
Substation Design | Power System Analysis

Direct Transfer Trip Scheme
Direct Transfer Trips (DTT) are initiated from station relays when a severe event occurs in the substation. Some of these events are breaker failure, bus faults, transformer failure, etc. A lockout relay (86 device) is assigned to each event.
The lockout relay in the station is pretty essential. When operated due to any of the events indicated above, it trips all the breakers connected to it. So for example, for a bus fault, the bus differential relay will operate the bus lockout relay which will trip and blocks re-closing of all the breakers connected to the bus. If the breaker is at a remote location and can’t be physically wired, a DTT signal is sent to it via the protective relays using the pilot channel.
The figure below shows which all lockout relays are typically used to initiate the DTT. The substation design affects this. For example, a ring bus substation or a breaker-and-a-half substation has a breaker failure lockout assigned to each breaker. For other designs, a breaker failure event trips the bus lockout relay. Whichever case you are presented with, a contact from the lockout is assigned to the relay that can key the DTT signal to the remote end breaker.
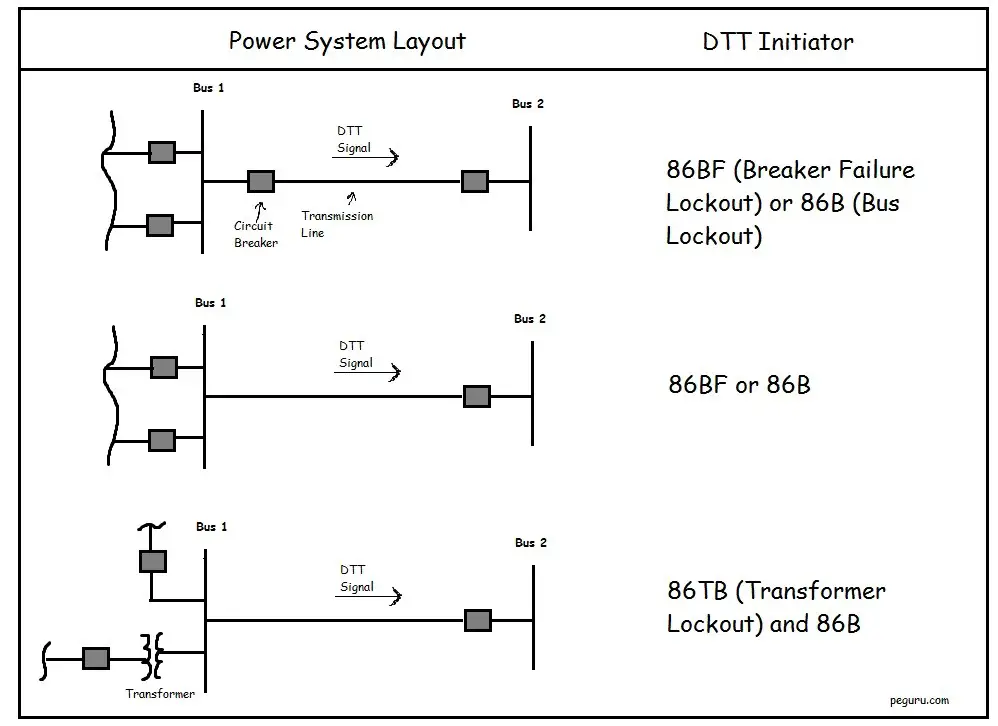
Note that lockout relays are typically used to initiate DTT. In which case, the intent is to trip all breakers without any delay. There is no logic or reasoning – just trip. Remaining events like faults on lines are taken care of by the pilot schemes which have intentional delay for coordinating the breaker trips.
Direct Transfer Trip Quiz
Get ready to learn this topic like never before.
For a fault on Bus 1, would you implement a direct transfer trip (pilot) scheme to trip breakers tied to the same bus?
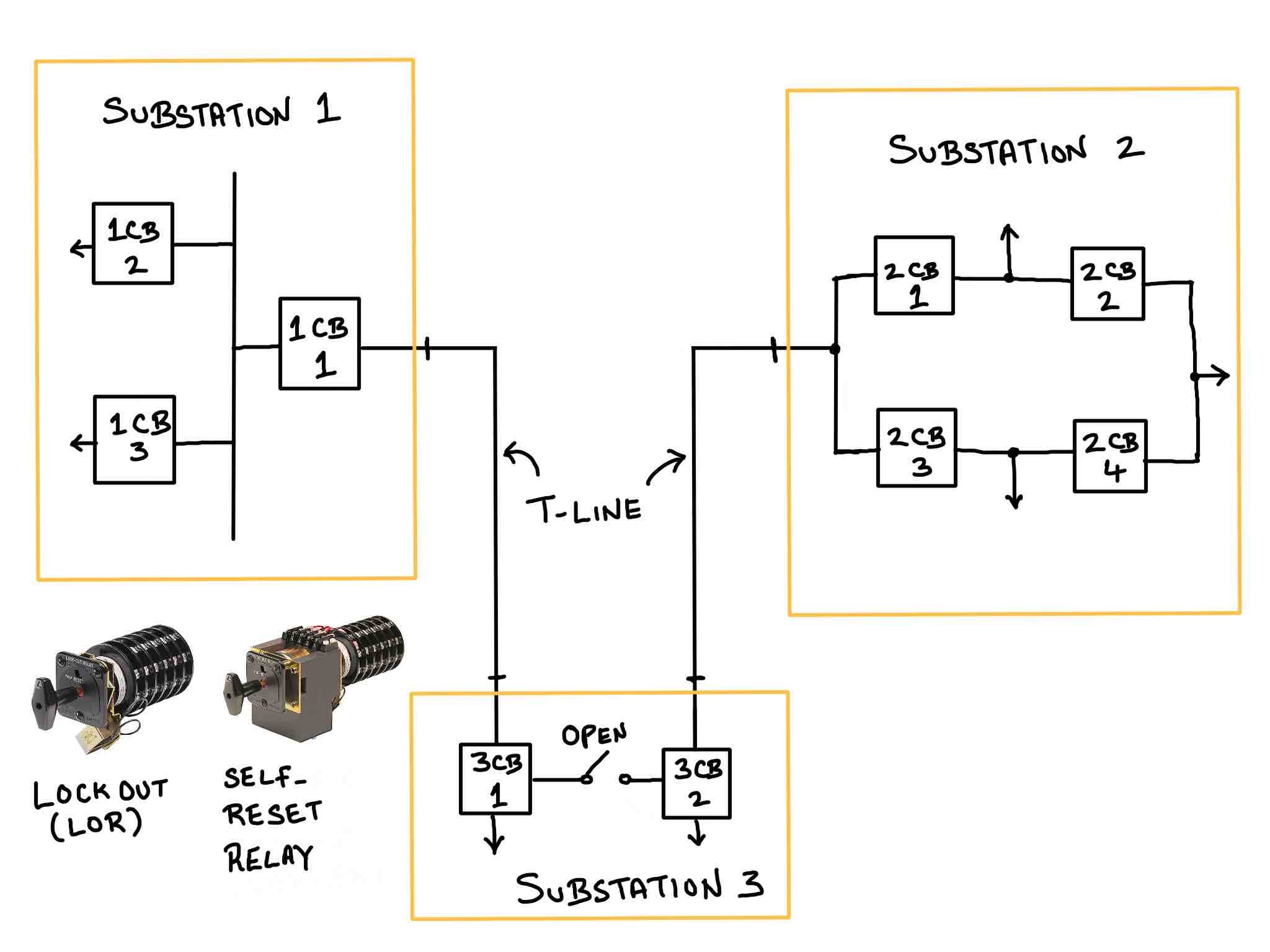
All breakers shown are within the substation. You can wire the trip 'a' contact from a lockout relay to breaker's trip coil physically. Therefore DTT scheme is not required.
Assume circuit breaker 3CB2 fails at substation 3. DTT is transmitted to Substation 2 to trip 2CB1 and 2CB3. Which auxiliary relay would you install at Substation 2 to trip breakers 2CB1 and 2CB3?

