terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping, arbitrary arrest of U.S. citizens and wrongful detentions .
Country Summary: U.S. citizens should not travel to Iran for any reason.
Iranian authorities continue to unjustly detain and imprison U.S. nationals, particularly dual U.S.-Iranian nationals--including students, journalists, business travelers, and academics--on charges including espionage and posing a threat to national security. Iranian authorities routinely delay consular access to detained U.S. nationals and consistently deny consular access to dual U.S.-Iranian nationals.
Violent extremist groups, including U.S. government-designated terrorist organizations, operate in Iran. ISIS and affiliated groups have claimed responsibility for bombings and other attacks in Iran. The threat of terrorist activity persists, as does the risk of death or injury to bystanders.
The U.S. government does not have diplomatic or consular relations with the Islamic Republic of Iran. The U.S. government is unable to provide routine or emergency consular services to U.S. citizens in Iran.
Companies offering surrogacy services in Iran are misrepresenting the security situation in Iran and the risks of the unregulated surrogacy tourism industry. Private companies that arrange such visits and services put U.S. citizens in danger.
Due to the risks of operating civilian aircraft within or in the vicinity of Iran, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has issued a Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM) and/or a Special Federal Aviation Regulation (SFAR). For more information U.S. citizens should consult the Federal Aviation Administration’s Prohibitions, Restrictions and Notices .
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Iran.
If you are currently in Iran:
- Consider the risks involved in possessing dual U.S. Iranian nationality .
- Review your personal security plan and visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
- Draft a will and designate appropriate insurance beneficiaries and/or power of attorney.
- Discuss a plan with loved ones regarding care/custody of children, pets, property, belongings, non-liquid assets (collections, artwork, etc.), funeral wishes, etc.
- Establish your own personal security plan in coordination with your employer or host organization or consider consulting with a professional security organization.
- Leave DNA samples with your medical provider.
- Have a plan for departing Iran that does not rely on U.S. government assistance.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter/X .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Iran Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Iran. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Global Dengue August 14, 2024 Dengue is a year-round risk in many parts of the world, with outbreaks commonly occurring every 2–5 years. Travelers to risk areas should prevent mosquito bites. Destination List: Afghanistan, and Austral Islands (Tubuai and Rurutu), and Bora-Bora), Brazil, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, including the Galápagos Islands, El Salvador, French Guiana (France), French Polynesia, including the island groups of Society Islands (Tahiti, Ghana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Iran, Laos, Mali, Marquesas Islands (Hiva Oa and Ua Huka), Mauritius, Mexico, Moorea, Panama, Samoa, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Uruguay
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic fever
- Tick bite
- Touching the body fluids of a person or animal infected with CCHF
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
- Scientists do not fully understand how the MERS virus spreads
- May spread from to others when an infected person coughs or sneezes
- May spread to people from camels.
Middle East Respiratory virus syndrome (MERS)
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Iran, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Iran. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Iran include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Iran. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Iran’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Iran. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Iran may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Iran, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Iran for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Iran travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: August 7, 2024 15:39 ET
On this page
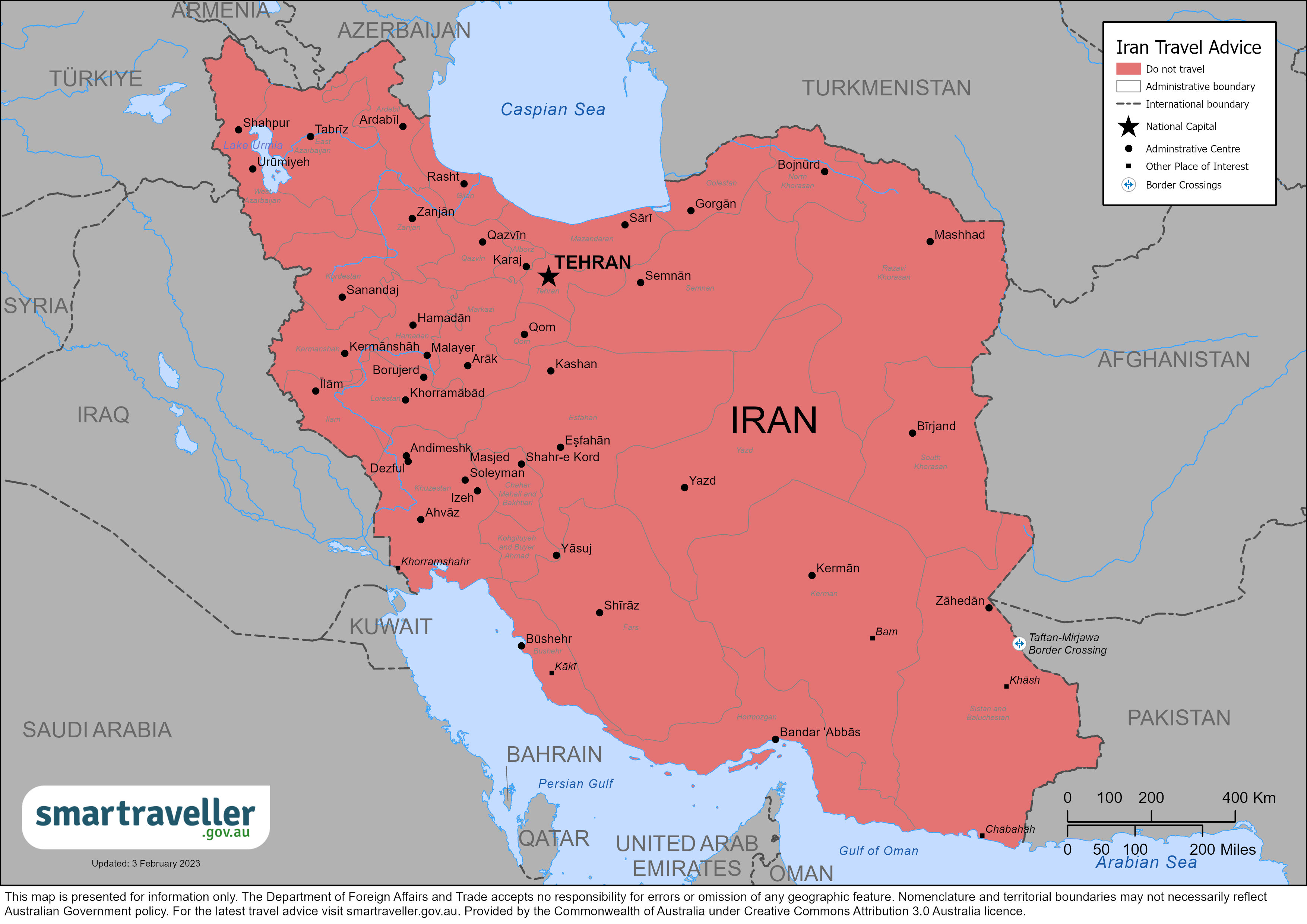
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, iran - avoid all travel.
You should leave by commercial means if you can do so safely. Our ability to provide consular services in Iran is extremely limited.
Back to top
In the context of recent developments between Canada and Iran, Iranian authorities could take retaliatory measures that could pose a risk to the safety and security of Canadians, including Canadian-Iranians.
Canadians in Iran are likely to be subject to increased surveillance by Iranian authorities for activities and behaviours that would be considered innocuous in Canada, including:
- taking photographs in public places
- travelling to remote areas not usually frequented by tourists
- interacting with the local population
Keep a low profile and don’t share your personal information with strangers.
There is no resident Canadian government office in Iran. The ability of Canadian officials to provide consular assistance is extremely limited.
Demonstrations
Political demonstrations and gatherings may occur.
Large-scale and violent protests took place across Iran in the Fall of 2022 following the strict enforcement of the hijab law by the Iranian authorities. Security forces strongly repressed demonstrators resulting in numerous arrests, injuries and casualties. In some cases, arrested individuals were sentenced to death for charges arising from their participation in the demonstrations.
The situation remains highly volatile and could escalate without notice. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. Security forces could use excessive and lethal force to disperse crowds. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation. Disruptions to telecommunications services, including mobile internet access, may occur during large-scale demonstrations.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Monitor local and international media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Border areas
Pakistan and afghanistan.
Bandits in border areas with Afghanistan and Pakistan are usually involved in drug trafficking and use kidnapping to secure the release of group members from prison.
Sistan-Baluchistan, which borders Pakistan, is regularly affected by ethnic conflicts and is also a known route for smugglers. Foreign nationals have been the target of kidnappings.
Terrorist attacks may also occur in this province.
If you decide to travel overland to Pakistan and Afghanistan despite this warning:
- travel only on main roads
- travel in organized groups
- avoid travel after dark
The province of Khuzestan borders Iraq. It is regularly affected by ethnic conflicts. Foreign nationals have been the target of kidnappings.
Border with Iraq is usually closed. It can be opened on a case-by-case basis to allow the passage of certain foreigners or to give refugees access to containment camps located on the Iranian side of the border.
Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan
The borders with Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are open only to citizens of those countries.
Foreigners travelling in the vicinity of these sensitive borders often attract the attention of local security forces, which can result in short periods of detention.
There is an increased threat of attacks against Western interests and of terrorist attacks in general. The security situation could worsen rapidly and with little warning.
Attacks have targeted:
- foreign interests
- Iranian military and government establishments
- tourist attractions and popular public places
- nightclubs and entertainment venues
- public transportation
Further attacks may occur, and terrorists may also target:
- crowded places
- places with high pedestrian traffic where foreigners may gather
- commercial establishments
- local government offices
- public transit stations
- busy streets
- places of worship
Exercise a high degree of caution at all times.
Kidnapping for ransom can occur, especially in Baluchistan and in the border areas with Afghanistan and Pakistan. Foreign nationals have also been the target of kidnapping.
Use varied and unpredictable routes and schedules when moving from one place to another.
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs. Violent crime affects both Iranians and foreigners.
Thieves often target four-wheel-drive vehicles.
Plainclothes individuals may pose as police officers and ask to see foreign currency and passports. If you are approached, you should politely decline to cooperate but offer to go to the nearest police station.
- Avoid showing signs of affluence, such as flashy jewellery
- Ensure personal belongings, including your passports and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- Carry a photocopy of your passport’s identification page at all times and leave a photocopy with a relative
- Don’t surrender any documents or cash
- Stay in touch with family and friends, especially if you’re travelling alone
- Avoid walking after dark
Women's safety
Women may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse. Gender-based violence is common in Iran.
Some Canadian and Canadian-Iranian women have been stranded in Iran or mistreated by an Iranian husband or a male relative. Local authorities consider domestic violence to be a private matter and rarely discuss it in public.
Women and children require the permission of the husband, or an Iranian male head of household, to obtain a passport or travel document. They also require permission to leave the country.
The dress code is strictly enforced in Iran. Women must wear a headscarf and a long jacket that covers the arms and upper legs while in public.
Advice for women travellers
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety can vary greatly throughout the country, and city streets are poorly lit. The highway system is relatively well developed.
Trucks run mostly at night, often without headlights. Motorists are reckless and don’t respect traffic laws. They almost never give way to pedestrians at designated crossing points. Parked cars may obstruct sidewalks on main roads in urban areas. Sidewalks are rare in residential areas.
Expect roadblocks and checkpoints.
- Avoid travelling at night
- Consider hiring a personal driver who’s familiar with local conditions
- If you are involved in an accident, remain at the scene until authorities arrive
Public transportation
Most taxis don’t have meters. Drivers often overcharge foreigners.
- Only hire official taxis from agencies or hotel-based companies
- Take pre-booked official taxis, which are safer than those hailed from the street
- Negotiate fares in advance, or insist that the driver use the meter
- Never enter a cab if it already has one or more passengers
- Note the licence plate number and name of the driver when you travel
- Immediately communicate this information to family or friends
Railway transport
Trains are comfortable and punctual, but service is limited and slow.
Iran and the United Arab Emirates both claim sovereignty over the islands in the Gulf and the military patrols the waters. Foreigners navigating Iranian waters have been arrested and detained. In September 2019, Iranian authorities specifically called for the seizure of Canadian assets and vessels.
Exercise caution if travelling by sea, including for recreational purposes, particularly around the disputed islands of Abu Musa and Tunb.
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Iranian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Canadians can verify this information with the Interests Section of the Islamic Republic of Iran of the Embassy of Pakistan in Washington, D.C.
- Interests Section of the Islamic Republic of Iran – Embassy of Pakistan in Washington, D.C.
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Iran.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Student visa: required Pilgrimage visa: required Press visa: required Transit visa: required
Overstaying your visa period may lead to detention, imprisonment and fines. You will be required to remain in Iran until the situation has been resolved.
- E-Visa Portal – Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Government of Iran
Transit pass
If you enter Iran with a transit pass issued by an Iranian embassy or consulate abroad, you may have to obtain an Iranian passport to exit the country.
Regional travel
Canadians have been denied entry into Iran because their passports bore an Israeli visa, an Israeli border stamp or an Egyptian or Jordanian border stamp issued by an office bordering Israel. Such a stamp would indicate the traveller entered from Israel.
- Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The level of risk may vary by:
The virus that causes chikungunya is spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can cause fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times.
Learn more:
Insect bite and pest prevention Chikungunya
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever is a viral disease that can cause fever, pain and bleeding under the skin. In some cases, it can be fatal. It spreads to humans through contact with infected animal blood or tissues, or from the bite of an infected tick. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Celebrations which include the slaughtering of animals and contact with their blood and/ or tissues may increase the risk of exposure to the virus.
Protect yourself from tick bites and wear gloves or other protective clothing if you are in contact with the blood and tissues of animals, particularly livestock. There is no vaccine available for Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever.
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis causes skin sores and ulcers. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) have been reported in this destination. The risk to travellers is low; MERS is primarily spread through contact with camels or camel-based products (raw milk, meat, urine). It can also spread through close contact, such as when caring for an infected person.
Avoid contact with animals (especially camels), camel-based products, and wash your hands frequently.
Prevention of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)
MERS symptoms range from mild and flu-like to more severe pneumonia-like symptoms, and can result in death.
There is no vaccine or medication that protects against MERS.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Air quality
Air pollution can be severe in major cities. It may affect people suffering from respiratory ailments.
During periods of high pollution:
- consult your doctor before traveling to see if the situation could affect you
- limit your activities outdoors
- monitor local media
- follow the instructions of local authorities
Medical services and facilities
Good health care is limited in availability. Quality of care varies greatly throughout the country.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Health and safety outside Canada
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Iran is under international and Canadian sanctions . While these sanctions don’t prohibit travel to Iran, they could be relevant to your travel.
Legal system
The Iranian legal system differs from the one in Canada.
You may be held for lengthy periods without access to legal counsel or consular officials if you are suspected of or witness to offences.
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs and alcohol are severe. Convicted offenders can expect severe penalties, including the death penalty.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Iran is an Islamic theocratic republic. A conservative interpretation of Islamic practices and beliefs is closely adhered to in the country’s customs, laws, and regulations.
Islamic law is strictly enforced. Breach of public morality, non-compliance with dress-code and making disparaging remarks about Islam, the clergy and religious symbols, including on social networks, are considered serious offences. They are punished severely.
Former Muslims who have converted to other religions have been subject to arrest and prosecution.
- Respect local traditions, customs, laws and religion at all times
- Be aware of your actions and behaviour
In 2024, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around March 10.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, refrain from:
Dress and behaviour
Iranian customs, laws and regulations reflect the conservative interpretation of traditional and Islamic practices and beliefs adhered to by the Iranian authorities.
To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
Shorts are considered inappropriate attire for both men and women.
Women should carry a headscarf to cover their head at all times while travelling in Iran.
There are reports indicating that the police are using surveillance cameras to identify and monitor women who don’t wear the hijab in public places, as required by Iranian law. Employers and owners of businesses such as stores, restaurants, cafés and shopping malls face closure and prosecution if they don’t enforce the hijab law.
If you promote unveiling while you are in Iran, you could face criminal charges.
Women who fail to comply with the law may face:
- arrest and detention
- jail sentences
- restricted access to public institutions such as hospitals, schools, airports and other social services.
- restricted access to mobile phones and Internet
Intimate and extramarital relations
Public displays of affection between two people of the opposite sex, especially between a non-Muslim man and a Muslim woman, is not well socially accepted.
If you engage in extramarital relationships, you may be subject to severe penalties, including the death penalty.
Canadian women who register their marriage with the Iranian authorities automatically become Iranian citizens. They are treated as such by Iranian law.
Marriage between an Iranian and a foreigner is subject to the rules of conduct and Islamic laws. As such, an Iranian husband may prevent his wife and children from leaving Iran, even if they are of foreign nationality.
Marriage Overseas
Iranian and Canadian family law systems are significantly different.
Iran doesn’t automatically recognize the orders of Canadian courts in matters of family law.
A Canadian divorce certificate is not automatically recognized in Iran.
You must get the Canadian divorce certificate authenticated by a Canadian Embassy prior to have it sanctioned by an Iranian Court for it to be recognized under Iranian law.
If an Iranian court doesn’t sanction your divorce, and you return to Iran as a woman, your ex-husband may request the Iranian authorities to confiscate your passport. As a husband, authorities may not allow you to leave Iran if you have not paid the dowry to your wife after divorce.
Children custody
Iran isn’t a signatory to The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction.
Children of a male Iranian national, including Canadian-Iranian citizens, are in the sole custody of their father. They require their father’s permission to leave Iran.
To avoid any difficulties in Iran, consult a Canadian and an Iranian lawyer before travelling. If you're involved in local legal proceedings such as divorce or custody, seek legal advice regarding your rights and responsibilities.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Iran.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Iran by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Iran to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
2SLGBTQI+ persons
Iranian law criminalizes sexual acts and relationships between persons of the same sex.
2SLGBTQI+ persons could also be discriminated against or detained based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, or sex characteristics.
If you are convicted, you could face corporal punishment, imprisonment or the death penalty.
2SLGBTQI+ persons should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Iran.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Iran doesn’t legally recognize dual citizenship.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Iran, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
If you're a Canadian-Iranian citizen, you must enter and exit Iran using your Iranian passport. You may also not be able to leave Iran unless you meet certain conditions.
Canadians, particularly dual Canadian-Iranian citizens, are at risk of:
- being arbitrarily questioned, arrested or detained
- having their passport confiscated
Canadian-Iranian dual citizens should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Iran.
Dual citizens
Mandatory military service
Military service is mandatory for male Iranian citizens aged 18 to 34, unless exempt. This also applies to dual Canadian-Iranian citizens, even those born in Canada.
If you are a Canadian-Iranian citizen older than 17 years, and planning to visit Iran, check your military service obligation prior to your travel. You may not be allowed to leave Iran without first having completed your military service.
Communications and political activities
Communications are closely scrutinized by local authorities. You may face severe consequences if you discuss, share or publish information on the political situation or criticize the regime in place, including on social media.
Photography
It is prohibited to photograph (including with drones);
- government buildings
- security forces, military and police installations and vehicles
- public buildings, including airports, ports, bridges, embassies and power plants
Such sites are not always well identified. In doubt, seek permission, or refrain from taking the photo.
Always ask permission before taking photographs of local residents.
All luggage may be subject to search upon arrival and departure.
Customs officials may screen your electronic device.
Prohibited items
Possession of prohibited items is forbidden and may result in detention and or imprisonment. Such items include:
- Magazines and DVDs with sexual or explicit content
- Satellite dishes
- Western CDs and film
Pork Products
It’s prohibited to import and consume pork-based products.
The workweek runs from Sunday to Thursday.
You must carry an International Driving Permit.
International Driving Permit
The currency in Iran is the Iranian rial (IRR).
The economy is exclusively cash-based. Credit cards aren’t accepted in Iran. ATMs exist only for local banking, for the use of Iranians. Due to international sanctions, it’s not possible to transfer funds to Iran using commercial banking system or money transfer company.
- Bring sufficient cash, preferably in U.S. dollars or euros
- Note that U.S. banknotes used must be in crisp condition
Seismic activity
Iran is located in an active seismic zone. Earthquakes occur.
Severe weather
Dust storms.
The weather is very dry and hot from May to October. Dust storms and sand storms may occur during the summer months.
Sand-laden winds can blow at high speeds for days, creating difficult driving conditions. Poor visibility can also affect flights. These storms can also cause respiratory problems, which can be fatal in some individuals.
If a dust storm is occurring:
- stay indoors
- keep windows closed
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- monitor local media for up-to-date information on the situation
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from November to March. During the rainy season, flooding, including flash flooding, can occur.
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable, due to mudslides and landslides. Bridges, buildings and infrastructure may be damaged.
- Monitor local media for the latest updates, including those on road conditions
- Stay away from flooded areas
- Monitor local news and weather reports
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 110
- medical assistance: 115
- firefighters: 125 / 123
Consular assistance
There is no resident Canadian government office in Iran. The Embassy of Canada to Türkiye in Ankara has consular responsibility for Iran.
Azerbaijan, Georgia. Offering consular services to Canadians in Iran.
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Türkiye in Ankara and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