A quick word on 94 and 86.
94 relay - when its operating coil is energized - it trips. When de-energized, it resets automatically.
86 relay - when its operating coil is energized - it trips. When de-energized, it does not reset. Someone needs to be at the substation to reset it.
Considering the severe event did not occur at Substation 2, it makes no sense in installing a lockout at this station and needlessly sending someone to reset it. A 94 relay is used in this scenario. Some utilities may also use microprocessor relays to trip the breaker (instead of a 94 aux relay).
For a temporary fault on the transmission line, would you transmit DTT from either one substation?
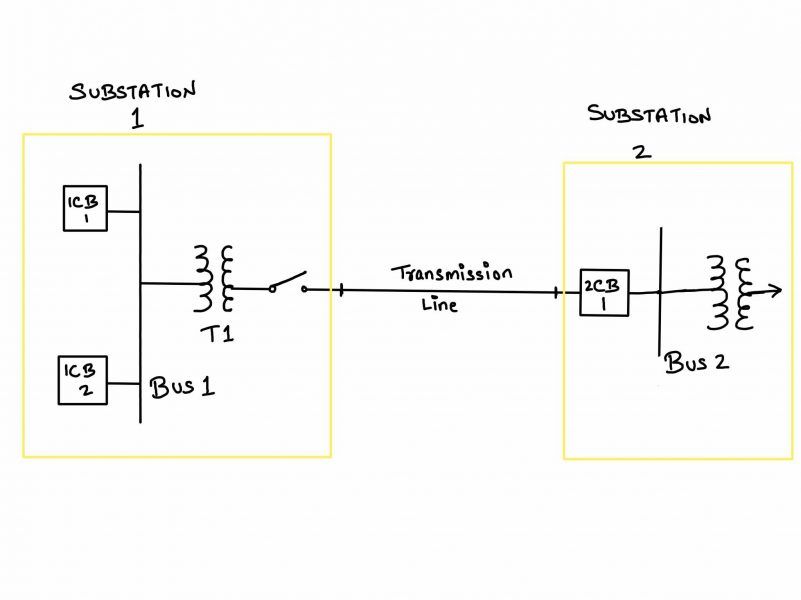
Faults on the transmission line are usually temporary. Line protection relays require time to implement its reclosing logic. DTT is not initiated.
Note that designing the protection system is an art and not an exact science. How the relay engineer "paints" differs from utility to utility. For instance, certain t-lines pass through a dense forest while others through an arid desert. The utility engineer dealing with the trees (causing higher temporary faults) may choose to go with reclosing logic - no DTT. In the case of the desert, the faults could be interpreted as permanent and whichever relay detects the fault using its Zone 1 elements, transmits DTT to the remote-end substation relay.
Note that designing the protection system is an art and not an exact science. How the relay engineer "paints" differs from utility to utility. For instance, certain t-lines pass through dense forest while others through an arid desert. The utility engineer dealing with the trees (causing higher temporary faults) may choose to go with reclosing logic - no DTT. In the case of the desert, the faults could be interpreted as permanent and whichever relay detects the fault using its Zone 1 elements, transmits DTT to the remote-end substation relay.
For what kind of fault at Substation 1 would you transmit a DTT to Substation 2 (to trip breaker 2CB1)?
For the fault scenarios listed, there is no way to stop the fault contribution from Substation 2. There is no breaker on the line-exit at Substation 1 (You cannot use a switch to interrupt load or fault current. Learn more ). If one existed, tripping it would suffice, and a DTT wouldn't be necessary.
For a transformer fault at substation 2, would you transmit DTT to substation 1?
Fault current contribution from substation 1 can be stopped by tripping 2CB1. DTT transmission to Substation 1 not required.
Fault current contribution from substation 1 can be stopped by tripping 2CB1. DTT transmission to Substation 1 not required.
Your score is
The average score is 53%
Restart quiz
This article, part of a series, covers the essentials on pilot relaying and pilot protection schemes. If not done already, start at the beginning.
- Basics of Pilot Relaying & Application Considerations For Transmission Line Protection
- Directional Comparison Blocking Scheme (DCB)
- Permissive Overreaching Transfer Trip Scheme (POTT)
- Directional Comparison Un-Blocking Scheme (DCUB)
- Direct Transfer Trip Scheme (DTT) (This is technically not a pilot scheme but requires a pilot channel)
5 thoughts on “Direct Transfer Trip Scheme”
What is the difference between DTT and Carreir aided protection
Awesome! simply explained, thank you!
Thanks a lot, for my reverensi supervisor E.M .PT.reCOnsult , in G.I.S 150kV. Jati Waringin .Jaka Mulya . Bekasi Barat.
Dear sir, Please leave me a test mail to [email protected]
hi . sir i want to ask you, about DTT , in my plant we used Relay UR GE L90 for line Upstream – Downstream arround 4 Kilometer. which event trip by DTT and force to 87 L trip and then Lockout relay 86 , but in may event record relay we not having any problem about diffrensial current it so normal , but DTT was aktif and trigger for DTT from Asym DET and LOSTPKT. can you explain to me why DTT its aktif ? and how about trigger DTT like ASYM DET & LOSTPKT because in my logic diagram i cant find them,
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Aleen Mohammed
Connect with me
- Online Training
- Access Your Courses
- Group Registration
- The Complete Relay Testing Handbook Series
- Book Extras
- Your Digital Downloads
- Hands-On Training Class Information
- Download Our Relay Training Brochure
- TechTalk (Our Blog)
- Add Your Post to TechTalk
- We Need Your Help!
- Why Choose Valence?
- About Chris Werstiuk
- Testimonials
- Contact Valence
- Subscribe to our Mailing List
- Your Shopping Cart
- The Relay Testing Handbook
- Your Account Info
No products in the cart.
Direct Transfer Trip and Direct Under-Reaching Transfer Trip Schemes Video
We’re continuing our end-to-end testing series by looking at the two simplest communication-assisted trip schemes used. Watch this Direct Transfer Trip and Direct Under-Reaching Transfer Trip Schemes Video to learn more about these two schemes. You can read the transcript below the video.
If you haven’t watched Understanding Line Distance protection (21) , watch it first.
Direct Transfer Trip and Direct Under-Reaching Transfer Trip Schemes Video Transcript
Welcome to the third video in our End-to-End Testing series. In this video we’re going to look at Direct Transfer Trip schemes or DTT schemes and then we’re going to look at Direct Under-Reaching Transfer Trip schemes (or DUTTs).
This video is part of a series. If you have not watched Understanding Line Distance Protection, the link is on the screen right now, then go watch that video first, so you get the foundation of what we’re going to talk about in this video so we don’t have to keep repeating ourselves over and over again. Let’s get started.
The first thing that we want to look at is the DTT, or the Direct Transfer Trip scheme and we don’t have a fancy animation built for that one because it’s really simple. What you’re looking at is an excerpt from The Relay Testing Handbook: End-to-End Testing and a DTT scheme is really just sending a signal from one side to the other. That’s what the direct part of Direct Transfer Trip stands for.
There is no reason for you to pull out your fancy GPS test equipment in order to test this scheme. The testing procedure for this scheme is very simple. Put one body at Relay 1, another body at Relay 2, get on your cell phones, and have Person 1 push the Trip button. The Trip button will go to the transmit of Relay 1. It’ll then send a signal to Relay 2. Relay 2 will receive that signal and open the breaker. Body Number 2 pushes their button and then the reverse should happen and Breaker Number 1 should open. Now it doesn’t have to be a trip contact. It could also be a breaker status contact or anything else, but it usually is something very simple. So there’s no reason for fancy test equipment.
The next scheme that we want to look at is the Direct Under-Reaching Transfer Trip and just like the Direct Transfer Trip scheme, Direct means that there’s no communication happening between the two relays. One relay sends the command to the other relay. So once again, there’s no reason for you to get out all your fancy GPS test equipment, because it’s a really simple test.
The top shows the standard distance protection scheme with no communication and the bottom shows the DUTT scheme with communication so that we can see what we’re gaining when we have the communication assisted trip schemes. And the first thing I’m going to do is, I’m going to put the fault really close to Relay 1. Now if you’ve watched the previous videos, or if you have any understanding of Distance Protection at all, you will know immediately that Relay 1 is going to see Zone 1 and it’s going to see Zone 2. Relay 2, because the fault is still on the line is going to see Zone 2. The difference between the standard distance scheme and the DUTT scheme is that the standard scheme Relay 1 is going to operate instantaneously and Relay 2 is going to operate after a 20 cycle delay, but if you look at the DUTT scheme, Zone 1 still trips the Relay 1 breaker immediately, but it also sends a command to the other side telling it to open as fast as it can, which is typically under 3 cycles, depending on communication delays. The DUTT scheme has saved us 17 cycles.
Now if I move the fault to the other side, you can see that the fault is now close to Relay 2 and the opposite is going to happen. Relay 2 is going to see Zone 1 and Zone 2. Relay 1 is going to see Zone 2 and the breaker connected to Relay 2 is going to open instantaneously and then we’re going to have that 17 cycle delay between the opening of the breaker on Relay 1.
If I go outside of the zone, this relay is going to see Zone 3 and Relay 2 is going to see Zone 2. Zone 2 has a faster time delay than Zone 3, so the Zone 2s are going to operate in the same amount of time. So the DUTT scheme gives us the benefit of saving 17 cycles for faults on the line and then giving us our normal backup protection for faults outside of the line. That 17 cycles might not seem like a big deal, but it is forever in electrical terms and there have been some papers presented that show that the longer a fault stays on the system, the more unstable it gets which is a big deal today.
If you like this animation, and you want to play with it some more, you can click the link below to go to our website and you can play with this animation or all the other ones that we’ve created for the communication trip schemes. I hope you’ve enjoyed this video. If you did, please subscribe to our channel, like, and also look for our next video, which should be about, Permissive Under-Reaching Transfer Trip schemes or PUTT schemes. We look forward to seeing you then, thank you.
Did you like this post?
You can share it with these links:
About the Author
Valence Announcements
Chris is an Electrical Engineering Technologist, a Journeyman Power System Electrician, and a Professional Engineer. He is also the Author of The Relay Testing Handbook series and founder of Valence Electrical Training Services. You can find out more about Chris here .
Read More Articles:
Valence will be at the NETA PowerTest 2016 Conference in Fort Worth, TN
I Want to Know How a High Impedance Differential Scheme Works
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Application Notes:
Direct transfer trip: three simple solutions to connect with fiber, t1 or ethernet.
Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) is a teleprotection scheme that involves sending trip signals from one location to another via a telecommunications transport, such as a phone line, radio, or fiber optics. It is commonly used for substations to detect substation faults and create lines of isolation while the faults are under investigation.
Because DTT signals have commonly been carried over leased telephone lines, many customers in industries such as utility and railway seek alternative DTT solutions as telecom providers either discontinue their leased line services or dramatically raise their prices to keep them.
In this application note, we explore three simple, drop-in solutions as a replacement for leased telephone lines in DTT systems, providing more cost-effective and reliable connectivity.
DTT Over a Leased Telephone Line (Conventional Method)
In this Direct Transfer Trip setup, a DTT relay is installed at both ends of a leased telephone line. The DTT relays are also each connected to circuit breakers, usually via fiber or pilot wire. This is represented by the diagram seen here:
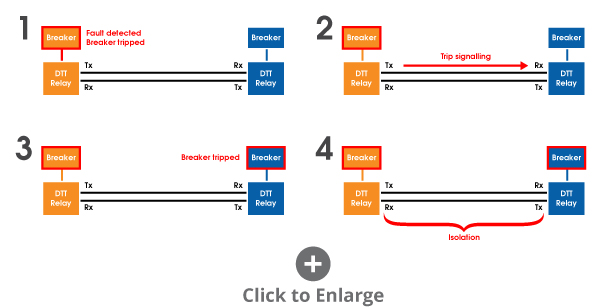
In simple terms, when the DTT relay on the left (for example) detects a fault occurring within the substation, it trips the circuit breaker on the right (shown in blue). At the same time, it transmits a signal to the DTT relay on the right (shown in blue), which trips the circuit breaker on the left (shown in orange), creating a line of isolation between the two circuit breakers (shown in black).
When connecting the DTT relays over a leased telephone line, the setup might be represented as follows:
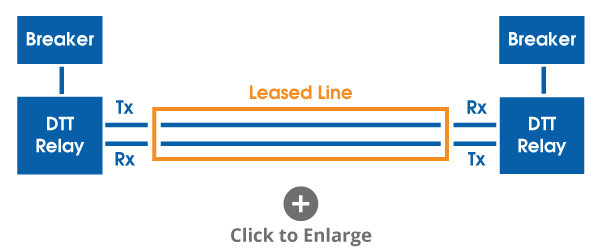
The leased line passes analog tones that ensure the DTT relays isolate the section of line with a fault present.
Three Alternative Solutions to Using Leased Lines
In situations where customers are looking to replace their leased lines or a leased line is otherwise unavailable, there are alternative solutions that TC Communications can provide. The three most common alternative transport methods for DTT are:
For these three methods, we use three main products for connecting over fiber, T1, and Ethernet, respectively:
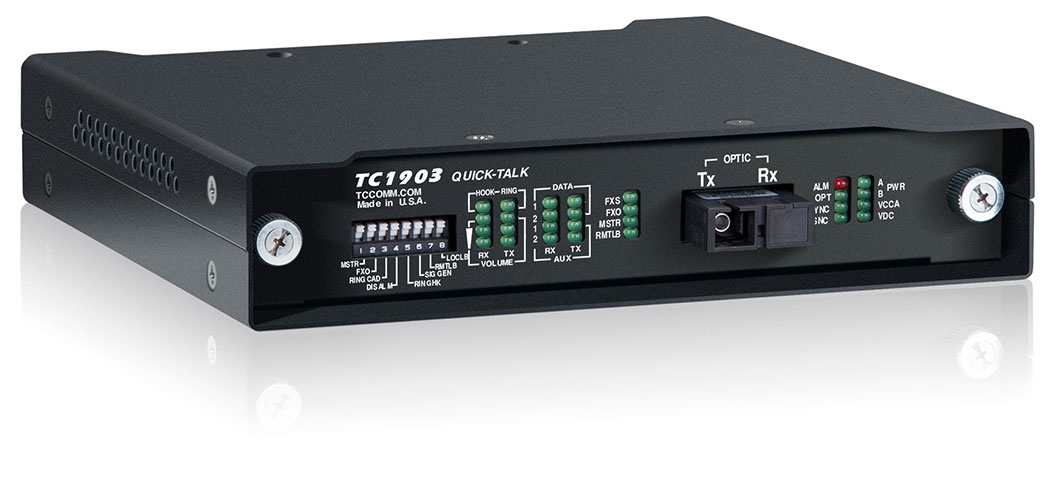
TC1903 : This Fiber Optic Phone/Analog Extender (with Bidirectional Single Fiber)* comes in a small, modem-sized form factor and extends analog and POTS telephone service to remote sites, in this case serving as an analog extender. It extends a 600 Ohm two- or four-wire line over fiber and is compatible with most PBXs or Key Systems.
*The TC1901 can be used in place of the single-fiber TC1903 for applications using dual fiber.

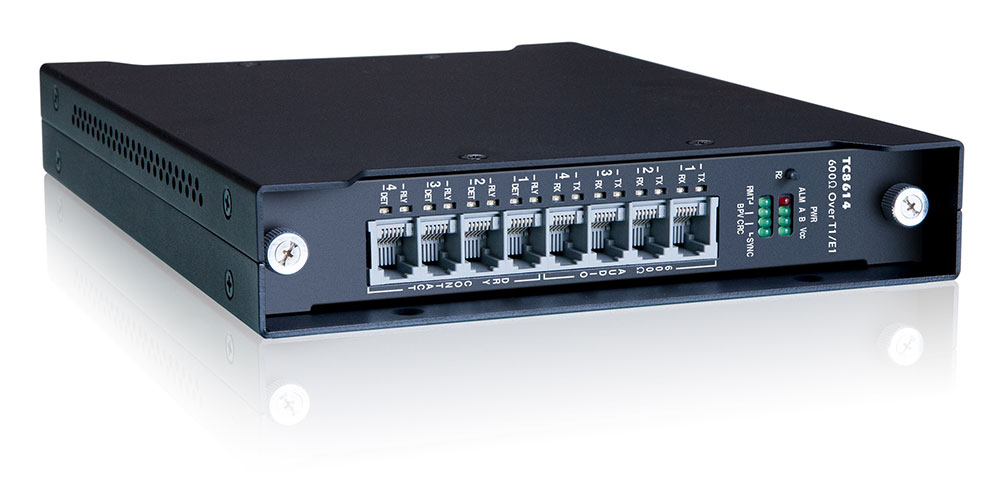
TC8614 : This 4 Channel 600 Ohm Analog and Dry Contact-over-T1/E1 Multiplexer, part of our Mini Channel Bank family, is typically used to link or extend various 600 Ohm analog, audio, and intercom devices (e.g. FSK modems, E&M, teleprotection relay controllers, etc.), and dry contacts over existing T1/ E1 links. It is also used as a backup network to ensure business continuity.