Announcements
Requirements for international travel to the Islamic Republic of Iran

فایل های ضمیمه
- CurrentRate

Iran Home Appliance Manufacturers Exhibition 2024

Postponement of the 15th Iran Petrochemical Forum

Persian Language Summer School

The second exhibition of coffee tea and related industries - June 11- 14 2024

Embassy Statement on the martyrdom of President Ebrahim Raisi and Foreign Minister Hossein Amirabdollahian

Iranian Foreign Ministry’s statement on martyrdom of President Raisi and his accompanying delegation

15th Iran Petrchemical Forum 23-24 June 2024

The 25th International of Medical Equipment Exhibition (Iran Health)

16th Intl Exhibition of Textile Industry (SITEX 2024)

8th Iran Intl Renewable Energy Exhibition Conference (Iran REC 2024)

Statement of the Embassy of the Islamic Republic of Iran- Copenhagen on the attack on the Iranian Diplomatic premises in Damascus

Call for Mustafa Prize 2025 Nomination

Press Release

Irans Embassy in Copenhagen Flying Flag at Half-mast

Embassy Statement on the 4th Anniversary of the Martyrdom of Major General Qassem Soleimani
Plan and book
- Before You Fly
Baggage information
Find out how much baggage you can take with you as well as what you can bring on board as cabin baggage. If you need a bit more, you can buy extra baggage allowance online. And you can find out how to check in items like sports equipment, musical instruments, or mobility aids.
Check if there are any prohibited items for your destination and read our guide to dangerous goods so there are no surprises at the airport.
Visa and passport information
Depending on your passport and destination you may need to arrange a visa before you fly. Check whether you need one and how to apply here. You can also see the different types of visa you can get for the UAE and how we can help you with the process.
We’ve also added useful information about US visa rules and airport security checks.
Travel information
This is where you’ll find information about family travel, booking our Unaccompanied Minors service, as well as all the details of our special meals for dietary requirements.
You’ll also find flying notices, rules and regulations, as well as your customer rights. And before you pack, check if you’re carrying an item that’s not allowed in the UAE as well as how to get approvals for certain medications.
Health information
Get set for a safe and comfortable journey with tips and health advice on vaccines, medication, travelling during pregnancy, arranging assisted travel and more.
We’ve also offered some reassuring advice on what to do if you feel unwell on board, as well as tips for staying healthy when you arrive like tackling insect bites and beating jet lag. There’s a list of our contact details so you can get in touch with us wherever you are.
Dubai International
Explore our home airport before you arrive. Learn how to get around and transfer between the different terminals. And have a look inside our hub at Emirates Terminal 3.
If you’re on your way through Dubai, make the most of your experience with a short stay at the Dubai International Hotel. Or add a few days with a Dubai Stopover package. If your connection time is particularly long, you could be entitled to our Dubai Connect service.
Iran orders travel ban and shutdown amid COVID surge
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Dubai newsroom; Editing by Andrew Cawthorne
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Captain of sunken Lynch family yacht put under investigation
This does not imply guilt and does not mean formal charges will necessarily follow, as investigation notices must be sent before authorities can perform autopsies.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
COVID-19 international travel advisories
Visitors to the U.S. do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check Department of State travel advisories for the country you will visit.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
You do not need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or take a COVID-19 test to enter the U.S. This applies to U.S. citizens and non-citizens.
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific travel advisories, including COVID-19 restrictions, from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel to learn:
- If you can travel if you recently had COVID-19
- What you can do to help prevent COVID-19
LAST UPDATED: May 31, 2024
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Warnings and insurance
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against advice from the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO).
FCDO advises against all travel to Iran
FCDO advises against all travel to Iran. British and British-Iranian dual nationals are at significant risk of arrest, questioning or detention. Having a British passport or connections to the UK can be reason enough for the Iranian authorities to detain you.
Find out more about why FCDO advises against travel .
Limited UK government support
UK government support is extremely limited in Iran. Assume that no face-to-face consular assistance will be possible in an emergency and the UK government will not be able to help you if you get into difficulty in Iran.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel to Iran against FCDO advice, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
About FCDO travel advice
FCDO provides advice about risks of travel to help you make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
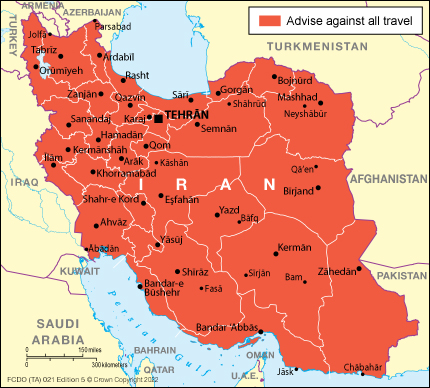
We continue to advise:
Do not travel to Iran as there's a high risk you could be arbitrarily detained or arrested.
Iran (PDF 927.2 KB)
The Middle East (PDF 1.45 MB)

Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 115 or go direct to the hospital.
Mountaineers can also contact the Red Crescent on 112 for help.
Call 110 or visit the nearest police station.
Advice levels
Do not travel to Iran.
Do not travel to Iran as there's a high risk you could be arbitrarily detained or arrested.
- Terrorist attacks could happen anywhere in Iran, including Tehran or other locations frequented by foreigners and tourists. They could occur at any time with little or no warning. Avoid possible targets and areas with a low level of security. Possible targets for attacks include embassies, hotels, places of worship, tourist sites, government interests, military parades and locations, Western businesses and other interests. Take official warnings seriously.
- An increased threat of military and terrorist attacks against Israel and Israeli interests across the region and ongoing military action in the Occupied Palestinian Territories could lead to increased tensions in other locations in the Middle East.
- Regional tensions are high, and the security environment could deteriorate with little or no notice. In an attack or other armed conflict, you should follow the advice of local authorities. See our general advice on protecting your safety ( There’s an armed conflict ).
- Increased tensions in the Middle East may result in airspace closures, flight cancellations and diversions and other travel disruptions.
- Dependants of Australian officials in Iran have been offered voluntary departure to return to Australia.
- Demonstrations and protests are expected. Small, localised protests continue in parts of Iran. Previously, security forces' response to protests has been severe, and many protesters and bystanders have been injured, killed or detained. There has been an increase in the number of foreign nationals arrested during previous protests. Avoid all demonstrations and protests.
- Australians, including dual nationals, should strongly consider leaving Iran as soon as possible. Foreigners in Iran, including Australians, are at a high risk of arbitrary detention or arrest. Foreign and dual nationals have been detained without due process of law. Iran does not recognise dual nationality. Our ability to provide consular support to dual Australian-Iranian nationals is extremely limited. We can't guarantee access to consular services or legal representation if you're detained or arrested.
- There are ongoing disruptions to telecommunications services, including mobile internet access.
- Regional tensions are high and could escalate rapidly. There is ongoing hostility between Iran and Israel, and military tensions between Iran, the US and other countries in the Middle East. The Iran-Iraq, Iran-Afghanistan, and Iran-Pakistan border areas are extremely dangerous.
- Regional and international politics can trigger protests. These may target Western or UN diplomatic missions. Avoid vigils, marches, demonstrations and large public gatherings, as they can turn violent without warning.
- Kidnapping for ransom can occur. Foreign nationals have also been the target of kidnapping. Terrorist groups, drug traffickers, smugglers and bandits are active in the Afghanistan and Pakistan border areas. They often clash violently with security forces. Bombings and shootings occur. Be alert to your surroundings, especially at night. Outside these areas, the level of violent crime is low.
- Women can face unwanted attention and harassment. If you're a woman, take care when travelling alone, particularly at night.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Outbreaks of insect borne diseases such as malaria, tick-borne encephalitis and leishmaniasis occur. Use insect and mosquito repellent.
- HIV/AIDS is a risk. Take precautions if you engage in high-risk activities.
- Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases occur. These include cholera, typhoid and hepatitis. Drink only boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
- Significant air pollution occurs in major cities. Sandstorms and dust storms happen often. Get medical advice if you have allergies or breathing difficulties.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don't use, carry or import illegal drugs. Punishments for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
- Get professional advice if you're involved in local legal proceedings. In particular, seek advice on matters of family law, such as divorce, child custody and child support.
- Same-sex relations are illegal for both men and women. Penalties include corporal punishment and death.
- Iran has strict codes of dress and behaviour. Women are required by law to wear a headscarf and loose-fitting clothing covering their arms and legs. Men face fewer clothing restrictions but should avoid shorts and sleeveless t-shirts. Close contact between unmarried men and women is illegal, as is being in a de facto relationship. This is particularly the case for interactions between Muslims and non-Muslims. It's against the law to behave in a way that offends Islam, such as encouraging a Muslim to convert.
- Be careful when taking photos. It's illegal to photograph military or government sites, critical civil infrastructure and public protests. It's illegal to use drones without authorisation.
- Iran has strict importation laws. You can't import alcohol, pornography, pork products or short-wave radios. It's also illegal to import printed or recorded Western materials, including religious material. You'll need to get permission to bring in certain types of electronic equipment, such as satellite phones, GPS trackers and walkie-talkies.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- We advise Australians not to travel to Iran. If you're in Iran, you should strongly consider leaving as soon as possible. If despite our advice you travel to Iran, you'll need a visa to enter and you'll need to get it before you travel. Contact your nearest Iranian embassy for details.
- Airlines may cancel or reduce their operations into and out of Iran at short notice.
- Some countries have restrictions on travellers coming out of Iran.
- If your passport contains Israeli stamps or visas, Iranian authorities will refuse your entry.
- If you overstay your visa in Iran for any reason, even one beyond your control, you'll incur a fine. The Australian Government cannot pay this fine for you. You must also apply for an exit visa. You can get more information on Iranian visa and exit permit requirements from the Iranian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Bureau for Aliens and Foreign Immigrant Affairs.
- Most Australian travel insurance policies won't cover you for travel to Iran. You'll need a specialised policy.
- The local currency is the Iranian Rial (IRR). Declare any foreign currency you have when you arrive in Iran or authorities may confiscate it when you leave. You can exchange major currencies in all big cities. You can't use international credit or bank cards. You can't transfer money using commercial banks or money transfer companies. Bring enough cash in Euros or US Dollars to cover your stay.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
- For consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Tehran . The Embassy's working week is from Sunday to Thursday.
- Our ability to provide consular support to dual Australian-Iranian nationals is extremely limited.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Security situation.
Regional tensions are high, and the security situation could deteriorate quickly with little or no notice. This may also result in airspace closures, flight cancellations, flight diversions, and other travel disruptions.
The security situation in Iran remains volatile. Tensions in the region are high and may escalate further, due to ongoing hostility between Iran and Israel, and military tensions between Iran, the US, and other countries in the Middle East.
If despite our advice you go to Iran, or decide to stay there, monitor media for possible threats and take extra precautions for your safety:
- keep a low profile.
- keep in contact with family and friends
- don't travel alone or at night
- check routes before you travel
- don't put your travel or other plans on social media
- work with only reliable, registered and authorised organisations and travel agencies
- don't carry large amounts of cash
Airlines may cancel or reduce their operations to and from Iran at short notice. If tensions escalate, your options to leave may be limited. The Australian Government may not be able to assist with your departure. Check the latest flight status with your airline or travel provider and make arrangements in case you can’t leave. Share those plans with family and friends.
Iranian authorities are active in and closely monitor border areas with Iraq, Afghanistan and Pakistan. The security situation within 10km of the Iran-Iraq border is extremely dangerous.
Do not visit military or nuclear sites; these are not always clearly marked. Follow the advice of local authorities and monitor the media.
Civil unrest and political tension
Political developments in the region and local political tensions can trigger protests, demonstrations and vigils with little notice. Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can potentially turn violent.
Australian embassy staff and their families in Tehran have been advised to monitor their surroundings and avoid protest areas.
Some airlines may cancel flights at short notice in response to security developments - check with your airline.
In late 2022 and early 2023, there were widespread protests across many cities and towns in Iran. Previously, security forces' response to protests has been severe, and many protesters and bystanders have been injured, killed or detained. During past protest periods, there have been increases in the number of foreign nationals arrested. You should avoid all protest activity.
Iranians sometimes protest against some Western and Middle East embassies and UN missions.
To protect yourself during periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, protests, large crowds and vigils
- do not photograph demonstrations, protests, large crowds or vigils
- monitor media for possible threats
- plan activities to avoid disruption on national or commemorative days
- follow the advice of local authorities
- share your itinerary with family and friends and keep in close contact so they know where you are.
Be prepared to change your plans in case of disruptions.
If civil unrest disrupts transport, ask your airline, travel agent or insurer for help.
More information:
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Risk of arbitrary detention or arrest
Travellers in Iran, including Australians, are at a high risk of arbitrary detention or arrest. A number of Australians, including dual nationals, have been detained in Iran without due process of law.
There's been an increase in the number of foreign nationals being arrested or detained in Iran.
You may be at greater risk of detention if authorities are suspicious of your activities or background. You could attract the attention of authorities if you:
- study or do other academic activity
- travel outside tourist areas
- are near crowds, demonstrations or sensitive sites
- take photos, except in major tourist sites
- have contact with Iranians who are of interest to authorities
- behave or express views perceived as anti-Iranian, anti-Iranian Government, or that could cause religious offence
- are affiliated with, or have links to, Iranian opposition or other political groups.
Iran does not recognise dual nationality. If you're a dual Australian-Iranian national and are detained in Iran, our ability to provide consular support is extremely limited.
The Australian Government may not be notified if you're detained. We can't guarantee consular access to any Australian detained or arrested. We also can't guarantee access to legal representation.
If you're in Iran, you should leave immediately.
- Advice for dual nationals
- Fact sheet: Arrested or jailed overseas
A terrorist attack could happen anywhere in Iran at any time, including in Tehran.
In January 2024, at least 84 people were killed and more than 200 wounded in suicide bombing attacks in Kerman, southern Iran, carried out by Islamic State Khorasan Province (ISKP).
On 26 October 2022, a terrorist attack on the Shah Cheragh Shrine in Shiraz killed at least 14 people and injured 40 others.
Possible targets for attacks include:
- places of worship
- tourist sites
- government interests
- military parades and locations
- Western businesses and other interests
To stay safe from terrorist risks:
- be alert to possible threats throughout the country
- avoid places where there is a low level of security and possible target areas
- monitor the media for new threats
- report suspicious activity or items to police
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the instructions of local authorities
If there's an attack:
- leave the area as soon as it's safe
- avoid the affected area in case of secondary attacks
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Kidnapping for ransom is a risk in Iran. Foreign nationals have been targeted. The kidnapping risk is heightened in the border areas with Afghanistan and Pakistan, including in the area east of Bam, Jask, and the Sistan and Baluchestan provinces. Terrorists, drug traffickers, smugglers and bandits are active in these regions.
Kidnapping happens with political, ideological and criminal motives.
To reduce the risk of being kidnapped:
- always be alert to your personal security and surroundings
- get professional security advice for travel in locations with a heightened kidnap risk
- check your accommodation has appropriate security measures
- vary your movements and don't set patterns
- avoid isolated locations, particularly when travelling alone
- notify family or friends of planned travel and share your location
- avoid talking about your money or business affairs
- use ATMs in public places and during daylight hours
- avoid giving personal details to strangers online or over the phone
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Ransom payments to kidnappers have funded further terrorist attacks and criminal activity. Paying a ransom to terrorist groups will likely break Australian counter-terrorism financing laws.
Violent crime
The level of violent crime in Iran is generally low, but petty crime is increasing due to the worsening economic situation.
Terrorists, drug traffickers, smugglers and bandits are active in the border areas near Afghanistan and Pakistan. This includes:
- Sistan and Baluchestan province
- east of the city of Bam in Kerman province
Violent incidents often occur in these areas, such as:
- clashes between security forces and smugglers
Travel at night in these areas is particularly dangerous.
Be alert to your surroundings, especially at night. Don't draw unwanted attention to yourself.
Petty crime
There have been increasing reports of thieves in passing vehicles and on motor bikes snatching bags from pedestrians, home break-ins and robberies.
Women can face unwanted attention and harassment. Women should take care travelling alone, particularly at night.
Scams and fraud
Men may approach foreigners and claim to be plain-clothes police. They say they're looking for foreign drug dealers and ask to see wallets and ID.
If this happens, it could be a scam . Ask a uniformed police officer for help.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you’re connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
Cyber security when travelling overseas
Climate and natural disasters
Earthquakes and severe weather occur in Iran.
If a natural disaster happens:
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- monitor local media
- follow the advice of local authorities
- keep in contact with your friends and family
Earthquakes
Iran is in an active seismic zone and experiences frequent earthquakes . There have been several major earthquakes in recent years.
Aftershocks often follow a major earthquake. They can cause further damage to already weakened structures.
Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
Severe weather
Iran experiences extremely high temperatures.
The temperature in some areas can reach over 50˚C in July and August, the hottest months of the year.
Some regions have heavy snowfall during winter.
Sandstorms and dust storms occur regularly.
Flash flooding can occur, particularly in Spring.
Travel insurance
If despite our advice you plan to travel to Iran, you'll need a specialised travel insurance policy that covers travel to high-risk destinations. Most Australian policies won't cover you for travel to Iran. Check that Iran is not excluded from your cover because of sanctions or its travel advice level of 'do not travel'.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care. The Australian Government won't pay for any costs or organise evacuation.
If you can't get or afford travel insurance , you should not travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some specialised medicines are in short supply in Iran.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Iran. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medicine is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Medical evacuation may be difficult.
Insect-borne diseases
Malaria is endemic outside the major towns in Iran's south and west.
Other insect-borne diseases are common, including:
- leishmaniasis
- tick-borne encephalitis
Ticks are most active in spring, summer and autumn.
To protect yourself from disease:
- ensure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
Get medical advice if you have a fever, muscle pain, rash or severe headache.
Infectious diseases
HIV/AIDS is a risk.
Take precautions if you engage in activities that may expose you to the virus.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases occur, such as:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food, such as salads
Get medical help if you have a fever or diarrhoea.
Air pollution
Significant air pollution occurs in major cities. Sandstorms and dust storms occur regularly.
Get medical advice if you have allergies or breathing difficulties.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities varies. Facilities in remote areas are extremely limited.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you'll need to be evacuated to a place with better facilities, such as London or Dubai. Medical evacuation can be very expensive and may not be possible.
Medical tourism
Medical tourism including for cosmetic operations is common in Iran. The standard of medical service providers can vary. If you're considering getting medical treatment in Iran, you should research and choose your medical service providers carefully. Serious post-surgery complications and deaths have occurred.
You should discuss your plans with your Australian doctor or specialist before committing to getting procedures done in Iran.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Iran does not recognise dual nationality. If you're an Australian citizen with Iranian nationality, our ability to provide consular assistance is extremely limited.
The Australian Government may not be notified if you're detained. We can't guarantee consular access to any Australian detained or arrested. We also can't guarantee access to legal representation of your choice.
Penalties for importing and possessing drugs are severe and include the death penalty.
Authorities have executed foreigners for drug-related offences in recent years.
Carrying or using drugs
Get professional advice if you're involved in local legal proceedings. In particular, seek advice on matters of family law, such as:
- child custody
- child support
Know your rights and responsibilities.
Penalties for serious offences include death and corporal punishment. Same-sex relations are considered serious offences.
These activities are illegal in Iran:
- homosexual acts for both men and women
- close contact between unmarried men and women
- being in a de facto relationship
- failing to meet the legal dress code
- importing alcohol, pornography, pork products or short-wave radios
- importing printed or recorded Western material, including those with a religious theme
Local authorities consider domestic violence to be a private family matter. Iranian law does not prohibit domestic violence.
Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
Dress and behaviour
Iran has strict Islamic codes of dress and behaviour.
It's illegal to behave in a way considered to offend Islam. For example, you must not encourage Muslims to convert to another religion.
In public women are required by law to wear:
- loose-fitting clothing to cover arms and legs
- a long coat
- a headscarf
If you fail to follow these dress requirements, you may be detained, fined or denied access to government and other services.
In public men should not wear shorts or sleeveless T-shirts.
Photography
You cannot photograph sensitive sites or events, including:
- military and nuclear sites
- government buildings and installations
- critical civil infrastructure
- public demonstrations
Electronic equipment
It's illegal to use drones without authorisation.
You will need permission to bring in a range of electronic equipment, including:
- satellite phones
- GPS trackers
- walkie-talkies
Unauthorised use may result in arrest or detention. Tracking software installed on mobile phones, tablets or other computer equipment may attract the attention of authorities.
For advice, contact your nearest Iranian embassy or consulate .
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual citizenship
Iran doesn't recognise dual nationality.
If you're a dual national, you may be at greater risk of arbitrary arrest or detention. Our ability to provide consular assistance is extremely limited.
If you're arrested or detained, it's highly unlikely the Government of Iran would:
- allow us to give you consular services
- notify the Australian Embassy that you've been arrested or detained.
Under Iranian law, Iranian dual nationals must enter and exit Iran on their Iranian passport. Iranian immigration officials routinely confiscate the foreign and Iranian passports of dual nationals. D ual nationals will not be able to depart Iran without their Iranian passport.
If you're an Australian-Iranian dual national, authorities may not allow you to leave Iran if:
- you're male and you haven't completed military service
- you're female and you don't have permission from your husband or a senior male relative to leave Iran
- you're male and have not paid back the dowry to your wife after divorce
We advise you not to travel to Iran if you are dual Australian-US or Australian-Israeli citizen, in line with those countries' advice to their citizens. For other nationalities, you should check with the relevant country’s travel advice for advice about your risks.
- Dual nationals
- US travel advice for Iran
- UK Government travel advice for Iran
Local customs
The Islamic holy month of Ramadan is observed in Iran. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws during this time.
During Ramadan, eating, drinking and smoking may be illegal in public during the day. If you're not fasting, avoid these activities around people who are. Seek local advice to avoid offence.
Explore our Ramadan page to learn more, including dates for Ramadan.
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Visitor visa
If despite our advice you decide to travel to Iran, you'll need a visa to enter. You must apply for a visa before you travel. Contact Iranian embassy in Australia to apply.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the embassy of Iran for details about visas, currency, customs and other travel requirements.
The Government of Iran issues Iranian visas. The Australian Embassy can't intervene in visa matters, including visas on arrival.
If you overstay your visa in Iran for any reason, even one beyond your control, you'll incur a fine. The Australian Government cannot pay this fine for you. You must also apply for an exit visa. You can get more information on Iranian visa and exit permit requirements from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Bureau for Aliens and Foreign Immigrant Affairs.
- Embassies and Consulates of Iran
Other formalities
If your passport has evidence you've travelled to Israel, such as an Israeli exit or entry stamp, authorities will refuse you entry to Iran.
Strict import restrictions apply.
If you're a dual national, you may not be able to leave Iran unless you meet certain conditions.
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport isn't valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible.
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The local currency is the Iranian Rial (IRR).
Declare any foreign currency you have when you arrive in Iran. If you don't, authorities may confiscate it when you leave.
You can change major foreign currencies in all major cities. However, recent government action has made it harder to change money in exchange bureaus.
You can't use international credit or bank cards.
You can't transfer funds into Iran using:
- the commercial banking system
- a money transfer company
Bring enough cash in Euros or US Dollars to cover your stay.
Local travel
Driving permit.
To drive in Iran you need both:
- a valid Australian driver's licence
- an International Driving Permit (IDP)
Get an IDP before leaving Australia.
Road travel
Iran has one of the highest rates of road accidents in the world.
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Iran than in Australia. Road accidents are a common cause of death and injury.
Hazards include bad roads and poor driving standards.
If you plan to drive:
- check you have enough insurance cover
- ensure you understand local traffic laws and practices
- don't drink and drive
Pedestrians should exercise extreme caution when crossing roads, as traffic can be very congested and road-users unpredictable or undisciplined.
Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check if your travel insurance policy covers you for using a motorbike, quad bike or similar vehicle.
Always wear a helmet.
Only use registered taxis and limousines. Book them through your hotel.
Public transport
Iran is serviced by extensive bus and rail options. Road conditions and road safety vary across the country. Rail services are more limited and slower. Public transport in the main cities is often very crowded.
The Gulf has many areas with security issues and territorial disputes. Authorities may inspect, detain and arrest vessels. Foreigners navigating Iranian waters have been arrested and detained.
Piracy occurs in the Gulf.
Check the International Maritime Bureau's piracy report .
The International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) hasn't audited air safety authorities in Iran.
The EU has operational restrictions in place for some of Iran Air's fleet. The airline hasn't met the EU's international safety standards.
Ageing planes on many of Iran's domestic air services create serious safety concerns.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Iran's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network .
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
English speakers are generally not available.
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Tehran.
Australian Embassy
No.11, Yekta Street Bahar Street, Shahid Fallahi Street Valie Asr Avenue Tehran, Iran
Phone: +98 21 7206 8666 Fax: +98 21 7206 8777 Website: iran.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australia in Iran Instagram: @AustraliaInIran
The Embassy's working week is from Sunday to Thursday.
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours, scheduled Embassy holidays and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
+61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Iran?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Find anything you save across the site in your account
How Iran Became a New Epicenter of the Coronavirus Outbreak

Iran’s deputy health minister, Iraj Harirchi, was pale and drenched in sweat during a press conference on Monday as he told reporters that the Islamic Republic had “almost stabilized” the country’s outbreak of coronavirus. He mopped his brow so often that an aide scurried to the lectern with a box of tissues. Harirchi dismissed as hype an Iranian lawmaker’s claim that fifty people had already died from COVID -19. “I will resign if the numbers are even half or a quarter of this,” he said , adding that Iran had only sixty-one confirmed cases, with twelve deaths. Iran opposed quarantines, he said, because they belonged to an era before the First World War—“to the plague, cholera, stuff like that.” The next day, Harirchi confirmed in a video—from quarantine—that he had contracted coronavirus.
Iran, a country of eighty-three million people, has now become one of the global epicenters of the coronavirus—with the highest mortality rate in the world. Based on official numbers, the mortality rate in Iran has fluctuated daily, between eight and eighteen per cent, compared to three per cent in China and less everywhere else. Iran is also unique, because a disproportionate number of confirmed cases are senior government officials. On Thursday, the Vice-President, Masoumeh Ebtekar—who gained fame in 1979 as Sister Mary, the spokeswoman for the students who seized the U.S. Embassy and took fifty-two Americans hostage—announced that she, too, had contracted the coronavirus. The day before, she had attended a meeting with President Hassan Rouhani and his cabinet. Two members of parliament, including the chairman of the Committee on National Security and Foreign Policy, have also been infected, as has the mayor of a district in Tehran and a senior cleric who had served as Iran’s Ambassador to the Vatican. One of the lawmakers, Mahmoud Sadeghi, tweeted on Tuesday, “I send this message in a situation where I have little hope of surviving in this world.” The former Vatican Ambassador, who was eighty-one, died on Thursday.

Iran’s official counts—three hundred and eighty-eight confirmed cases and thirty-four deaths, as of Friday—may be grossly underreported. In an early analysis published on Monday, six Canadian epidemiologists calculated that Iran probably had more than eighteen thousand cases of coronavirus. Their mathematical model was based on Iran’s official death toll, the disease’s infection and mortality rates worldwide, inflections in other countries traced to Iran, flight data, and travel patterns. “Given the low volumes of air travel to countries with identified cases of COVID-19 with origin in Iran (such as Canada), it is likely that Iran is currently experiencing a COVID-19 epidemic of significant size,” they concluded. Because of the wide margin of error, the number of cases could range from as low as thirty-seven hundred to as high as fifty-three thousand. In the end, the Canadian epidemiologists settled on eighteen thousand three hundred, with a ninety-five-per-cent confidence rate. All of their estimates are many, many times higher than the figures that Iran has reported. Their model was published on medRxiv, which posts preliminary research that has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Kamiar Alaei, a widely recognized Iranian global health-policy expert who co-founded an innovative H.I.V. clinic in Tehran, also emphasized the tricky and still evolving mathematics of coronavirus contagion. “The mortality rate elsewhere is around one to two per cent, and three per cent in China,” Alaei, who is now a co-president of the Institute for International Health and Education, in Albany, told me. “Iran has announced thirty-four deaths, although some unofficial reports claim it is at least a hundred and thirty-four and even two hundred. So if the death rate is only one per cent, then the total number of cases would be between thirty-four hundred and ten thousand or even twenty thousand.”
The outbreak appears to have started in Qom, the conservative city of Shiite seminaries run by leading ayatollahs, about two hours from Tehran. It is also home to the Fatima Masumeh shrine—famed for its giant gold dome and intricate blue tilework—which draws pilgrims from all over the world. (For its historic beauty, I visit the shrine complex whenever I go to Qom.) The first mention of the disease by the government was a report of two deaths in the city on February 19th. Initial reports indicate that the carrier of the virus may have been a merchant who travelled between Qom and Wuhan, in China, where COVID -19 is believed to have originated. The outbreak is estimated to have begun between three and six weeks ago, which would mean that the two Iranians who died could have been sick and infecting others for weeks.
Within eight days of the first reported death in Iran, COVID -19 had spread to twenty-four of the country’s thirty-one provinces. The number of cases has roughly doubled daily since Tuesday. Instead of closing down public sites, a measure that public-health experts have taken in other countries, the head of the shrine in Qom called on pilgrims to keep coming. “We consider this holy shrine to be a place of healing. That means people should come here to heal from spiritual and physical diseases,” Mohammad Saeedi, who is also the representative of Iran’s Supreme Leader in Qom, said in a video . Cases traced back to Iran have been reported in Azerbaijan, Afghanistan, Bahrain, Canada, Georgia, Iraq, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Pakistan, and the United Arab Emirates. Many of these cases have been linked specifically to visits to Qom.
Politics may have played a role in the government’s handling of the health crisis, Alaei, the health-policy expert, told me. The outbreak coincided with two major milestones—the anniversary of Iran’s revolution, on February 11th, and the parliamentary election, on February 21st. “The government didn’t want to acknowledge that they had a coronavirus outbreak because they feared it would impact participation in these two events,” he said. “So for weeks there was a huge silence.” Less than forty-three per cent of Iranian voters turned out for the election, the lowest rate of participation since the 1979 revolution. Both voters and poll workers were photographed wearing masks.
“It was the political decision that led to this outbreak in Iran,” Alaei said. “It’s very unfortunate, as Iran has a very well-established infrastructure for the health system and well-educated doctors.” Alaei was imprisoned in 2008 for “communicating with the enemy,” running espionage rings, and trying to “launch a velvet revolution” against the government in Tehran. He spent thirty months in the notorious Evin Prison. He moved to the United States after his release.
The coronavirus is also becoming a new flashpoint between Iran and the United States. After the election, the Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, accused Iran’s enemies of exaggerating the threat of coronavirus to scare voters away from the polls. “This negative propaganda about the virus began a couple of months ago and grew larger ahead of the election,” he said. “Their media did not miss the tiniest opportunity for dissuading Iranian voters and resorting to the excuse of disease and the virus.” On Wednesday, the U.S. Secretary of State, Mike Pompeo, countered that Iran was lying about “vital details” of the spread of the virus.
The timing of the epidemic is particularly dire for Iran’s economy. As part of President Trump’s “maximum-pressure campaign,” the U.S. reimposed economic sanctions on Iran—and any foreign company or country that does business with it—in November, 2018. Iran’s economy contracted more than nine per cent last year. Since the coronavirus outbreak began, ten days ago, eleven countries, including major trading partners such as Afghanistan, Iraq, and Turkey, have closed their borders to the Islamic Republic, according to Adnan Mazarei, an economist at the Peterson Institute for International Economics, in Washington. “The entire Middle East region could soon be affected by Iran’s role as an epicenter of this contagion,” he wrote on Thursday. “The Middle East region will certainly be hit by a new round of downward pressure on oil prices on account of a decline in demand for oil by China and elsewhere,” he added. And China has accounted for a quarter of all Iranian trade.
Internal commerce is also likely to take a hit on the eve of Nowruz, the Persian New Year, in three weeks. Nowruz is the country’s biggest holiday, and the ritual is to buy new clothes and toys—and to travel to the Caspian coast or other vacation spots to take a break from Iran’s mounting crises. The more that Nowruz celebrations are curtailed, the greater the danger for protests about the epidemic, global isolation, and unanticipated economic setbacks. Two waves of protests have challenged the regime since November.
Iran took steps this week to check the contagion’s spread. In Tehran’s subways, cars were disinfected and snack shops were shut. In more than a dozen provinces , public venues—college campuses, schools, and cultural centers—were closed. Events drawing large audiences, including soccer games and movie screenings, were postponed. Friday prayers were cancelled in the twenty-four provinces where the virus has appeared. Schools across Iran will be closed for three days, as of Saturday. The Health Ministry has urged people not to shake hands and to avoid crowded places. Social media was filled with parodies—a video of young men on the street shaking their shoes with one another, to avoid shaking hands, and a barber cutting the hair of a customer, who was wearing a mask, with a razor attached to an extender pole. Yet the regime has been fighting the image of a nation crippled by an epidemic as much as it has been fighting the coronavirus itself. Speaking at a national headquarters established to deal with the virus, Rouhani said , “In schools, high schools, universities, and workplaces, everybody should pay attention to health recommendations. But we must all continue our work and activities, because it is one of the enemies’ plots to spread fear in our country and close down the country.”
The ailing deputy health minister was more candid. “I’m saying this deep from my heart . . . take care of yourselves,” Harirchi said in a video that he posted from quarantine. “This is a democratic virus, and it doesn’t distinguish between poor and rich, statesman and an ordinary citizen. It may infect a number of people.” In the Islamic Republic, that number may be frighteningly large.
A previous version of this piece reported the death of an Iranian soccer player. The victim was subsequently revealed to be a different woman sharing the same name and age.
A Guide to the Coronavirus
How much of the world is likely to be quarantined ?
Donald Trump in the time of coronavirus .
The coronavirus is likely to spread for months, if not more than a year , before a vaccine could be widely available.
We are all irrational panic shoppers .
The strange terror of watching the coronavirus take Rome .
How pandemics change history .

The mpox strain spreading now is different from the one in 2022: Here's what to know
The World Health Organization’s decision to declare mpox a global public health emergency for the second time in two years may seem like déjà vu — but there are key differences between the strain that’s causing international concern now and the one that spread in 2022.
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral infection characterized by painful lesions. It’s spread by direct contact with an infected person, animal or contaminated items like clothing or bedding.
The virus is classified into two distinct groups: clade I and clade II.
Clade II was responsible for the 2022 outbreak, which has led to around 100,000 cases worldwide .
But now, a version of clade I has spread internationally. The outbreak started in January 2023 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, and has since reached 12 other countries in the region.
On Thursday, Sweden confirmed the first known infection of clade I outside Africa , though Swedish health officials said the person was infected while spending time in Africa. Health authorities in Pakistan also confirmed a case of mpox on Friday but have not identified the strain yet.
Clade I is more transmissible than clade II and capable of being more severe, so infectious disease experts are concerned about further international spread.
“We should have learned a lesson from 2022 that an infection anywhere is potentially an infection everywhere,” said Anne Rimoin, an epidemiology professor at the University of California, Los Angeles Fielding School of Public Health.
How does this version of mpox spread?
Mpox has historically spread in a few ways. The first is through close, personal contact with an infected person, such as skin-to-skin contact with rashes or with saliva or mucus. The second is via contact with contaminated materials. And the third is contact with infected animals: hunting, trapping or cooking them, touching sick rodents or getting bitten or scratched.
In 2022, the version of clade II that spread globally, dubbed clade IIb, was passed primarily through sexual contact, particularly among men who have sex with men.
In the Democratic Republic of Congo recently, clade Ib has also been spreading through sexual contact among female sex workers and men who have sex with men. Research that hasn’t yet been published or peer reviewed linked an outbreak in an eastern mining town in Congo to professional sex work in bars.
But that’s not the only way the virus is being transmitted. Dr. Stuart Isaacs, an associate professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, said much of the spread of clade I could be due to exposure to animals and transmission within households, but limited surveillance in the regions where the virus is make it difficult to know for sure.
Isaacs said there’s early evidence that clade Ib has certain “properties that are allowing it to spread more readily person to person.”
How severe are the recent cases?
In the past, outbreaks of clade I have been deadlier than clade 2, killing up to 10% of people who got sick . But more recent outbreaks have had lower death rates. Out of an estimated 22,000 cases in this outbreak in Congo , more than 1,200 people have died — which puts the fatality rate at just above 5%.
By comparison, clade II outbreaks in Africa have generally had a mortality rate of around 1%, and just 0.2% of cases linked to the 2022 global outbreak were fatal.
Rimoin said the disease’s severity “can have less to do with the actual clade and more to do with route of transmission, the immune system of the individual, the source of the infection.”
The threat in the U.S. could be milder than in Africa, according to Marc Siegel, an associate professor of medicine at the George Washington School of Medicine and Health Sciences.
“The underlying health conditions of the population in the DRC are probably contributing to the current case fatality rate,” he said, using the acronym for the Democratic Republic of Congo. “With less malnutrition and better access to health care resources, I would imagine that the case fatality rate will not be as high as we’re seeing in the DRC.”
Vaccines for mpox are also widely available in the U.S., following a major rollout effort in 2022. Two doses of the mpox vaccine or a previous clade II infection should protect against severe illness from clade I, the Department of Health and Human Service said Wednesday.
Do mpox symptoms differ between the clades?
Symptoms of the two mpox clades can be difficult to distinguish from each other.
The illness generally starts with a rash that progresses to small bumps on the skin, followed by blisters that fill with whitish fluid — a hallmark of the disease — and eventually scab over. People may also experience a fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, low energy and swollen lymph nodes.
These symptoms often disappear on their own within a few weeks. But in severe cases, people may develop larger, more widespread lesions, secondary bacterial infections, pneumonia, heart inflammation or swelling of the brain. Immunocompromised people may develop atypical symptoms and have a greater risk of hospitalization and death.
Historically, mpox lesions have tended to appear on the face, chest, palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. But during the 2022 outbreak, people frequently developed lesions around the genital and anal region or inside the mouth and throat, presumably because of how the virus was spreading at the time . The lesions were also fewer in number and less pronounced overall.
Some cases of this nature have also been detected in the current outbreak in Congo.
“There is talk that there are more people that have lesions around the genitals this time around than previous clade I outbreaks,” said Amira Albert Roess, a professor of global health and epidemiology at George Mason University. “It’s going to take us some time to really understand what may be going on here.”
Aria Bendix is the breaking health reporter for NBC News Digital.
- aid.govt.nz
- mfat.govt.nz
- NZ Embassies