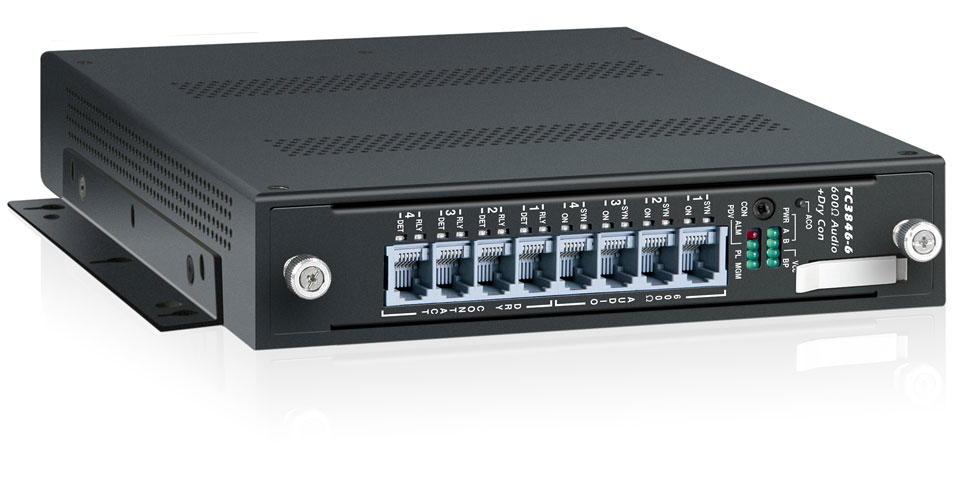
TC3846-6 : This 2W/4W E&M 600 Ohm over IP Gateway is one of our most popular JumboSwitch® products. It links or extends up to four channels of 600 Ohm 2 or 4-wire analog and dry contacts across Layer 2/3 Ethernet/IP, CE, or MPLS networks.

Next, we will take a look at three similar drop-in replacement solutions for DTT using these products.
Connecting Over Fiber Using the TC1903
In this application, a leased line is replaced by two TC1903 cards that are connected via single bi-directional fiber.
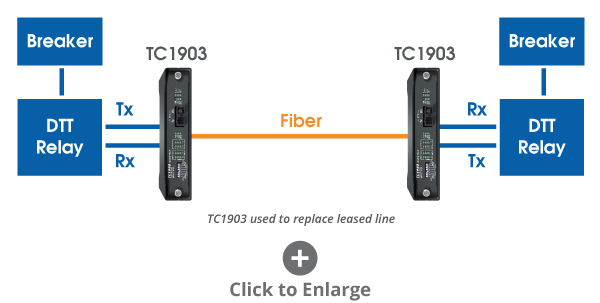
The DTT relays on each end connect to the TC1903 cards via the typical transmit and receive ports. With this setup, the DTT relays operate exactly as they would if they were still connected to a four-wire analog or leased line circuit, providing a fast and reliable means of transmitting and receiving DTT signals to trip the circuit breakers when a fault is detected.
For customers that have the capability or preference to use dual fiber instead of single fiber, the exact same effect can be achieved using two TC1901 cards instead.
Connecting Over T1 Using the TC8614
In this application, in place of a leased line, two TC8614 cards connected over a T1 line. It is another drop-in replacement that functions in much the same way as the TC1903 application over fiber.

Each DTT relay connects to a TC8614 card via the Tx and Rx ports, enabling fast and reliable transmission and receiving of DTT signals when a fault is detected, tripping both circuit breakers and creating an isolated line between them.
Many telecom providers discontinuing their leased lines, such as Verizon and AT&T, are now offering T1 services as a generally lower-cost alternative. When T1 lines are available, the TC8614 can seamlessly provide the solution.
Connecting Over Ethernet Using the TC3846-6
In this application, two TC3856-6 JumboSwitch cards are connected over Ethernet/IP to extend a circuit between two DTT relays.
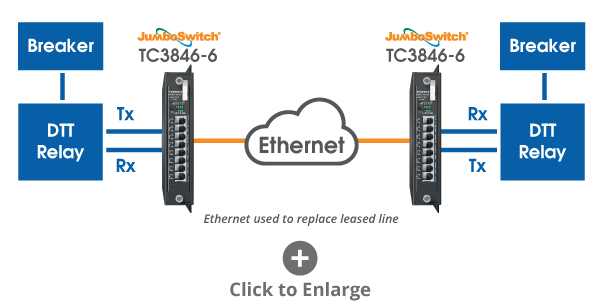
Each DTT relay connects to a TC3846-6 card via the Tx and Rx ports, enabling it to transmit and receive DTT signals to and from the other relay. One, two, or four channels may be used over 2 or 4-wire analog over Ethernet.
This is an excellent choice for sites where Ethernet connectivity is already present and due to the JumboSwitch connecting with extremely low latency, it is fully compatible with all DTT applications.
A Customer Example
A major greater Chicago metropolitan transit organization needed to connect DTT relays between the sites.
To achieve this, we installed a pair of TC1903 cards at each site (26 total) and connected them via 12 strands of single-mode fiber to link the 13 sites together in a chain fashion. (For illustration purposes, only three sites will be shown in the diagram below).
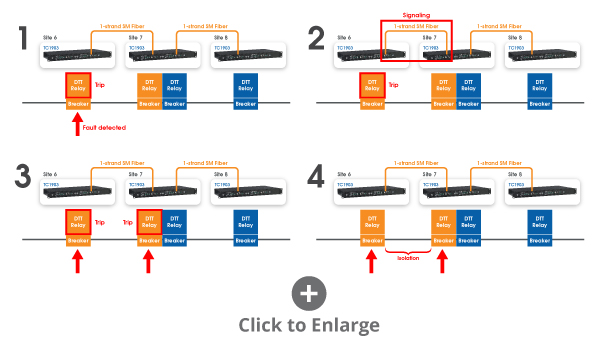
Let's take a look at three of their sites and how they work. We have a power line with breakers providing power to transit locomotives between site six and seven.
We have a single strand of fiber connecting two DTT relays via two TC1903s. If the breaker at site 6 is triggered, the signal will reach the breaker at site 7 over fiber and cause an isolation.
The same event can occur only between site 7 and 8 and so on.
With average leased line costs exceeding $1,500 a month and even as high as $10,000 a month, more customers are seeking alternative solutions for Direct Transfer Trip applications. The three solutions covered here over dedicated dark fiber, T1, and Ethernet connectivity provide customers with the flexibility to use what is available to them or reduce costs through leased line replacement.
Each of the TC Communications products used in these solutions is covered by a five-year warranty and available in an extreme temperature version with an operating range between -40 to 80 degrees Celsius (-40 to 176 degrees Fahrenheit), making them ideal for withstanding harsh weather conditions, helping to maintain reliable in DTT teleprotection.

JumboSwitch® Multi-service Ethernet Platform

2W/4W E&M 600 Ohm and Dry Contact over IP TC3846-6

"Quick-Talk" Asynchronous RS-232 or Fiber Telephone Extender (Supports 1-Fiber Bi-Directional) TC1903