Official advice for New Zealanders living and travelling overseas
- Before you go
- Quick checklist and tips
- Disability information
- Dual Citizenship
- Going to Australia?
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
- Staying healthy while travelling
- Passports and visas
- Solo travellers
- Travel insurance
- Travelling with a criminal conviction
- Work and income benefits
- Travel advisories
- By destination
- Central Asia
- Central/South America
- Travel tips - travel to Europe
- Middle East
- North America
- Travel tips - travel to the United States
- South East Asia
- About our advisories
- Travel advisory risk levels
- News features
- When things go wrong
- Arrest and detention
- Contingency planning for New Zealanders overseas
- Financial difficulties
- Hostage taking and kidnapping
- Illness and injury
- Internet dating scams
- Internet fraud and international scams
- Large-scale emergency
- Lost, stolen or damaged passport
- Missing persons
- Nuclear incident
- Victims of crime
- Family issues
- Child abductions
- Combating sex crimes against children
- Inter-country adoptions
- Travelling with children
- Our services
- New Zealand embassy locator
- Travel Advice /
- Section pages:
- Reviewed: 17 July 2024, 16:27 NZST
- Still current at: 27 August 2024
- Get updates by RSS
- Get updates by email
Related news features
- Brexit: New Zealanders in the United Kingdom Reviewed: 5 February 2020, 15:15 NZDT
- Travelling as a Dual Citizen Reviewed: 21 January 2020, 11:58 NZDT
- View all news
If you are planning international travel at this time, please read our COVID-19 related travel advice here , alongside our destination specific travel advice below.
Do not travel
Do not travel to Iran due to the potential for violent civil unrest, the risk of arbitrary arrest or detention and the volatile security situation in the region (level 4 of 4).
New Zealanders who are currently in Iran, including dual nationals, are strongly advised to consider leaving as soon as possible.
Regional Tensions Regional tensions in the Middle East are high and could escalate quickly, and the security situation could deteriorate with little or no notice. In an attack or other armed conflict, you should follow the advice of local authorities. Increased tensions may also result in airspace closures, flight cancellations and diversions and other travel disruptions.
Civil Unrest In 2019 and 2022, violent protests occurred throughout Iran resulting in a large number of arrests, injuries and deaths.
Since 2022, there have been protests over social restrictions throughout the country. Many protesters and by-standers have been arrested and detained in the security response, including foreign nationals.
Political developments and tensions within Iran and in the region, as well as international events and sanctions against Iran all have the potential to trigger demonstrations and result in civil unrest. Protests may occur at Western and Middle Eastern embassies and UN missions in Iran.
New Zealanders in Iran are advised to avoid all demonstrations, rallies and large public gatherings as they could turn violent with little warning. Keep a low profile and monitor both local and international media to stay informed of developments that may have the potential to impact on your security. You should leave any areas where police or security forces are deployed as your presence alone could be misinterpreted, leading to your arrest and detention.
Risk of Arbitrary Arrest or Detention Travellers in Iran are at risk of arbitrary arrest or detention, including New Zealanders. There has been a recent increase in the number of foreign nationals being arrested.
You may be at greater risk if you undertake activities that could attract the attention of local authorities, such as study or academic activity, travel beyond well-established tourist areas, taking photos outside of major tourist sites, being near crowds or sensitive sites, having contact with Iranians of national interest or any other behaviour that could be perceived to be anti-Iranian or that could cause religious offence. If you choose to travel against our advice, we strongly suggest that you do not put your travel or other plans on social media.
It is illegal to use drones or other unmanned aerial vehicles without authorisation. It is also illegal to photograph military or government sites, critical civil infrastructure and public protests.
Dual nationals are at an even higher risk of arbitrary arrest or detention. This is because Iran doesn't recognise dual citizenship/nationality. Under Iranian law, Iranian dual nationals must enter and exit Iran on their Iranian passport. If you're a dual New Zealand/Iranian national, it is highly unlikely the New Zealand Government would be informed of your arrest or granted access to provide consular assistance to you. See our advice for travelling as a dual citizen.
In all cases of arbitrary arrest or detention in Iran the ability of the New Zealand Government to provide consular assistance to New Zealanders is extremely limited. We can't guarantee consular access, or that you’ll have access to legal representation, if you're detained or arrested in Iran.
Terrorism Terrorism is a threat in Iran, including in Tehran.
- On 3 January 2024, at least 90 people were killed in a terrorist attack targeting a commemoration for the deceased former Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps General Suleimani in Kerman, southeast Iran.
- On 13 August, 2023, one person was killed and 8 wounded in a terrorist attack at a Shia Muslim shrine in the Iranian city of Shiraz, southern Iran.
- On 26 October 2022, 15 people were killed at a Shia Muslim shrine in Shiraz, southern Iran.
A terrorist attack could happen anywhere and at any time, including those places frequented by foreigners. In recent years, there have been a number of attacks, bombings and kidnappings in the south-eastern province of Sistan-Baluchistan, usually targeting police, security forces and religious sites. The security situation within 10km of the Iran-Iraq border is also extremely dangerous. Possible targets for attacks include embassies, hotels, places of worship, government interests, military parades and locations, tourist attractions, entertainment venues, public transport, airports and identifiably Western businesses and other interests.
Due to the threat of terrorism, New Zealanders are advised to be security conscious at all times and exercise particular care in public and commercial areas. The security situation could deteriorate rapidly and without notice. Crime Drug-traffickers and bandits are active in areas of Iran near Afghanistan and Pakistan, including the Sistan va Baluchestan Province and Kerman province east of the city of Bam. Violent incidents occur regularly in these areas and there have been kidnappings of foreign tourists .
Petty theft and street crime such as pickpocketing, burglary and bag snatching also occur in Iran. Thieves in passing vehicles have snatched bags from people walking on the street or through open car doors and windows. We advise New Zealanders to be alert to their surroundings at all times and take steps to safeguard and secure their personal belongings. As victims of robbery are often targeted due to their perceived wealth, it is advisable to avoid wearing or displaying items that appear valuable, such as electronic devices, cameras and jewellery. Only use pre-booked registered taxis, preferably through your hotel.
There have been reports of robberies by fake police officers, usually in civilian clothing. Politely ask to see their ID and request the presence of a uniformed police officer before complying with any requests.
Border Areas/Local Travel The Iranian authorities regard border areas as particularly politically sensitive. The border with Iraq is usually closed. New Zealanders in Iran should be aware of and adhere to any travel restrictions and care should be taken not to cross any borders inadvertently.
Many areas of the Caspian Sea and Gulf are also highly sensitive, in particular the waters around the islands of Abu Musa and Tunbs in the southern Gulf which are militarily patrolled. Foreign nationals have been detained for entering waters near these islands without express permission from Iranian authorities.
Many areas in the Gulf are sensitive because of security issues and territorial disputes. There are reports of vessel inspections, detentions and arrest. Piracy remains a threat and mariners are advised to be vigilant and take appropriate precautionary measures in these waters. For more information view the International Maritime Bureau's piracy report.
Travellers who intend on entering neighbouring countries by land should be aware of possible taxes, import charges or levies at these borders. Some countries also have minimum money entry requirements – travellers may need to prove they have sufficient funds to support themselves. You should check requirements with the Embassy or Consulate of the country to plan to visit .
General Travel Advice Remain vigilant and exercise a high degree of personal security awareness at all times. Follow the advice of local authorities and monitor the media for the latest developments. Avoid any demonstrations, marches and processions.
Do not watch or photograph demonstrations, military and government facilities or security personnel, as this is strictly prohibited and could lead to your detention or arrest. As military and government installations are often difficult to identify, and are commonplace throughout Iran, camera use is best avoided outside of well-known tourist locations. When in doubt, ask for permission.
Travellers often have difficulties accessing funds in Iran. International debit/credit cards are not accepted anywhere in Iran, and there are no ATMs or money transfer services accessible for travellers in Iran. Travellers are advised to carry sufficient hard currency on them, including emergency funds (Euros being the most widely accepted foreign currency in Iran), to meet the needs of their travel for the duration of their stay in Iran. The Ministry cannot assist with the transfer of funds to New Zealanders in Iran, or advance cash to New Zealanders in Iran.
Iran is a Muslim country in which Islamic law is strictly enforced. New Zealanders are advised to respect religious and social traditions in Iran to avoid offending local sensitivities. Iran has strict codes of dress and behaviour. Women are required by law to wear a headscarf and loose-fitting clothing covering their arms and legs. Some religious sites have additional dress requirements.
A non-exhaustive list of illegal activities in Iran includes: close contact between unmarried men and women, homosexual acts, religious proselytising, importing pork or western materials, acting in a way considered to offend or challenge Islam and possession, use or trafficking of alcohol or drugs. Penalties for these activities can be severe, including the death penalty and corporal punishment.
If your passport has stamps from Israel or other countries’ border crossing points with Israel, you may be refused entry to Iran. You should carry a photocopy of your passport identification page and visa at all times. Keep your original passport separate and in a safe place.
Iran lies in an active seismic zone, and is subject to regular and sometimes major earthquakes. Familiarise yourself with general safety procedures in the event of an earthquake.
New Zealanders in Iran should have a comprehensive travel insurance policy in place, and confirm that the policy covers Iran and includes provision for medical evacuation by air. The restrictions on transferring funds to Iran may make it difficult to pay costs relating to travel insurance claims (such as for emergency medical treatment).
New Zealanders in Iran are strongly encouraged to register their details with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade.
Travel tips
- For current health alerts
The New Zealand Embassy Tehran, Iran
Street Address No 11, Yekta Street, Bahar street, Shahid Fallahi Street, Valie Asr Avenue, Tehran Postal Address Post Code: 1973633651 Telephone +98 212 273 5962 Email [email protected] Web Site http://www.mfat.govt.nz/iran Hours Sun-Thurs 0900-1200 hrs
See our regional advice for the Middle East
Top of page
Share this page:
Related News features
New zealand embassy iran.
Telephone: +98 212 273 5962
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://www.mfat.govt.nz/iran
Hours: Sun-Thurs 0900-1200 hrs
Related advice from other countries
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
Other pages in this section:
Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade 195 Lambton Quay Private Bag 18 901 Wellington 5045 New Zealand
- About this site
- Accessibility

- What is a visa?
- Electronic Visa (eVisa)
- Visa on Arrival
- Appointment Required Visa
- Invitation Letter
- Arrival Card
- Passport Renewal
- Project Kosmos: Meet the man with the world's most challenging travel schedule
- Australia Visa and ETA requirements for US citizens explained
- Brazil eVisa for US citizens
- India Tourist Visa for UK citizens
- Possible B1/B2 Visa questions during the interview
Select Your Language
- Nederlandse
- 中文 (Zhōngwén), 汉语, 漢語
Select Your Currency
- AED United Arab Emirates Dirham
- AFN Afghan Afghani
- ALL Albanian Lek
- AMD Armenian Dram
- ANG Netherlands Antillean Guilder
- AOA Angolan Kwanza
- ARS Argentine Peso
- AUD Australian Dollar
- AWG Aruban Florin
- AZN Azerbaijani Manat
- BAM Bosnia-Herzegovina Convertible Mark
- BBD Barbadian Dollar
- BDT Bangladeshi Taka
- BGN Bulgarian Lev
- BIF Burundian Franc
- BMD Bermudan Dollar
- BND Brunei Dollar
- BOB Bolivian Boliviano
- BRL Brazilian Real
- BSD Bahamian Dollar
- BWP Botswanan Pula
- BZD Belize Dollar
- CAD Canadian Dollar
- CDF Congolese Franc
- CHF Swiss Franc
- CLP Chilean Peso
- CNY Chinese Yuan
- COP Colombian Peso
- CRC Costa Rican Colón
- CVE Cape Verdean Escudo
- CZK Czech Republic Koruna
- DJF Djiboutian Franc
- DKK Danish Krone
- DOP Dominican Peso
- DZD Algerian Dinar
- EGP Egyptian Pound
- ETB Ethiopian Birr
- FJD Fijian Dollar
- FKP Falkland Islands Pound
- GBP British Pound Sterling
- GEL Georgian Lari
- GIP Gibraltar Pound
- GMD Gambian Dalasi
- GNF Guinean Franc
- GTQ Guatemalan Quetzal
- GYD Guyanaese Dollar
- HKD Hong Kong Dollar
- HNL Honduran Lempira
- HTG Haitian Gourde
- HUF Hungarian Forint
- IDR Indonesian Rupiah
- ILS Israeli New Sheqel
- INR Indian Rupee
- ISK Icelandic Króna
- JMD Jamaican Dollar
- JPY Japanese Yen
- KES Kenyan Shilling
- KGS Kyrgystani Som
- KHR Cambodian Riel
- KMF Comorian Franc
- KRW South Korean Won
- KYD Cayman Islands Dollar
- KZT Kazakhstani Tenge
- LAK Laotian Kip
- LBP Lebanese Pound
- LKR Sri Lankan Rupee
- LRD Liberian Dollar
- LSL Lesotho Loti
- MAD Moroccan Dirham
- MDL Moldovan Leu
- MGA Malagasy Ariary
- MKD Macedonian Denar
- MNT Mongolian Tugrik
- MOP Macanese Pataca
- MUR Mauritian Rupee
- MVR Maldivian Rufiyaa
- MWK Malawian Kwacha
- MXN Mexican Peso
- MYR Malaysian Ringgit
- MZN Mozambican Metical
- NAD Namibian Dollar
- NGN Nigerian Naira
- NIO Nicaraguan Córdoba
- NOK Norwegian Krone
- NPR Nepalese Rupee
- NZD New Zealand Dollar
- OMR Omani Rial
- PAB Panamanian Balboa
- PEN Peruvian Nuevo Sol
- PGK Papua New Guinean Kina
- PHP Philippine Peso
- PKR Pakistani Rupee
- PLN Polish Zloty
- PYG Paraguayan Guarani
- QAR Qatari Rial
- RON Romanian Leu
- RSD Serbian Dinar
- RUB Russian Ruble
- RWF Rwandan Franc
- SAR Saudi Riyal
- SBD Solomon Islands Dollar
- SCR Seychellois Rupee
- SEK Swedish Krona
- SGD Singapore Dollar
- SHP Saint Helena Pound
- SLL Sierra Leonean Leone
- SOS Somali Shilling
- SRD Surinamese Dollar
- SVC Salvadoran Colón
- SZL Swazi Lilangeni
- THB Thai Baht
- TJS Tajikistani Somoni
- TOP Tongan Pa anga
- TRY Turkish Lira
- TTD Trinidad and Tobago Dollar
- TWD New Taiwan Dollar
- TZS Tanzanian Shilling
- UAH Ukrainian Hryvnia
- UGX Ugandan Shilling
- USD United States Dollar
- UYU Uruguayan Peso
- UZS Uzbekistan Som
- VND Vietnamese Dong
- VUV Vanuatu Vatu
- WST Samoan Tala
- XAF CFA Franc BEAC
- XCD East Caribbean Dollar
- XOF CFA Franc BCEAO
- XPF CFP Franc
- YER Yemeni Rial
- ZAR South African Rand
- ZMW Zambian Kwacha
Apply for and track your visa with our new app!
Download Now
Get Your Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration Online Now!
1.2M happy customers
24/7 support
+46,000 reviews
10 years of experience
98% visa approval rate
How to Apply: COVID-19 Self Declaration
Our application form is 100% digital and easy to fill-in, complete it and pay it with credit card or PayPal.
No need to deal with the embassy. We do it for you so you don't lose valuable time.
Present your Passport and the Health Declaration we provide when you arrive at the airport.
How to Apply: Embassy Registration
Complete our easy online application and pay with credit card or PayPal
Your embassy will assist you if an emergency (eg. Natural disasters, civil unrest, etc) occur
Why Register with the Embassy
Required information to apply.
Once You Have Registered With Your Embassy Or Consulate, You Will Need To Update Your Data If:
- your contact details change,
- your civil status changes,
- you are going back to your home country.
Learn More: COVID-19 Self Declaration
What you need to know.
Remember that this document does not replace a visa, so you must check if your country of citizenship requires a visa to enter Iran.
Foreign travelers who cannot provide the results of a PCR test will be turned away from entering Iran.
All arriving passengers would be subject to medical screening and clinical assessment in case of showing symptoms of COVID-19 or if the presented certificate is issued more than 72 hours before arrival.
Masks are compulsory within airports, and on all public transportation and aircraft.
Not wearing a mask carries a fine of IRR 1,000’000 (USD 3.3).
Breaking quarantine carries a fine of IRR 2’000’000 (USD 6.6).
Remember to check your country's safety recommendations before travelling, for a better travel experience
IRAN IS OPEN: Iran is open for tourism.
DOCUMENT OVERVIEW The Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration is a mandatory form that all arriving passengers are required to fill out before entry to Iran.
It is a necessary document in accordance with the laws of the Government of Islamic Republic of Iran as a part of public health measures in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, and will be used only by the ministry of health of I.R.Iran.
Apply now for your Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration with iVisa.com
WHO CAN ENTER IRAN WITH THIS DOCUMENT All citizens who wish to travel to Iran are eligible to apply for the Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration . You won't be able to enter without filling one out.
Any traveler's passport must be valid for at least 6 months from the proposed departure date and all unvaccinated travelers over the age of 12 must provide a negative PCR test to the Ministry of Health upon arrival in Iran. The test must be conducted within 72 hours before arrival. Fully vaccinated travelers from Iraq are exempted for testing.
All citizens eligible can apply for the document here .
OBTAIN THE IRAN COVID-19 SELF DECLARATION To obtain the Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration with iVisa.com it's a quick and easy process. You just need internet access and to provide us with some basic personal, flight, travel and health information.
You can fill our online form out within 10 minutes and once you have paid the processing fee and sent your application, you will receive email confirmation from us.
Visit the application page to complete the Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration .
DISPLAY THE FORM After applying online, travelers should receive a confirmation email with the completed Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration. You should download and print this form, so you have both a digital and physical copy to show when you enter Iran.
You will be subject to a health screening procedure on arrival so make sure you have your Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration ready to show to the officials at the airport.
Visit the FAQs below to view the quarantine rules for Iran.
Related Articles