2W/4W E&M 600 Ohm and Dry Contact over T1/E1 TC8614

Rail Networks

Leased Line Replacement

Teleprotection over IP
Interested in similar content? Subscribe to our mailing list.
Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) leveraging redundant cellular communication channels
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Direct Transfer Trip Use Case over Cellular for DER Sites White Paper
Available languages, download options.
- PDF (1.1 MB) View with Adobe Reader on a variety of devices
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Table of Contents
Wireless technologies offer an alternative solution to enable communications for the various distribution grid use cases. These technologies are especially useful in providing connectivity to the various Distributed Energy Resources (DER) assets and local distribution substations.
Typically, protection equipment will operate locally and does not use data from other devices to operate. However, some schemes do use communications for normal operations. One such scheme is Direct Transfer Trip (DTT), where upstream substations need to trip DER assets off the network in the event that the substation feeder breaker opens.
Traditionally, DTT signals were sent between substations and remote Distributed Generation (DG) sites using leased telephone lines. DTT systems are installed for critical high-speed tripping of circuit breakers on either side of a feeder interconnecting substations or between the substation breaker and a DG site’s station equipment.
Cisco and Verizon have undertaken work to validate the use of cellular networks to provide a flexible and easy-to-deploy connectivity solution to provide the backhaul technology. Today, cellular networks are reliable and can be deployed at a low cost compared to dedicated fiber.
The focus of this work was on leveraging standards-based and scalable communication technologies to provide encrypted connectivity between sites while supporting the transport of Layer 2 multicast non routable IEC 61850 GOOSE messaging in peer-to-peer topologies. Plus, the same solution will also natively allow Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) data to be transported within the same encrypted tunnels.
It was important to evaluate the latency, jitter, and packet loss applicable to these private and commercial cellular networks when applied to the DTT use cases:
● IEEE 1547-2018 states that for DTT operation, DER assets should be disconnected within 2 seconds (however, the communications budget for this operation is much smaller).
● Customer requirements for the actual communications budget range from 40 to 80 ms.
Cisco provided the Cisco Catalyst ™ 1101 Rugged Router (IR1101), used widely in distribution automation networks today, with plug-in cellular modules to support the various commercial and private spectrum bands, including Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS), Anterix, and commercial bands (such as FirstNet and First Responder).
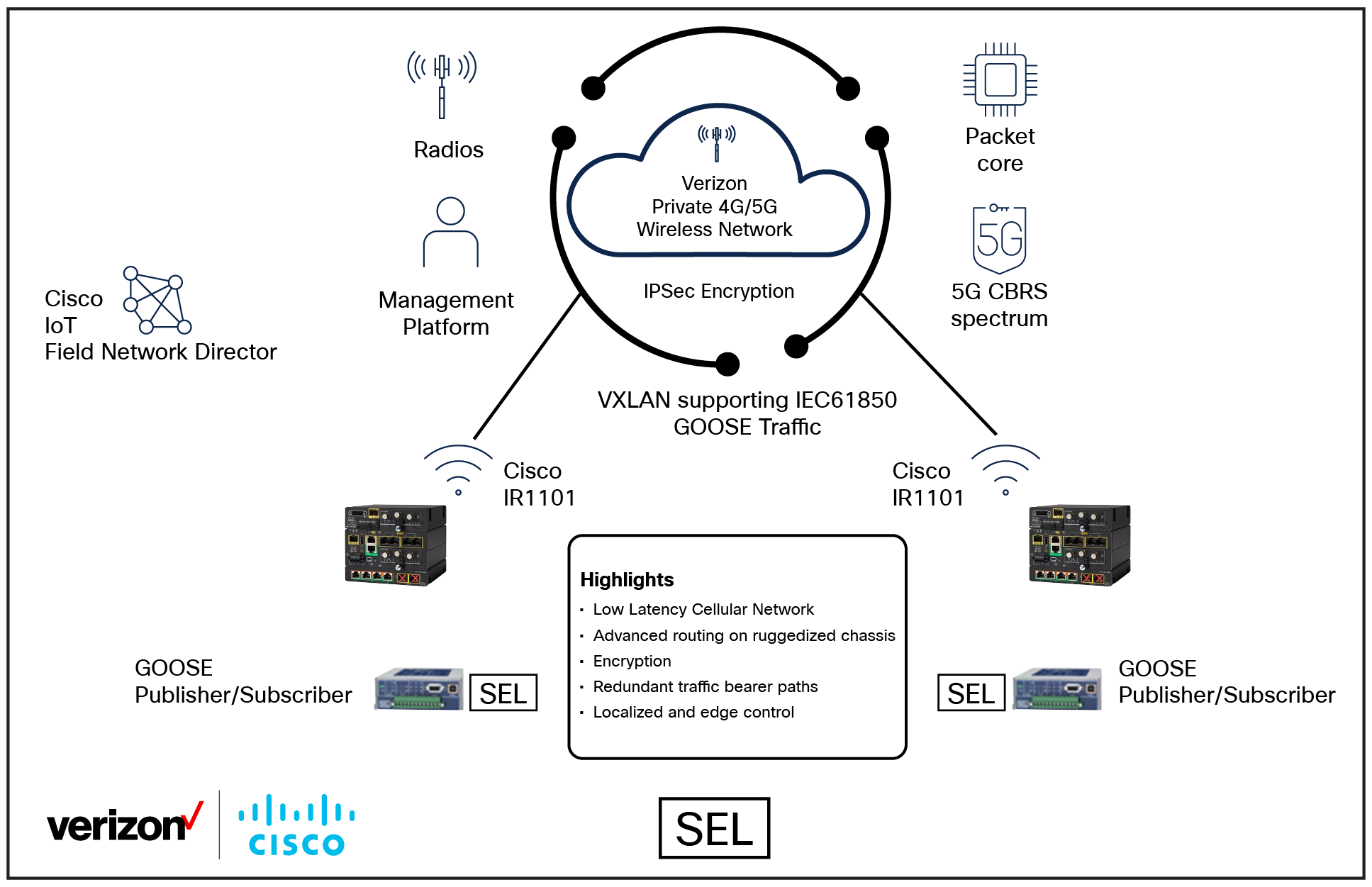
Architecture of the Cisco and Verizon DTT system
Key points for the DTT use case:
● The DER site monitors upstream reclosers for a trip signal.
● The DER site disconnects itself from the grid when it receives the required trip signal.
● The Catalyst IR1101 router with Cisco ® cellular plug-in modules is used to allow flexibility in the selected cellular module required.
● Standards-based VXLAN is used to transport the Layer 2 multicast GOOSE messages.
● IPsec/IKEv2 tunnels are used for security between all endpoints.
● Scalability is required for more complex topologies.
● Security, IPsec for WAN side encryption, and the Catalyst IR1101 router also support MACsec on the LAN ports with SEL-651R reclosers.
Cisco will be releasing an updated validated design for distribution automation that will include the DTT use case over cellular.
Cisco Catalyst IR1101 Rugged Router data sheet
Cisco IoT Field Network Director data sheet
Eversource Transforms Direct Transfer Trip with LTE
Quick facts.
Eversource Energy www.eversource.com
Eversource Energy is a publicly traded Fortune 500 energy company headquartered in Berlin, Connecticut and Boston, Massachusetts. The company provides retail electricity, natural gas service and water service to approximately 4 million customers in Connecticut, Massachusetts and New Hampshire.
- Develop reliable, secure Real-Time Automation Control (RTAC) to safely integrate renewables onto the grid
- Integrate communications solution that provides mission-critical reliability and security
- Eversource RTAC integrates AirLink® MG90 which provides multi-network access to cellular and assures reliability
- AirLink Connection Manager enables secure communications
- AirLink MG90
- AirLink Connection Manager
Eversource Energy is a publicly-traded Fortune 500 energy company headquartered in Berlin, Connecticut and Boston, Massachusetts. The company provides retail electricity, natural gas service and water service to approximately 4 million customers in Connecticut, Massachusetts and New Hampshire.
With the MG90 and ACM, we have the availability, latency and reliability we need to make this viable as the communications solution to support all the new renewable sources coming onto our network. Being connected to each of the “inputs” we have complete situational awareness of energy coming onto and leaving the grid, allowing us to effectively balance supply with customer demand.
Tim Callahan, Senior Engineer, Distribution Standards, Eversource Energy
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency 1 in April 2019, renewable energy accounts for one third of global power capacity. With governments around the world setting goals to increase power generation from renewables, and utilities setting objectives to make corresponding increases, integrating these new power sources into the grid is a challenge.
Eversource Energy provides electricity across three states and is working with many renewable energy companies that want to get their energy onto the grid. While the company needs to be able to accommodate these new producers, it needs to be able to do so safely. It’s not as simple as just giving a generator a connection to the grid. The nature of renewables is that they are unpredictable. Solar energy can only be generated when the sun is shining, and wind energy can only be generated when the wind is blowing.
As this energy comes onto the grid, the company needs “situational awareness” to balance supply and demand. During a fault in the system, utilities need to be able to quickly identify the source and isolate that segment of the distribution network to avoid damage to grid equipment and also protect utility workers servicing the fault. While the transmission network has long allowed for the integration of third party sources, it is a new challenge for the distribution network.
Utilities have used “direct transfer trip” (DTT) for many years, and DTT has always required highly reliable communications between all the components of the system. In the past, the energy company would have deployed copper telephone lines for this mission-critical communication, but with local telephone companies investing less in copper landlines, this has resulted in declining levels of communications service.
Eversource has been an early leader in integrating these new sources onto their distribution grid. Fiber optic cable was considered but can be cost-prohibitive. Eversource wanted cellular communications for this application and went in search of a solution that would meet its needs
With the increasing cyberattacks on utilities, Eversource needed to ensure that all these communications could be protected via a virtual private network (VPN). The ACM sets up the VPN when the cellular connection is established, and automatically moves that encrypted tunnel to the new cellular network as required.
Eversource evaluated a number of cellular solutions for this application. As the team worked through evaluation, it realized that to achieve the level of reliability they would need, they had to have a router that would support multiple cellular carrier networks.
Eversource developed a solution using a combination of SEL’s RTAC and Sierra Wireless’ MG90 cellular gateway to get the situational awareness it needed.
Eversource selected the AirLink® MG90 because it enables two cellular carrier connections in each router. Eversource can select one cellular network as “primary,” but in circumstances where a connection cannot be established on the primary network, the MG90 automatically selects and switches to the secondary cellular network. The switching happens automatically and transparently. When the primary cellular connection is reestablished, the router is switched back to the primary in real time. This multi-cellular capability provides the reliability Eversource needs.
“While the dual carrier aspect of the MG90 was a critical part of our decision, the AirLink® Connection Manager (ACM) was equally important for security. With the increasing cyberattacks on utilities, Eversource needed to ensure that all these communications could be protected via a virtual private network (VPN). The ACM sets up the VPN when the cellular connection is established, and automatically moves that encrypted tunnel to the new cellular network as required,” explained Tim Callahan, Senior Engineer, Distribution Standards at Eversource. “With the MG90 and ACM, we have the availability, latency and reliability we need to make this viable as the communications solution to support all the new renewable sources coming onto our network. Being connected to each of the “inputs” we have complete situational awareness of energy coming onto and leaving the grid, allowing us to effectively balance supply with customer demand.”