- Iran eVisa for Citizens of UAE

- Is there a travel ban to Iran? See the complete answer here

Iran eVisa for Citizens of India
How do processing times work, where can i read more.
- Iran eVisa for Citizens of Canada
- Iran eVisa for Citizens of Afghanistan
- Iran eVisa for Citizens of Belgium
- Documents required for Iran visa
- How to apply for Iran visa
- Iran eVisa cost
- Iran eVisa processing time
- Iran eVisa for Citizens of Australia
Other Available Visas: Iran?
- eVisa Application

Iran: Coronavirus Pandemic Country Profile
Research and data: Edouard Mathieu, Hannah Ritchie, Lucas Rodés-Guirao, Cameron Appel, Daniel Gavrilov, Charlie Giattino, Joe Hasell, Bobbie Macdonald, Saloni Dattani, Diana Beltekian, Esteban Ortiz-Ospina, and Max Roser
- Coronavirus
- Data explorer
- Hospitalizations
Vaccinations
- Mortality risk
- Excess mortality
- Policy responses
Build on top of our work freely
- All our code is open-source
- All our research and visualizations are free for everyone to use for all purposes
Select countries to show in all charts
Confirmed cases.
- What is the daily number of confirmed cases?
- Daily confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
- What is the cumulative number of confirmed cases?
- Cumulative confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
- Biweekly cases : where are confirmed cases increasing or falling?
- Global cases in comparison: how are cases changing across the world?
Iran: What is the daily number of confirmed cases?
Related charts:.
Which world regions have the most daily confirmed cases?
This chart shows the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases per day . This is shown as the seven-day rolling average.
What is important to note about these case figures?
- The reported case figures on a given date do not necessarily show the number of new cases on that day – this is due to delays in reporting.
- The number of confirmed cases is lower than the true number of infections – this is due to limited testing. In a separate post we discuss how models of COVID-19 help us estimate the true number of infections .
→ We provide more detail on these points in our page on Cases of COVID-19 .
Five quick reminders on how to interact with this chart
- By clicking on Edit countries and regions you can show and compare the data for any country in the world you are interested in.
- If you click on the title of the chart, the chart will open in a new tab. You can then copy-paste the URL and share it.
- You can switch the chart to a logarithmic axis by clicking on ‘LOG’.
- If you move both ends of the time-slider to a single point you will see a bar chart for that point in time.
- Map view: switch to a global map of confirmed cases using the ‘MAP’ tab at the bottom of the chart.
Iran: Daily confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
Differences in the population size between different countries are often large. To compare countries, it is insightful to look at the number of confirmed cases per million people – this is what the chart shows.
Keep in mind that in countries that do very little testing the actual number of cases can be much higher than the number of confirmed cases shown here.
Three tips on how to interact with this map
- By clicking on any country on the map you see the change over time in this country.
- By moving the time slider (below the map) you can see how the global situation has changed over time.
- You can focus on a particular world region using the dropdown menu to the top-right of the map.
Iran: What is the cumulative number of confirmed cases?
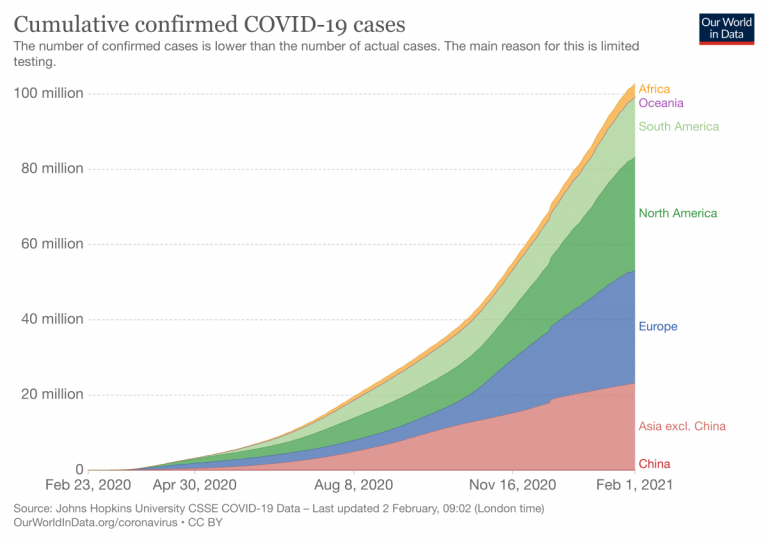
Which world regions have the most cumulative confirmed cases?
How do the number of tests compare to the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases?
The previous charts looked at the number of confirmed cases per day – this chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed cases since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In all our charts you can download the data
We want everyone to build on top of our work and therefore we always make all our data available for download. Click on the ‘Download’-tab at the bottom of the chart to download the shown data for all countries in a .csv file.
Iran: Cumulative confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
This chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed cases per million people.
Iran: Biweekly cases : where are confirmed cases increasing or falling?
Why is it useful to look at biweekly changes in confirmed cases.
For all global data sources on the pandemic, daily data does not necessarily refer to the number of new confirmed cases on that day – but to the cases reported on that day.
Since reporting can vary significantly from day to day – irrespectively of any actual variation of cases – it is helpful to look at a longer time span that is less affected by the daily variation in reporting. This provides a clearer picture of where the pandemic is accelerating, staying the same, or reducing.
The first map here provides figures on the number of confirmed cases in the last two weeks. To enable comparisons across countries it is expressed per million people of the population.
And the second map shows the percentage change (growth rate) over this period: blue are all those countries in which the case count in the last two weeks was lower than in the two weeks before. In red countries the case count has increased.
What is the weekly number of confirmed cases?
What is the weekly change (growth rate) in confirmed cases?
Iran: Global cases in comparison: how are cases changing across the world?
In our page on COVID-19 cases , we provide charts and maps on how the number and change in cases compare across the world.
Confirmed deaths
- What is the daily number of confirmed deaths?
- Daily confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
- What is the cumulative number of confirmed deaths?
- Cumulative confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
- Biweekly deaths : where are confirmed deaths increasing or falling?
- Global deaths in comparison: how are deaths changing across the world?
Iran: What is the daily number of confirmed deaths?
Which world regions have the most daily confirmed deaths?
This chart shows t he number of confirmed COVID-19 deaths per day .
Three points on confirmed death figures to keep in mind
All three points are true for all currently available international data sources on COVID-19 deaths:
- The actual death toll from COVID-19 is likely to be higher than the number of confirmed deaths – this is due to limited testing and challenges in the attribution of the cause of death. The difference between confirmed deaths and actual deaths varies by country.
- How COVID-19 deaths are determined and recorded may differ between countries.
- The death figures on a given date do not necessarily show the number of new deaths on that day, but the deaths reported on that day. Since reporting can vary significantly from day to day – irrespectively of any actual variation of deaths – it is helpful to view the seven-day rolling average of the daily figures as we do in the chart here.
→ We provide more detail on these three points in our page on Deaths from COVID-19 .
Iran: Daily confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
This chart shows the daily confirmed deaths per million people of a country’s population.
Why adjust for the size of the population?
Differences in the population size between countries are often large, and the COVID-19 death count in more populous countries tends to be higher . Because of this it can be insightful to know how the number of confirmed deaths in a country compares to the number of people who live there, especially when comparing across countries.
For instance, if 1,000 people died in Iceland, out of a population of about 340,000, that would have a far bigger impact than the same number dying in the United States, with its population of 331 million. 1 This difference in impact is clear when comparing deaths per million people of each country’s population – in this example it would be roughly 3 deaths/million people in the US compared to a staggering 2,941 deaths/million people in Iceland.
Iran: What is the cumulative number of confirmed deaths?
Which world regions have the most cumulative confirmed deaths?
The previous charts looked at the number of confirmed deaths per day – this chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed deaths since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Iran: Cumulative confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
This chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed deaths per million people.
Iran: Biweekly deaths : where are confirmed deaths increasing or falling?
Why is it useful to look at biweekly changes in deaths.
For all global data sources on the pandemic, daily data does not necessarily refer to deaths on that day – but to the deaths reported on that day.
Since reporting can vary significantly from day to day – irrespectively of any actual variation of deaths – it is helpful to look at a longer time span that is less affected by the daily variation in reporting. This provides a clearer picture of where the pandemic is accelerating, staying the same, or reducing.
The first map here provides figures on the number of confirmed deaths in the last two weeks. To enable comparisons across countries it is expressed per million people of the population.
And the second map shows the percentage change (growth rate) over this period: blue are all those countries in which the death count in the last two weeks was lower than in the two weeks before. In red countries the death count has increased.
What is the weekly number of confirmed deaths?
What is the weekly change (growth rate) in confirmed deaths?
Iran: Global deaths in comparison: how are deaths changing across the world?
In our page on COVID-19 deaths , we provide charts and maps on how the number and change in deaths compare across the world.
- How many COVID-19 vaccine doses are administered daily ?
- How many COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in total ?
- What share of the population has received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine?
- What share of the population has completed the initial vaccination protocol ?
- Global vaccinations in comparison: which countries are vaccinating most rapidly?
Iran: How many COVID-19 vaccine doses are administered daily ?
How many vaccine doses are administered each day (not population adjusted)?
This chart shows the daily number of COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people in a given population . This is shown as the rolling seven-day average. Note that this is counted as a single dose, and may not equal the total number of people vaccinated, depending on the specific dose regime (e.g., people receive multiple doses).
Iran: How many COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in total ?
How many vaccine doses have been administered in total (not population adjusted)?
This chart shows the total number of COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people within a given population. Note that this is counted as a single dose, and may not equal the total number of people vaccinated, depending on the specific dose regime as several available COVID vaccines require multiple doses.
Iran: What share of the population has received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine?
How many people have received at least one vaccine dose?
This chart shows the share of the total population that has received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. This may not equal the share with a complete initial protocol if the vaccine requires two doses. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric goes up by 1. If they receive the second dose, the metric stays the same.
Iran: What share of the population has completed the initial vaccination protocol ?
How many people have completed the initial vaccination protocol?
The following chart shows the share of the total population that has completed the initial vaccination protocol. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric stays the same. If they receive the second dose, the metric goes up by 1.
This data is only available for countries which report the breakdown of doses administered by first and second doses.
Iran: Global vaccinations in comparison: which countries are vaccinating most rapidly?
In our page on COVID-19 vaccinations, we provide maps and charts on how the number of people vaccinated compares across the world.
Testing for COVID-19
- The positive rate
- The scale of testing compared to the scale of the outbreak
- How many tests are performed each day ?
- Global testing in comparison: how is testing changing across the world?
Iran: The positive rate
Here we show the share of reported tests returning a positive result – known as the positive rate.
The positive rate can be a good metric for how adequately countries are testing because it can indicate the level of testing relative to the size of the outbreak. To be able to properly monitor and control the spread of the virus, countries with more widespread outbreaks need to do more testing.
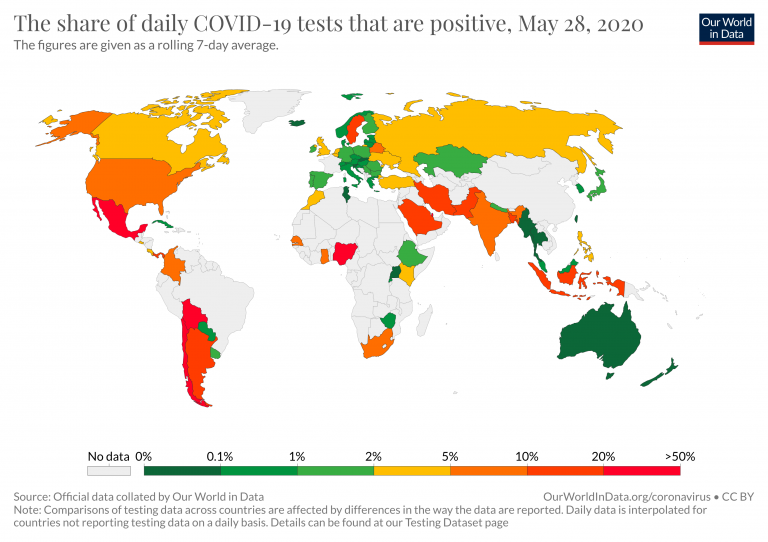
It can also be helpful to think of the positive rate the other way around:
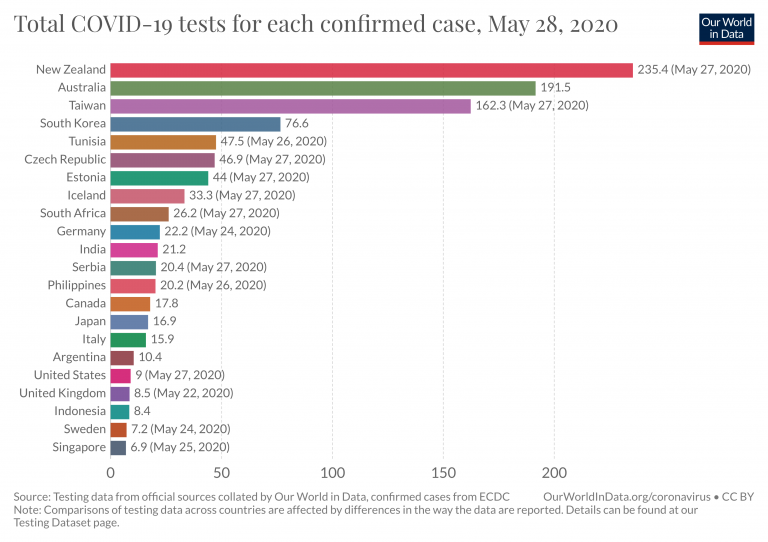
How many tests have countries done for each confirmed case in total across the outbreak?
Iran: The scale of testing compared to the scale of the outbreak
How do daily tests and daily new confirmed cases compare when not adjusted for population ?
This scatter chart provides another way of seeing the extent of testing relative to the scale of the outbreak in different countries.
The chart shows the daily number of tests (vertical axis) against the daily number of new confirmed cases (horizontal axis), both per million people.
Iran: How many tests are performed each day ?
This chart shows the number of daily tests per thousand people. Because the number of tests is often volatile from day to day, we show the figures as a seven-day rolling average.
What is counted as a test?
The number of tests does not refer to the same thing in each country – one difference is that some countries report the number of people tested, while others report the number of tests (which can be higher if the same person is tested more than once). And other countries report their testing data in a way that leaves it unclear what the test count refers to exactly.
We indicate the differences in the chart and explain them in detail in our accompanying source descriptions .
Iran: Global testing in comparison: how is testing changing across the world?
In our page on COVID-19 testing , we provide charts and maps on how the number and change in tests compare across the world.
Case fatality rate
- What does the data on deaths and cases tell us about the mortality risk of COVID-19?
- The case fatality rate
- Learn in more detail about the mortality risk of COVID-19
Iran: What does the data on deaths and cases tell us about the mortality risk of COVID-19?
To understand the risks and respond appropriately we would also want to know the mortality risk of COVID-19 – the likelihood that someone who is infected with the disease will die from it.
We look into this question in more detail on our page about the mortality risk of COVID-19 , where we explain that this requires us to know – or estimate – the number of total cases and the final number of deaths for a given infected population.
Because these are not known , we discuss what the current data on confirmed deaths and cases can and can not tell us about the risk of death. This chart shows both those metrics.
Iran: The case fatality rate
Related chart:.
How do the cumulative number of confirmed deaths and cases compare?
The case fatality rate is simply the ratio of the two metrics shown in the chart above.
The case fatality rate is the number of confirmed deaths divided by the number of confirmed cases.
This chart here plots the CFR calculated in just that way.
During an outbreak – and especially when the total number of cases is not known – one has to be very careful in interpreting the CFR . We wrote a detailed explainer on what can and can not be said based on current CFR figures.
Iran: Learn in more detail about the mortality risk of COVID-19
Learn what we know about the mortality risk of COVID-19 and explore the data used to calculate it.
Government Responses
- Government Stringency Index
To understand how governments have responded to the pandemic, we rely on data from the Oxford Coronavirus Government Response Tracker (OxCGRT), which is published and managed by researchers at the Blavatnik School of Government at the University of Oxford.
This tracker collects publicly available information on 17 indicators of government responses, spanning containment and closure policies (such as school closures and restrictions in movement); economic policies; and health system policies (such as testing regimes).
How have countries responded to the pandemic?
Travel bans, stay-at-home restrictions, school closures – how have countries responded to the pandemic? Explore the data on all policy measures.
Iran: Government Stringency Index
The chart here shows how governmental response has changed over time. It shows the Government Stringency Index – a composite measure of the strictness of policy responses.
The index on any given day is calculated as the mean score of nine policy measures, each taking a value between 0 and 100. See the authors’ full description of how this index is calculated.
A higher score indicates a stricter government response (i.e. 100 = strictest response).
The OxCGRT project calculates this index using nine specific measures, including:
- school and workplace closures;
- restrictions on public gatherings;
- transport restrictions;
- and stay-at-home requirements.
You can see all of these separately on our page on policy responses . There you can also compare these responses in countries across the world.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
Iran's Hard-Line Parliament Approves All Members of President's Cabinet, First Time Since 2001
Iran’s hard-line parliament has approved all members of reformist President Masoud Pezeshkian’s Cabinet, the first time in over two decades a leader has been able to get all of his officials through the body
Iran's Hard-Line Parliament Approves All Members of President's Cabinet, First Time Since 2001