The sites that have been installed are up and running well and Eversource is in the process of deploying the new solution across its operating regions.
“The SEL RTAC and MG90 combination is going to be a great solution for our distribution management system (DMS) – safely bringing renewables onto the grid and enabling us to manage supply and demand effectively. We’re seeing new applications that make the packaged solution a building block for future grid operations,” said Callahan. “We are now looking at how it will help us in dynamic volt VAR optimization and DSCADA operations, also with electric vehicles, modelling and forecasting and streamlining distributed generation interconnection processes.”
Eversource is now examining integrating AirLink® Mobility Management into their operations. “With us using the RTAC and MG90 combination for each renewable source, we’re going to need a way to manage all these remote devices, and being able to have an on-premises system to do this makes sense,” said Callahan.
Many utilities are struggling to bring new generation sources to the grid, and Eversource sees the RTAC and MG90 package as a solution to the challenge. “We’re talking to other energy companies regularly and they are all looking for better ways to bring in new supplies safely.” Eversource credits its team of engineers – from protection and control, IT telecom and SCADA teams to making this solution a reality. Our team’s efforts to make this a great solution is really a credit to the talent of our team and the superior technology of our partners like Sierra Wireless and SEL,” explained Callahan.
- https://www.irena.org/newsroom/pressreleases/2019/Apr/Renewable-Energy-Now-Accounts-for-a-Third-of-Global-Power-Capacity

Related Products

Eversource Energy
EMEA Germany NAM
Smart Grid Utilities
MG90 Router AirLink Connection Manager AirLink Mobility Manager
© 2024 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
- 5G Japan Site
Partner Community
Airlink management services, maingate manager, subscribe to our iot newsletter, sierra wireless is now semtech.
- Site Search Search Posts Find A Forum Thread Number Threads by Name Search FAQs
- ENGINEERING.com
- Eng-Tips Forums
- Tek-Tips Forums

Join Eng-Tips ® Today!
Join your peers on the Internet's largest technical engineering professional community. It's easy to join and it's free.
Here's Why Members Love Eng-Tips Forums:
- Notification Of Responses To Questions
- Favorite Forums One Click Access
- Keyword Search Of All Posts, And More...
Register now while it's still free!
Already a member? Close this window and log in.
Join Us Close
What is an IRA account?
Types of ira accounts.
- Benefits of IRAs
- IRA Contribution limits 2024
Choosing the right IRA
Withdrawals and distribution, ira accounts: types, benefits, and how to choose the right one.
Paid non-client promotion: Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate investing products to write unbiased product reviews.
- An Individual Retirement Arrangement (IRA) is a type of retirement account for individuals that provides various tax advantages.
- Depending on which type of IRA you have, you contribute either pre- or post-tax dollars and invest the funds.
- IRAs come with more investment flexibility than 401(k)s, which are employer-sponsored plans.
IRAs are some of the best retirement plans for growing your nest egg through compound interest and investment opportunities. An IRA is just one of many retirement account options, and there are several types to choose from. The right choice will depend on your retirement goals, timeline, and expectations for future taxes.
Here's everything you need to know about opening an IRA, contribution limits, tax advantages, and the best IRA investment strategies in 2024.
Definition and purpose of an IRA
Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs) are retirement accounts for individuals to save pre- or after-tax dollars toward their post-working years. Like a 401(k), IRAs have compounding power that can help them grow significantly over time.
"IRAs are simple and are an extremely easy investment plan to help save for your retirement years," says Wilson Coffman, CFA, the president at Coffman Retirement Group .
IRAs have many tax benefits and can allow you to invest funds in various assets. However, there are age limits on when you can withdraw funds (or face a penalty), and in many cases, the contribution maximums may be lower than on other retirement accounts. For example, 401(k)s allow you to contribute up to $23,000 annually.
You can't start withdrawing from your IRA until you are at least 59 1/2, or the IRS will charge you a 10% penalty fee. The purpose of this penalty is to discourage the misuse of funds and promote long-term growth for future retirees.
This rule has some expectations, as you won't be charged the 10% fee if you meet IRS hardship guidelines for a qualified, penalty-free withdrawal .
Opening and funding an IRA account
To open an IRA, you go through a brokerage or local back. "IRAs are extremely easy to establish and set up," Coffman says. "Most banks offer an IRA, and any broker will offer IRA accounts. There are also many investment firms, like Fidelity , that can offer investment platforms for online retirement savings accounts as well."
Once set up, you'll fund the account using bank payments, checks, or an IRA rollover if you have a different retirement account or old 401(k). The best rollover IRAs offer direct rollovers or trustee-to-trustee transfer by contacting your existing plan's administrator.
You can also take a distribution and deposit it in your new IRA within 60 days.
Traditional IRA
This type of IRA is funded with pre-tax earnings. Contributions are tax-deductible; you'll pay taxes on the funds when you withdraw them in retirement. They're typically best if you expect your retirement tax bracket to be lower.
With Roth IRAs, you fund the account with after-tax earnings. This allows the money to grow tax-free, and you'll pay no additional taxes upon withdrawal. They're a good option if you predict your retirement tax bracket will be higher.
Original Roth IRA contributions (not the growth) can be withdrawn penalty-free at any point before you're 59 1/2, essentially acting as an emergency fund. That said, you'll get the most out of your Roth IRA by leaving the funds alone for as long as possible and contributing regularly.
SEP IRAs are for employees of self-employed professionals or small businesses who are at least 21 years old and have worked for the employer for at least three of the last five years. They have much higher contribution limits than traditional and Roth IRAs and are taxed upon withdrawal.
All contributions from the employer to the SEP-IRA are 100% vested immediately.
SIMPLE IRAs are another type of small business retirement account for self-employed individuals or businesses with 100 employees or less. Qualifying employees must also have made at least $5,000 in the last two years and expect the same amount in the current year.
Employers must match employee contributions dollar for dollar up to 3% of the employee's salary. Employee contributions are 100% vested immediately.
Benefits of IRA accounts
Tax advantages.
One of the biggest benefits of contributing to an IRA is the tax advantages. Since IRAs can be funded with either pre-tax (traditional IRA) or after-tax (Roth IRA), you can receive one of two tax benefits: tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals.
You deduct your contributions from your current taxes by funding your account with pre-tax dollars. During retirement, you'll only pay tax on the amount withdrawn, including the growth. This is especially beneficial if you predict you'll be in a lower tax bracket during retirement and, therefore, pay a lower tax rate on your contributions.
After-tax contributions mean you pay tax now to receive tax-free growth and withdrawals later. You won't have to worry about moving to a state with a higher tax rate or diminishing potential gains. This tax advantage is best for individuals who predict their tax bracket will be higher during retirement.
Potential for growth and compound interest
In addition to tax advantages, IRAs are known for their powerful wealth-building capabilities. Money in your IRA can be invested in securities like stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds. IRAs also grow with the magic of compounding.
With compound interest , the interest earned each period (month, year, etc.) gets added to your principal amount. This means the next time interest is calculated, it's applied to a larger amount, leading to faster growth over time. The longer your money is allowed to compound, the greater the growth potential.
IRA Contribution limits for 2024
The IRS has set contribution limits on IRAs, but the exact amount depends on your age, your taxable compensation for the year, and the type of IRA you've established.
Annual contribution limits
Here's how IRA contributions break down for 2024:
Income limits and eligibility for a Roth IRA 2024
Factors to consider.
Some factors to consider when choosing the right IRA include:
- Investment strategy: Consider the investment strategy you prefer to grow your nest egg. Generally, the best IRA investment strategy for long-term wealth building is a buy-and-hold strategy, which mitigates risk and volatility while utilizing compound interest. However, some pre-retirees (particularly younger traders) may prefer an active, riskier strategy with the potential for higher gains.
- Investment options: What kinds of investable securities do you want to buy and sell in your IRA? IRA companies offer a wide range of investment options, including stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds. Some providers offer alternative investment options like real-estate, art, and cryptocurrencies.
- Fees and expenses: Ensure you understand all the fees associated with the IRA provider you sign up with. This includes account fees, annual fees, management fees, transaction fees, and expense ratios. Fees can diminish potential returns over time, so it's important to compare fees between different providers.
- Investment tools and research: Consider the kinds of investment tools, services, and research that can help you make smart investment decisions. These could include educational resources, portfolio analysis tools, tax-loss harvesting, and market research reports.
- Minimum investment requirement: Some online brokerages and apps require a minimum investment to open an IRA and start investing. There are many low-cost IRAs with no minimums and other more robust IRA providers with minimums ranging from $5 to $100. Before signing up, know how much you need to invest to get started.
- IRA match: Some IRA providers now offer an IRA match, similar to a 401(k) employer match. When you contribute to your retirement account, your IRA may contribute a matching contribution up to a certain percentage. However, only a handful of investment platforms offer this perk.
Comparing traditional and Roth IRAs
The most common types of IRAs are traditional and Roth. They act very similarly, providing the same investment options and contribution limits. Most IRA providers typically offer both kinds to anyone with earned income.
Pre-tax dollars fund traditional IRAs, so you only have to pay income tax on the amount withdrawn during retirement. Whereas after-tax dollars fund Roth IRAs. That means you pay tax now for tax-free growth and withdrawals later on.
Most people choose between traditional and Roth IRAs. According to Clark Howard, author and host of The Clark Howard Podcast , future taxes should play a big role in this decision.
"The biggest difference between a traditional IRA and a Roth IRA is the treatment of taxes," Howard says. "ln general, tax rates are likely to go up over the years no matter which political party is in power. That means it may make more sense to skip the tax deduction you get up front with a traditional IRA to avoid tax later by investing with a Roth IRA."
Our traditional IRA vs. Roth IRA comparison guide examines fees, investment strategies, tax advantages, and more to provide a closer IRA comparison. It's common for people to have both types of IRAs for double the tax benefits.
However, a SEP or SIMPLE IRA may be a better option for small businesses or self-employed people.
You'll want to wait until at least 59 ½ to withdraw funds on all IRA types. Withdrawals before this point face a 10% penalty, one of the most significant IRA withdrawal rules and penalties. There are some exceptions on Roth IRAs if you've funded it with a rollover, so talk to your tax advisor if you plan to withdraw early from this type of account.
The tax treatment of an IRA depends on the type of account. With traditional, SIMPLE, and SEP IRAs, contributions are tax-deductible, and you fund the account with pre-tax dollars. With Roth IRAs, you contribute post-tax dollars — or money you've already paid income taxes on. This allows for tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
"IRAs are either taxed at the beginning or the end," says Christy Matzen, CFP, senior manager and global planning for Northstar . "When you make a contribution, you can pay tax on the dollars before you put it into the account — this will let you take the money out tax-free, or you can take a tax deduction when you make the contribution, but then the money will be taxed when you take it out."
Required minimum distributions (RMDs)
Your Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) is the minimum amount you must start withdrawing from your IRA based on your birthdate. Generally, you must start withdrawing from your IRA by April 1 of the following year when you turn 72. If your birthdate is after December 31, 2022, then your RMD is age 73.
After the first required year, you must continue making subsequent annual withdraws by December 31. How much you withdraw depends on the total value of your account and life expectancy.
IRA account FAQs
The difference between traditional and Roth IRAs is that a traditional IRA is funded by pre-tax dollars, and a Roth IRA is funded by after-tax dollars. With a traditional IRA, you only pay tax on the amount withdrawn during retirement, which is especially helpful if you are in a lower tax bracket. On the other hand, Roth IRAs grow tax-free and have tax-free withdrawals, which is great if you expect your income to be higher in your post-working years.
You can contribute up to $7,000 to a traditional or Roth IRA in 2024. Individuals age 50 or older can contribute up to $8,000. You can contribute up to $16,000 (or $19,500 if you're 50 or older) to a SEP IRA. For SIMPLE IRAs, you can contribute $69,000 or 25% of your compensation, whichever is less.
Anyone with earned income is eligible to open an IRA. However, you can only open one of each type. There are no age restrictions on IRAs either. For Roth IRAs, your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) must be less than $161,00 for single filers to qualify (less than $240,000 for married couples filing jointly).
You can start withdrawals from your IRA without penalties at age 59 1/2. There are exceptions to this rule, however, as certain hardship guidelines allow penalty-free early withdrawals. For example, the loss of a job or permanent disability may allow you to withdraw early from your IRA without incurring the 10% penalty fee.
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) are the mandatory withdrawals you must start taking from your IRA during retirement. You must start taking RMDs by April 1 of the year following your 72 birthdate (73 if your birthdate is after December 31, 2022).
- Credit cards
- Investing apps
- Retirement savings
- Cryptocurrency
- The stock market
- Retail investing
- Real estate
- Main content
Campaign Finance Laws Give Harris Big Boost in Biden Dropout Scenario
If Biden were to withdraw his candidacy, only Kamala Harris could seamlessly use funds raised by the Biden-Harris campaign committee.
by David Dayen
July 2, 2024