Vahid Salemi
Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian, center, is greeted by lawmakers while leaving the parliament after the conclusion of his speech during the debate on his proposed ministers, in Tehran, Iran, Wednesday, Aug. 21, 2024. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
TEHRAN, Iran (AP) — Iran's hard-line parliament on Wednesday approved all members of reformist President Masoud Pezeshkian's Cabinet, the first time in over two decades a leader has been able to get all of his officials through the body.
The approval marks an early win for Pezeshkian , a longtime lawmaker who found himself catapulted into the presidency after a helicopter crash in May killed his hard-line predecessor.
Getting his officials approved shows Pezeshkian picked a Cabinet of consensus with names palatable to all of the power centers within Iran's theocracy, as opposed to going for controversial choices as well.
Underlining that point, Pezeshkian immediately posted an image online with him standing next to Iran's judiciary chief, a Shiite cleric, and the country's parliament speaker, a hard-liner he once faced in the election.
“Consensus for Iran,” he wrote in the caption.
Former Foreign Minister Mohamamad Javad Zarif, who campaigned for Pezeshkian in his election, later resigned as a vice president for the new leader over the Cabinet selections.
Among those in Pezeshkian's new Cabinet is Abbas Araghchi, 61, a career diplomat who will be Iran’s new foreign minister.
Araghchi was a member of the Iranian negotiating team that reached a nuclear deal with world powers in 2015 that capped Tehran’s nuclear program in return for the lifting of sanctions.
In 2018, then-President Donald Trump pulled the U.S. out of the deal and imposed more sanctions on Iran. Pezeshkian said during his presidential campaign that he would try to revive the nuclear deal.
The candidate who received the most support from lawmakers was the country's new defense minister, Aziz Nasirzadeh, who received 281 votes out of 288 present lawmakers. The chamber has 290 seats.
Nasirzadeh was chief of the Iranian air force from 2018 to 2021.
Health Minister Mohammad Reza Zafarghandi received the lowest number of votes with 163.
The only female minister proposed, Housing and Road Minister Farzaneh Sadegh, a 47-year-old architect, received 231 votes. She is the first female minister in Iran in more than a decade.
The parliament also approved Pezeshkian’s proposed Intelligence Minister Ismail Khatib, as well as Justice Minister Amin Hossein Rahimi, both of whom served under the late President Ebrahim Raisi. Pezeshkian also put Raisi’s minister of industries, Abbas Aliabadi, in the post of energy minister.
Dropping proposed ministers has been a tradition in Iran’s parliament, making Pezeshkian's success that much more striking. Former reformist President Mohammad Khatami was the only president who received vote of confidence for all of his proposed ministers in both 1997 and 2001.
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Photos You Should See - July 2024

Join the Conversation
Tags: Associated Press , politics , world news
America 2024

U.S. News Decision Points
Your trusted source for the latest news delivered weekdays from the team at U.S. News and World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

The Best Cartoons on Donald Trump
Aug. 16, 2024, at 4:34 p.m.

Joe Biden Behind The Scenes
Aug. 20, 2024

Economy, Campaign Enter Critical Period
Tim Smart Aug. 26, 2024

Trump on Defense After DNC
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder Aug. 23, 2024

RFK Jr. Campaign Comes to Bizarre End
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton Aug. 23, 2024

The RFK Jr. Campaign's Weirdest Moments
Laura Mannweiler Aug. 23, 2024

Powell: Time to Lower Interest Rates
Tim Smart Aug. 23, 2024

Highlights of the Democratic Convention

5 Takeaways: Harris Accepts Nomination

Advertisement
Supported by
Iranian Military Official Hints Strike on Israel May Be Delayed
The comments from an Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps leader suggested that a widely feared regional conflict might be averted, at least for the moment.
- Share full article