AP Photo/Ronda Churchill
Dayen-HarrisFundraising-070224
Vice President Kamala Harris speaks at a post-debate campaign rally last Friday in Las Vegas.
There does not at this moment seem to be any movement from the Biden campaign, the Biden family, or Joe Biden himself toward exiting the 2024 presidential race after last week’s disastrous debate. On the contrary, the campaign has its back up and is devising operatic strategies to get back in contention, dismissing the debate as a “bad night,” using surrogates to silence dissenters, and soldiering on. They were so proud of Biden’s Friday speech in North Carolina that they made a one-minute ad about it. Biden resents the elite opinion-makers calling for his ouster, and relishes the opportunity to show that they underestimated him again.

My sense in talking with people in a position to know is that it would take much more than what has already happened in public to get Biden to drop out. Team Biden surely hopes that the Supreme Court’s immunity ruling creates a “rally round the leader” effect that will continue to fade memories of a president who was wildly inarticulate and frail in a pressure scenario just five days ago.
That hasn’t stopped the endless fantasy league scenarios from those who see no avenue for Biden to defeat Donald Trump in November. Among these ideas is the concept of a quick-strike primary, just for Democratic National Convention delegates, leading up to an open convention at the DNC in Chicago in August. The Biden camp has actually engaged with this, warning of “chaos” if the president were to withdraw.
This is a tremendous insult to Kamala Harris, who Biden himself handpicked as his second in command. If the obvious line of succession from President to Vice President is not possible because of Harris’ presumed deficiencies, what does that say about the man who chose her? Or is it maybe why he chose her, to insulate himself from attack?
More from David Dayen
But all of this talk, and everyone’s feelings about Harris’s chances in a general election, is missing something: the main Biden campaign committee has raised hundreds of millions of dollars for the presidential election, invested in staff and booked airtime across the country. And the only person under campaign finance law who would be able to seamlessly continue to use that money for the general election is his ticket mate, Kamala Harris.
There’s been mostly handwaving about how difficult it would be for another candidate to come in and run his campaign from a standing start, with zero dollars and no campaign organization in late August. But it’s the primary reason why, practically speaking, Biden and Harris are really the only two choices available at this late stage of the campaign.
The experts at the Campaign Legal Center explained to the Prospect the scenarios for Biden campaign funding in the event of his withdrawal. The Biden for President campaign committee controls candidate contributions for the 2024 election. It has received $220 million up through May 31; we know that in the four days from last Thursday’s debate through Monday, the campaign committee raised another $33 million. As of May 31, the committee had $91.5 million in cash on hand.
If Biden, as candidate, wanted to contribute money from this account to another candidate for the presidency, he’s limited to $2,000 per election. If Biden withdraws, he could convert this campaign committee to a political action committee. In that case he could direct $3,300 to another candidate. These numbers, it must be said, are significantly smaller than what’s in the account. It’s simply not allowable for a presidential candidate to directly transfer millions of dollars to another candidate.
That brings up two options. First, the Biden PAC could operate an independent expenditure campaign on behalf of the new candidate. But that PAC would not be able to coordinate with the new candidate, and it would have significantly higher advertising rates for television commercials, for example, relative to direct candidate expenditures. This would have the effect of lopping off millions of dollars in terms of value.
The only person under campaign finance law who would be able to seamlessly continue to use Biden campaign money for the general election is Kamala Harris.
Second, Biden could refund all the remaining funds to donors, who could then make separate contribution to the new candidate’s campaign. But that would involve a complicated set of calculations. Money earmarked for the general election (like if a donor maxed out to the primary and the general election) should be unspent, so those donors would be first in line for refunds. Who gets the leftover funds, if any, is an open question, since at least some of it was spent. And whether or not donors redirect this money to the new candidate is completely up to them and not binding in any way. Donors could just take their money and keep it. The belief that all of that money would get over to the new candidate is somewhat wishful.
The only way these complications are nullified is if Vice President Harris is the nominee. Harris and Biden share this campaign committee, as the federal campaign finance laws allow for one fund when the president and vice president run on the same ticket. So if Harris succeeded Biden, she would control all the funds in the campaign committee and could use them in the election campaign.
The difference between these two scenarios is pretty significant. Either a series of steps with some degree of risk have to be undertaken to get money to a new candidate, or Harris can just use what’s in the account. Money matters a little less as you go up the political ladder—Donald Trump has a pretty sky-high name recognition and most people have formed their opinion of him—but if you are behind in the race, and especially if you need to boost your own profile, you can’t really do that without a well-resourced campaign. Only one person has guaranteed resources on day one, as well as an existing organization that doesn’t have to be instantly created or established.
I am not making a normative statement about Kamala Harris’ candidacy or how she would do as a presidential candidate. I’m merely saying that the realities of campaign finance bring us to a place where she would have an enormous advantage in a critical facet of a campaign over every other person in America. Like it or not, that makes it extremely difficult to opt for anyone else, should Biden drop out.
It is incredible that this has not been part of the public debate. Biden isn’t going anywhere right now, although polls over the next couple weeks may change that calculation. People are going through all kinds of reasons why or why not Harris would be the nominee in the aftermath. They barely touch the one that involves what legendary California politician Jesse Unruh called the mother’s milk of politics : money.
UPDATE: There is a possibility that the campaign committee funds could be transferred to the Democratic National Committee. But the DNC could then only give up to $5,000 directly to a candidate. It could use the funds on behalf of the candidate, but again the coordination and ad rate questions come up. And it is possible that Kamala Harris would have to comply with a transfer of those funds in that manner, in a scenario where she was just passed over for the top of the ticket.
You can count on the Prospect , can we count on you?
There's no paywall here. Your donations power our newsroom as we report on ideas, politics and power — and what’s really at stake as we navigate another presidential election year. Please, become a member , or make a one-time donation , today. Thank you!

About the Prospect / Contact Info
Browse Archive / Back Issues
Subscription Services
Privacy Policy
DONATE TO THE PROSPECT

Copyright 2024 | The American Prospect, Inc. | All Rights Reserved
The Daily Show Fan Page

Explore the latest interviews, correspondent coverage, best-of moments and more from The Daily Show.
The Daily Show
S29 E68 • July 8, 2024
Host Jon Stewart returns to his place behind the desk for an unvarnished look at the 2024 election, with expert analysis from the Daily Show news team.
Extended Interviews

The Daily Show Tickets
Attend a Live Taping
Find out how you can see The Daily Show live and in-person as a member of the studio audience.
Best of Jon Stewart

The Weekly Show with Jon Stewart
New Episodes Thursdays
Jon Stewart and special guests tackle complex issues.
Powerful Politicos

The Daily Show Shop
Great Things Are in Store
Become the proud owner of exclusive gear, including clothing, drinkware and must-have accessories.
About The Daily Show

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Direct Transfer Trip Scheme (DTT) (This is technically not a pilot scheme but requires a pilot channel) Direct Transfer Trips (DTT) are initiated from station relays when a serious event occurs in the substation. Some of these events are breaker failure, bus faults, transformer failure, etc. A lockout relay (86 device) is assigned to each event.
Watch this Direct Transfer Trip and ... We're continuing our end-to-end testing series by looking at the two simplest communication-assisted trip schemes used. Watch this Direct Transfer Trip and
Direct transfer trip - Sends a trip signal to the DG when an upstream breaker opens. Due to the remote location, communication is required. Existing Direct Transfer Trip Methods Traditional methods incorporate the monitoring of circuit breakers and reclosers that could island a DG system
In this video we're going to look at Direct Transfer Trip schemes or DTT schemes and then we're going to look at Direct Under-Reaching Transfer Trip schemes (or DUTTs). This video is part of a series. If you have not watched Understanding Line Distance Protection, the link is on the screen right now, then go watch that video first, so you ...
Underreaching transfer trip schemes include two variations: direct underreach and permissive underreach. The communications for this type of relaying are generally the same as for the overreaching systems, using audio tones with frequency shift keying over microwave, leased line, or fiberoptic communications channels .
Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) is a teleprotection scheme that involves sending trip signals from one location to another via a telecommunications transport, such as a phone line, radio, or fiber optics. It is commonly used for substations to detect substation faults and create lines of isolation while the faults are under
a line breaker, or a condi-tion, such as bus undervoltage, at the remote line terminal. This has applications for protection, co. trol, or monitoring and is easily accomplished with relay-to-relay logic communication. Sim-ply program the transmit logic bit with the appropriate relay element, either internal or exte.
Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) is a teleprotection scheme that involves sending trip signals from one location to another via a telecommunications transport, such as a phone line, radio, or fiber optics. It is commonly used for substations to detect substation faults and create lines of isolation while the faults are under investigation.
This is achieved via Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) signals, traditionally sent between substations and remote DG sites using leased telephone lines. Due to the highly specialized and critical nature of DTT systems, the equipment, including the communication infrastructure, must be extremely reliable and conform to highest substation standards. ...
We're continuing our end-to-end testing series by looking at the two simplest communication-assisted trip schemes used. Watch this Direct Transfer Trip and Direct Under-Reaching Transfer Trip Schemes Video to learn more about these two schemes.
a direct transfer trip or intertrip technique, the logic of which is shown in Figure C4.4. A contact operated by the Zone 1 relay element is arranged to send a signal to the remote relay requesting a trip. The scheme may be called a 'direct under-reach transfer tripping scheme', 'transfer trip under-reaching scheme', or 'intertripping
TC Communications provides three products that can achieve Direct Transfer Trip, whether you're transmitting over Fiber, T1, or Ethernet.Read more about TC C...
Fig. 3. (Point of Circuit Connection "PCC" Direct Transfer Trip logic) From Fig. 3 the PCC-DTT initiate a DTT trip on the receipt of a DTT "GOOSE" from the either the delivery point substation or the distribution substation in addition if a communication failure is detected at any of the DTT devices. A reverse power
transfer scheme. They first e valuated a direct Ethernet solutionbut found that standard industrial equipment provided insufficient contact power voltage ratings (125 Vdc is rare); required auxiliary relays and other additional equipment; had questionable tolerance to heat, cold, and surges; and still only provided v, nondeterministicariable
We're continuing our end-to-end testing series by looking at the Permissive Over-Reaching Transfer Trip communication-assisted trip schemes. You can read th...
A "Direct" trip may have stops, but no transfers. Stops vary by trip length, since the driver must stop to pick up other passengers, to let off passengers, for fuel or for rest. The time a bus is stopped is called a " Layover ". Some " Direct " trips may be " Non-Stop ", usually common in non-stop plane tickets or on bus trips shorter than 2-3 ...
"Application of Direct Transfer Trip for Prevention of DG Islanding", R. Walling, IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting 2011. Fault on feeder detected by substation relay. Trip signal sent to distributed location. DTT signal trips distributed breaker or relay. Wireless communications provide a cost-effective alternative to wired
Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) signals, traditionally sent between substations and remote DG sites using leased telephone lines. Due to the highly specialized and critical nature of DTT systems, the equipment, including the communication infrastructure, must be extremely reliable and conform to highest substation standards.
Architecture of the Cisco and Verizon DTT system. Key points for the DTT use case: The DER site monitors upstream reclosers for a trip signal. The DER site disconnects itself from the grid when it receives the required trip signal. The Catalyst IR1101 router with Cisco ® cellular plug-in modules is used to allow flexibility in the selected ...
• Schedule #1, Terms and Conditions for Standard Offer and Direct Access Services. • Schedule #2, Terms and Conditions for Energy Purchases from Qualified Cogeneration and Small Power Production Facilities. • Schedule #4, Totalized Metering of Multiple Service Entrance Sections at a Single Site for Standard Offer and Direct Access Service.
Utilities have used "direct transfer trip" (DTT) for many years, and DTT has always required highly reliable communications between all the components of the system. In the past, the energy company would have deployed copper telephone lines for this mission-critical communication, but with local telephone companies investing less in copper ...
It was explained to me that the SEL-2100 was being used to pass mirror bit signals for DTT tripping to the SEL-351 relay associated with breaker designated to trip. ... Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) signal through Multiplexer davidbeach (Electrical) 9 Nov 22 02:36. An RTU is a SCADA device, not a protection device. The two should not mix.
dedicated T1 communication circuit for the DER Direct Transfer Trip (DTT) scheme. T1 Order communication line shall be point-to-point from the DER facility to the applicable LIPA substation. If Developer have a Dedicated Verizon Account Team, they would perform all the ordering- if not - order circuit from Local Verizon Business Office:
The best rollover IRAs offer direct rollovers or trustee-to-trustee transfer by contacting your existing plan's administrator. You can also take a distribution and deposit it in your new IRA ...
The experts at the Campaign Legal Center explained to the Prospect the scenarios for Biden campaign funding in the event of his withdrawal. The Biden for President campaign committee controls candidate contributions for the 2024 election. It has received $220 million up through May 31; we know that in the four days from last Thursday's debate ...
The source for The Daily Show fans, with episodes hosted by Jon Stewart, Ronny Chieng, Jordan Klepper, Dulcé Sloan and more, plus interviews, highlights and The Weekly Show podcast.