By Farnaz Fassihi
A senior Iranian military official said on Tuesday that retaliation against Israel over the killing of a Hamas leader in Tehran may be long in coming and take any number of forms, suggesting that an attack against Israel may have been placed on hold.
The comments came from Gen. Ali Mohammad Naeini, the spokesman for the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps, the branch of the armed forces that would lead such an attack and that is responsible for securing Iran’s borders.
“Time is on our side, and it’s possible that the wait period for the response could take a long time,” General Naeini said at a news conference in Tehran, according to video footage on state media. “It’s possible that Iran’s response will not be a repeat of previous operations. The quality of the response, scenarios and tools are not always the same.”
While General Naeini did not elaborate on what options Iran is considering, his reference to “previous operations” appeared to mean the Iranian strike on Israel in April, when Iran launched hundreds of missiles and drones against its longtime adversary. That attack was done in retaliation for an Israeli strike on an Iranian embassy compound in Damascus, Syria, that killed several senior Iranian military commanders.
General Naeini’s comments suggested that the regional war widely feared should Iran strike Israel again might be averted, at least for the moment.
Since the late July assassination of the Hamas leader on Iranian soil — for which Israel has not acknowledged responsibility — international leaders have been alarmed as Iranian officials pledged to avenge his death. Complicating matters, Iranian-backed Hezbollah forces in Lebanon were also vowing to attack Israel, in their case over the killing in Beirut of one their top commanders shortly before the Tehran assassination.
But it appears that for now in Iran, national interests and domestic considerations are outweighing ideological fervor. General Naeini said that senior commanders of the Guards Corps and the army, along with other senior Iranian leaders, were “weighing all the aspects of the situation and will make a careful and wise decision.”
For three weeks the Middle East has been on edge, anticipating that Iran and Hezbollah would launch coordinated or separate military strikes on Israel in response to the assassinations.
With Israel threatening to strike back forcefully in both Iran and Lebanon, diplomats and world leaders warned that what has been contained, tit-for-tat strikes could spiral out of control and engulf the region in a wider war.
The United States dispatched naval warships and a submarine to the region to help defend Israel, its close ally, as it did in April. And Secretary of State Antony J. Blinken has doubled down on the push for a cease-fire between Israel and Hamas in the Gaza Strip in the hope that it would lower regional tensions.
But it may be that if Iran does defer a strike on Israeli, domestic calibrations will have played a bigger role than international diplomacy.
For more than three decades, Iran’s supreme leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, has ruled with one basic tenet: keep the Islamic Republic regime in power.
And so while Mr. Khamenei ordered a direct strike on Israel on the morning after the Hamas leader, Ismail Haniyeh, was killed, analysts say that as time has passed, the shock and humiliation have given way to a more realistic assessment of the risk and reward of war with Israel. Moreover, Iran’s new president, Masoud Pezeshkian, says his agenda is to defuse tensions and engage with the West.
“The hubris and luster that circulated after Haniyeh was killed has given way to much more caution that is more reflective of the Revolutionary Guards’ careful and long-term approach,” said Sanam Vakil, Middle East director for Chatham House.
Ms. Vakil said: “The assessment is that they can’t do it all. It’s a very sensitive time for the new president.”
An Israeli strike on Iran’s critical infrastructure such as power plants, oil refineries and nuclear facilities might set the country back years and further deepen its economic crisis. The government already faces a crisis of legitimacy at home with waves of protests over the past few years by Iranians demanding an end to clerical rule. A disruption to electricity and gasoline could erupt into another uprising.
More important, a war would place Mr. Pezeshkian’s new government on a confrontational course not just with the West but also with Arab countries in the region at a time when Iran is trying to foster closer ties.
“We have tension, bloodshed and war in the region,” the new president Mr. Pezeshkian told Parliament this week. “Our relations with our neighbors is weak, our social capital has shrunk at home, and our unity is weak, and the government has lost its credibility with the public.
Analysts said also playing into Iran’s calculations were the religious holiday of Arbaeen next week, and the annual United Nations General Assembly gathering of world leaders in mid-September in New York. Mr. Pezeshkian will be making his debut on the world stage there, and is expected to deliver a message of change and moderation, not one of war and mayhem. Iran uses Arbaeen to showcase its leadership among Shia Muslims in the region, and the observances typically draw millions of pilgrims.
Iranian leaders might also have concluded that a military strike would not really change anything.
“This idea that even if they launch thousands of missiles — what then?” said Afshon Ostovar, an associate professor of national security affairs at the Naval Postgraduate School and an expert on Iran’s military. “The risks are really clear.”
Farnaz Fassihi is the United Nations bureau chief for The Times, leading coverage of the organization, and also covers Iran and the shadow war between Iran and Israel. She is based in New York. More about Farnaz Fassihi
Our Coverage of the Middle East Crisis
Israel-Hezbollah Tensions: Amid fears of an all-out war between Israel and Hezbollah in Lebanon, the two sides mounted the biggest round of cross-border strikes since the war in Gaza began. But both sides signaled that they were de-escalating , for now.
Gaza Cease-Fire Talks: After senior Israeli and Hamas officials arrived in Cairo to meet with mediators, four days of talks concluded with no breakthrough. Officials said discussions will continue .
Polio Concerns in Gaza: Polio vaccines arrived in Gaza, kicking off an expansive effort to vaccinate more than 640,000 Palestinian children after the first confirmed case of the disease in the territory in 25 years.
Seeing Hope in Hamas: In Ein al-Hilweh, Lebanon’s largest community of Palestinian refugees that has long been mired in despair, Hamas recruitment is up and the downtrodden air has given way to defiance and celebration.
Gaza’s Orphans: The war in Gaza is making so many orphans that no agency or aid group can count them. Extended families, hospital staff and volunteers are stepping in to care for the children.
- Mon August 26, 2024
- PCR test mandatory for passengers entering Iran
TEHRAN – All travelers to Iran must have a negative PCR test certificate or a health card during the Covid-19 pandemic, IRINN reported.
Due to the prevalence of delta variant, negative PCR test is also mandatory for vaccinated passengers, Mohammad Reza Seif, head of safety and quality assurance department of Imam Khomeini Airport Town Co, said.
All passengers entering Iran, even if they have been vaccinated and have a vaccination card, must have a negative test result, he stated.
PCR tests for over 59,000 passengers at border points
PCR tests have been performed on 59,510 passengers at the country’s official borders based on a plan launched on March 10 to rapidly identify suspected cases of coronavirus.
Around 8,000 individuals enter the country via borders on a daily basis. Some 544,182 passengers have so far been screened for coronavirus by thermal tests at the country's official borders, Mehdi Valipour, head of Relief and Rescue Organization affiliated to the Iranian Red Crescent Society (IRCS), has stated.
During the aforesaid period, IRCS forces have conducted 78,186 rapid tests, he said, ISNA reported on Saturday.
He went on to lament that some 199 individuals, who tested positive, have so far been temporarily quarantined.
Some 471 members of the IRCS cooperate for carrying out the plan in 16 provinces across the country, Valipour concluded.
With the cooperation of ministries of health and transport, a plan is being implemented with the goal of rapidly identifying and testing incoming passengers and keeping them in quarantine facilities, if necessary.
Thirty border checkpoints have been selected, including 18 land borders, nine air borders, and three sea borders, all incoming passengers will be tested and referred to the quarantine facilities in case of necessity.
Around 8,000 individuals enter the country via borders on a daily basis.
FB/MG
- negative coronavirus PCR test
- passengers entering Iran
Leave a Comment
Ukraine war latest: Zelenskyy pleads with allies for help after deadly Russian strikes
At least three people were killed this morning after Russia launched a round of air strikes against several cities in Ukraine. Below, watch a Sky News exclusive on the Ukrainian resistance operating behind Russian lines.
Monday 26 August 2024 18:20, UK
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Russia unleashes missile and drone barrage across Ukraine
- At least three dead as 15 regions hit - with explosions heard in Kyiv
- Ukraine says it shot down 102 missiles in 'most massive' attack
- Zelenskyy pleads with allies for help - as Kremlin issues warning
- Search under way for military object that landed in Poland
- Watch: Who are Ukraine's secret resistance?
- Your questions answered: Can Ukraine advance further inside Russia?
"Fierce battles are raging" around the eastern city of Pokrovsk, according to the general staff of the Ukrainian armed forces.
Russian forces have made 38 attempts to storm Ukrainian positions near the strategic logistics hub today, with clashes ongoing in 14 locations, it said.
"There remains a tense situation in the Pokrovsky direction," the general staff said, referring to the name for the district.
Volodymyr Zelenskyy said Ukraine has decided to "further strengthen" Pokrovsk after being briefed by his army chief on the situation in the area.
Russian forces have been inching forward for months in the Donetsk region, where Pokrovsk is located.
The advance quickened in recent weeks as Moscow's troops mounted relentless attacks in the direction of Pokrovsk.
The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) has identified areas of the frontline from which the Russian military is likely redeploying forces to Kursk.
Moscow is drawing troops from northern Kharkiv, Chasiv Yar and western Zaporizhzhia - the latter of which readers may remember was a focal point of Ukraine's counteroffensive last year.
Russian command is resisting pressure to redeploy forces away from its "high priority offensive" on Pokrovsk in Donetsk, said the ISW.
It will "likely continue to draw forces from lower priority offensive operations elsewhere throughout the theatre to defend in Kursk", the ISW said.
The Russian defence ministry says it struck Ukrainian forces with airstrikes at more than a dozen places along the front in the Kursk region today.
Moscow said it also repelled attacks in seven areas of Kursk.
The ministry said it was hunting for Ukrainian sabotage units which had hidden in the forests in an attempt to penetrate deeper into Russian territory.
Russia's attack on Ukraine today was its largest air bombardment, Reuters reports Ukraine's air force commander as saying.
The air force shot down 102 of 127 Russian missiles and 99 of 109 drones, Mykola Oleshchuk said.
Russia has bombarded Ukraine for more than two and half years, and launched attacks on 15 regions this morning.
Mr Oleshchuk said the attack included:
- 109 Shahed drones launched from Primorsko-Akhtarsk, Kursk, Yeisk, Chauda and Crimea
- 77 Kh-101 cruise missiles from fighter jets over Volgograd and the Caspian Sea
- 28 Kalibr cruise missiles from surface/underwater carriers in the Black Sea
- 10 Kh-59/Kh-69 guided air missiles from fighter jets over Belgorod and Mariupol
- Six Iskander-M/KN-23 ballistic missiles from Kursk, Voronezh and Crimea
- Three Kinzhal ballistic missiles fired from the Ryazan and Lipetsk regions
- 3 Kh-22 cruise missiles from the Voronezh region
Poland has released more information on a military object that entered its airspace during Russia's bombardment of Ukraine.
Jacek Goryszewski, spokesperson for the Polish army's operational command, said it was likely a drone and that it may have landed on Polish territory.
Searches were underway, he said, ruling out that the object was a missile.
"The object is being searched for by 100 soldiers on the ground and one helicopter," he said.
Mr Goryszewski said it was impossible to say whether the object was Russian or Ukrainian as weather conditions had not allowed for visual identification.
The object entered Polish airspace at 4.43am GMT and radars lost sight of it at 5.16am.
"Due to the prevailing weather conditions, it was not possible to clearly identify it, which prevented the decision to shoot it down," operational command posted on X.
The head of the international nuclear watchdog will front a mission to inspect a power plant in Russia on Tuesday.
Rafael Grossi, the head of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), said today he will head to the Kursk Nuclear Power Plant.
This is due to the "serious situation" in the region.
He said: "Given the serious situation, I'm personally leading tomorrow's IAEA mission to the Kursk Nuclear Power Plant in Russia.
"I reiterate that the safety and security of nuclear facilities must, under no circumstances, be endangered."
The photographs below show the interior of a residential building damaged by a Russian missile strike in the village of Novohupalivka today.
Russia launched dozens of missiles and drones at Ukraine, targeting gas compression stations in three regions, according to Moscow.
Ukraine does not appear to be letting up on its surprise invasion of the Kursk border region in Russia which began earlier this month.
Readers have been sending in their questions to our senior correspondents and military experts for their take on what could happen next.
Today, Justice asks:
Will Ukraine be able to advance more inside Russia?
Military analyst Sean Bell says this…
Ukraine's audacious military incursion into Russia's Kursk region - the first such action by a military power since 1941 - appears to have caught Vladimir Putin by surprise.
Although it is unclear what Ukraine is ultimately seeking to achieve, it has stated it does not intend to "hold" ground, so its current occupation is temporary.
But what next? If Ukraine had planned to push further into Russia it would probably not have blown three key bridges across the Siem river which would have been vital to its further plans.
What's the goal?
Instead, it looks likely Ukraine was seeking to seize the initiative, to demonstrate Russia is not in control of the war, and to force Moscow to respond to the attack by transferring forces from the frontline in the Donbas, thus relieving pressure on embattled Ukrainian forces.
Destroying the bridges would make it more difficult for Russia to counterattack and expel Ukrainian forces.
Although Ukraine could push further into Russia, it would create an increasing logistics challenge to keep those forces resupplied, and also divert scarce resources from the front line.
Militarily the incursion into Kursk might appear risky, but it is probably designed to apply political pressure on Mr Putin, albeit we have yet to see whether the military or political objective prevails.
A Ukraine foreign ministry official has claimed a Russian attack on Monday targeted a hydropower plant in the Kyiv region.
"Today's Russian attack ... targeted Ukraine's civilian infrastructure, including Kyiv HPP," Andriy Sybiha said on X.
Meanwhile, the Russian defence ministry claimed gas compression stations were hit in three regions of Ukraine.
It also alleges to have hit power substations and Western-supplied weapons airfields in a heavy round of bombardment on Monday morning.
Telegram says its chief executive Pavel Durov has "nothing to hide" after he was arrested in France, adding the charges against him are "absurd".
The billionaire founder of the encrypted messaging app was detained after his private jet landed at Le Bourget airport on the outskirts of Paris on Saturday.
News broadcasters BFMTV and TF1 have quoted unnamed sources as saying the Russian-born entrepreneur - who became a French citizen in 2021 - was the subject of a search warrant.
Both outlets suggest the investigation was focused on a lack of moderators on Telegram and potential criminal activity by users.
They said the warrant alleges his platform has been used for money laundering, drug trafficking and other offences, though French authorities are yet to comment.
As we've been reporting today, Russia has claimed that Ukraine has launched a number of drone attacks on buildings in Saratov.
Ukraine has yet to respond to these claims, but the video below alleges to show the moment a drone hit a high-rise apartment building in Russia.
Russian officials say a number of people were injured.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


COMMENTS
The Travel Advisory for Iran is Level 4, Do Not Travel. The Department of State recommends U.S. citizens do not travel to Iran due to the risk of terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping and the arbitrary arrest of U.S. citizens. Exercise increased caution due to wrongful detentions. Iranian authorities continue to wrongfully detain and imprison U.S ...
All costs of PCR COVID testing and quarantine measures in Iran are borne by the tourist, through insurance coverage. If foreign people who enter across land borders are symptomatic, despite presenting a vaccine card and a negative PCR test. Failure to provide a self-declaration form by the tourist. Failure to provide valid international travel ...
Travel Advisory. August 14, 2024. Iran - Level 4: Do Not Travel. O D K U T. Reissued after periodic review with minor edits. Do not travel to Iran due to the risk of terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping, arbitrary arrest of U.S. citizens and wrongful detentions. Country Summary: U.S. citizens should not travel to Iran for any reason.
COVID-19: All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information. COVID-19 vaccine. ... Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Iran for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Sea travel. Iran and the United Arab Emirates both claim sovereignty over the islands in the Gulf and the military patrols the waters. Foreigners navigating Iranian waters have been arrested and detained. In September 2019, Iranian authorities specifically called for the seizure of Canadian assets and vessels. ... COVID-19. Coronavirus disease ...
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Iran. If you are currently in Iran: Read the Department of State's COVID-19 page before planning any international travel, and read the COVID-19 page for the U.S. Virtual Embassy in Iran for country-specific COVID-19 information.
All passengers traveling to Iran must demonstrate proof of full vaccination against COVID-19 by presenting a valid corona passport document (digital vaccination card) with at least two rounds of corona vaccinations, the last one administered at least 14 days prior to travel, or proof of a negative COVID-19 test taken within 72 hours prior to travel. The answer to the PCR test and the ...
The Department of Foreign Affairs strongly advises against all travel to Iran at this time due to the risk of arbitrary arrests of European citizens by the Iranian authorities. Iran does not recognise dual nationality. If you are an Irish citizen with Iranian nationality, or a dual Irish citizen who enters Iran on a non-Irish passport, our ...
COVID-19 rules There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Iran. ... If you want to travel to Iran with a British passport, the Iranian Embassy has told FCDO ...
Explore our home airport before you arrive. Learn how to get around and transfer between the different terminals. And have a look inside our hub at Emirates Terminal 3. If you're on your way through Dubai, make the most of your experience with a short stay at the Dubai International Hotel. Or add a few days with a Dubai Stopover package.
Iran is to impose a one-week lockdown and a ban on road travel amid a fifth COVID-19 surge in the worst-hit country in the Middle East, state television reported on Saturday.
Iran's President Rouhani ordered shopping centres and bazaars across the country to shut for the 15-day holiday. The only exceptions are for pharmacies and grocery stores. Getty Images
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S. Find country-specific travel advisories, including COVID-19 restrictions, from the Department of State. See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel to learn: If you can travel if you recently had COVID-19. What you can do to help prevent COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Iran has resulted in 7,627,863 [2] confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 146,837 [2] deaths.. On 19 February 2020, Iran reported its first confirmed cases of infections in Qom. [5] The virus may have been brought to the country by a merchant from Qom who had travelled to China. [6] In response, the Government of Iran cancelled public events and Friday prayers; closed schools ...
If you choose to travel to Iran against FCDO advice, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance. Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an ...
If despite our advice you plan to travel to Iran, you'll need a specialised travel insurance policy that covers travel to high-risk destinations. Most Australian policies won't cover you for travel to Iran. ... COVID-19; Serious outbreaks sometimes occur. To protect yourself from illness: drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids;
"Given the low volumes of air travel to countries with identified cases of COVID-19 with origin in Iran (such as Canada), it is likely that Iran is currently experiencing a COVID-19 epidemic of ...
The virus is classified into two distinct groups: clade I and clade II. Clade II was responsible for the 2022 outbreak, which has led to around 100,000 cases worldwide.. But now, a version of ...
COVID-19. If you are planning international travel at this time, please read our COVID-19 related travel advice here, alongside our destination specific travel advice below.. Do not travel. Do not travel to Iran due to the potential for violent civil unrest, the risk of arbitrary arrest or detention and the volatile security situation in the region (level 4 of 4).
EPA. Iranians have been asked to avoid non-essential travel to affected areas. Iran has no plans to quarantine any cities and towns despite the spread of the new coronavirus outbreak across the ...
Dec 26, 2021. Iran has banned the entry of travelers from Britain, France, Denmark and Norway for 15 days as part of curbs following the discovery of the highly transmissible omicron variant of COVID-19 in the Middle East's worst-hit country. State television said on Sunday a similar ban imposed in late November on travelers from South Africa ...
IRAN IS OPEN: Iran is open for tourism. DOCUMENT OVERVIEW The Iran COVID-19 Self Declaration is a mandatory form that all arriving passengers are required to fill out before entry to Iran.. It is a necessary document in accordance with the laws of the Government of Islamic Republic of Iran as a part of public health measures in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, and will be used only by the ...
The actual death toll from COVID-19 is likely to be higher than the number of confirmed deaths - this is due to limited testing and challenges in the attribution of the cause of death. The difference between confirmed deaths and actual deaths varies by country. How COVID-19 deaths are determined and recorded may differ between countries.
TEHRAN, Iran (AP) — Iran's hard-line parliament on Wednesday approved all members of reformist President Masoud Pezeshkian's Cabinet, the first time in over two decades a leader has been able to ...
Labor Day travel. World News. Iran's hard-line parliament approves all members of president's Cabinet, first time since 2001 ... Wednesday, Aug. 21, 2024. Iran's hard-line parliament on Wednesday approved all members of reformist President Masoud Pezeshkian's Cabinet, the first time in over two decades a leader has been able to get all ...
A senior Iranian military official said on Tuesday that retaliation against Israel over the killing of a Hamas leader in Tehran may be long in coming and take any number of forms, suggesting that ...
August 22, 2021 - 20:0. TEHRAN - All travelers to Iran must have a negative PCR test certificate or a health card during the Covid-19 pandemic, IRINN reported. Due to the prevalence of delta variant, negative PCR test is also mandatory for vaccinated passengers, Mohammad Reza Seif, head of safety and quality assurance department of Imam ...
Ukraine's President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has just responded to this morning's barrage of Russian strikes on his country. He says more than 100 missiles have been used, and around 100 drones, and ...